- Benefits of potassium and magnesium
- Sources of potassium and magnesium
- When is supplemental potassium and magnesium supplementation necessary?
| If we mostly try to resist hypovitaminosis, then we often forget about the lack of minerals. In winter and in the off-season, we rush to replenish the first aid kit with ascorbic acid, and to strengthen the general immune system, drink some vitamin and mineral complex. |
At the same time, our body may lack very specific minerals, such as potassium and magnesium . Their role in metabolism is far from minor.
The role of potassium and magnesium in the human body
A set of foods high in magnesium and potassium
Potassium is an intracellular element that is part of most human body fluids. It is present in the cells of the nerve pathways and brain, in the kidneys, liver, and its most important purpose is to participate in the regulation of heart contractions. A lack of potassium in the heart muscle leads to disruption of its function, which can ultimately lead to a life-threatening condition. The daily norm in human metabolism is 2 grams, and for athletes and those involved in physical labor, the norm rises to 2.5 grams. Potassium deficiency can occur not only due to poor nutrition; several other factors lead to it:
- Removal of potassium from the body after taking hormonal, laxatives, diuretics and other drugs. “Weight loss tea”, which has a diuretic effect, is especially dangerous in this regard. Since it is not treated as a medicine, eventually its uncontrolled use can lead to disruption of the heart and serious conditions.
- Constant stress and lack of sleep, heavy physical activity combined with poor nutrition. All this leads to a decrease in the amount of potassium in the cells, which can later cause diseases.
- Disorders of the excretory system, in particular kidney and liver diseases. Metabolic disorders can lead to concomitant negative processes.
Magnesium is another extremely important microelement that performs several functions at once. First of all, it plays a significant role in the formation of bone tissue and the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. It also affects the functioning of the nervous system: a lack of magnesium leads to a constant feeling of overwork, loss of appetite and heart rhythm disturbances.
Magnesium deficiency and heart rhythm disturbances
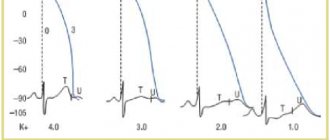
Magnesium controls the spontaneous electrical activity of the cardiac conduction system, ensuring normal functioning of the cardiomyocyte at the subcellular level. That is why the microelement plays a universal role in cardioprotection. Magnesium also takes part in the synthesis of lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and ATP. The trace element is necessary for many energy and reparative processes, as well as normal electrolyte metabolism. Magnesium promotes relaxation of muscle fibers, maintains the necessary transmembrane potential in electrically excitable tissues, and reduces the aggregation ability of platelets. In autonomic cardiopathy, microelement deficiency may be indicated by long QT interval syndrome, paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia (torsades de pointes type), episodes of syncope, and acute cardiac arrest. The following signs can be seen on the ECG:
- prolongation of the QT interval;
- widening of the QRS complex;
- nonspecific decrease in the ST segment;
- slowing of AV conduction;
- pronounced U wave.
What foods contain potassium?
You can eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of micronutrient deficiency by diversifying your menu with foods with a high potassium content. The list is quite large, so it will not be difficult to choose something that will suit your individual taste preferences. The number of potassium-rich foods includes the following:
- Dried fruits: figs, dates, prunes, dried apricots and much more. They can be called real “natural tablets”, they are so rich in microelements. However, most dried fruits contain a large amount of sugar, so diabetics and people prone to obesity should not eat them in excess. It is better to discuss their use with a nutritionist: in small quantities they will not only not cause harm, but will also turn out to be very healthy and tasty.
- Green vegetables: spinach, parsley, cabbage, bell peppers, cucumbers and much more. This group also includes the most common root vegetables: carrots, radishes, beets, etc.
- Cereals of almost all varieties, bread with bran, sprouted wheat germ. Cereals are especially useful; they prolong youth and strengthen the immune system. Eating various cereals not only stimulates metabolism thanks to microelements, but also has a beneficial effect on intestinal function.
- Nuts. Hazelnuts and walnuts are especially rich in microelements; other varieties also contain potassium. Potassium is also included in various meat products and offal; in addition, fresh champignons and some other types of mushrooms are rich in it.
A varied, nutritious diet, including various natural products, can completely compensate for the lack of potassium; this does not require taking additional medications. It is very important to prevent a lack of potassium in the body: if the doctor prescribes diuretics, or intense sports training is ahead, it is necessary to immediately replenish the diet with foods high in this trace element.
Causes of potassium-magnesium deficiency
The lack of these two essential microelements can be caused by errors in nutrition (abuse of salty foods), severe forms of diarrhea and vomiting, and kidney pathologies. Potassium-magnesium deficiency is often observed in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A lack of microelements can result from prolonged and/or uncontrolled use of certain medications.
Draw your attention to! This article is not a call for self-medication. It is written and published to improve the reader's knowledge about his own health and understanding of the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor. If you experience similar symptoms, be sure to seek help from a doctor. Remember: self-medication can harm you.
Foods High in Magnesium
Nuts are a source of essential microelements
Research that has confirmed the important role of magnesium in metabolism has been carried out for a very long time. It has been proven that it affects the functioning of the heart, the level of cholesterol in the blood, and it also affects the functioning of the nervous system. In many areas, the main source of magnesium salts is hard water: although it is not very beneficial for metabolism, it is becoming an important means of preventing cardiovascular diseases.
If a person drinks only soft water, purified from salts, he requires a mandatory additional intake of microelements. The list of foods that contain magnesium is quite wide: since this is a common element, it will not be difficult to include foods in the menu that will allow you to get the required dose. What should you eat to compensate for your magnesium deficiency?
- Various fruits: bananas, apricots, peaches, etc. Raspberries, strawberries and blackberries contain a lot of magnesium. This is a tasty and very healthy addition to the diet; eating fruits not only supplies the body with vitamins and microelements, but also improves your mood.
- Legumes. Among them, white beans and soybeans occupy an important place: dishes made from them occupy an important place in many cuisines of the world; one should not neglect the regular consumption of these healthy and nutritious crops.
- Cereals, especially millet, as well as bread with bran. Wholemeal bread is doubly useful: it activates the intestines and also supplies the body with useful substances.
- Low-fat dairy products. This is a source of not only magnesium, but also calcium: cottage cheese, sour cream and other products help strengthen the musculoskeletal system.
At the same time, drinking strong tea and coffee, alcoholic beverages, sweets, and fatty foods slows down the absorption of magnesium and impairs metabolism. Diabetics have to especially carefully monitor their diet, since magnesium plays an important role in insulin metabolism.
Interaction of potassium with other elements
Sodium chloride
: potassium softens the pressor effect of sodium chloride, preventing a sharp increase in blood pressure. Dietary potassium increases urinary excretion of sodium chloride.
Sodium
: Potassium and sodium are closely related, an imbalance in the dynamic balance can lead to the appearance of kidney stones and the development of hypertension.
We recommend
“Microelements in the body: consumption standards and methods of replenishing the deficiency” Read more
Calcium
: Potassium improves calcium reabsorption and also has a positive effect on bone mineral density.
Magnesium
: It is necessary for optimal potassium metabolism in cells, and the correct ratio of magnesium, calcium and potassium reduces the risk of stroke.
Foods rich in potassium
Sources of potassium for humans are many products, both plant and animal origin. In this table, foods rich in potassium:
| Products | Potassium content (mg/100g) |
| apricots | 340 |
| pineapples | 124 |
| oranges | 166 |
| watermelons | 1705 |
| artichokes | 375 |
| beans | 1020 |
| broccoli | 320 |
| ham | 205 |
| grape | 215 |
| cherry | 289 |
| cabbage | 150 |
| cauliflower | 360 |
| kohlrabi | 420 |
| onion | 250 |
| carrot | 310 |
| nectarine | 167 |
| peach | 150 |
| rhubarb | 310 |
| plums | 85 |
| dates | 510 |
| apples | 108 |
| eggs | 140 |
| cocoa powder | 1660 |
| almond | 780 |
| tea | 2367 |
| coffee beans | 1750 |
| wheat bran | 1150 |
| Pine nuts | 760 |
| almond | 740 |
| peanut | 740 |
| sunflower | 700 |
| walnuts | 440 |
| buckwheat | 380 |
| oatmeal | 350 |
| Wheat flour | 140 |
| rice | 100 |
| hard cheese | 100 |
| beef | 100 |
| pork | 100 |
| herring | 90 |
Those who have been on a strict diet for a long time should definitely pay attention to foods rich in potassium. Especially if laxatives or diuretics were taken at this time. Another category that constantly needs potassium is athletes. During exercise, a large amount of this element is spent to maintain muscle tone. Therefore, after training, a nutritionist prescribes potassium-enriched drinks to prevent a sharp decrease in its level in the body. Each time, those who spent a long time in the open sun (for example, on the beach) and those who had to sweat a lot while treating a cold accompanied by a high temperature will need to replenish the amount of an important element.
Daily requirement of potassium for the body
The daily need for potassium depends on age, physical condition and even place of residence. Healthy adults need 2.5 g of potassium, pregnant women – 3.5 g, athletes – up to 5 grams of potassium daily. The amount of potassium for adolescents is calculated by weight - 20 mg of potassium per 1 kg of body weight.
Potassium norms are calculated for all age categories and are presented in the table below:
| Categories | Daily norm |
| Children under 2 years old | 400-600 mg |
| Children from 3 to 5 years old | 3000 mg |
| Children from 6 to 8 years old | 3800 mg |
| Children from 9 to 13 years old | 4500 mg |
| Teenagers under 18 years old | 4600 mg |
| Women | 4700 mg |
| Women during pregnancy and lactation | 5 100 mg |
| Men | 4800 mg |
The body's daily need for potassium increases
:
- in patients with type 1 diabetes, as well as in those prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- when taking diuretics;
- with a low-carbohydrate and high-protein diet: in such cases, the diet practically does not include fruits, the alkaline composition of which regulates potassium metabolism;
- during sports activities: potassium is intensively excreted from the body through sweat.
Targeted nutrition tips
that will increase your energy level by 10 out of 10
From TOP nutritionists of the MIIN
Get tips
The body's daily need for potassium decreases
:
- in patients suffering from chronic renal failure, end-stage kidney disease, heart failure;
- in pregnant women with preeclampsia, since with an active intake of potassium into the body, there is a risk of developing hyperkalemia.
Our body does not store potassium, using only as much as it can absorb at the moment. Therefore, it is impossible to talk about stable indicators of the presence of an element in the body - the data is constantly changing. Often the cause of its deficiency is the incorrect eating behavior of the person himself, which can lead to malfunctions in the functioning of various body systems. And they can manifest themselves in a very short time.
Potassium in dietary supplements
Dietary supplements contain potassium in bound forms: potassium chloride, potassium citrate, phosphate, aspartate, bicarbonate and gluconate. In potassium iodide supplements, the primary mineral constituent is iodine.
Food manufacturers are forced to limit potassium content to 99 mg, which is about 3% of the daily value. And there are serious reasons for this.
Firstly, studies have found that oral preparations containing potassium chloride, which in terms of net weight contain more than 99 mg of pure metal, are dangerous to health. They can cause damage to the walls of the small intestine.
Secondly, based on the existing health risks, some regulatory organizations require manufacturers to label food products warning that they contain more than 99 mg of potassium.
Potassium is available in tablets, capsules, drops and powder. The use of supplements is only as prescribed by a doctor, since - and this was mentioned earlier - excess potassium is also dangerous to health.
Not much research has been done to determine the effectiveness of potassium supplements. Tests in 2021 showed how well potassium is absorbed in the body. According to the results, about 94% of potassium gluconate is absorbed by the body through dietary supplements at the same rate as if the element came from potatoes.
Previous evidence has been obtained that potassium chloride solution (used as a medicine to treat digitalis intoxication or arrhythmia due to hypokalemia) is completely absorbed within a few hours. But potassium chloride in the form of enteric tablets (their shell prevents the tablets from dissolving in the stomach, but only in the small intestine) is absorbed more slowly than in liquid form.
Rules for storing and preparing potassium-containing products
Basic requirements for vegetables and fruits
– freshness and absence of damage. There is noticeably less potassium in wilted fruits. It is best to store them in a dry and cool place.
During food processing, the potassium contained in products does not all reach the table; most of it is lost in the process, which is due to the high solubility of salts of this metal in water. For example, cooked spinach has 17% less potassium than fresh spinach. And when cooked, curly cabbage loses up to 50% of the valuable element it contains.
The amount of nutrients in finished food is affected by the cooking temperature, interaction with oxygen, and the acidity level of the dish. Potassium, like most vitamins, is destroyed by strong heat, especially during prolonged cooking. Therefore, you need to cook quickly, trying to reduce the processing temperature as much as possible.
Basic recommendations to help preserve the maximum amount of nutrients, including potassium, in ready-made dishes: do not boil at 100 ° C, do not use a microwave, avoid frying, minimize the amount of vegetable oil. Steamed vegetables are very healthy. But if possible, it is much healthier to eat them raw.
Risks of excess potassium
The causes of excess potassium are
:
- renal failure;
- hemolytic anemia;
- malignant tumors;
- dehydration;
- anaphylactic shock;
- hypofunction of the adrenal cortex (Addison's disease).
When potassium levels increase, symptoms may include:
:
- increased excitability of the nervous system, irritability, anxiety;
- sweating;
- weakness;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- intestinal colic;
- frequent urination.
If potassium levels are elevated, it is recommended to limit foods containing it.