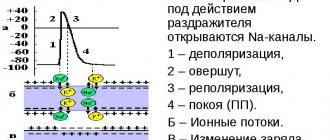
The world is just beginning to recover from the coronavirus epidemic, which has literally divided the lives of millions of people into “before and after.”
As a practicing cardiologist at the “Healer” medical clinic in Khasavyurt, I have to deal every day with patients who come for appointments with manifestations of cardioneurosis.
I can assure you that recently this is primarily due to the consequences of the epidemic. The fact is that cardiac neurosis occurs against the background of mental factors or, as experts say, it is a functional cardiac disorder that has a psychogenic etiology.
Types of pathology and its symptoms
In medical sources you can find various names for cardioneurosis, such as: cardiac neurosis or cardiac neurosis, neurocirculatory, vegetative-vascular dystonia, functional cardiopathy or psychovegetative syndrome. These are all different names for the same disease.
The main forms of manifestation of cardioneurosis are:
1. Cardiological, which is expressed by attacks of pain in the heart.
- Panic. This form is characterized by manifestations of a panic attack.
Factors causing cardioneurosis
- some features of the psychotype, congenital instability of the psyche;
- consequences of stress, neuropsychic shocks;
- overwork of the nervous system;
- endocrine diseases that provoke the appearance of hormonal disorders;
- periods of hormonal changes in the body (menopause, puberty);
- presence of severe chronic diseases;
- unhealthy lifestyle (lack of physical activity, bad habits).
Signs of the disease
Among the most common symptoms of the disease are:
- pain in the chest area. The pain can be pressing and aching. Often, clinic patients complain of piercing, sharp pain in the heart area, to the point where it feels like the heart has stopped, followed by an increase in heart rate;
- physical or mental stress leads to heart rhythm disturbances or increased heart rate;
- a feeling of chills or, conversely, a rush of heat, sweating, possible shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air;
- high blood pressure, often accompanied by headache, weakness, dizziness;
- panic, fear of death, anxiety, sleep disturbances.
Candidate of Medical Sciences, psychiatrist V. E. Medvedev. In 1871, a disorder was described characterized by complaints of palpitations, pain in the heart area, rapid pulse, a feeling of shortness of breath, headaches, irritability, and sleep disturbances. The author who identified this syndrome, whose name is also used in modern literature (Da Costa syndrome, cardiac neurosis ), emphasizes that the clinical picture is dominated by unpleasant sensations in the chest, which are comparable to typical ischemic pain that develops in the form of attacks or attacks. To designate these conditions in the medical literature, the term “ neurocirculatory (vegetative-vascular) dystonia ” (NCD) has been used for a long time; in foreign sources – “asthenia”. Currently, vegetative-vascular dystonia is a common designation in medical practice for vegetative disorders of various origins and manifestations, but fundamentally functional, caused by a violation of the neurohumoral regulation of vegetative functions.
At the same time, ICD-10 presents a different position: in this classification, built on a syndromic basis, “Somatoform disorders” (F45) occupy the position of an independent taxon, within which the category “Somatoform autonomic dysfunction” (F45.3), including diagnostic rubric “Somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the heart and cardiovascular system” (F45.30). It is under this heading that such forms as cardiac neurosis, Da Costa syndrome, and neurocirculatory asthenia are included. However, the question of the identity of the diagnoses of neurocirculatory dystonia and cardioneurosis remains controversial to this day.
According to the observations of domestic and foreign authors, the number of patients with functional disorders of the cardiovascular system - cardioneurosis ( neurocirculatory dystonia , d'Acosta syndrome, tension syndrome, "soldier's", "broken" heart) reaches 15-30% of patients in specialized cardiology hospitals. According to the results of an epidemiological study (2181 patients, of which 1718 were multidisciplinary hospitals and 463 territorial clinics) carried out at the Scientific Center for Healthcare of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, cardioneurosis occurs in 4.7% of patients in the general medical network. Among the outpatient population, this disorder is detected much more often - 15.6% versus 2% in a multidisciplinary hospital.
Cardioneurosis (neurocirculatory asthenia, dystonia, d'Acosta syndrome, tension syndrome, "soldier's", "broken" heart) is an independent psychosomatic disorder of a circle of organ neuroses, in which the formation of autonomic dysfunctions, somatoform disorders and algia occurs according to functional mechanisms.
Manifestation and repeated exacerbations of symptoms in approximately 30% of patients are provoked psychogenically, alcohol abuse, trauma or surgical interventions, repeated pregnancies and childbirth. In other patients, the disease occurs without visible provocation and is often associated with periods of hormonal changes in the body (puberty, first pregnancy) and/or the presence of morphological abnormalities of the heart (mitral valve prolapse, accessory chord).
Patients with cardioneurosis are characterized by the presence of persistent or episodic symptom complexes for at least 2 consecutive years: various somatoform disorders simulating symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular system (including bodily fantasies, conversions, cardialgia), anxiety-phobic disorders (fear of stroke, heart attack, death from cardiac arrest, etc.), accompanied by sensations of irregular heartbeat with a tendency to tachycardia, revealed during physical examination by lability of blood pressure (hyper/hypotension), acute vegetative symptom complexes simulating urgent cardiovascular pathology (orthostasis, fainting, dizziness), as well as depressive symptom complexes (low mood, apathy, pessimistic assessment of the future, etc.). Other signs of cardioneurosis are symptoms of autonomic dysfunction detected during physical examination: local sweating, marbling or coldness of the extremities, persistent white dermographism; lability and nonspecific changes in the final part of the ventricular complex; temporary reversion of the T wave during exercise testing.
Cardioneurosis with dominance of bodily sensations (sensopathy) is characterized by a predominance of idiopathic cardialgia, tachycardia and bradycardia, orthostatic phenomena, syncope and autonomic disorders (subsyndromal panic attacks). The clinical picture of cardioneurosis with a predominance of anxiety-phobic disorders is characterized by polymorphism. Against the background of anxiety-phobic disorders with fears of cardiovascular catastrophe and death, panic attacks, 5-10% of patients exhibit agoraphobia, as well as bodily fantasies, acute autonomic disorders and symptom complexes of organoneurotic disorders of other organ systems (irritable bowel or bladder syndrome, hyperventilation) . A feature of the clinical picture of cardioneurosis with a predominance of affective disorders is the persistence of cardioneurotic symptoms against the background of depressive phases within the dynamics of affective personality disorders. The picture of depression is dominated by astheno-apathetic or hypochondriacal manifestations.
The criteria for cardioneurosis, taking into account the complexity of psychosomatic relationships, provide for a comprehensive assessment of the condition, with the participation of a psychiatrist and cardiologist. At the same time, the diagnosis of cardioneurosis is a “diagnosis of exclusion”; To stage it, it is necessary to completely exclude the presence of cardiovascular pathology (coronary heart disease, hypertension, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, etc.), as well as any other somatic disease, the features of which could explain the existing symptoms. The diagnosis of NCD (cardioneurosis) is confirmed during repeated examinations, including the assessment of physical, instrumental and laboratory parameters (including routine clinical and biochemical blood tests, lipid spectrum, ECG, ECHO-CG, daily Holter ECG and blood pressure monitoring, treadmill, peak expiratory flow (PEF), capnography study, blood gas composition, voluntary hyperventilation test, spirometry). To exclude organic pathology of the brain, MRI and EEG studies were performed. In addition, during a psychopathological examination, it is necessary to exclude the manifestation of endogenous psychosis (schizophrenia, schizoaffective/affective psychosis).
Therapy of cardioneurotic disorders includes both various methods of psychotherapy and the prescription of psychotropic drugs. It is advisable to begin psychopharmacotherapy already at the stage of examining the patient, at the first signs of symptoms of anxiety or depression. At the same time, in order to reduce the possibility of the influence of synthetic psychotropic drugs on the patient’s clinical and laboratory parameters, herbal remedies (valerian, St. John’s wort, Persen, etc.) can be recommended. If therapy is ineffective, the progression of a psychopathological disorder, depression or severe anxiety disorders, it is necessary to use combination or monotherapy with antidepressants (taking into account the effectiveness/tolerability ratio) of the group of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (paroxetine, sertraline, fluvoxamine, citalopram, S-citalopram, fluoxetine) or double-acting (milnacipran, duloxetine, venlafaxine), anxiolytics (non-benzodiazepine and benzodiazepines), low-dose antipsychotics (sulpiride, quetiapine) and nootropic drugs.
Make an appointment for a consultation with psychiatrist V.E. Medvedev.
How does pain in the heart during ischemia differ from cardioneurosis?
Experienced cardiologists can name a number of differences in the pain syndrome that manifests itself in coronary heart disease (CHD) and cardiac neurosis. Here are the main ones:
- With cardioneurosis, the pain has a clear localization, and with ischemic heart disease, pain can cover the entire chest and even radiate to the back area.
- A painful attack with cardioneurosis, as a rule, lasts less than an hour, and with ischemia it lasts much longer (from several hours to several days).
- With cardiac neurosis, pain arising from psycho-emotional stress can easily be relieved after relaxation, which does not happen in the case of cardiac ischemia.
- Nitroglycerin is effective in relieving pain from ischemia, but does not help with cardioneurosis, in which sedatives and hypnotics help.
- During studies (ECG, ultrasound), specialists in functional diagnostics of medical centers confidently diagnose the presence of pathological changes from coronary artery disease, and if pain in the heart is neurotic in nature, then violations are not detected during such studies.
What examinations are necessary to make a reliable diagnosis of cardioneurosis?
In order to exclude organic heart pathology and other serious diseases hidden behind a variety of symptoms, the patient must be observed for at least 2 months. At the same time, the connection of attacks with stressful situations and circumstances that have a stimulating effect on the patient’s psyche is of decisive importance in favor of cardioneurosis. Only after excluding structural changes and making sure of the functional nature of the symptoms can a diagnosis of cardioneurosis be made.
Specifically, the examination plan should include the following activities: • Detailed and thorough history taking. • Physical (physical) examination of the patient with determination of signs of asthenia, excessive sweating, skin color, etc. • Electrocardiographic examination (one-time and in the form of daily monitoring), ultrasound of the heart, ultrasound of the cervical vessels, etc. • Breathing tests to study the function of external respiration . • Clinical and biochemical blood test with determination of AST, LDH, lipid profile, C-reactive protein, creatine kinase, thyroid hormones and potassium. To exclude the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction, cardiac troponins and myoglobin are determined. • FGDS for severe dyspeptic syndromes. • Electroencephalogram for studying the brain and identifying its pathologies (epilepsy, neoplasms, inflammatory processes and vascular disorders).
Consultations with specialized specialists are required - cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist, gastroenterologist, etc.
Causes of the disease and methods of treatment
There are many different reasons that can cause the pathology of functional cardiopathy, but the most common in practice are the following:
- chronic stress. This can happen due to conflicts at work, an unfavorable psychological situation in the family, long-term painful conditions, etc.
- all kinds of phobias, fears, anxieties, depression and panic attacks;
- chronic infections and toxic effects on the body;
- hormonal changes, which, for example, can be caused by pregnancy or menopause;
To effectively carry out a course of therapy, a qualified attending cardiologist uses a variety of modern options for complex and auxiliary treatment, including:
- Psychotherapy. Cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy has proven to be the most effective method.
- Medication. Antidepressants and sedatives are prescribed. This method is considered auxiliary for cardiac neurosis.
- Reflexology.
- Physiotherapy;
- Spa treatment.
Nukhova Aminat Idrisovna, cardiologist.
Tell us in more detail about vegetative failures, what causes them and how they manifest themselves?
To begin with, we should remember that the main function of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is to regulate the activity of all internal human organs. Its two departments are responsible for this, acting in different directions: • Sympathetic, when activated, there is an increase in heart rate (tachycardia), increased blood pressure and body temperature, tremor, etc. • Parasympathetic, responsible for slowing the heart rate (bradycardia), lowering blood pressure and temperature , decreased activity, etc.
With balanced and synchronized work of both departments, the body functions like a well-oiled clockwork mechanism. Adequately responds to environmental changes, is resistant to stressful situations, has a strong immune system, all its reactions are aimed at protecting the body from negative influences and survival.
When the coordinated work of the ANS departments is unbalanced, the body loses many of its advantages in this duel with the outside world, and with pronounced autonomic dysfunction, various diencephalic crises can develop: • With predominant and excessive activity of the sympathetic ANS, a sympathoadrenal crisis occurs in the form of an attack of headache and heart pain, tachycardia , increased blood pressure and temperature, chills, flushing or pallor of the face. All these phenomena are often accompanied by fear of death and anxiety for one’s life. And this is quite understandable. After all, normally a person does not feel his heart, except under severe anxiety and stress. You can imagine how he feels the whole range of symptoms that have befallen him, especially if he is experiencing a crisis for the first time. Fear can be so strong that it forever settles in a person’s memory and plunges him into constant anxious anticipation of a repetition of the attack. It turns out to be a vicious circle: attack → fear → anxiety → new attack. It is almost impossible to interrupt this cycle without the help of specialists and appropriate treatment. • With hyperactivity of the parasympathetic division of the ANS, we are dealing with the so-called vagoinsular crisis. Its main manifestations are sudden severe weakness up to fainting, darkening of the eyes, sweating, dizziness, nausea, decreased blood pressure and body temperature, bradycardia (slow heart rate).
With particularly severe vegetative failures, accompanied by severe fear and panic, we are already dealing with panic attacks, which are easier to prevent than to stop. But this is a topic for another discussion.
Autonomic instability most often develops after infectious diseases, head injury, severe stress, during hormonal changes and taking hormonal medications.
General clinical picture
The cardiac symptoms of cardioneurosis worry patients most of all, but other manifestations are also characteristic of the disease. Their intensity varies depending on the individual characteristics of the person. General symptoms of cardiac neurosis during an attack are usually the following:
- a feeling of anxiety that develops into panic;
- obsessive thoughts (obsessive syndrome) about imminent death and the development of fatal pathologies;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- lack of oxygen;
- frequent shallow breathing;
- feeling tired even with the slightest overload;
- inability to take a deep breath;
- headache;
- excessive sweating;
- alternating sensations of heat and cold throughout the body;
- loss of consciousness or faintness.
After the attack ends, the person feels a loss of strength and drowsiness. Heavy thoughts appear in your head that prevent you from falling asleep at night.
How to help with a panic attack of cardialgia?
It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis of cardioneurosis at the level of the first person you meet and even an ambulance. If your loved ones are already familiar with the disease, you should:
- provide access to air - open a window, turn on the air conditioner, loosen the collar or belt clasp;
- place the patient in a quiet place;
- try to make it clear by your behavior that the fear is unfounded;
- If possible, measure pulse and blood pressure;
- distract the patient from his worries;
- You can massage the limbs, collar area (it is not advisable to use cold or hot compresses);
- Novo-passit solution, tablets or tincture of Valerian, Motherwort, Corvalol, Persen, Valocordin are recommended as home sedatives for cardioneurosis. You can take the drops again after 4 hours.
If the symptoms do not disappear, weakness increases, you should call an ambulance.
Despite the difficulties in diagnosis and selection of therapy, the patient needs to be patient and undergo a full examination. You should not treat cardioneurosis on your own. Changing your regimen and playing sports should be equated to medication. Without them, it is impossible to get rid of cardioneurosis. For women suffering from menopausal symptoms, the gynecologist will offer a special course of therapy. You cannot trigger neurosis and complicate your life.
Helpful tips for patients with panic attacks
For people suffering from chronic osteochondrosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia, to effectively treat attacks and prevent their relapses, it is necessary to adjust their lifestyle and diet. And follow medical prescriptions and recommendations. The tips below will help you learn to live with such diagnoses. And to prevent their exacerbation, therefore it is necessary to observe them for all patients with a history of panic disorders.
How to become stress-resistant
- One of the main conditions for preventing panic attacks is a complete cessation of smoking and drinking alcohol. A generally safe dose of alcohol for such people can be considered 1 bottle of light unfiltered beer or 200 ml of dry red wine (no more than once a month). You should completely forget about stronger drinks.
- Drinks with a lot of caffeine should be limited to 1-2 cups per day. For everyday use, it is better to use natural herbal teas from chamomile, thyme, oregano, lemon balm, and lemongrass. They enrich the body with essential oils, tannins and organic acids. And they have a calming effect and normalize sleep.
- The use of medications that contain caffeine should also be monitored. For example, for headaches, instead of Citramon, it is better to use Paracetamol.
Paracetamol drug - If a patient has had panic attacks at least once, doctors should be warned about this when visiting various medical institutions (including boarding houses and sanatoriums). This is due to the fact that many procedures and medications can inhibit the functioning of the central nervous system, provoking the development of a panic attack.
- Sleep should be at least 8 hours a day. If a person needs a nap during the day, it is necessary to organize his day in this way. It is necessary that time be allocated in his daily routine for daytime sleep (at least in the acute period of pathology).
Swimming, gymnastics, hardening procedures, and breathing techniques are also used as preventive measures. If you are susceptible to stress, you should learn relaxation techniques at home. This could be salt baths, audiotherapy, aromatherapy. Walk more. Get out into nature more often in picturesque places with green parks or forests.
Video - Panic disorder with cervical osteochondrosis
Panic attacks with cervical osteochondrosis occur in almost 35% of patients. Pathology without treatment is dangerous due to its complications. The most severe of which are organic brain lesions. For treatment, not only specific therapy with tranquilizers and antidepressants is used. But also comprehensive treatment of the root cause of attacks - cervical osteochondrosis. Mild to moderate paroxysmal anxiety is treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a psychotherapist or neurologist. In more severe cases, hospitalization in a neuropsychiatric hospital may be required.
Methods for treating cardioneurosis
Adequate treatment of cardioneurosis requires the involvement of a psychiatrist or psychoneurologist. A big mistake of patients and doctors is refusing the help of specialists. After all, conventional drugs used in cardiology do not work in this case. And the inability to relieve an attack with Nitroglycerin is known as a diagnostic sign of cardioneurosis.
Experts recommend starting to treat cardioneurosis with psychotherapy. It provides:
- reduction of general anxiety;
- distracting the patient from unnecessary negative thoughts and emotions;
- helps to set the intention for healing.
Psychotherapists will recommend classes in a group or individually, and the possibility of using auto-training. Currently, psychological attitudes that can be used on the Internet are important.
It is believed that in a group of like-minded people it is easier for a person to talk about his illness
Patients should change their routine, walk more often, and do what they love and enjoy.
You should exclude spicy and fatty foods, smoked foods, alcohol, preservatives from your diet, do not abuse sweets, and do not overeat. You need to quit smoking, and when working with occupational hazards, reconsider your capabilities and move on to safer work. After morning exercises, a contrast shower is necessary.
Physical therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, and herbal treatment have a good effect.
Herbal mixtures to improve the functioning of the nervous system in case of cardioneurosis include:
- mint,
- Melissa,
- valerian root,
- hop cones,
- hawthorn fruits,
- chamomile flowers,
- motherwort leaves.
You can prepare the decoction yourself in a thermos.
Origin of violations
The causes of cardioneurosis are considered to be many factors that can provoke too strong and complex irritation.
An excessive process of inhibition or excitation in cortical structures contributes to the formation of pathology
There is an opinion that such a pathology develops in individuals with congenital inferiority of brain cells and too strong a connection between the cerebral cortex and the heart.
The impetus for the development of cardiac neurosis can be given by:
- both physical and mental trauma;
- violent conflict situations (family quarrels);
- unsatisfied desires (sexual disorders);
- very stressful work, study (anxiety during exams, lack of sleep);
- poor nutrition (with various diets, physical overload);
- chronic intoxication (alcohol, nicotine, drugs, industrial toxic substances).
Endocrine disorders play a significant role in cardioneurosis, especially in women (during menopause, thyrotoxicosis, ovarian hormone deficiency). In these cases, there is a mismatch in the work between the pituitary gland and the peripheral glands. A similar mechanism is “triggered” in adolescents during pregnancy.
Which doctor should I contact?
Since a patient with cardioneurosis always fears for the condition of his heart, he is recommended to undergo examination by a cardiologist. If the doctor does not find cardiac diseases, the patient should consult a neurologist, psychotherapist or psychiatrist, depending on the severity of the panic attacks. Additionally, you need to consult with an endocrinologist and rule out thyroid diseases accompanied by hyperthyroidism. For women with a pathological course of menopause, it is advisable to choose hormone replacement therapy by visiting a gynecologist.
Video version of this article:
Relationship between cervical osteochondrosis and panic disorders
Autonomic crises against the background of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine are diagnosed to varying degrees in every fifth patient. The patient may complain of a feeling of inexplicable fear or anxiety. Which occurs suddenly and therefore cannot be controlled. The duration of attacks can also vary and range from several minutes to several hours and even days. On average, this figure is 20-30 minutes. It has been established that in younger patients the frequency and intensity of attacks are usually several times higher compared to patients over 45 years of age, which is explained by the characteristics and speed of blood movement in the vessels of the microvasculature.
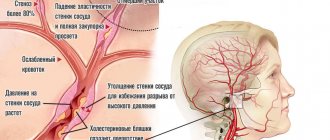
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
When a person seeking medical help from a neurologist or psychotherapist for panic attacks of unknown origin receives a referral for an X-ray of the neck, he usually does not understand how diseases of this part of the spine can be associated with disorders of a psychogenic or somatic nature. In fact, there really is a connection. With cervical osteochondrosis, degeneration of the vertebrae occurs against the background of severe degeneration and dehydration of the intervertebral discs. The fibrocartilaginous formations that fix the vertebrae in a vertical sequence are 88% composed of connective tissue and water. Their nutrition is carried out through cartilaginous plates. Nutrients enter the end plates of the intervertebral disc through the blood vessels of the central spinal canal.
The pathogenetic mechanism of panic attacks in patients with osteochondrosis is based on circulatory disorders. It can occur as a result of the following pathological conditions characteristic of this disease:
- displacement of the jelly-like core of the intervertebral disc (protrusion, hernia), which compresses nerve endings and blood vessels;
Stages of progression of osteochondrosis - swelling of paravertebral muscle tissue, leading to impaired muscle-tonic tension and muscle spasm. During a muscle spasm, the blood vessels in the neck, which carry blood to the brain, are in a state of compression;
- disturbance of calcium metabolism. Calcium is one of the main regulators of neuromuscular transmission.
Against the background of cervical osteochondrosis, cellular respiration is also disrupted. Which provokes chronic hypoxia of all tissues and organs, including the brain.
Visual representation of cervical osteochondrosis
Gymnastics for heart neurosis
Experts have developed a special complex of physical therapy for this pathology.
- Lunges for 1-1.5 minutes, first with one leg, then the other.
- Deflection of the torso. The leg is pulled back, the upper body also bends back. Then the same is done with the other leg. The exercise is repeated 5-8 times on each leg.
- Squat on one leg, while holding onto a chair. Repeat 2-5 times with each leg.
- Rotational movements of the body, first in one direction, then in the other. Repeat 3-6 times.
- Imitation of boxer punches. You need to breathe in a random order. Make 8-15 blows with each hand.
In some specialized neuropsychiatric clinics, there are special neurosis departments in which patients with different variations of this disease are treated. Often, patients are brought to such departments by the presence of panic attacks, which can often be combined with migraines or other pathologies that debilitate the patient.
The mechanism of pathology development
The formation of a pathogenic phenomenon is based on a violation of the inhibition processes of the central nervous system; why this happens is a big question. Tumor processes in the chiasmatic-sellar region or cerebral hemispheres are possible, hormonal imbalance, abnormalities in the thyroid gland, pancreas, and adrenal glands are possible.
The heart, despite all its autonomous functioning, does not exist in isolation. It is an integral part of the system. The frequency of contractions is regulated by hormones, as well as impulses from cerebral structures. As a result of pathological excitation from the central nervous system, the signal reaches the cardiac structures. The sinus node begins to work more actively, producing electrical impulses that spur functional activity, hence the characteristic symptoms of cardioneurosis.
Against the background of a long course of the problem, organic changes begin. This is the result of wear and overload. The best time for treatment is considered to be the first 3-4 years from the beginning. Then everything is much more complicated.
Cardioneurosis is provoked by a conflict of rupture in a person with highly ambivalent traits. A person discovers, on the one hand, the ability to self-defense. On the other hand, there is a certain limitation of one’s capabilities, as well as depressing dependence and unfulfilled expectations. A conflict in the form of a break is clearly connected with the situation that provokes it: the death of a loved one, departure, relocation, illness - with everything that threatens loneliness in a person’s mind.
There is also a connection between the occurrence of cardioneurosis in people with a depressive type of response to stress (depressive neurotic structure). With this type of reaction, a person also has a strong ambivalent attitude, and an aggressive desire for death constantly appears in fantasies simultaneously with the expectation of miraculous salvation and/or healing.
There is a tendency towards symbiotic relationships, the presence of depressive-symbiotic fantasies on the topic of merging (convergence), which is caused by external or internal difficulties in breaking close ties with the mother or father. It is difficult to perceive the death of others or even the message about death, which patients experience as if it concerned them, as their own fate.
Who can develop cardioneurosis?
Psychologists have identified the character traits of a person with possible neurotic disorders. These include:
- tendency to anxiety and suspiciousness;
- excessive self-control;
- panic attacks in the event of a tense situation;
- frequent mood changes;
- causeless fatigue.
People with various phobias (fear, for example, of heights, darkness, enclosed spaces) are susceptible to cardioneurosis