If you have chronic headaches, chest pain, a systematic increase in blood pressure, a general deterioration in health due to changes in atmospheric pressure, we recommend that you read our article “Types of medical examinations for weather-dependent people”, take care of your health!
In each region of Russia, different atmospheric pressure is considered normal. Therefore, in weather reports, when the number of millimeters of mercury is announced, weather forecasters always say what pressure it is for this area, above or below normal.
In addition to atmospheric pressure, many factors influence our well-being. What to do if you have breathing problems, it becomes difficult to breathe, or a cough appears? Take care of your health, this is the only thing that no amount of money can buy!
You can find out how air density depends on temperature here, it’s very interesting!
What is atmospheric pressure?
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure of the gaseous shell of our planet, the atmosphere, which acts on all objects in it, as well as the earth's surface. Pressure corresponds to the force that acts in the atmosphere per unit area.
Earth's atmosphere (photo from the ISS)
In simpler terms, this is the force with which the air around us acts on the surface of the earth and objects. By monitoring changes in atmospheric pressure, it is possible, in conjunction with other factors, to predict weather conditions.
Physiotherapy
Healing baths and mud have a good effect. In addition, any water procedures (circular shower, wiping with cold water, swimming pool) cause a positive effect and increase the body's reserve capabilities. Essential oils have positive tonic and calming properties. You can perform inhalation with essential oils of citrus and coniferous plants, mint, rosemary and other substances, or conduct an aromatherapy session.
Sensitivity to changes in pressure is an unpleasant condition that disrupts normal well-being and interferes with a full life. To avoid this, you need to increase the body’s natural resistance and monitor your health.
Why and due to what is atmospheric pressure created?
Specialists who study the Earth's atmosphere and various meteorological phenomena carefully monitor how air masses move. This is the main factor influencing the climatic conditions of a particular area. These observations made it possible to understand why atmospheric pressure arises.
It's all because of gravity.
Through many experiments it has been proven that air is by no means weightless. It consists of various gases that have a certain weight. Thus, the force of gravity of the Earth acts on the air, which contributes to the formation of pressure. Interesting fact : all the air on the planet (or the entire atmosphere of the Earth) weighs 51 x 1014 tons.
The air mass around the globe is not the same. The level of atmospheric pressure fluctuates accordingly. Areas with more air mass experience higher pressure. If there is less air (it is also called rarefied in such cases), then the pressure is lower.
Movement Sun
Why does the weight of the atmosphere change? The secret of this phenomenon lies in the heating of air masses. The fact is that the heating of the air does not occur at all from the sun's rays, but due to the earth's surface.
Near it, the air heats up and, becoming lighter, rises. At this time, the cooled flows become heavier and fall down. This process occurs continuously. Each air flow has its own pressure, and its difference causes wind.
Symptoms of health problems
The mercury pressure (the norm is individual for each person) can be increased or decreased, which causes different symptoms in weather-dependent people.
Description of signs depending on changes in pressure:
| During an anticyclone. A weather phenomenon is characterized by a change from normal atmospheric pressure to increased pressure. | During a cyclone, normal atmospheric pressure changes to low. |
| Pain in the heart area | There is a lack of oxygen, accompanied by shortness of breath and the release of red blood cells (the phenomenon is dangerous due to the formation of blood clots) |
| Increased heart rate | The number of heartbeats increases, but the force of the blow decreases |
| Severe headache with sensation of pulse in temples, dizziness | Headaches may be unbearable |
| Increased fatigue and general malaise | Rapid fatigue and general weakness (feeling of “woolly legs”) |
| A rush of blood to the face, causing a feeling of heat and redness | Deterioration in quality of vision |
| An increase in blood pressure may be accompanied by nosebleeds | Feeling of noise and buzzing in the ears |
| A decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood, which is dangerous due to colds and other infectious diseases or exacerbation of chronic pathologies | Exacerbation of joint diseases and numbness of the limbs |
| Increased sweating | Decreased blood pressure |
| Feeling of ringing in the ears | Increased intracranial pressure |
| Loss of vision sharpness | Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by flatulence |
| Bowel dysfunction (constipation) | The appearance of swelling of the limbs |
When pressure changes in any direction, chronic pathologies worsen.
How does the composition of the atmosphere affect pressure?
The atmosphere contains a huge amount of gases. These are mainly nitrogen and oxygen (98%). There is also carbon dioxide, neon, argon, etc. The atmosphere begins with a boundary layer 1-2 km thick and ends with the exosphere at an altitude of about 10,000 km, where it smoothly passes into interplanetary space.
Atmospheric composition
The composition of the atmosphere affects pressure due to density. Each component has its own density. The higher the altitude, the thinner the layer of the atmosphere and the lower its density. The pressure decreases accordingly.
Nutrition and regimen
One of the factors that influences the development of pressure sensitivity is excess weight. Obese patients are more likely to suffer from heart and vascular diseases and, accordingly, are more likely to react to weather disasters. If the patient decides to cope with this disease, then first of all you need to reconsider your lifestyle and diet:
- A complete and balanced diet with a normal content of vitamins and microelements.
- Refusal or limitation of alcohol and nicotine consumption.
- During an attack, you need to switch to a light dairy-vegetable diet to help the body cope with the disease.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the use of adaptogens - drugs that increase the natural adaptive ability of the body. They are of plant and synthetic origin. Some of the most famous adaptogens are ginseng, eleutherococcus, bee products and reindeer antlers. Before taking them, you need to consult a doctor, since there are a number of contraindications and side effects.
Atmospheric pressure measurement
In the International System of Units, atmospheric pressure is measured in pascals (Pa). Also in Russia, units such as bar, millimeters of mercury and their derivatives are used. Their use is due to instruments that measure pressure - mercury barometers. 1 mmHg corresponds to about 133 Pa.
There are two types of barometers:
- liquid;
- mechanical (aneroid barometer).
Liquid barometers are filled with mercury. The invention of this device is the merit of the Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli. In 1644, he conducted an experiment with a container, mercury and a flask, which was lowered into the liquid with an open hole.
Interesting: Tsunami: what is it, causes, types, consequences, photos and videos
As the pressure changed, the mercury rose and fell in the flask. Modern mercury barometers with scales are considered the most accurate, but not very convenient, so they are used at meteorological stations.
Barometers
Aneroid barometers are more common . The design of such a device includes a metal box with rarefied air inside. When the pressure decreases, the box expands. With increasing pressure, the box compresses and acts on the attached spring. The spring moves a pointer that displays the pressure level on a scale.
Interesting fact : there is a standard unit of pressure (as well as other units of physical quantities). The primary standard, which displays absolute pressure as accurately as possible, is located at the All-Russian Mendeleev Research Institute of Metrology (St. Petersburg).
Normal atmospheric pressure for humans
Normal atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg or 101,325 Pa at 0℃ at sea level (45º latitude). At the same time, the atmosphere acts on every square centimeter of the earth's surface with a force of 1.033 kg. A column of mercury 760 mm high balances the mass of this air column.
The figure of 760 mm was also determined by Torricelli during the experiment. He also noticed that when a flask is filled with mercury, there is a void at the top. Subsequently, this phenomenon was called the “Torricelli void.” Then the scientist did not yet know that during his experiment he created a vacuum - that is, a space free from any substances.
At a standard pressure of 760 mmHg a person feels most comfortable. If we take into account the previous data, then the air presses on a person with a force of about 16 tons. Why then do we not feel this pressure?
The fact is that there is also pressure inside the body. Not only people, but also representatives of the animal world have adapted to atmospheric pressure. Each organ was formed and developed under the influence of this force. When the atmosphere acts on a body, this force is distributed evenly over the entire surface. Thus, the pressure is balanced and we do not feel it.
Atmospheric pressure map of Russia
The atmospheric pressure norm should not be confused with the climate norm. Each region has its own standards for a certain time of year. For example, residents of Vladivostok are lucky, since the average annual atmospheric pressure there is almost equal to the norm - 761 mm Hg.
And in settlements located in mountainous areas (for example, in Tibet), the pressure is much lower - 413 mm Hg. This is due to the altitude of about 5000 m.
Meteoneurosis
This disease is not among the officially recognized ones, but according to statistics, every 4 inhabitants of the planet suffer from it. It is determined not only by dependence on changing weather conditions, but also by the adaptive potential of the body. People suffering from meteoneurosis may complain of a deterioration in their health, which doctors cannot prove.
That is, from a medical point of view, this fact cannot be confirmed. Poor health is not an exaggeration or simulation and is associated with psychological factors.
This condition may be caused by the following reasons:
- High mental load.
- Obesity.
- Heredity.
- Weak motor activity.
- Insufficient time spent outdoors.
- Neglecting recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle.
A person may suffer from sudden onset of dizziness for no apparent reason, shortness of breath, increased heart rate and headaches. In addition, the mood noticeably worsens, nervousness and irritability appear. When tests are taken during the examination, all indicators remain normal, without confirming the presence of the disease.
Increase and decrease in pressure
When the pressure exceeds 760 mm. Hg Art., it is called elevated, and when the indicator is less than normal - reduced.
Several changes in atmospheric pressure occur within 24 hours. In the morning and evening it increases, and after 12 noon and night it decreases. This happens due to the fact that the air temperature changes and, accordingly, its flows move.
During the winter period, the highest atmospheric pressure is observed over the mainland of the Earth, because the air has a low temperature and is highly dense. In summer, the opposite situation is observed - minimal pressure is observed.
On a more global scale, pressure levels also depend on temperature. The Earth's surface heats up unevenly: the planet has a geoid (rather than perfectly round) shape and revolves around the Sun. Some zones heat up more, others less. Because of this, atmospheric pressure is distributed zonally over the surface of the planet.
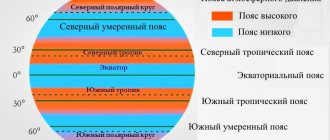
Atmospheric pressure belts
Scientists identify 3 belts where low pressure predominates and 4 belts with predominant highs. The equator area warms up the most, so light warm air rises, and low pressure forms at the surface.
Interesting: Climatic zones of the world - classification, map, description of climate types, photos and videos
Near the poles, the opposite is true: cold air sinks, so there is high pressure. If you look at the diagram of pressure distribution over the surface of the planet, you will notice that the belts of minimums and maximums alternate.
In addition, you need to remember about the uneven heating of both hemispheres of the Earth throughout the year. This leads to a certain displacement of the low and high pressure belts. In summer they move northwards, and in winter – southwards.
What to do if you are weather dependent
If increased sensitivity to changing weather conditions is present, but there are no diseases leading to it, then the following recommendations will help you cope with unpleasant sensations.
In the morning, it is advised to take a contrast shower, then drink a cup of good coffee to keep yourself in good shape. It is recommended to drink more tea during the day. Better - green with lemon. It will be useful to do exercises, several times a day.
Towards evening it is advised to relax. Herbal teas and decoctions with honey, valerian infusion and other mild sedatives will help with this. It is recommended to go to bed early and eat less salty foods during the day.
By following these recommendations, discomfort from pressure changes will be minimized. You should listen to your body and on days with changes in weather conditions, you are advised to go to bed early.
Impact on humans
Atmospheric pressure has a serious impact on the human body. This is quite natural, if we take into account all of the above regarding the force with which the air presses on our body and the resistance provided.
How changes in weather affect people
There is a concept of meteorological dependence, confirmed by science and medicine. Meteopaths are people whose body reacts to even minimal pressure deviations from the norm. These also include people with certain chronic diseases (in particular cardiovascular, nervous system, etc.).
In general, the human body can adapt to changing climatic conditions. For example, when traveling to a country with completely different weather conditions, it may take several days to acclimatize.
Significant deviations from the norm will be noticeable for absolutely any person. This includes both high and low blood pressure.
In ordinary life, an increase in atmospheric pressure to a critical level, at which a person’s well-being deteriorates, does not occur (with the exception of the above-mentioned weather-dependent and chronically ill people). You can feel its effect, for example, when diving to great depths.
Low and high blood pressure
Low atmospheric pressure is more dangerous. Its effects can be easily felt at high altitudes. There is a concept of altitude sickness, in which the amount of carbon dioxide increases. In this case, the volume of oxygen, on the contrary, decreases, so the body tissues feel oxygen starvation. The vessels quickly react to this, provoking a sharp increase in pressure in the body.
Fluctuations within normal limits
Changes of up to 5 mm are considered normal, and our body copes with them absolutely calmly. In this case, the person does not experience any discomfort or unpleasant sensations.
Fluctuations of 5 to 10 millimeters of mercury can cause discomfort for people with poor health.
More sudden changes can be fatal.
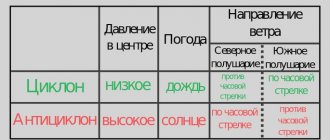
Cyclone
A cyclone is a huge mass of air that rotates in the form of a vortex around a vertical axis with a diameter of up to several thousand kilometers. At the center of this vortex there is low pressure.
Cyclones
In the Northern Hemisphere, the atmospheric vortex of a cyclone rotates counterclockwise, in the Southern Hemisphere it rotates clockwise. Cyclones occur regularly, since their formation is directly related to the rotation of the Earth. There are no cyclones near the equator.
There are two types of cyclones:
- Tropical. They occur in tropical latitudes and are relatively small in size. However, they are characterized by enormous, destructive wind power.
- Extratropical. Formed in polar and temperate latitudes. They reach several thousand kilometers in diameter.
Interesting fact : in tropical cyclones, the “eye of the storm” is often observed - this is an area of about 20 km in size in the very center of the vortex, in which clear and calm weather remains.
The main distinguishing features of a cyclone are colossal energy, which manifests itself in the form of strong winds, storms, thunderstorms, squalls, and precipitation. Powerful tropical cyclones are given unique names or names, for example, Katrina (2005), Nina (1975), Dorian (2019).
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is not only the opposite of a cyclone. This phenomenon has a different mechanism of occurrence. The wind in both hemispheres of the Earth moves in the opposite direction compared to the cyclone.
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is an area of high pressure. It is characterized by closed isobars - these are lines that mark places with the same atmospheric pressure.
An anticyclone brings stable weather conditions corresponding to the time of year. In summer it is windless, hot weather, in winter it is frosty. Characterized by few or no clouds.
Interesting: How is wind speed measured?
Anticyclones form in certain areas. For example, most often they occur over large bodies of ice: in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic. Also found in the tropics.
Anticyclones also carry danger and unpleasant consequences. They can contribute to fires and prolonged droughts. When there is no wind for a long time in large cities, harmful substances and gases accumulate, which is especially acute for people with respiratory diseases.
Difference between cyclone and anticyclone
Interesting fact : there are blocking cyclones that form over a certain area and do not move anywhere. At the same time, they do not allow other air masses to pass through. Usually they last no longer than 5 days, but regularly in the European part of Russia anticyclones last for about a month. The last time this happened was in 2015. The result is heat, drought, forest fires.
How does atmospheric pressure change with altitude? Formula, graph
Atmospheric pressure directly depends on altitude. The higher, the lower the pressure and vice versa. If you rise 12 m above sea level, the mercury in the barometer will decrease by 1 mm.
Pressure is often displayed in hectopascals instead of mmHg. Art.: 1 mm = 133.3 Pa = 1.333 hPa. You can show the relationship between height and pressure using a simple formula:
∆h/∆P=12 m/mm Hg. st or ∆h/∆P=9 m/hPa,
where ∆h is the change in height, ∆P is the change in pressure.
Thus, with an increase of 9 meters, the pressure level decreases by 1 hPa. This indicator is called the pressure level. The standard atmospheric pressure is 1013 hPa (can be rounded to 1000).
How can you use this data to calculate the change in pressure at a different altitude? For example, when rising 90 m, the pressure will decrease by 10 hPa. In this case, it turns out that when you rise to 900 m, the pressure will drop to 0.
But the air density also changes with altitude, therefore, when it comes to longer distances (starting from 1.5-2 km), all calculations must be carried out taking this indicator into account.
Height versus pressure graph
A graph of changes in atmospheric pressure with altitude clearly displays all of the above. It takes on the appearance of a curved line rather than a straight line. Due to the fact that the density of the atmosphere is not the same, with increasing altitude the pressure begins to decrease more and more slowly. However, it will never reach zero because there is some matter everywhere - there is no vacuum in the Universe.
Physical entity
Celestial bodies, including the Earth, attract the matter surrounding them, including the gas shell - the atmosphere (if there is one). The force of attraction (also called the gravitational field) depends on the mass of the body. The Earth is 80 times heavier than the Moon, so the Moon is a satellite of the Earth, and not vice versa.
The air attracted by the Earth presses on its surface, thus creating atmospheric pressure.
At sea level, atmospheric air pressure is slightly more than 1 kg/cm2. It is estimated that an air column weighing 13-15 tons , and about 150 kg on the palm.
But we do not feel this, since the pressure of the external environment is balanced by the pressure created by the air in the tissues of our body.
Atmospheric pressure in the mountains
In the mountains the pressure will be lower in any case. How a person feels depends on the altitude, as well as additional conditions. For example, with normal humidity, an ascent of 3000 m can cause weakness and decreased performance. This is due to a lack of oxygen.
In a humid climate, similar sensations arise already at an altitude of 1000 m. The fact is that water molecules displace oxygen molecules - there is less of it in humid air. And in a dry climate you can climb to 5000 m with almost no problems.
Pressure decreases with altitude
Different heights and their effects:
- 5 km - feeling of lack of oxygen.
- 6 km is the maximum height at which permanent settlements are located.
- 8.9 km is the height of Everest. Water boils at a temperature of +68℃. Trained people can only stay at this level for a short time.
- 13.5 km - you can only be safe if you have pure oxygen. The maximum permissible height at which you can stay without special protection.
- 20 km is a height unacceptable for humans. Only if you are in a sealed cabin.