Myocardial infarction: symptoms, signs of the need for first aid
Myocardial infarction in medicine is defined as the development of necrotic changes in the heart.
This is one of the most acute clinical forms of IHD (coronary heart disease). The disorder occurs due to acute insufficiency of blood flow due to a failure in the supply of oxygen to the heart muscle. A heart attack may be indicated by sudden sweating, nausea, pain in the sternum, forearm and other parts of the body. Heart attacks in men occur 5 times more often than in women, which is especially noticeable in young and middle-aged people. Heart attacks in women develop on average 10-12 years later than in men. Among the reasons is the later development of atherosclerotic changes, which is facilitated by less widespread bad habits and the protective effect of estrogens in women.
Cardiac, neurogenic (vegetative) manifestations
Chest pain is the first and most obvious symptom of microinfarction in women. However, not required. A microinfarction (abbreviated as “micro MI”) is a small-area necrosis of the heart muscle (myocardium).
Despite the continued high risk of death from cardiac arrest and complications in general, the intensity and presence of pain depend on the location of the ischemic site.
If the septum or posterior wall is affected, the manifestations are extremely scanty or absent. It happens that a microinfarction is suffered on the legs, and its consequences are discovered by chance, years later, during echocardiography.
The pain syndrome is weak, burning or pressing. Localized in the center of the chest or slightly to the left.
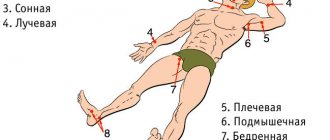
A distinctive feature is the inability to show the place with a finger. Discomfort is not in one point, it covers an entire area. Recoil (reflection) occurs in the left arm, shoulder blade, neck, jaw, back, and rarely the stomach (epigastric region, where the stomach is).
Sharp shooting pains are not typical, as is aching discomfort. This is rather an indication of neuralgia or pulmonary syndromes, myalgia, but not a microinfarction.
Objective diagnostics puts an end to the issue. At the everyday level, it’s enough to take a deep breath and move around. If there are changes in the severity of pain, the likelihood of a cardiac origin is low.
Blood pressure instability
As a result of malnutrition of the heart muscle, the contractility of the myocardium decreases. The body strives to artificially compensate for the condition and causes the cardiac structures to contract more actively.
Systoles become more powerful, pressure on the walls of blood vessels increases, as does the heart rate. This is extremely dangerous and can cause a full-blown heart attack. Within one hour, the change can reach 30-40 mmHg and more.
To prevent blood pressure surges, it is recommended to sit down and move less. Calm down as much as possible. Sudden movements are strictly contraindicated.
Subjectively, rapid changes in blood pressure are manifested by chest pain, cephalalgia (headache) of unknown origin.
Hypertensive patients and heart patients, accustomed to the disorders and already adapted to them, practically do not notice the difference, which is even more dangerous.
Panic attack
Mental disorder of the neurotic series. Occurs in 95% of patients with cardiac disorders.
What this is connected with is not known exactly. Apparently, the release of a large amount of stress hormones and signals from the nervous system, activation of the central nervous system.
Persons with a microinfarction experience a strong fear of death, psychomotor agitation, and inappropriate behavior are observed.
A woman poses a danger to herself and may be injured or die as a result of a fall or other factors. If a pathological process develops, you need to try to keep your emotional situation within normal limits.
Other mental disorders
As the process progresses or enters the subacute stage, depression of the nervous system is observed.
The patient is apathetic and does not want anything. Reacts poorly to external stimuli and stimuli. He communicates reluctantly or is completely silent, and remains in a depressed mood for a long time.
Possible tearfulness, disturbances of mnestic functions, slowing down of thinking and cognitive activity of varying degrees of severity (from slight absent-mindedness to complete inability to think logically).
This “stupor” can last up to several hours; there is no special need to bring it out of it. Everything will go away on its own.
In some women, similar symptoms develop immediately, instead of a panic attack. Depends on the individual characteristics of the nervous system and psyche.
Arrhythmias
Business card of the state. The first signs of a microinfarction are irregularities in heart rate and/or uneven intervals between each subsequent beat. There are a lot of variations.
The classic picture is an acceleration of heart rate. Sinus type. It is a compensatory mechanism. The phenomena of ischemia (oxygen starvation) of cardiac structures increase, hemodynamics (blood flow speed) decreases, the body tries to restore the volume of release into the large and small circles in order to provide itself with nutrients and oxygen.
The effect is minimal, so the process goes in cycles until it is interrupted by artificial methods.
The paroxysmal type of tachycardia is much more dangerous. It no longer develops due to the sinus node. It manifests itself as an acceleration of heart rate to levels of 190-250 beats or more. May result in cardiac arrest.
Ventricular fibrillation, group extrasystole (like bigeminy/trigeminy) affects the same way, but the prognosis is even more serious. Both are considered life-threatening forms of arrhythmia.
Excessive sweating
Hyperhidrosis is another characteristic precursor of microinfarction in female patients. Develops as a result of circulatory disorders in the brain and nerve tissues. In particular, the hypothalamus, which is responsible for thermoregulation.
Malnutrition causes the generation of chaotic impulses and signals. A generalized process begins. Sweating occurs without connection with physical activity - it is a reflex phenomenon. There is no need to stop it as such, but it is an indicative sign of a vegetative disorder.
Pale skin
The shade of the dermal layer, as well as the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (gums), and nail plates changes. There is coldness in the fingertips and limbs in general.
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle
Blue discoloration of the area around the mouth and lips.
Actually, cardiac manifestations occur first, proceed most actively and require immediate elimination.
Causes of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction develops for various reasons, some of which are contributed by the person himself, others by his environment. Let us highlight 3 main groups of provoking factors:
- Factors that directly depend on the person - eating large amounts of fatty foods, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption.
- Factors that indirectly depend on a person are obesity, menopause and postmenopause.
- Factors that do not depend on a person - old age, genetic predisposition.
Myocardial infarction develops with atherosclerosis and inflammation in the walls of the arteries resulting from trauma, radiation exposure, vascular embolism, congenital anomalies and disruptions of the hematopoietic apparatus.
What diagnostic methods can be used to make a correct diagnosis?
The main method for diagnosing microinfarction is electrocardiography (ECG). Changes are characterized by the presence of:
- coronary negative T wave;
- downward shifted ST interval;
- absence of disturbances of the ventricular QRS complex.
It is possible to establish the localization of the focus of necrosis by the ratio of changes in standard and chest leads, the depth of the lesion (usually subendocardial location). Transmural necrosis is not possible for small lesions.
When scars are identified after a microinfarction, bundle branch blocks and signs of metabolic disorders are detected.
Laboratory indicators are less typical and therefore are not very informative in diagnosis:
- moderate leukocytosis is found in half of the patients;
- acceleration of ESR up to 15-40 mm/hour;
- a slight increase in fibrinogen concentration;
- enzymes indicating myocardial necrosis may be normal.
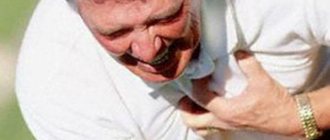
Heart attack: symptoms and first signs
- Patients do not always associate symptoms of a heart attack with the manifestation of this pathology. The patient’s feelings depend on what period of its development the disease is at. Common signs of a heart attack:
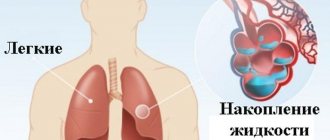
- severe dizziness, feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath;
- feeling of chronic fatigue, cold sweat on the body;
- uneven heartbeat, severe arrhythmia;
- pain impulses in the arms, forearms, shoulders, side, sternum;
- nausea, unpleasant heaviness in the stomach, loss of consciousness.
The first signs of a heart attack are not always obvious, but they attract attention. There are several periods of development of pathology:
- Pre-infarction stage - the first signs here are increased fatigue, weakness, fatigue, a feeling of squeezing and rapid heartbeat. There is no significant pain yet. In a patient with myocardial infarction, the lips and nail plates turn blue, the pulse becomes erratic and uneven. At this time, the severity of the disease increases, the duration of the period ranges from a couple of hours to a month.
- The most acute stage of heart attacks is pain. The patient begins to feel as if his chest is being squeezed in a vice. Behind the sternum there is a burning sensation, fiery heat, pulsating pain. With the development of an extensive heart attack, the pain is severe and prolonged. Strong and abrupt impulses are observed in young patients. Muffled pain, indicating myocardial infarction, is more often observed in patients with diabetes mellitus. The duration of the period is from half an hour to 2-4 hours. Complications that pose a direct threat to life are possible.
- Acute stage of a heart attack - among the first symptoms, the final formation of a focus of dead tissue and the occurrence of life-threatening conditions are noted. The duration of the period is 2-14 days.
- Subacute period - dead areas are replaced by connective tissue. The duration of the stage is 6-8 weeks.
- The post-infarction period lasts from two months to six months. During this time, the body adapts to new conditions.
If there are signs of a heart attack, you should not self-medicate; you should urgently consult a doctor, undergo an examination and get specialist recommendations.
Case from practice
A 54-year-old woman came to the clinic with complaints of weakness and nausea.
The problem was associated with malnutrition. During the interview, it turned out that she had been experiencing angina pectoris for 10 years; attacks occurred several times a month and were relieved with Nitroglycerin. The ECG shows signs of acute ischemia along the lower wall of the left ventricle, without the formation of a Q wave. Diagnosis: Small focal infarction.
The woman completed a full course of treatment in hospital, her condition improved, and she was discharged under the supervision of a local cardiologist. Recommended: following a diet, taking Aspirin Cardio, Metoprolol, Atrovastatin.
Where is the pain hidden during myocardial infarction?
Pain during myocardial infarction is localized in the chest area, spreading mainly to the left side of the chest space or being fixed in the central zone. The patient’s appearance also attracts attention: the skin is pale, moist, blue discoloration is visible in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
Myocardial infarction is often characterized by pain spreading to the left or right arm. Patients often talk about unpleasant sensations in their wrists, so similar to being put on squeezing handcuffs. The pain can go to the left shoulder blade and spread around the neck. The abundance of such places often complicates diagnosis, especially since pain symptoms are cyclical, increase and disappear in waves, and then everything repeats again.
Sometimes symptoms are observed for several days, and people do not rush to see a doctor because they are not aware of the development of signs of a dangerous disease. Another interesting symptom of a heart attack is known, when a person experiences hallucinations against the background of acute intense pain.
Atypical forms of the disease attract attention when the symptoms and first signs of a heart attack are manifested not by pain, but by shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air and an irregular heartbeat. Acute infarction develops when a focus of necrotic tissue is finally formed. At this time, the pain disappears, the pressure drops, and the pulse quickens. The pain may persist if the affected area during a heart attack expands.
Expert advice
It is very important to recognize a small focal infarction in time. It is necessary to immediately take emergency measures and call a doctor if the following signs occur:
- panic, fear of death;
- skin cold and clammy from sweat;
- pain in the chest on the left, radiating under the shoulder blade, in the back, jaw, half of the head;
- the pulse is poorly palpable or not detectable;
- The nasolabial triangle turns blue.
You should also know that sometimes (especially in patients with diabetes and the elderly) a small-focal heart attack occurs without symptoms or manifests itself in the form of asthma attacks, abdominal pain, and rhythm disturbances. But any form can develop into a large-focal or transmural infarction, and therefore requires urgent qualified help.
Scheme of development of myocardial infarction
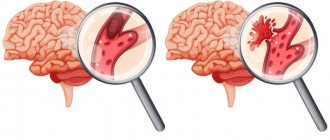
The atherosclerotic plaque loses its integrity and undergoes rupture. Its surface is corroded by erosion, which provokes inflammation. Plaque rupture is possible under the following circumstances: increased blood pressure, serious and exhausting physical activity, smoking, etc.
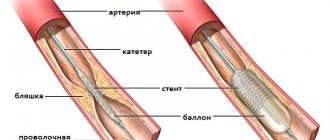
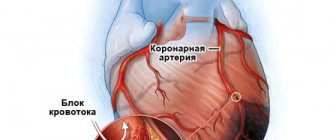
A blood clot forms that blocks the lumen of the coronary artery (thrombosis). The blockage occurs due to the clumping of platelets. A thrombus forms inside the plaque when its membrane ruptures, and only then comes out, closing the lumen of the coronary artery. If the blockage is sudden, a through myocardial infarction develops with necrotization of the entire thickness of the heart muscle. This is one of the most severe forms of the disease due to the high risk of death.
The coronary artery narrows sharply. With spontaneous or drug-induced dissolution of a blood clot and incomplete blockage of the artery, non-through infarctions are formed.
Disease prevention
To prevent the disease, the following rules should be followed:
- Undergo an annual examination and take a cardiogram. This is a mandatory condition for people over 45 years of age.
- Control body weight. This will help reduce the load on the heart and prevent the development of type II diabetes.
- Exercise regularly. This improves the general condition of the body and optimizes metabolic processes. A trained heart can more easily tolerate pressure surges and the release of catecholamines during a stressful situation.
- Refrain from smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Monitor blood pressure and sugar levels, treat hypertension or diabetes in a timely manner.
- Review the menu towards a healthy diet, reduce the consumption of salt and animal fats.
Secondary prevention consists of the constant use of Aspirin, statins and beta blockers. During the recovery period, you should gradually increase physical activity, perform physical therapy exercises and walk in the fresh air.
Diagnosis and treatment for heart attack
An experienced doctor makes an accurate diagnosis at the first signs of illness. To help him - characteristic symptoms, a detailed clinical picture of a heart attack, electrocardiography indicators and identification of blood biomarkers indicating necrotic changes in the heart area. The first examinations upon treatment include a general blood test, biochemistry, echocardiography, and emergency selective coronary angiography.
Cardiologists deal with heart attacks; treatment depends on the severity of the pathology and how severe the symptoms are. The first signs of a heart attack in a woman or man indicate the need for urgent medical attention. The first and main tasks of doctors are to stop the development of necrosis of cardiac tissue, eliminate pain and associated complications.
In therapy, priority is given to the administration of painkillers, thrombolytic therapy, antiplatelet agents, and intravenous anticoagulants. In case of heart attacks, surgery of the heart muscle is possible - stenting and coronary artery bypass grafting.
Characteristics of the pathology
Fine-focal damage to myocardial cells followed by necrosis occurs as a result of:
- incomplete closure of the lumen of the vessel;
- the presence of collateral blood flow pathways;
- complete blockage of small arteries.
All these factors lead to subtle changes that rarely lead to complications. But with a repeated attack or disruption of the patency of several small-caliber vessels at once, the pathology can develop into a large-focal process with severe symptoms and serious consequences.
There are two types of microinfarction: intramural (located deep in the myocardium and does not affect the inner and outer layers) and subendocardial (on the inner lining of the heart). In the first case, a negative T wave is recorded on the ECG in the area of the disorder. In the second, the ST segment shifts below the isoline, as can be seen in the photo:
Prognosis after heart attacks
In case of heart attacks, you should be observed by a specialized specialist. After an illness, the situation may be complicated by cardiac arrhythmias, acute heart failure, cardiogenic shock, pericarditis, mental disorders and other pathologies. A professional doctor will help reduce the risks of exacerbations after myocardial infarction.
Our clinic provides services to patients with all types of cardiac pathologies, including those who have suffered a cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke). It is these complications of brain damage that are considered one of the main causes of increased mortality throughout the world. Despite this, our doctors do everything possible to maintain and improve the quality of life of their patients.
Types of pathological process
Classification is carried out on several grounds.
Based on the form of functional impairment:
- Circular. It is one of the heaviest types. Several branches of the coronary circulation are blocked (there are two arteries in total, each branching along the path into the tissue).
Generalized malnutrition leads to the impossibility of adequate trophism. Mortality is about 80%; with timely assistance and transportation to a hospital within the first hour, the chances increase slightly.
Partial work of the affected area may remain; necrosis is not always complete.
- Transmural form. The exact amount of tissue involved is not known. But total necrosis of the area is observed, it is excluded from functional activity. Even with proper treatment and survival, severe heart failure develops for this reason.
- Actually large-focal MI. When a group of areas is involved in the pathological process. They are usually located asymmetrically.
Depending on the location, we can talk about an infarction of the anterior or posterior wall of the heart. The first option is less noticeable from a clinical point of view; false symptoms or the absence of a clear picture are possible.
Classification is carried out according to the prevailing symptom complex, the involvement of third-party organs and tissues:
- Cerebrovascular form. It can proceed in parallel with the classical one. The trophism of nerve clusters and cerebral structures is disrupted. The likely consequence is a stroke.
- Arrhythmic type. The main manifestation is a violation of heart rate. Tachycardia or a decrease in heart rate occurs in parallel with a change in the intervals between beats. The process is represented by extrasystole, fibrillation.
- Abdominal form. The clinical picture of an acute abdomen is typical. Nausea, vomiting, and unbearable pain in the abdominal cavity occur. Such patients are falsely mistaken for gastroenterological patients and sent to the appropriate department. Precious time is wasted and chances of survival are diminished.
- Asthmatic appearance. Shortness of breath, impaired consciousness, asphyxia and other “delights” are included.
All four are called atypical, and together they account for barely more than 10% of clinical situations worldwide.
What if the changes are no longer fresh?
If a microinfarction in the scar stage is detected on the ECG, the patient needs to deal with the prevention of more widespread changes in the myocardium.
Regular activities and nutrition do not differ from the general requirements. They should be followed throughout your life.
Diseases that contribute to myocardial ischemia are treated with specific drugs: antihypertensive drugs - hypertension, hypoglycemic drugs - diabetes.
A previous microinfarction indicates poor coronary circulation and developed atherosclerosis. Monitoring the level of lipoproteins in the blood and coagulation is necessary.
The doctor usually prescribes a course of statins if it is impossible to manage with a diet.
To reduce thrombosis, drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid (Cardiomagnyl, Thrombo Ass) are indicated.
According to indications for microinfarction, coronary lytics and β-blockers are prescribed. These drugs allow you to preserve and develop the remaining heart muscle tissue.