Currently, extensive cerebral stroke is one of the leading causes of mortality. Even with a relatively favorable outcome, serious consequences occur. Recovery and rehabilitation require many months and even years, and not all patients manage to return to a full life. From our article you will learn what a major stroke is, what symptoms it is accompanied by, and what are the chances of survival for the victim.
Causes of major stroke
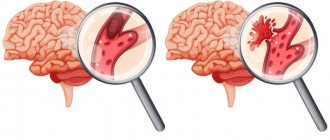
As a rule, a stroke occurs for two reasons - due to ischemia (deterioration of blood circulation in the brain) and due to hemorrhage. The first type of stroke is called ischemic. The second is hemorrhagic.
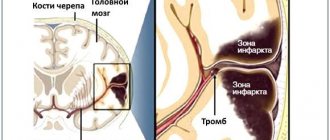
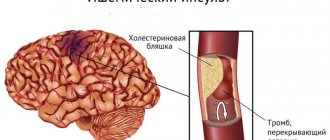
Extensive ischemic stroke is caused by prolonged spasm, compression or blockage of the main branches of the great vessels - the carotid arteries.
Hemorrhagic disorders are caused by rupture of arterial walls and subsequent saturation of brain tissue with blood. Hemorrhage can develop against the background of a sharp jump in blood pressure, with congenital pathologies and acquired diseases of the cerebral vessels, as well as with open and closed craniocerebral injuries.
Provoking factors for extensive cerebral stroke can be:
- atherosclerotic damage to cerebral vessels;
- hypertension (especially in the absence of adequate treatment);
- blood pathologies associated with an increased risk of thrombosis;
- heart diseases (CHD);
- metabolic disorders (in particular, overweight and obesity);
- endocrinopathies (including diabetes mellitus);
- asymptomatic stenosis of the carotid arteries.
Please note: The likelihood of acute cerebrovascular accident is significantly higher in patients with a history of panic attacks.
How to increase your chances of survival
The ideal way to increase your chances of survival is to take every precaution to prevent the disease from occurring. You should lead a healthy lifestyle, constantly monitor your blood pressure, and periodically undergo a comprehensive medical examination in specialized medical institutions.
You need to be especially careful in the following cases:
- if you have problems with the cardiovascular system. Hypertension, arrhythmia, and vascular atherosclerosis become the main causes of major stroke;
- in the presence of excessive mental and physical stress. The body must have enough time to fully recover;
- If there have been cases of stroke among close relatives, the risk of the disease increases significantly. Such patients need to be very careful about their health.
Doctors strongly recommend that patients who have suffered an ordinary stroke move to permanent residence in those localities where it is possible to receive effective and qualified medical care as soon as possible. After an attack, time passes by minutes; even a slight delay can be fatal.
Difference between left-sided and right-sided lesions
If extensive cerebral circulation disorder is located in the right hemisphere, the following are observed:
- left-sided paralysis;
- paralysis of facial muscles on the left side;
- passivity and general depressed state of the victim;
- memory impairment.
Important: In some cases, speech dysfunction is minor, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
If the focus of the pathology is located in the left hemisphere, the following comes to the fore:
- right-sided paralysis;
- serious mental disorders;
- speech disorders;
- pronounced problems with logical thinking.
Healing Fitness
In addition to caring for the person and proper nutrition, many patients are prescribed special physical exercises. Physical education helps to quickly tone muscles and restore the ability to self-care.
The first exercises are for the patient to learn to sit independently, then lower his legs from the bed, and walk. These simple elements are given to most patients with great difficulty. Later, the load gradually increases. The patient performs exercises designed to work different muscle groups. Bending, swinging your arms, turning your head - all these elements help restore normal motor activity and prevent stagnation.
In rehabilitation centers, the following types of treatment are used to restore a person:
- mirror therapy;
- modeling;
- drawing;
- collecting puzzles.
Therapy based on biofeedback has good results. This method involves controlling the affected arm or leg using your imagination. This is believed to help revitalize areas of the brain damaged during a stroke.
Characteristic symptoms
Clinical manifestations of extensive damage to brain tissue are always pronounced. If they appear, you should call an ambulance as quickly as possible, since the patient needs urgent hospitalization. His life depends on how quickly adequate treatment is started.
Characteristic symptoms:
- intense headache;
- dizziness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- instability in a vertical position;
- loss of orientation in space;
- nausea and vomiting;
- hyperemia of the facial area;
- cold sweat;
- dry mouth;
- cardiopalmus;
- disorders of visual, auditory or olfactory perception;
- loss of consciousness;
- speech disorders (indistinct pronunciation of words and individual sounds);
- muscle spasms (cramps);
- paralysis and paresthesia of half the body;
- memory losses.
In cases where the victim is unconscious, it is advisable to conduct a pupillary test. One of the important signs of a stroke is the lack of reaction (constriction) of one pupil to a light stimulus.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke are varied and are divided into two large groups: general cerebral and focal. Also, the symptoms strongly depend on the location of the hemorrhage, its size, the somatic condition of the patient and many other factors.
General cerebral symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke include the following:
- Impaired consciousness (stunning, stupor, coma). The larger the focus, the lower the level of consciousness. However, with damage to the brain stem, even a small focus of hemorrhage leads to severe depression of consciousness.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Headache.
- General weakness.
- Breathing disorders.
- Hemodynamic disorders.
Predominantly focal symptoms include the following:
- Paresis or plegia in the limbs, hemiparesis is more common.
- Paresis of facial muscles.
- Speech disorders develop mainly with damage to the left temporal lobe.
- Visual impairment (including the development of anisocoria).
- Hearing impairment.
A stroke should be suspected if the patient has any type of speech impairment, weakness in the arm and leg on one side, the development of epileptic seizures without provoking factors (for example, such factors include alcohol consumption), impaired consciousness up to coma. In any suspicious cases, it is better to play it safe and call an ambulance. Behavior and assessment of the situation when a stroke is suspected should be considered in a separate article.
Consequences (complications)
The sooner therapy is started, the greater the patient’s chances for the most complete restoration of body functions.
Consequences of a major stroke:
- hemiplegia (paralysis of half the body);
- complete paralysis (if both hemispheres are affected);
- problems with speech (with an extensive lesion in the left hemisphere);
- cognitive impairment (difficulty perceiving and processing information);
- amnesia (partial memory loss);
- hearing and (or) vision impairment;
- decreased tactile and pain sensitivity;
- loss of ability to concentrate.
Often the possibility of full rehabilitation is excluded, and severe consequences persist for the rest of your life.
Coma as a consequence of a stroke. Principles of treatment
A comatose state is characterized by a complete lack of consciousness and lack of reactions. It can develop rapidly, but often (in approximately every fourth case) the cause is untimely provision of assistance.
Coma with a major stroke, as a rule, lasts from several hours to 1-1.5 weeks, but can drag on for months and even years. According to statistics, the chances of partial recovery after several months in this condition are less than 15%. The mortality rate for this complication is very high. Even if the patient manages to emerge from a long coma, there can be no talk of complete rehabilitation.
The danger of this condition is that not only brain functions are affected; there is often no control of breathing and cardiac activity, and therefore the patient must be connected to a life support system. In this condition, the likelihood of repeated acute cerebral circulation disorders remains high.
The first signs of coma:
- incoherent, quiet speech;
- rave;
- lethargy;
- confusion;
- body lethargy;
- weak pulse filling;
- tachypnea (rapid breathing).
Falling into a coma is accompanied by a lack of control over the functions of the pelvic organs (involuntary urination and defecation are noted).
In the first degree, reflexes are generally preserved (skin ones are weakened), and muscle tone is increased. In the second case, there is no reaction to external stimuli; the victim is in a state of deep sleep. The third degree is characteristic of extensive hemorrhage and is characterized by the absence of basic reflexes and the reaction of the pupils to light. In the fourth, against the background of suppressed reflexes, there is a sharp decrease in pressure and depression of respiratory function.
The prognosis for life in a coma after a second stroke is disappointing, especially when it comes to the hemorrhagic type. After ischemia, the chances of recovery from this condition and partial recovery are significantly higher.
Measures must be taken to combat brain swelling, seizures and the risk of infections. The victim requires constant care. Prevention of bedsores is of great importance. Treatment also includes vitamin therapy and general massage.
Factors that increase the risk of death
A patient's chances of survival depend on several factors, some of which can be influenced, while others cannot be changed. In what cases is the possibility of survival after a major stroke significantly reduced?
- The patient had already had a stroke, and coma occurred after a second major stroke. The vessels of the brain are so atrophied that previously used therapeutic measures do not have a noticeable positive effect. Moreover, one should not hope for their effectiveness after a coma, when all vital functions are suppressed and the effect of the active substances of medications is weakened.
- Advanced age. Over time, the body's defenses and capabilities are depleted, and a large number of concomitant diseases appear. This significantly limits the possibilities of drug or surgical treatment.
- The patient is in a coma for a long period of time. There are examples when it is possible to resume the vital functions of the body after a long stay in a critical condition, but these cases are rare exceptions to the rule, and not a real pattern. As a result of prolonged immobility, very dangerous changes appear in the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, many muscles atrophy, bedsores appear, and tissue necrosis begins.
First aid
Irreversible changes in the brain begin within a few hours after the first signs of a major stroke appear. There is the concept of a “therapeutic window” - a period of 4.5 hours, during which it is still possible to prevent the death of a critical number of nerve cells. In practice, doctors have significantly less time to carry out a set of measures - on average, about one and a half hours.
If symptoms appear that indicate an acute circulatory disorder, you need to call a medical team without wasting a minute. Before their arrival, it is necessary to calm the victim and help him take a semi-lying or horizontal position with his head raised. If the patient is unconscious, the head should be turned to the side to prevent aspiration of vomit. The shirt collar should be unbuttoned, the trouser belt should be loosened, and other clothing that may restrict breathing should be removed. To ensure the flow of fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent.
If the attack began against the background of a hypertensive crisis, to improve the outflow of blood from the brain, you can lower the patient’s legs into a basin of hot water.
Important: It is strictly forbidden to give vasodilators, as well as give water and food to the patient! You should not take him to the hospital on your own, especially by public transport!
Relatives or friends need to accompany him to the hospital by ambulance, so that they can then describe the symptoms in detail to the doctors. This will help specialists objectively assess the situation and quickly make the correct diagnosis.
If necessary, the ambulance team can perform mechanical ventilation and tracheal intubation, as well as administer drugs to lower blood pressure and begin correcting the water and electrolyte balance by placing a drip with saline solution. The basic principle that guides transportation is “delivery with the least possible deterioration in condition.”
Some general recommendations
You can increase your chances of life only by observing a few general conditions.
- If the patient’s relatives, after an attack of a major stroke, provide him with the necessary pre-medical care and take all measures for the fastest delivery to the hospital.
- The medical institution has the necessary diagnostic and therapeutic equipment to ensure an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. It is desirable to be able, if necessary, to immediately perform craniotomy to remove hematoma or cerebral edema.
- Having returned to consciousness, the patient makes enough moral and physical efforts to fight for life.
After carrying out a set of emergency medical measures to maintain the vital functions of the body during a coma, the final result largely depends not on the doctors, but on the body itself. This refers not only to the general physical condition, but also to psychological factors that have not been studied by official medical science and operate at the subconscious level. Relatives should constantly talk to the patient, instill optimism in him, and support him. Let the doctors say that he can’t hear, don’t pay attention to it. No one can say with complete certainty how the brain in a coma reacts to the speech of the closest people.
As soon as consciousness returns to the patient, it is recommended not only to talk to him, but also to try to do simple gymnastic exercises. Everyone knows about the benefits of massage performed by a trained specialist. But no one can explain why simply stroking the hand of a loved one has a huge healing effect. Over time, it is advisable for relatives to learn proper massage care; this can significantly improve the results of treatment and significantly speed up the rehabilitation process.
The patient should not feel like a burden to relatives; such a condition can completely eliminate the influence of the body’s internal forces on the course of the disease. As a result, deaths increase significantly. A sick person should always know that he is loved in any condition, that all relatives are making every effort to restore health.
Video - Hemorrhagic stroke
Treatment and rehabilitation after a major stroke
The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account the diagnostic results. The type of stroke, location and probable size of the lesion are taken into account. Diagnostic procedures include blood pressure measurement, computed tomography, electrocardiogram, Doppler ultrasound, chest x-ray and laboratory blood tests - general and biochemical.
The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit. For any type of disruption of the blood supply to the brain, control of breathing, heart function and swallowing function is necessary.
For ischemic stroke, anticoagulants, vasodilators and angioprotectors are indicated. Thrombolytics are effective within the first 6 hours.
Hemorrhagic stroke may require surgical removal of the hematoma.
As the patient’s condition stabilizes, he is transferred from the intensive care unit to the intensive care unit, where he stays for an average of 2-3 weeks.
In the post-stroke period, long-term and carefully planned rehabilitation is required. It is desirable that it be carried out in a specialized medical center. Some victims remain bedridden, while others have to be re-taught basic skills. A lot of time and effort needs to be spent on restoring speech functions. For this purpose, classes are held with a speech therapist.
Caring for seriously ill patients requires certain skills. The most important activities in the recovery period are hygiene procedures, prevention of bedsores, physical therapy, adherence to the prescribed diet and socio-psychological adaptation.
What affects life expectancy after an attack?
When considering the question of how long people live after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, several factors should be highlighted on which the patient’s life expectancy often depends:
- diameter of brain tissue damage. With extensive hemorrhage or ischemia, patients require immediate hospitalization. In a hospital setting, resuscitation measures are carried out, including artificial ventilation of the lungs, maintaining the vital activity of the heart and blood vessels. If the diameter of the affected area is large, such patients, as a rule, do not survive;
- Complications affect a person’s quality of life and its duration. With paralysis, the patient is forced to spend all his time in a horizontal position, without movement. This entails bedsores, pneumonia and many other diseases that shorten life;
- Age plays a big role. The consequences of a stroke in old age are more significant, and the risk of developing severe consequences increases over the years. After 50–60 years, the chances of recovery become less and less. Younger patients are able to overcome the disease and return to normal life faster;
- competent organization of space. This is another factor that plays an important role. After an attack, many people experience dizziness and fainting, which often causes falls and broken bones. The patient’s place of residence must be safe and equipped with special handrails;
- decreased mobility after a stroke leads to blood stagnation and blood clots. This causes repeated attacks.
If a person who has suffered a stroke is at a young age, follows all the rules of rehabilitation, eats right, and engages in physical exercise, he can live quite a long time. The situation is different for the older generation. Unfortunately, the disease causes many irreversible changes, which can be very difficult to overcome, which significantly reduces life expectancy.
Diagnostics
How to diagnose a stroke at home
Every person needs to know the signs of a stroke. Being able to recognize a dangerous condition in a loved one in time means saving his life and preserving his health. Remember that anyone can have a stroke.
A stroke affects the nerves of the head and nearby limbs, causing muscles to lose healthy functionality.
Hemorrhagic stroke manifests itself sharply and clearly. You can recognize a dangerous condition by doing a few simple tests:
1. Ask to smile. Normally, both sides of the face are symmetrical, and smiling is effortless. A sick person will not be able to smile straightly; one side of the face will sag and be “late.” 2. Ask to raise both hands and hold them in front of you for a few seconds. A healthy person will be able to raise both arms at the same time, and they will be at the same level. With a stroke, one arm will lag behind the other, or it will not be possible to raise it at all. 3. Ask to repeat a simple phrase. A healthy person will be able to do this, speech will be clear and understandable. The patient's speech is slurred, incomprehensible, and it is difficult to pronounce words. 4. Ask to stick out your tongue - it will tilt to the side. 5. Ask to bare your teeth. You can bare your teeth with only one half of your mouth. 6. Ask to frown. One eyebrow will be furrowed more than the other.
If a person fails these tests, he may be suspected of having a stroke. Call an ambulance immediately.
Ischemic stroke can be detected at home by hypertensive crises and ischemic attacks. This results in a lack of blood supply to the brain. For diagnosis, you can use L. S. Manvelov’s questionnaire. Each “yes” answer receives a point if the symptom has been observed at least once a week over the past 3 months:
1. Headache due to overwork and changes in weather. It is not associated with hypertension, the nature of the pain is non-localized; 2. Tinnitus – regular or periodic; 3. Short loss of consciousness and dizziness when moving (getting out of bed/chair, bending over); 4. Short-term memory loss; 5. Lethargy, insomnia, decreased performance.
If a person answered yes to two or more points, it can be assumed that a stroke will develop in the near future. You need to go to an appointment with a therapist and get a referral to a neurologist from him.
Diagnostics in the hospital
To determine the type of stroke, different techniques are used: magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, electroencephalography, head X-ray, cerebrospinal fluid examination and blood tests.
The data obtained helps determine the type of stroke, the location of the pathology, and discover connections with parts of the brain. The sooner the patient is taken to the hospital, the more accurate his examination will be and the more effective the assistance. In the first 6 hours after an attack, medical care is most effective. This is especially important in acute strokes, which can severely damage the brain within 3-5 days.