Brain nutritional disorders occur, according to statistics, in every ten thousand people on the planet.
Representatives of the fairer sex suffer 4 times less often than men, which is due to the properties of estrogen hormones. They promote the natural dissolution of cholesterol plaques, the removal of low-density lipids and the prevention of stenosis of large arteries.
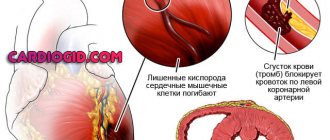
Pre-stroke is an emergency. This is not yet acute necrosis of cerebral tissue, but already an alarm bell, a harbinger of a dangerous process.
Within the framework of medical science, it has several names: cerebrovascular insufficiency, transient ischemic attack or microstroke. These are interchangeable concepts, and therefore they need to be considered as identical phenomena.
Symptoms are represented by several groups of moments: neurological, mental, and others not related to the brain and higher activity of the central nervous system.
The first signs of pre-stroke in women are nonspecific: headache, nausea, disturbances in the functioning of the sensory organs. The same can happen against the background of a hypertensive crisis, a drop in sugar levels and other conditions.
The issue of differential diagnosis using routine methods, on site, before or immediately after transporting the patient to the hospital is relevant.
Despite the fact that pre-stroke differs in identical moments in men and women, the development of pathology in women has its own patterns:
- Long preceding period. Transient ischemia does not develop suddenly; there is always an initial stage. It lasts about 2-3 weeks, sometimes longer.
- General severity of the condition. The paradox is that, despite the comparative rarity of its occurrence, pre-stroke in women is more severe and more often ends in complete necrosis.
- Expressiveness of manifestations. Directly related to the previous point.
- Finally, there is a high probability of an emergency. Mainly tissue death.
General cerebral symptoms
They appear first. Common to all patients without exception in an acute pre-stroke condition.
There is no specificity, therefore it is impossible to say only from the indicated manifestations what caused the deterioration in well-being.
Headache
Expressed unbearable. It occurs suddenly, there is no clear factor in the development of the symptom. The patient takes a forced position, usually lying on her side, to relieve the unpleasant sensation.
Discomfort is localized in the back of the head or temples. Sometimes the localization of the syndrome cannot be determined at all; it spreads throughout the head.
Analgesics have a partial effect; complete pain relief does not occur. Discomfort creeps in, spreading to the back of the head following the beating of the heart.
The sudden disappearance of a symptom in such a case indicates an improvement in the condition.
In this case, you need to pay attention:
- Against the background of a pre-stroke, no organic changes occur in the brain, so the episode is eliminated completely and without a trace.
- As for a full-fledged stroke, the cessation of discomfort most likely indicates a further expansion of neuronal death.
Dizziness
It also arises spontaneously. The reasons are disruption of the normal nutrition of cerebral structures. The world is spinning, the earth is literally disappearing from under your feet.
The manifestation of a pre-stroke can be caused by damage to several areas of cerebral structures: the cerebellum, hippocampus, and frontal lobe.
The patient lies down and cannot navigate in space. Relief occurs only after the acute episode ends.
Nausea, vomiting
The result of reflex irritation of special centers of the brain. Under normal conditions, they react to high concentrations of toxic components in the blood.
Poisons stimulate clusters of nerve cells, giving a signal to the digestive tract to evacuate the contents. After this, the amount of harmful substances drops sharply due to reduced absorption.
There are no toxic compounds against the background of pre-stroke. Causes of nausea and vomiting are reflex stimulation. And this, in turn, is the result of ischemia (oxygen starvation). Neurons do not receive enough blood, hence the chaotic spontaneous excitation.
Drowsiness, weakness, manifestations of asthenia
Any time of the day. Signs develop immediately after the onset of acute cerebrovascular accident. The patient lies down and cannot do anything.
Fatigue is usually associated with apathy. There is neither the strength nor the desire to work, to perform some actions, and there is no such opportunity due to the pronounced accompanying clinic.
After restoration of cerebral blood flow, the general tone of the nervous system returns after a few hours; this is not a momentary process.
Excessive sweating
It also has a reflex origin. An abnormal expansion of peripheral vessels develops, which leads to increased heat transfer.
The reason is chaotic signals from the hypothalamus, namely the preoptic nucleus, which is responsible for thermoregulation. During one pre-stroke episode, a symptom may develop more than once.
Subjectively, the patient feels hot flashes, regardless of the ambient temperature.
Attention:
If a woman is not on the street, this is extremely dangerous, because increased heat transfer will very soon lead to hypothermia.
Pale skin
Occurs as a result of activation of the autonomic nervous system. May confuse doctors by falsely indicating cardiac pathologies. To clarify the condition, a number of specific tests are carried out.
Impaired consciousness
By type of fainting. Usually shallow. The patient can be easily brought out of syncope by loudly shouting or using an ammonia solution (ammonia).
The depth of manifestation depends on the location of the ischemic focus. The most pronounced disorders occur with damage to the hippocampus and frontal lobe.
Symptoms of the pre-stroke condition in women are represented by neurogenic disorders. Later, other signs are added that are local in nature from the point of view of the brain.
Causes
If a person shows signs of a pre-stroke condition, there are a number of reasons for this. These include: strong feelings, heavy physical activity, unhealthy lifestyle and bad habits. Most often, a pre-crisis situation is observed in patients with a number of serious pathologies. This group of patients belongs to the risk group, that is, to the category of people who need to be attentive to their health.
The following factors can precede a crisis:
- prolonged exposure to stress or severe nervous disorder;
- hard physical labor, overwork;
- addiction to alcohol and tobacco;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- severe hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- non-compliance with diet, fatty, spicy foods, lack of fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet;
- changes in weather conditions, atmospheric pressure, magnetic storms, etc.
Risk group:
- hypertonic disease;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- high cholesterol;
- blood clotting disorder;
- sedentary or bedridden patients;
- advanced age;
- gender (crisis occurs more often in men than in women);
- genetic predisposition (parents have had a stroke or heart attack);
- psychosis, depression;
- migraine;
- atherosclerosis;
- vascular diseases;
- angina pectoris, heart attack, ischemic disease.
Stroke can occur at any age, even in young people suffering from a number of chronic diseases. If a girl, boy or child is at risk, they need to constantly monitor their well-being in order to recognize an approaching crisis. If pre-stroke signs appear, you should consult a doctor.
Frontal lobe of the brain
Responsible for mental activity, the ability to make logical constructs, synthesis of new information from existing data, behavior, muscle tone and some other functions.
- Infantilism. The patient relapses into childhood. Primary reflexes, such as grasping and sucking, return. Behavior is inappropriate for age; this is a temporary phenomenon. Recovery after the end of the pre-stroke state is spontaneous. The intervention of doctors contributes to rapid correction.
- Thinking disorders. By type of productivity decline. The patient is unable to solve basic logical problems. Inferences are impossible, judgments do not have an adequate basis. Formally, intelligence is preserved. But the woman is unable to use the resources because the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted.
- Unsteadiness of gait. The victim cannot walk in a straight line. This is due not so much to a violation of orientation in space, but to insufficient muscle tone, a partial loss of control over the muscles.
- Behavioral disorders. The woman becomes inappropriately cheerful, whiny, and aggressive. Accented personality traits are sharpened. Therefore, the pattern (model) of the disorder is determined by the individual properties of a particular person. His character.
- Paralysis, paresis. On the one hand, opposite to the localization of the lesion. The upper and lower limbs and face are affected. The notorious distortion of facial muscles occurs, which is inherent in a classic stroke.
- Epileptic seizures. Total or large with loss of consciousness and tonic-clonic convulsions. They cover all muscle groups and the body as a whole. It is necessary to distinguish the pathological process from classic true epilepsy. This can be done both due to accompanying symptoms, clinical picture, and based on the results of instrumental diagnostics.
Lack of smell on one side. A specific sign of damage to the frontal lobes. When subcortical structures and the limbic system are involved in ischemia, the absence of odor perception is complete.
Prevention of micro-stroke
Prevention is always simpler and more effective than treatment, and preventive measures are usually the same, so by following simple rules, you can eliminate many diseases from your life. What should be done?
- Maintain normal blood pressure. Any stroke is a surge in pressure, so just measure your blood pressure at least once a day using a home blood pressure monitor;
- Give up bad habits: for example, coffee and alcohol increase blood pressure, smoking thins the walls of blood vessels. All this provokes strokes of varying severity;
- Follow the diet recommended by your doctor: it is aimed at reducing cholesterol levels and, accordingly, preventing the appearance of plaques;
- Exercise regularly: physical activity keeps all body systems in good shape;
- Monitor your sleep status, sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- Monitor hormonal levels;
- Seek help for head injuries;
- Visit doctors periodically and promptly treat vascular diseases.
Temporal lobe
The work of this area ensures normal memory, internal speech and mental activity, and hearing in general.
- Epileptic seizures. As is the case with those with lesions of the frontal lobes, they develop suddenly. But they last less time. Otherwise, it is not possible to notice the difference without instrumental techniques. The difference is in the localization of the pathological impulse.
- Lack of hearing. The so-called cortical deafness. The patient completely loses the ability to navigate sounds. This is a temporary phenomenon; treatment as such does not make sense.
- Lack of speech perception. Formally, there is a noise stimulus, but it is impossible to evaluate the logic of the statements, the meaning of them, and even recognize the words.
- Verbal hallucinations of the mental type. So-called pseudohallucinations in outdated terminology. The proverbial voices in my head. Associated with disruption of Wernicke's area.
It is responsible for the production of inner speech. As a result of the anomaly, the signal moves to Broca's center.
He, in turn, identifies external stimuli and perceives them as such, as outside speech. A paradoxical reaction arises.
- Memory impairments of various types. Amnesia, failures. The feeling of a repetition of something that once happened (déjà vu).
Parietal lobe
Responsible for tactile sensitivity and some other functions.
- Inability to recognize objects blindly.
- Physical hallucinations. They manifest as unpleasant sensations under the skin. The patient complains of movements and swarming.
This is the result of false signals from the brain to the nerve endings along the reflex arc. Hence the itching, burning, desire to scratch the suspected location of discomfort.
Something similar is observed in mental illnesses; it is necessary to distinguish the conditions from each other.
The main differential feature is complete criticism of one’s own position. These are the so-called senestopathy.
Another option is apparent touches from the outside, which in reality are not there. Tactile sensations are false.
Possibly inverted state. The patient does not pay attention to individual parts of her own body and does not recognize them as her own.
- Complex clouding of consciousness. Oneiroids. All senses are involved, the patient is completely at the mercy of the illusory world that her consciousness creates. Duration - from a couple of minutes to several hours. The critical state ends with apathy and a depressive mood under the influence of negative false images.
- Lack of purposeful mental activity. The victim cannot perform simple arithmetic operations and lacks the ability to read and write.
Focal symptoms of the disease
One or another part of the brain is responsible for specific processes occurring in the body. When normal blood flow ceases to be provided in one of them, specific symptoms are observed. This is what the doctor relies on when making a diagnosis. You can find out which area is affected by the nature of the clinical manifestations. Frontal cortex:
- convulsions;
- slurred speech;
- inability to make voluntary movements;
- a sudden change in habitual behavior.
Parietal lobe cortex:
- tactile sensitivity is lost;
- skills in basic arithmetic, writing and reading are lost.
Temporal lobe cortex:
- deafness develops, tinnitus is recorded, and certain hallucinations appear;
- Memory is impaired and a feeling of déjà vu develops.
Symptoms are nonspecific. Rather, for the doctor, these are additional signs that help make a diagnosis.
Occipital lobe
The functions of this part of the nervous system include color recognition and normal vision. Processing incoming visual information and converting it into understandable images.
- Complete blindness. Temporary or so-called transient. The disorder has no connection directly with the retina or the visual tract up to the brain.
- Inability to estimate the distance to an object. Understand its dimensions. Metamorphopsia occurs. Small objects appear larger than the patient herself and vice versa. The small room seems like a huge hall.
This is a direct indication of the neurogenic origin of the disorder, because the eye is not able to independently process information. This is just a source, an input for images; the processes of transformation and analysis take place in the cerebral cortex.
- Induced color blindness. Inability to recognize colors.
- Scotomas. Loss of areas of the visual field. They look like black spots that block your view. In the paracentral areas and along the periphery, usually from the side of the temples.
- The simplest visual disturbances. Photopsias. Flashes of light, bright dots, lines. Rings, geometric shapes. There is no objective source of irritation. The central nervous system is excited spontaneously. Restoring blood flow leads to compensation of the condition.
Detection of stroke: diagnosis
Detection of brain diseases is complicated by their location deep in the skull. However, it is possible to diagnose a disease such as a stroke in a timely manner!
80% of people who have had a stroke become disabled, a third of whom need help from strangers. Only 20% recover from the disease and can return to normal life!
The initial diagnostic stage includes a number of necessary studies:
- Blood tests: clinical and biochemical;
- Electrocardiogram;
- Computed tomography and MRI.
Brain stem
With ischemia, life- and health-threatening manifestations develop. Like stopping breathing, cardiac activity. This is the only case when a pre-stroke in a woman can lead to death even without the death of cerebral tissue.
Additionally, it is possible to develop elevated body temperature. Thermoregulation is disrupted, the readings fluctuate, from 35 to 38 degrees Celsius or more.
The sign is also considered threatening and requires urgent correction in a hospital setting. The patient is constantly monitored for timely resuscitation.
Limbic system
{banner_banstat9}
The key symptom of damage to subcortical structures (in particular the cerebellum) is a violation of orientation in space.
The patient loses understanding of the spatial structure and her position in it. A painful manifestation. If during dizziness the sense of place is formally preserved, in this case it is also lost.
At the same time, there may be a loss of the ability to learn, absorb new information and use it.
Pre-stroke, transient ischemia of the limbic system is rare: 3-5% of the total number of cases.
Treatment of microstroke
Treatment is aimed at normalizing blood supply and metabolism, preventing relapses and preventing stroke. In case of hemodynamically significant occlusion of large arteries, surgical treatment by angiosurgeons is possible. Patients with a ministroke are usually prescribed:
- Drugs aimed at restoring blood microcirculation in blood vessels;
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow;
- Agents that prevent platelet accumulation;
- Drugs that improve brain activity;
- Vitamins.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient visits:
- Exercise therapy (to restore motor activity);
- Massage sessions (to stimulate motor activity in the limbs);
He also follows a diet (without fatty, spicy and salty foods) and does special breathing exercises (to ensure that sufficient volume enters the body).
But if the patient delays diagnosis and treatment, complications may arise. In this case, with a microstroke, the doctor prescribes the following groups of drugs responsible for restoring the body:
- improving blood microcirculation;
- improving metabolic processes in blood vessels;
- dilating vessels;
- preventing the formation of blood clots;
- stimulating brain activity;
- vitamins (to strengthen the immune system and improve brain activity).
Manifestations not related to the neurological sphere
- Menstrual irregularities due to dysfunction of the central nervous system (relevant for people under 50 years of age).
The central nervous system regulates endocrine processes, the production of hormones, and the beginning of monthly changes in a woman’s body depends on the concentration of specific substances.
An acute process can interrupt or delay menstruation.
- Depressive states. Psychiatric disorder.
- Apathy.
- Weakening of digestive processes.
The key symptom of pre-stroke in women is headache. It is layered with weakness, fatigue, asthenia, loss of consciousness and other manifestations. Cupping is always carried out in a hospital. The patient cannot be helped at home.
First aid
If a person has signs of a pre-stroke condition, it is necessary to urgently seek help from medical professionals. After a few minutes, the symptoms may go away on their own, but you need to wait for the doctors to arrive and undergo an examination. It is impossible to treat the victim at home with folk remedies. Before the ambulance arrives, the patient can only be given first aid.
First aid for pre-stroke:
- provide the patient with a horizontal position;
- raise your head a little, put a pillow under it;
- do not bend your neck;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- open the windows in the room to bring in fresh air;
- calm the patient;
- when vomiting, turn your head to the side;
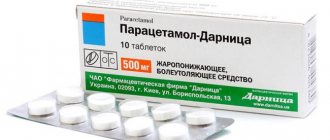
- measure the temperature, if high, give an antipyretic (Paracetamol);
- if possible, measure blood pressure;
- if blood pressure is high, give Captopril or Nifedipine;
- if there are no medications, then to reduce the tone you need to bandage the thumb of your left hand with an elastic band, hold for 2-3 minutes, vigorously rub the hand towards the fingertips;
- Place 2 Glycine tablets under your tongue.
Doctors who arrive on call will provide the patient with the necessary assistance and give an injection. If the condition is critical, the person is hospitalized in a hospital. If not, he will be prescribed treatment at home.