Symptoms of high hemoglobin
Initially, it is necessary to sort out what complaints does a woman have with increased hemoglobin?
The condition of increased hemoglobin is called hyperhemoglobinemia and very often occurs without the manifestation of clinical signs. In most cases, high hemoglobin in women and men is detected only during a routine general clinical examination. In some cases, hyperhemoglobinemia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased blood pressure and swollen veins;
- a feeling of aching in bones and joints;
- decreased performance;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- shortness of breath even when walking calmly;
- slight blueness of the fingertips;
- pallor or flushing of the face;
- losing weight for no apparent reason;
- decreased concentration and absent-mindedness;
- long and painful menstruation;
- neurotic disorders, psychoses, insomnia, depression.
Often the causes of high hemoglobin levels in women and men are a concomitant disease. In this case, the symptoms of hyperhemoglobinemia are similar to the clinical manifestations of the underlying pathology. This fact explains the difficulties for differential diagnosis of hyperhemoglobinemia itself and identifying its causes.
Hemoglobin during pregnancy
During pregnancy, elevated hemoglobin is extremely rare. As a rule, a single increase in Hb concentration is not significant, since the levels of all indicators change during the day against the background of physical or emotional activity. However, consistently high levels may indicate a lack of B vitamins or the development of a pathological process. In this case, a comprehensive examination of the patient is prescribed to eliminate the hyperhemoglobinemia condition as quickly as possible. This is necessary to reduce the risk of developing thrombosis and fetal hypoxia.
Pregnant women are more often characterized by a state of hypohemoglobinemia - a deficiency of hemoglobin levels against the background of blood thinning, as a result of an increase in its volume.
For early diagnosis of deviations from the norm when planning to conceive a child, a course of preventive measures is recommended to prevent a decrease in Hb concentration. This will significantly reduce the risk of developing any type of anemia.
Read further: What is hemoglobin in the blood, its types, how is it tested. How does alcohol affect? The influence of periodic women's days
Why does the increase happen?
The causes can be physiological or pathological.
Physiological reasons are due to:
- Temporary stay or residence in the highlands where the air is thin.
- Heavy, long-term physical activity, typical for women involved in professional sports.
- Smoking, which is accompanied by the formation of carboxyhemoglobin in the blood, which is not capable of carrying oxygen.
- Severe stress. In such cases, the body usually experiences oxygen starvation, and the bone marrow is given a signal to increase hemoglobin production.
- Dehydration. This can happen due to insufficient drinking, a strict diet, or taking diuretics or laxatives.
Pathological causes of high hemoglobin concentration in the blood can be caused by:
- diabetes mellitus;
- heart failure;
- taking medications, including anabolic steroids;
- volvulus, etc.
High hemoglobin can be hereditary and does not pose a risk to a woman's health.
This table shows the normal hemoglobin content for different groups of women:
| Women's group | Hemoglobin, norm g/l |
| Common indicator for everyone | 115-140 |
| Smoking | up to 150 |
| Sportswomen | up to 160 |
| Pregnant women in the 1st and 3rd trimesters | 110-115 |
| Pregnant women in the 2nd trimester | 115-120 |
High hemoglobin in women - what does it mean and what should be done
Doctors are often asked the question - what does it mean if a woman has increased hemoglobin? As a rule, this condition is caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood. In order to compensate, the body begins to actively produce red blood cells containing Hb molecules.
To prevent the risk of developing complications in the form of thrombosis, mandatory correction of high hemoglobin levels is necessary. If such a condition is caused by external factors, then when they are eliminated, the Hb value returns to normal. In a situation where hyperhemoglobinemia is a concomitant symptom of the disease, initial elimination of the underlying pathology is necessary.
Reasons for the increase
Factors that cause an increase in hemoglobin levels can be exogenous (external) or endogenous (internal).
Exogenous causes. An increase in hemoglobin levels may be associated with a person’s type of activity. Thus, pilots, residents of high mountains and climbers who spend significant time at high altitudes experience hypoxia. Therefore, immediately after the flight, the Hb concentration will be higher than normal. Taking certain medications, such as steroids, also affects this laboratory indicator.
During long-term training with heavy loads, a huge amount of oxygen is consumed, which, with the correct technique, is compensated by frequent and deep breathing. If technology is violated, an increase in hemoglobin levels is observed in the body.
Endogenous causes. Diabetes mellitus and mental disorders accompanied by stress reactions can also cause Hb deviations from the norm. And in the case of a benign tumor process of the circulatory system (Vaquez disease), an increase in the concentration of red blood cells becomes malignant.
When taking medications that lead to excessive absorption of iron ions in the blood against the background of malfunctions of the enzymatic system, the Hb level increases.
Reasons for the downgrade
Low Hb concentrations are observed against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- anemia of various types;
- failures of hemoglobin synthesis processes;
- liver diseases;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- chronic kidney disease, which results in a decrease in the concentration of the hormone erythropoiesin, the main role of which is the activation of the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- blood hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells;
- oncological diseases accompanied by metastases to the bone marrow;
- chronic pathologies of connective tissue;
- infectious process.
Read further: Tables of norms with explanations of indicators in a biochemical blood test
Reasons for increasing protein
An increase in hemoglobin levels can be caused by two main reasons:
- exposure to external factors and lifestyle;
- pathological deviations.
Lifestyle
In the first case, the metabolism in the body is not disturbed, the number of red blood cells does not increase, but for some reason the body needs oxygen more, so the hemoglobin level automatically increases. This situation is temporary, and the body will return to normal as soon as the cause of the lack of oxygen is eliminated. This group of temporary factors that contribute to an increase in hemoglobin includes:
- living in mountainous areas: for people living in high mountainous areas, high hemoglobin in the blood is the norm;
- features of the profession: climbers and pilots (lack of oxygen in the blood is a consequence of high altitude), bodybuilders (taking anabolic steroids and steroids and excessive physical activity cause oxygen starvation);
- excessive nicotine consumption: smoking increases blood viscosity, increasing iron levels in the blood;
- non-compliance with the drinking regime: if the body lacks fluid, the amount of protein in the blood automatically increases;
- unhealthy diet: predominance of protein foods in the diet.
Pathological deviations
The second group of reasons causing an increase in protein includes pathological disorders in the body. With such disorders, the body's metabolism is disrupted and red blood cells are reduced. To compensate for the lack of red blood cells, the body begins to increase the production of hemoglobin. The pathological group includes:
- kidney dysfunction;
- hormonal disorders;
- pulmonary fibrosis;
- congenital heart defects;
- intestinal obstruction;
- diabetes;
- cancer;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- poisoning;
- liver pathologies;
- stress;
- dehydration;
- pernicious or hemolytic anemia;
- bone marrow dysfunction;
- hereditary hemoglobinemia.
Hemoglobin levels may increase in response to an increase in platelets in the blood. The number of these blood cells increases with serious disturbances in the functioning of the body and a number of dangerous diseases.
The general causes of increased protein are the same for all sexes and ages, but some factors in the development of the disorder are unique to certain categories of patients.
Among women
Previously, it was believed that women did not face the problem of high hemoglobin levels. But doctors have refuted this opinion and found that an increase in iron-containing protein in women is most often caused by:
- pneumonia;
- infectious infections;
- asthma;
- malignant neoplasms;
- mental and emotional overload.
Sometimes an increase in hemoglobin-containing proteins is associated with a woman’s lifestyle or is a consequence of taking certain medications.
During pregnancy, increased hemoglobin in women, the causes and consequences of which are unpredictable, is considered a dangerous condition. With this disorder, pregnant women may experience disturbances in the functioning of the liver or kidneys, and may cause developmental abnormalities in the unborn child. In this case, doctors recommend that the pregnant woman follow a certain diet and take a course of vitamins to maintain normal hemoglobin levels.
In men
The stronger sex is more often susceptible to excess iron-containing protein in the blood. This is due to the fact that men are more prone to bad habits, and they often eat unhealthy “cholesterol” foods. Also, men are more often diagnosed with heart and vascular diseases, which contribute to an increase in hemoglobin levels in the blood.
Among men, more often there are representatives of professions in which disorders are associated with the implementation of their activities: miners, pilots, submariners, climbers, bodybuilders. In order to avoid the development of the disorder, doctors recommend that the stronger sex adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
In children
During intrauterine development, the fetus cannot breathe through the lungs on its own, but takes in air from the mother’s blood. The pregnant woman and the baby may not have enough oxygen between them, which is why the fetus's body begins to adapt to low oxygen levels by increasing protein levels.
In a newborn, according to recent studies, intrauterine hypoxia with placental insufficiency is often the cause of high hemoglobin. Over time, with the development and growth of the baby, the situation stabilizes, and by the age of two, the protein concentration returns to normal. If this does not happen, then the baby may have serious health problems: heart defects, blood diseases, neoplasms.
In adolescence, the reasons for elevated protein levels are the same as in adults. But more often in adolescents, the pathological condition is caused by pulmonary fibrosis, dehydration, intestinal obstruction, and blood diseases. Parents of boys involved in sports should pay attention to the use of anabolic steroids by teenagers, which increase the level of transport protein in the blood.
Treatment methods for high hemoglobin
High hemoglobin in women poses a serious threat, especially during pregnancy. Therefore, when diagnosing a pathological condition, mandatory treatment is necessary. How to reduce hemoglobin?
Treatment and correction methods for elevated hemoglobin in women are aimed at thinning the blood and reducing the concentration of red blood cells. For this purpose, for example, the following drugs are prescribed:
- aspirin®;
- cardiomagnyl®;
- chimes®.
Important: independent selection of medications and dosages for treatment is prohibited. Such behavior can lead to a worsening of the condition and severity of the disease.
It is acceptable to prescribe hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches. When a leech bites, the enzyme hirudin contained in their saliva enters the human bloodstream. Hirudin has a bidirectional effect on the blood: on the one hand, it slows down the processes of blood clotting, and on the other, it reduces the risk of blood clots. It should be noted that for therapy it is necessary to use only medicinal leeches sold in pharmacies and diluted in laboratory conditions. For one session, 5 leeches are enough, each of which sucks no more than 15 ml of human blood when biting.
Menu for women with high hb
In combination with drug treatment and hirudotherapy, it is necessary to adhere to a certain menu:
- the amount of red meat in the diet should be reduced, and offal (liver, tongue, kidneys) should be completely excluded;
- the diet should be dominated by white meat and low-fat fish;
- the consumption of legumes (peas, beans, lentils) is allowed, since iron, which predominates in their composition, is poorly absorbed by the human body;
- vitamin complexes containing folic acid and B vitamins are excluded;
- It is forbidden to consume juices and rosehip decoctions;
- You need to drink clean water without gas often and in small portions: every half hour - 1 glass of water.
Symptoms of erythrocytosis
The general symptoms of high hemoglobin differ little from the symptoms of other diseases and are mild:
- high blood pressure, swollen veins;
- aches and difficulty moving the joints;
- drowsiness and increased fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- fingertips become bluish;
- loss of appetite, nausea;
- absent-mindedness;
- irritability;
- During the test, blood flows from the finger with difficulty.
When hemoglobin reaches 190 g/l, the palms and sclera of the eyes may turn yellow due to the heavy load on the liver.
Diagnostic methods and preparation
Diagnosis of hemoglobin level is mandatory when conducting a general blood test. The duration does not exceed 1 day. The biomaterial for analysis is venous or capillary blood. To obtain the most reliable results, you must follow the preparation recommendations:
- eliminate fatty and fried foods for 1 day;
- blood is donated strictly on an empty stomach, the last meal taken at least 8 hours before;
- within half an hour, physical and emotional stress is limited;
- You must not smoke for 1 hour.
Interpretation of results and norm
Important: the interpretation of the data obtained should only be carried out by the attending physician.
Otherwise, the risk of incorrect diagnosis and selection of treatment methods that will worsen the patient’s condition cannot be excluded.
Reference (normal) values are selected individually for each patient, taking into account gender, age and menstrual cycle.
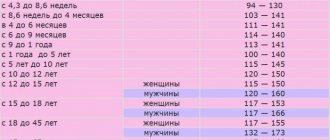
| Floor | Age | Hemoglobin norm, g/l |
| Both | 0 – 14 days | 135-200 |
| Up to 1 month | 100-170 | |
| 1-2 months | 95-130 | |
| 2-4 months | 100-140 | |
| 4-6 months | 110-140 | |
| 6-9 months | 100-150 | |
| 9-12 months | 115-145 | |
| 1-5 years | 110-150 | |
| 5-10 years | 115-145 | |
| 10-12 years | 120-160 | |
| Man | 12-15 years | 120-160 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-170 | |
| 18-45 years old | 130-170 | |
| 45-60 years | 140-175 | |
| Over 60 years old | 120-175 | |
| Woman | 12-15 years | 110-150 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-155 | |
| 18-45 years old | 115-160 | |
| 45-60 years | 120-160 | |
| Over 60 years old | 110-170 |
It should be noted that even with a normal quantitative content of red blood cells in the blood, a deviation from the reference values of the Hb indicator may be observed.
A small one-time deviation from the norm is not a cause for concern. In other words, if hemoglobin 160 is detected in a patient under the age of 18, then there is no need for additional laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Despite the difference in normal values for different sexes, hemoglobin 150 g/l is considered the optimal value for both women and men.
Age norms of hemoglobin
Normal hemoglobin levels vary depending on the age and gender of the patient. For men, this figure is slightly lower than for women. They are characterized by the following norms.
| Age | Norm, g/l |
| 3 months | 114 |
| 6 months | 117 |
| 1 year | 116 |
| 3 years | 118 |
| Teens and mature men | 135-160 |
Since the functions of hemoglobin are to transport oxygen, its level is very important for the proper functioning of the body. For female patients, the table looks like this.
| Age | Norm, g/l |
| 3 months | 115 |
| 6 months | 119 |
| 1 year | 118 |
| 3 years | 120 |
| Teens and mature women | 120-140 |
If normal values increase by 10 or more units, it is necessary to prescribe therapeutic therapy and a diet that allows you to restore balance in the blood composition. Neglecting your own health can cause the development of many complications and pathologies that could have been avoided with timely diagnosis and treatment.
Consequences of increased hemoglobin in women
High hemoglobin levels are dangerous for women due to complications that affect the functioning of various systems and organs. Thus, an increase in blood viscosity leads to the formation of clots, which can cause bleeding, pulmonary thromboembolism, stroke, heart attack or thrombosis. Any of these conditions requires immediate assistance from medical personnel, since it threatens the life and health of the patient.
Hyperhemoglobinemia is especially dangerous for people with chronic diseases of the lungs and cardiovascular system, since their risk of developing thrombosis increases several times. Timely monitoring of Hb level concentrations is necessary during and after treatment of pathologies.
Can it be elevated in pregnant women?
During pregnancy, this figure usually falls due to an increase in blood volume.
But sometimes, during a period of hormonal changes, hemoglobin may increase. This is possible in the second trimester, when the placenta is actively forming.
After childbirth, the body may also be “scared” of large blood loss and begin to increase the production of red blood cells.
But this indicator (otherwise this phenomenon is also called “erythrocytosis”) should not remain above normal for more than two weeks.
With persistent erythrocytosis, urgent hospitalization is necessary , since this condition threatens:
- pregnant woman - thromboembolism;
- and the fetus may have problems with growth due to viscous and thick blood, which cannot provide it with the necessary nutrients.
During pregnancy and after childbirth, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a doctor and systematically do a general blood test.
If erythrocytosis persists, the doctor will refer you to a hematologist, who will give the necessary recommendations and prescribe the necessary blood thinners.
Read about sports nutrition for weight loss. Find out what it should be like for women!
In the next article we will tell you everything about uterine prolapse and what exercises there are to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Prevention of elevated hemoglobin
Preventive measures against increasing the concentration of Hb in the blood consist of maintaining a healthy lifestyle:
- cessation of alcohol abuse, smoking and psychotropic drugs;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- drinking large amounts of clean water without gas;
- limiting physical and emotional overload;
- health status monitoring – annual scheduled examinations and maintenance therapy for chronic diseases.
What is dangerous, possible consequences
With increased hemoglobin, the blood becomes thick and viscous. At the same time, the internal organs, oddly enough, do not receive enough oxygen and other nutrients.
Therefore, with prolonged erythrocytosis, the following may develop:
- disruption of the kidneys and genitourinary system, up to painful colic;
- infertility;
- recurrent miscarriages;
- decreased visual acuity;
- heart attack;
- heart attack;
- thrombosis.
In this regard, it becomes clear that high hemoglobin can be no less dangerous than low hemoglobin levels and requires medical help.
How to increase hemoglobin in an elderly person
There are several ways to increase hemoglobin in the blood of an elderly person, which depend on the type of anemia.
1. For iron deficiency anemia (IDA).
This is the most common type of anemia among older people and a blood test will show:
- the presence of microcytosis and hypochromia of erythrocytes;
- the process of reducing serum iron levels;
- a decrease in ferritin and an increase in the iron-binding function of blood serum, which indicates a deficiency of iron-containing components.
Anemia in an elderly person is determined by the color indicator of the blood, which is calculated using the formula (the hemoglobin indicator is divided by the number of red cells). Its norm is from 0.85 to 1.1. If there is iron deficiency in an elderly person, this value will be below 0.7. Hemoglobin in the cell (standard from 27 to 35 picograms) is also determined by a blood test. The blood is also examined for the percentage of microcytes and the total number of blood cells.
If there are symptoms of hypochromia, studies speak of IDA in an elderly person.
If you need to accurately determine whether there is anemia or not, then the blood serum is examined for the amount of iron. This information needs to be known before therapeutic therapy to increase hemoglobin with iron-containing drugs is prescribed. If the cause of anemia is a lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid, then differential diagnosis is carried out.
It is necessary to begin treatment of the cause that caused the pathology, and not its consequences. This means we need to consider the factors that provoked the process of decreasing hemoglobin in an elderly person. Adjuvant therapy that raises hemoglobin includes iron-containing drugs. However, often due to the impossibility of surgery, this method of treatment is the main one.
There are strict requirements for drugs that increase hemoglobin:
- Contains a large amount of divalent iron.
- The presence of additional components to improve the absorption of metal ions.
- Ease of use (dosage and conditions of administration).
- Not very high cost.
If you take divalent metal fumarate or ferrous sulfate in an amount of 150–300 mg, the iron level will rise. You need to take 1 or 2 tablets during the day with meals.
Side effects may occur when taking this group of drugs. These may be disturbances in the functions of the stomach (nausea, vomiting), intestines (frequent constipation). Sometimes the vascular walls of the veins become inflamed, painful sensations appear behind the sternum, as well as hypotension and allergic reactions.
The level of iron in the blood is increased by adhering to a special diet. For example, meat can be of great benefit: the bioavailability of the metal in it reaches 30%.
2. Anemia due to deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
If there is a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12 in the human body, a disorder occurs in the cellular synthesis of DNA in the blood. With this type of anemia, red blood cells turn into macrocytes.
Indicative factors:
- Increase in blood color index.
- Presence of megalocytosis.
- Presence of nuclear remains in erythrocytes.
- The presence of leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, reticulocytopenia.
- Raising serum iron levels.
- Development of megaloblastic hematopoiesis in the bone marrow.
- Presence of mental and neurological disorders.
This kind of anemia and hemoglobin deficiency in older people may occur due to:
- progressive atrophic gastritis or malignant tumor in the fundus of the stomach;
- inflammatory processes in the small intestine, gastric surgery;
- the presence of diverticulosis and pancreatitis;
- dysbacteriosis and chronic hepatitis;
- lack of substances necessary for the body;
- improper use of medications.
This type of anemia is more accurately diagnosed after a bone marrow test. But it happens that it is not possible to conduct such a study due to objective reasons. In this situation, the doctor makes empirical conclusions and prescribes a course of vitamin B12 to the elderly patient. To improve the general condition and composition of the blood, you will only need 1 or 2 injections.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, long-term vitamin therapy is carried out. At the beginning of treatment, an elderly person is given injections daily until the hemoglobin level is completely normalized. Then the number of injections is reduced to 1-2 every 30 days. If therapy is not enough, there is a risk of relapse of the disease. For anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12, folic acid is not prescribed, since there is a high probability of neurological symptoms.
We recommend
“Pneumonia in old age: diagnosis and treatment methods” Read more
Lack of folic acid in the body of an elderly person can cause anemia, very similar to B12 deficiency. However, it is not that common. In addition, the factors that provoke it are different. The causes of this type of anemia:
- the human body experiences constant alcohol intoxication;
- cancer, Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis, destruction of red blood cells - all this leads to increased consumption of folic acid by the body;
- the presence of nutritional deficiency, as well as enteritis, aggravated by malabsorption;
- Anticonvulsant drugs, as well as Methotrescat, Barbiturate, Triamterene, have an adverse effect on the body condition of an elderly person.
If a pensioner has a severe form of the disease due to a significant lack of hemoglobin, he will be prescribed folic acid injections. In other cases, a sick person must take this drug in tablets (the norm is 5 mg per day). If it is impossible to eliminate the factor that provokes anemia (tumor, hemolysis), patients are prescribed a long course of folic acid. In cases where a pensioner has epilepsy, treatment must be carried out very carefully, since neurological symptoms may intensify.
How to increase hemoglobin in an elderly person with diet? It is very useful for anemia to eat:
- meat and meat products (for example, sausages);
- liver, fish;
- eggs (yolks);
- whole grain flour products;
- sunflower seeds, pumpkin and sesame seeds;
- nuts, especially pistachios;
- various greens: spinach leaves, fennel, parsley;
- various types of cabbage and beets;
- black currant;
- wheat germ and sprouts;
- apricots, prunes, figs, dates.
Practical recommendations for increasing hemoglobin:
- Drink 1 cup of fermented yeast for 5 days.
- Pickled beet juice (200 ml per day) is very useful.
- Soups made from bran (wheat or rye) with cream help to normalize hemoglobin levels in older people.
- You need to take 20–25 g of nettle tincture prepared in May every day before bed.
- Apples, carrots (grated), and parsley are also very useful.
- The diet should contain high amounts of protein and low fat.
- Dried apricots, 3-4 pieces per day, help increase hemoglobin. It is not recommended to eat the seeds, as they are poisonous.
- Adhering to a meal schedule (4–5 times a day) has a positive effect on the body. Moreover, breakfast should be more substantial, and dinner should be light.
- Products containing vitamin B1 and any type of whole milk bring invaluable benefits.
With the help of such a diet, you can increase hemoglobin in an elderly person and eliminate the early symptoms of anemia. Modern medicine has special drugs that cure this disease. You can combine drug therapy and treatment with folk remedies. If you strictly follow the recommended recipe and dosage, then natural medicines will provide significant assistance in eliminating the problem. After a month-long treatment course, it is necessary to take a blood test. If the hemoglobin level is insufficient, therapy should be continued.
There are methods that allow you to quickly increase hemoglobin in an elderly person at home.
Here are the most effective:
- Peel the carrots, black radishes, and beets. Wash and grate on a fine grater. Squeeze the juice from the resulting mixture, mix equally and place in the oven for 3 hours. Take 1 tablespoon daily.
- An excellent remedy for raising hemoglobin is a medicinal cocktail. It is necessary to squeeze the juice of pomegranate, apple, carrot, lemon. Mix in a ratio of 2:1:1:1 and add honey (70 g) to the mixture. Then pour the mixture into a jar and leave to infuse for 2 days in the refrigerator. Dosage: 2 tbsp. l. 3 rubles each per day.
- A tincture of meadow clover will help solve the problem. You need to pour 10 g of inflorescences with 1 glass of hot water. Leave the solution to infuse for 45 minutes and then strain. Take 2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
- Rosehip can be consumed instead of tea 3 times a day. To prepare it, you need to pour 1 tablespoon of berries with 1 glass of boiling water and let it brew for 8 hours.
- A mixture of currant juice, strawberries, and red rowan in equal proportions is suitable as berry therapy. Drink 100 ml daily, 2 times a day.
- Take garlic tincture three times a day, one medium spoon. To prepare it, peel and chop 300 g of garlic. Pour the mixture with 1 liter of alcohol and leave to infuse for 3 weeks.
How to lower the level
To lower your hemoglobin level, you must first determine the cause. To thin the blood, doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- Chime;
- Aspirin, or salicylic acid;
- Trental;
- Cardiomagnyl.
You should not self-medicate. These drugs can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
Sometimes the doctor recommends electrophoresis. This is a very effective procedure that has stood the test of time.
What should be the diet for high cholesterol in women? We will tell you about the rules of nutrition at high levels in our project.
In our next article, read about the symptoms of weakened immunity in adults, as well as ways to maintain it.
Read about the normal level of cholesterol in the blood of pregnant women in our special review: .