Main symptoms of stroke
Important elements in diagnosing a stroke are a person's smile, conversation and movements.
- Smile. If you suspect a stroke, you need to ask the person to smile. In most cases of stroke, there is a distortion of the smile, all this happens because paralysis of one side of the face occurs.
- Speech. You just need to ask the person to tell you a complex sentence. For example: “Birds are singing outside.” If you hear unclear, lisping, or slurred speech, you should be wary of a stroke.
- Movements. You need to ask the person to raise both hands. If you have a stroke, your arms will be at different levels, or one arm will not rise at all.
causes of stroke
In addition, there are two more options for how to recognize a stroke :
- You need to ask the person to stick out his tongue. Due to the same nerve paresis, the tongue will be crooked or have an irregular shape. In addition, it can deviate to one side.
- You need to ask the person to extend his hand forward, palm up, and close his eyes. Also repeat with the second hand. If one of them begins to descend, then most likely the person is having a stroke.
Note! If you notice symptoms of a stroke in a person, you should immediately call an ambulance.
How to determine a stroke. First aid for stroke
What do you know about stroke? This is an insidious disease that can strike suddenly. And how quickly a person receives help after a stroke depends on how he will live after such a stroke and whether he will live at all.
Take your time and read the article. Perhaps this knowledge will help and you will save someone’s life!
Stroke attacks just a few decades ago were observed mainly in the elderly. Today, this disease increasingly affects young and able-bodied people. Many people who have a stroke die, while others become disabled. Those who died from a stroke could have been saved if the people nearby could have determined in time that the person was having a stroke and provided him with the necessary first aid in time.
If in the first three to six hours after an attack the patient is taken to a hospital, then there is a high probability that it will be possible to save him and reduce the degree of complications.
A time period of three hours from the onset of a stroke attack is called the “therapeutic window” in medicine. This is the time when inpatient care can be effectively provided. Today, there are medications that can dissolve old blood clots in blood vessels or perform timely surgery to remove a hematoma, which will keep parts of the brain healthy.
Stroke. What it is?
A stroke is a sudden disruption of blood circulation in the brain due to the fact that one of its vessels was either blocked by a blood clot, or spasmed, or ruptured. Depending on which part of the human brain is affected, various vital functions are impaired. The development of stroke is a response to diseases associated with vascular pathology.
Stroke causes
More often, men over 50 years of age and young people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle are susceptible to stroke.
- Hereditary predisposition
- Poor nutrition, stress and smoking, physical inactivity
- Obesity and high cholesterol levels
- Hypertension and hypertensive crisis
- Vascular disease, vascular elasticity disorder, aneurysm
- Atherosclerosis and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques
- Thrombosis (formation of a blood clot on the wall of a vessel) or embolism (entry into the vessels of the brain of a detached blood clot from the place where it was formed)
I will not go into details of the types of stroke, I will focus on how to determine whether a sick person has a stroke or not.
How to determine if a patient is having a stroke
Look at the picture below. The AIF newspaper suggests that you always have it on hand so that you can know how to identify a stroke in a patient.
Symptoms of a stroke
The stroke itself occurs without symptoms. It is only when brain cells begin to die that the manifestations of a stroke can be observed.
- Dizziness, weakness, fainting, or even coma
- Unsteadiness of gait and lack of coordination of movements
- Numbness of the arms and legs on one side, paralysis. When you raise your hand, it falls like a whip. The paralyzed foot is always turned outward
- Paralysis of half the face
- Eyeballs are shifted to the side
- Speech is impaired, tongue is positioned unnaturally
It is vitally important to immediately determine that this is nothing more than a stroke. Always remember: you only have three hours when you can avoid irreversible processes.
Therefore, if there are at least two of the listed symptoms, regardless of any excuses from the patient, urgently call an ambulance for hospitalization.
How to determine if a person is having a stroke
You can always have this sign on hand so that there is no question of how to determine whether a person has had a stroke or not.
First aid for stroke
- Place the patient so that the shoulder blades and head lie on the pillow 45 degrees above the body
- Provide access to fresh air: open the window, unfasten the outer and underwear (collar and belt)
- Measure blood pressure and, of course, pulse every 5 minutes. If it is high, try to correct it by holding your breath.
- If there are signs of nausea, turn the patient on his side and remove dentures.
- Give me some water to drink - this is necessary to thin the blood.
- Glycine (aminoacetic acid) can be given to calm the patient's nervous system and improve cerebral circulation. Doctors recommend taking 10-12 tablets of glycine at once. It’s good if you always have glycine in your home medicine cabinet. By the way, ambulance teams are equipped with this drug without fail, just for cases of hospitalization of patients with stroke and heart attack.
Attention!
- Do not give diuretics or blood pressure lowering drugs. If you have a stroke, you cannot sharply reduce your blood pressure! This can lead to paralysis. For hypertensive patients, you can give medications that are familiar to them and in the usual dose.
- Do not give vasodilators (no-spa, papaverine, etc.) - the vessels may dilate and blood from one part of the brain will spread to undamaged areas.
Prevention or how to avoid stroke
- If you have a hereditary predisposition to stroke, then you should be on your guard. Observation by a doctor, regular blood tests, cardiogram, blood pressure measurement should accompany your life.
- Healthy lifestyle: Establish a healthy diet that excludes salt, sugar, fried and excessively fatty foods, canned food, and sausages.
- Give up bad habits: smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol and drugs.
- Organize physical activity: daily minimum - 3000 steps.
It is much easier to prevent a stroke than to treat or rehabilitate a patient after an attack. Therefore, in case of any cerebrovascular accident, it is urgent to take measures to prevent stroke.
Be healthy!
What to do before the ambulance arrives?
Don't just stand there until the ambulance arrives. First of all, you need to put the person on a flat surface in a horizontal position. If a person has fallen, then you just need to give him a more comfortable position. It is important to control your breathing. If it is completely absent, place the person on his side, clean the oral cavity of food debris, vomit or dentures. They can be a barrier to normal breathing. To make breathing easier, you also need to unbutton your blouse or other tight items. It is advisable to loosen the belt. Open a window and allow fresh air to flow.
what to do before the ambulance arrives
If you have a tonometer at hand, you should immediately measure your blood pressure and record the readings. With high pressure, you need to raise your head, and with low pressure, you need to raise your legs. If a person has convulsions, under no circumstances should you try to restrain the person. Just put something soft under your head to avoid injuring your head. The only thing worth doing at the end of a seizure is to turn the person on his side.
It is strictly forbidden to unclench your jaw, try to insert any objects into your mouth, or fix your tongue. Such actions will only lead to harm to the person providing assistance. You should not worry about asphyxia through tongue swallowing; this is not possible during a convulsion.
If breathing and heartbeat stop, CPR should be started immediately. All resuscitation actions must be performed until the ambulance arrives.
What foods must be present in the diet?
Speaking about a healthy diet, it is necessary to note the mandatory inclusion of vegetables and fruits of different colors. Fortifying your diet with flavonoids (found in citrus fruits) has also been shown to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke.
Proteins of plant and animal origin are building materials. The daily diet should include meat and fish dishes. It is better to give preference to low-fat varieties and sea fish. To ensure your body gets protein, eat more nuts and legumes.
Plant foods also lower blood pressure and improve vascular elasticity. Add whole grains, brown unprocessed rice, and vegetable oils such as canola, olive, and flaxseed to your diet.
Dairy products should be consumed with a low percentage of fat, especially since many people are now diagnosed with lactose intolerance. If this is your case, and after consuming dairy products you feel discomfort, it is better to drink low-lactose milk or plant milk, or avoid it altogether.
Nutrition is an essential part of preventing stroke and dementia. Without a balanced diet and healthy foods, not a single pill will protect you from atherosclerosis. We are what we eat, don't forget that!
What is prohibited?
The main rule when providing assistance is to do no harm! Therefore, you should not carry out the following manipulations:
- After the person feels better, do not call an ambulance. During the first 3-6 hours, the patient must be examined by a doctor and all necessary manipulations must be performed.
- Under no circumstances should a person be given any medications. All medications that will be taken by a person with a stroke should be supervised by a doctor.
- Under no circumstances should you give food or water to a person with a stroke. This is because in such an unstable state it is difficult to control the functioning of the oropharynx.
- Do not use ammonia or other irritants to revive a person. They can lead to the development of respiratory failure.
- Do not leave the person alone until the doctor arrives. If a person tries to start moving and going somewhere, don’t let him do it. A person with a stroke can feel worse at any time.
If you or your loved ones experience even one symptom of a stroke, call an ambulance immediately!
Recovery in a boarding house
Rehabilitation of an elderly person after a stroke at home requires the full-time employment of one of the relatives for the next six months. While the patient is bedridden, he cannot be left at home alone for two reasons: he is helpless and it is necessary to deal with him several times a day. The volume of care is so large and multidirectional that soon the caregiver himself will need support and replacement.
In boarding houses for the elderly, professionals are involved in the rehabilitation of patients. Special equipment is used for treatment. An individual program is developed for each patient. Restoration methods that have been developed over the years produce positive results within a month.
Nutrition problems after cerebral stroke
Experts highlight certain problems and features of caring for people who have had a stroke:
- Possible difficulties with chewing and swallowing food;
- if the mobility of the hand is affected, it may be difficult to use a fork or spoon;
- Appetite may worsen, moodiness and selectivity in eating may occur;
- memory impairment is possible - the patient forgets what and when he ate.
- Many patients are prescribed strict bed rest due to the threat of recurrent stroke, general serious condition, and partial impairment of motor functions.
Patients after a stroke need a diet that will help quickly restore lost body functions, while also providing the necessary substances for life (including in cases of impaired swallowing reflex and chewing process).
The first signs of myocardial infarction: when to take action?
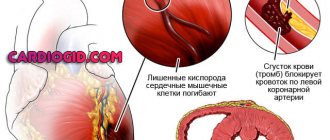
Myocardial infarction is an acute condition that occurs due to coronary heart disease and is accompanied by severe circulatory failure in the coronary vessels and necrosis of part of the heart muscle tissue. In 10–12% of cases it is life-threatening for the patient. More often, heart attacks occur in men over 60 years of age, but after menopause, women are also at risk. In recent years, there has been a significant “rejuvenation” of this condition and the development of anesthesia of the heart muscle in 20-30 year old young people is observed more and more often.
In 90% of patients with coronary artery disease, a heart attack is provoked by coronary artery thrombosis caused by atherosclerosis. The following reasons can also provoke coronary circulatory insufficiency:
- thrombosis and spasm of coronary vessels;
- heart injuries;
- tumors or metastases.
- The risk group for developing a heart attack includes people with the following pathologies and conditions:
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertonic disease;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- increased levels of LDL in the blood;
- adynamia;
- bleeding disorders;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- excessive psycho-emotional and physical stress.
Usually the attack begins suddenly, but in some patients there may be a pre-infarction condition, manifested by an increase in temperature, tachycardia and arrhythmia, cyanosis of the mucous membranes, severe pallor, an increase in blood pressure with its subsequent decrease. This condition can last from several hours to several days or weeks.
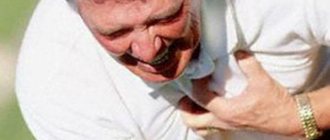
The main sign of a heart attack is severe pain in the chest, which is prolonged. It differs from the pain that occurs with angina pectoris in that it manifests itself for more than 15 minutes and is not eliminated even by repeated administration of Nitroglycerin. Usually pain occurs after physical or psycho-emotional stress.
Immediate first aid actions for a heart attack should be performed immediately after the following symptoms occur:
- severe and prolonged pain behind the sternum of a burning, stabbing, tearing, squeezing nature (it is present for half an hour and is not eliminated or is only partially relieved by the usual intake of Nitroglycerin);
- severe anxiety and fear of death;
- pain radiates to the left (sometimes to the right) arm, shoulder blade, interscapular area, neck, teeth;
- cold clammy sweat;
- dizziness or fainting;
- pallor;
- nausea;
- difficulty breathing and shortness of breath (sometimes);
- rapid and arrhythmic pulse.
In approximately 20% of cases, myocardial infarction occurs in an atypical form and is not accompanied by pain in the heart area. In such cases, symptoms may be as follows:
- with an atypical location of pain - it is concentrated in the left hand, at the tip of the little finger of the left hand, in the cervicothoracic spine or in the scapula, in the area of the lower jaw or neck, the pain syndrome is complemented by typical manifestations of a heart attack;
- with the gastric type of attack - indigestion and abdominal pain;
- with asthmatic – shortness of breath and suffocation, dry cough;
- with arrhythmic – rapid and arrhythmic pulse;
- with cerebral – confusion, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, speech disorders;
- with edema – severe weakness, shortness of breath, rapid increase in edema;
- if painless - discomfort in the chest, weakness, increased sweating.
The first signs of a heart attack and any suspicion of its development are a reason to call an ambulance. The operator must be informed about the symptoms and the possibility of a heart attack. After this, you should immediately begin providing pre-hospital emergency care.