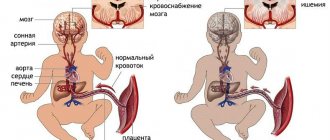
The placenta is formed in the uterus after pregnancy. It is necessary to connect the body of mother and child with one blood circulation. With the help of the placenta, oxygen and nutrients necessary for the development and formation of organs are delivered to the fetus. In the opposite direction, unnecessary substances formed as a result of biochemical processes are removed.
Impaired uteroplacental blood flow causes a condition called placental insufficiency. This leads to fetal death and miscarriage.
For 36 weeks, three mandatory ultrasound examinations are performed. It allows you to promptly identify the disorder, develop a plan for managing pregnancy and childbirth, prescribe treatment, and prevent the death and abnormal development of the child.
Modern requirements of obstetricians and gynecologists are aimed at examining pregnant women using safe methods to assess uteroplacental blood flow by volume.
How does blood circulation function between mother and fetus?
The mother-fetus circulatory system is based on such anatomical structures as the placenta, umbilical arteries, and veins.
Blood enters the placenta through the uterine arteries. The structure of their walls is distinguished by the presence of a muscle layer that can contract and block the lumen. Before pregnancy occurs, this mechanism helps reduce blood loss during menstruation.
At 4–5 weeks of consolidation of the fertilized egg (gestation process), the muscle layer disappears. Blood flow to the placenta no longer depends on vascular contraction. And by the sixteenth week, the arteries are transformed for constant blood supply. This turns out to be dangerous when bleeding occurs, since it is impossible to stop it by reducing the lumen of the vessels.
Under normal conditions, the placenta is fixed on the inner surface of the uterus with the help of villi that penetrate deep into the thickness of the mucosa. They grow into the walls of blood vessels and come into direct contact with maternal blood.
What happens here at the cellular level:
- exchange between the maternal body and the fetal bloodstream;
- two differently directed flows meet;
- the transfer of necessary substances takes place (diffusion).
The other part of the general blood circulation is provided by the vessels of the umbilical cord (normally there are 2 arteries and a vein). The main volume of blood flows to the fetus through the arteries, and flows through the veins towards the placenta.
As the uterus grows, the arteries expand and form anastomoses.
Violation of fetal-placental blood flow is most difficult for a developing child. Creates conditions for an unsatisfactory prognosis for the development of internal organs and systems and the birth of a healthy baby.
The essence of Doppler measurements of fetoplacental blood flow
During pregnancy, a new structure is formed in the female body, within which the relationship “future mother - placenta - baby” takes place.
Its blood flow system is also separate. Any violation of it can have a negative impact on the fetus. To diagnose such disorders, Doppler measurements of fetoplacental blood flow are used. It allows you to assess the movement of blood through the vessels within this blood flow system, thanks to which the doctor is able to identify any violations that pose a threat to the health and life of the mother and child.
Dopplermetry (abbreviated as “DPM”) is an ultrasound examination technique that allows you to determine the indicators of blood movement in the vessel being examined. It is based on the Doppler effect, which causes a frequency shift when acoustic ultrasonic waves are reflected from objects in motion. In this case, these objects are blood cells that move through the vessels, forming blood flow.
During the procedure, blood flow in the uterus and umbilical cord arteries is assessed in pregnant women.
What reasons can break the blood flow between the mother, placenta and fetus?
The causes of disruption of the circulatory system between the maternal body and the fetus (fetoplacental insufficiency) have been well studied. Some factors are formed only during pregnancy. The other depends on the woman’s general health.
Pregnancy pathologies include:
- Low attachment of the placenta (obstetricians say - previa, "placentation") - the lower parts of the uterus are distinguished by a thinner muscle layer. Through it, not enough blood flows to the fetus. A similar situation develops in the case of presentation in the area of a postoperative scar (for example, from a cesarean section).
- Late toxicosis is accompanied by damage to small vessels of the uterus; the complication is the most common blood flow disorder.
- Anemia - low hemoglobin levels cause a compensatory increase in heart rate, increasing blood flow through the uterine arteries to compensate for the lack of oxygen. Circulation also changes in the uteroplacental circle.
- Incompatibility between the blood of the mother and the fetus according to Rh - an immune conflict arises with the development of hemolytic disease of the child, anemia. The same situation is possible when transfusion of different blood types from a donor.
- The load on the kidneys due to toxicosis can cause an increase in blood pressure. This helps change blood flow.
- Pathology of the umbilical cord arteries is rarely detected. If there is only one umbilical artery, then there is insufficient blood flow to the fetus.
- Multiple pregnancy - the placenta is increased in size and requires increased nutrition. Sometimes blood flow changes from one fetus to another.
It turns out that the first child is a constant donor for the twin, develops worse, because he transfers blood to his brother, and he himself is “malnourished”
Such changes are called fetotransfusion syndrome. The donor has a lower body weight. And the recipient experiences an increased load on the developing heart. Both kids have problems.
The most dangerous diseases for women are:
- Acute infections during pregnancy - pathogens can penetrate the placental barrier and destroy the vascular network.
- Malformations of the uterus - the most significant is the “bicornuate” uterus. Inside the cavity there is a partition dividing it into 2 parts. Pregnancy is possible only in one of them. The main violation is not the compression factor (the cavity has the ability to stretch sufficiently), but the lack of communication between the uterine arteries, insufficient development of the vascular network, and placental hypoxia.
- Endometriosis is a change in the inner lining of the uterus that occurs after inflammatory diseases (including sexually transmitted infections), frequent abortions, and diagnostic curettages. One of the reasons is smoking and alcohol.
- Uterine tumor - if a woman has even a small fibroid (benign tumor), then pregnancy stimulates the growth of nodes. They take over part of the blood supply, and the fetal blood flow is “robbed.” Failure directly depends on the size of the tumor.
- Diabetes mellitus affects the walls of blood vessels and often occurs in women with risk factors during pregnancy.
Prevention and treatment of placental insufficiency
Tutorial. Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology named after. BEFORE. Ott RAMS, St. Petersburg State University
Methods for the prevention and treatment of placental insufficiency depend on timely diagnosis and treatment of concomitant diseases and pregnancy complications that cause it.
Miscarriage is one of the main risk factors for the development of placental insufficiency. It should be taken into account that a complex of unfavorable factors leads to miscarriage and the formation of placental pathology. Therefore, treatment of PN will be more effective if it is carried out taking into account the causes leading to miscarriage, and during periods of maximum growth and development of the fetus.
In women with insufficient ovarian function preceding pregnancy, in the event of a threat of miscarriage, hormone therapy is administered in the first trimester.
If estrogen levels are low, there are signs of chorionic detachment and bleeding in the early stages, it is recommended to treat with small doses of estrogen: 0.025-0.050 mg of microfollin per day for 5-7 weeks with gradual withdrawal of the drug.
If the basal level of human chorionic gonadotropin is low in the first trimester, therapy is carried out with appropriate drugs (pregnyl, prophasia) in a dose of 500-1500 units 1-2 times a week until 12 weeks of pregnancy.
To maintain the function of the corpus luteum, progesterone is prescribed (1% 1-2 ml daily or 2.5% 1 ml every other day) up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, utrozhestan - natural progesterone in capsules for oral and intravaginal use - at a dose of 200-600 mg or duphaston (10-40 mg per day) until 16-20 weeks of pregnancy.
In the presence of concomitant endocrine and autoimmune disorders (hyperfunction of the androgenic zone of the adrenal cortex, autoimmune thyroiditis), treatment is carried out with dexamethasone and L-thyroxine.
Therapeutic and preventive measures should include diet therapy, vitamin therapy, products and means that stimulate intestinal function (fermented milk products, wholemeal bread, laminolact), and means aimed at normalizing sleep.
To prevent PN in pregnant women at risk, antioxidants (α-tocopherol acetate, ascorbic acid) and hepatoprotectors (potassium orotate, essentiale, ho-phytol) are used as regulators of tissue metabolism to normalize redox processes. To normalize the processes of excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system in pregnant women with an asthenic constitution and an increased level of anxiety, nootropics (nootropil, piracetam) are prescribed; glycine, which has a distinct anti-stress effect. In case of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypotonic type, adaptogens (tincture of lemongrass, eleutherococcus, ginseng, aralia) have a good effect. To normalize sleep, complex herbal remedies containing extracts of valerian, hawthorn, lemon balm, hops, peppermint and lemon mint are used: novo-passit, persen, sanosan.
An important component of the treatment of renal failure during miscarriage is therapy with drugs containing magnesium ions. N. G. Kosheleva (1997), in addition to traditional magnesium preparations, recommends prescribing Magne B6, containing 470 mg of magnesium lactate and 5 mg of pyridoxine, 2 capsules 2-3 times a day in courses in the I, I and III trimesters of pregnancy.
It is advisable to include in the complex therapy of miscarriage and prevention of placental insufficiency:
- endonasal galvanization,
- acupuncture,
- immunotherapy with washed allogeneic lymphocytes,
- systemic enzyme therapy (Wobenzym).
Dysfunction of the placenta when there is a threat of miscarriage is associated primarily with an increase in myometrial tone. Increased excitability of the uterus is accompanied by a slowdown in blood outflow and venous stagnation in the uteroplacental blood flow. With a prolonged threat of miscarriage, the risk of hypoxic damage to the fetus increases.
The main drugs used to maintain pregnancy are b-adrenergic agonists, magnesium sulfate and metacin.
B-adrenergic agonists (ginipral, bricanil, alupent, salbutamol) have a regulatory effect on the contractile activity of the uterus without causing significant changes in hemodynamic parameters of the mother and fetus. The drugs can be used long-term without harm to the general condition of the woman, starting from 16 weeks of pregnancy until clinical and laboratory signs of threatened miscarriage disappear. The optimal use of b-mimetics in combination with calcium channel blockers, for example, verapamil (finoptin). To ensure a tocolytic effect, b-adrenergic agonists are administered as infusions: an aqueous solution in a dose of 10 mcg is diluted in 300-500 ml of physiological solution or 5% glucose solution. Administration of the drug begins at a rate of 10-12 drops per minute; if necessary, the rate of administration can be increased to 16-24 drops. Before completing the infusion, oral administration of the appropriate drug should be started - 0.5 mg every 6-8 hours. Verapamil (finoptin) is administered at a dose of 40 mg 15-20 minutes before the start of the infusion orally. The combined use of b-adrenergic agonists with calcium channel blockers leads to an improvement in uteroplacental blood flow and fetal condition.
When there is a combination of PN and the threat of miscarriage, it is recommended to use Actovegin in combination with b-adrenergic agonists in order to prevent hypoxic damage to the fetal organs. In case of disturbance of blood flow in the umbilical cord artery and/or cerebral vessels of the fetus, it is recommended to use Actovegin in the form of an intravenous infusion: 80-160 mg (2-4 ml) of Actovegin in 200 ml of 5% glucose solution No. 5.
Chophytol, a purified extract of artichoke leaves, has a hepatoprotective, antioxidant, membrane-stabilizing effect, and helps normalize the balance of vitamins and microelements in the body. To prevent fetoplacental insufficiency, hofitol is used 2 tablets 3 times a day for 3-4 weeks in periods up to 12 weeks, 20-22 weeks, 30-32 weeks of pregnancy.
To prevent placental insufficiency in high-risk pregnant women, including women suffering from recurrent miscarriage, or in multiple pregnancies, it is recommended to use Actovegin and ginipral orally: Actovegin-dragee prolonged action (200 mg) - 1 dose per day + ginipral (0 .5 mg) 1/2-1 tablet 2 to 3 times a day. The combined use of b-adrenomimetics and actovegin has a positive effect on the tone of the myometrium and blood flow in the placenta, which ensures the prevention of hypoxic damage to the fetus due to prolonged contractions of the uterus with the threat of miscarriage.
Hofitol was used in the complex therapy of placental insufficiency during IUGR and cholestatic hepatosis in pregnant women. Before treatment, all women underwent liver ultrasound to exclude cholelithiasis. The drug was administered intravenously in a dose of 5 ml in 00 ml of 5% glucose solution or saline solution for -10 days. Subsequently, oral administration was used, 1-2 tablets 3 times a day after meals. A beneficial effect was obtained in the treatment of cholestatic hepatosis in pregnant women and placental insufficiency. There was an improvement in biochemical parameters, good tolerability and no side effects on the body of the mother and fetus.
Upon receipt of data on infection - exacerbation of pyelonephritis, the presence of polyhydramnios, detection of urogenital infection
etiotropic antibacterial therapy and vaginal sanitation are carried out. When choosing drugs, pay attention to sensitivity, absence of side effects and negative effects on the fetus. Eubiotics are widely used, acting by competitively displacing pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic flora. Antimycotic and vitamin preparations and enzymes are used. Timely detection and etiotropic treatment of urogenital infection reduces the percentage of premature births and fetal malnutrition.
Considering the importance of changes in the vascular-platelet component of hemostasis in pregnant women with preeclampsia,
Drug correction of these disorders is used. For this purpose, magnesium sulfate, clonidine, calcium channel blockers, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants from the group of low molecular weight heparins are used.
Magnesium sulfate
traditionally refers to the main drugs for the treatment of late gestosis. In recent years, the methods and doses of administration, as well as contraindications for administering the drug, have been clarified. It has been shown that magnesium therapy has the greatest effect for the treatment of gestosis with increased diastolic blood pressure and low (up to 1 g/l) proteinuria. Contraindications to the use of magnesium preparations are kidney diseases with impaired kidney function and severe forms of diabetes mellitus. Treatment regimens for gestosis with magnesium sulfate are well known.
Interestingly, magnesium sulfate has an endothelial protective effect and reduces intravascular platelet aggregation, which is important for the treatment of PN. A faster and more persistent antiaggregation effect in the treatment of late gestosis was obtained with the combined use of magnesium sulfate and clonidine.
Clonidine in doses of 0.05-0.5 mg/kg has an inhibitory effect on the contractile activity of the uterus, reducing the frequency and amplitude of myometrial contractions by 70-80%. The use of clonidine does not change the nature of fetal cardiac activity. Clonidine significantly reduces intravascular platelet aggregation, reduces the severity of vascular disorders, and has a stimulating effect on uteroplacental blood flow. Clonidine is the optimal drug for the treatment of threatened abortion in women suffering from hypertension, as well as for the treatment of hypertensive disorders in pregnant women. In case of a high degree of threat or initially high blood pressure, the drug is prescribed intravenously in a dose of 1 ml of a 0.01% solution in 200 ml of saline. After achieving the tocolytic and hypotensive effect, continue taking clonidine orally at a dose of 0.075-0.0375 mg (1-1/2 tablets 2-3 times a day). With a moderate degree of threat and to maintain blood pressure at a “working level,” clonidine is prescribed orally at a dose of 0.075 mg 2-3 times a day for a long time, in some cases throughout pregnancy.
To prevent placental insufficiency in pregnant women suffering from hypertension,
as well as for the treatment of placental insufficiency and the threat of miscarriage in cases where hypertensive disorders in the mother are accompanied by circulatory disorders in the placenta and delayed intrauterine development of the fetus, the use of clonidine in combination with Actovegin and antiplatelet agents (chimes, aspirin) is more effective.
In order to prevent placental insufficiency in pregnant women suffering from hypertension, treatment with clonidine and Actovegin is carried out for a long time, prescribing drugs orally in doses: clonidine - 0.075-0.15 mg 2-3 times a day, Actovegin-dragee - 200 mg - 1 -2 times a day.
For the treatment of placental insufficiency and fetal malnutrition in women with hypertensive disorders, it is better to combine clonidine with intravenous Actovegin at a dose of 160-200 mg (4-5 ml) in a 5% glucose solution. The method of administration and dose of clonidine are determined taking into account the severity of arterial hypertension (intravenous drip administration of 1 ml of a 0.01% solution or oral administration of the drug 2-3 times a day).
We have obtained good results with the use of verapamil in pregnant women at high risk for the development of late gestosis, as well as in pregnant women with hypertension and with developed gestosis. Finoptin and long-acting verapamil - isoptin-retard-240 - were used. In order to prevent the development of hypertensive complications in high-risk pregnant women, it is recommended to prescribe isoptin-retard-240 orally in a daily dose of 120 mg starting from 20-24 weeks and use it for a long time, on average up to 34-36 weeks. Prophylactic use of verapamil makes it possible to prevent the development of severe forms of late gestosis and PN.
Pregnant women who initially have hypertensive complications (vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type, stage 1-2 hypertension, vasorenal hypertension) are advised to prescribe verapamil in combination with clonidine.
In the complex therapy of placental insufficiency in IUGR, in the treatment of gestosis, hofitol is used, which has a diuretic and hypoazotemic effect. The drug improves kidney function, increases the excretion of creatinine and urea, and also has an antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect. Thanks to its membrane-stabilizing effect, influence on lipid peroxidation and increased antioxidant activity of the blood, hofitol improves the condition of the fetoplacental system and is used both for the treatment and prevention of the development of placental insufficiency in late gestosis. Depending on the stage of the process, hofitol therapy can begin with intravenous drip administration for 5-10 days, followed by transition to oral administration. When treating gestosis, hofitol is administered intravenously, 5-10 ml in 200 ml of 5% glucose solution or saline solution for 10-12 days and then 2 tablets 3 times a day for 3-4 weeks.
In case of disturbances in blood flow in the uteroplacental vessels and the presence of IUGR in pregnant women with gestosis, it is advisable to supplement antihypertensive therapy with intravenous infusions of Actovegin or Essentiale.
In recent years, antiplatelet agents (dipyridamole, acetylsalicylic acid) have been widely used in obstetric practice for the prevention and treatment of placental insufficiency.
The following requirements apply to antiplatelet agents used in obstetrics:
- absence of teratogenic and embryotoxic effects,
- normalization of the ratio of prostanoids (increase the synthesis of PG I2),
- improvement of microcirculation and placental blood flow,
- no risk of bleeding and weakening of the hypotensive effect of drugs used to treat gestosis.
Disturbances in the hemostasis system, for which the use of antiplatelet agents is indicated, occur in obstetric pathology (preeclampsia, placental insufficiency), which developed mainly against the background of the following extragenital diseases and pathological conditions:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart defects, hypertension and varicose veins),
- chronic kidney and liver diseases,
- thrombophlebitis and thrombosis of venous vessels,
- endocrine metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, etc.),
- antiphospholipid syndrome,
- DIC syndrome.
The safest antiplatelet agent and angioprotector for use at any stage of pregnancy is dipyridamole (Curantil®).
It combines well with other drugs, including antihypertensives, acetylsalicylic acid, and heparin. By promoting the production of endogenous interferon, chimes thereby increases the body's antiviral defense. Improvement of microcirculation in the placenta under the influence of chimes occurs due to an increase in the intensity of collateral blood flow, increased synthesis of PGI2, and a decrease in platelet activation and adhesion.
Curantil as a means of preventing and treating placental insufficiency in pregnant women with gestosis is used in doses of 75-225 mg/day. The maximum daily dose of the drug is 450 mg. When using chimes, there is no danger of drug overdose and bleeding, so during pregnancy it can be used until delivery, and, if necessary, starting from the first days after birth.
In the presence of varicose veins in pregnant women with APS, it is advisable to prescribe Lyoton-1000 gel
locally for 7-10 days.
In pregnant women suffering from severe forms of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, as well as in women whose cause of adverse pregnancy outcomes is proven antiphospholipid syndrome, low-molecular-weight heparins and heparinoids (fraxiparin, sulodexide) are effective means for the prevention and treatment of placental insufficiency. The timing and duration of therapy with these drugs should be selected individually in each case. Recently, the therapeutic value of the drug mildronate has been proven for the treatment of PN with circulatory disorders.
In Fig. 3 presents treatment options for placental insufficiency, which can be used in various combinations.
For the treatment of APS
during pregnancy, antiplatelet agents, low molecular weight heparins, and intravenous immunoglobulins are used as the main agents; additional - fish oil and vo-benzym.
Treatment for women suffering from APS is recommended to begin before pregnancy. During the period of preparation for pregnancy, an examination is carried out to identify concomitant autoimmune pathologies, sanitation of chronic foci of infection, and in case of a high aPL titer, a course of plasmapheresis is carried out. It should be taken into account that after plasmapheresis there is a temporary decrease in aPL titer, which returns to the original level after a few weeks.
Prevention of PN in women with APS is recommended to begin in the first trimester of pregnancy. From the moment the fetal cardiac activity is registered by ultrasound, aspirin (Bayer) is prescribed at a dose of 100 mg per day for a long time. Therapy with antiplatelet agents (aspirin, chimes) is continued for an average of 34 weeks. pregnancy. During the formation of the placenta (12-16 and 20-24 weeks) or when symptoms of APS appear, fracsiparin is prescribed at a dose of 0.3-0.6 ml per day in courses of 10-12 days. To treat concomitant autoimmune pathology, glucocorticoids are prescribed, but their use does not reduce the risk of thrombosis in patients with APS.
How does insufficient placental blood supply threaten the fetus?
All disorders of both uteroplacental and fetoplacental nature lead to oxygen deficiency of the fetus (hypoxia). Complications are caused precisely by this mechanism:
- the formation of the internal organs of the fetus is disrupted, there is a lack of weight, this is called “intrauterine growth retardation”;
- the heart reacts with rapid contractions (tachycardia) or arrhythmias, bradycardia;
- the composition of electrolytes and acid-base balance are disrupted;
- the functioning of the endocrine system is disrupted, the fetus experiences a hormonal imbalance;
- fat depots are not formed.
The most severe complications are fetal death and threatened miscarriage.
Myomatous nodes take away part of the vascular network from the fetus for its growth
Types of blood flow disorders in the placenta
There are fetoplacental (between the fetus and placenta) insufficiency and uteroplacental insufficiency.
Fetoplacental hypoxia can occur as:
- Acute deficiency - occurs during any period of pregnancy and during labor. Causes premature placental abruption, vascular thrombosis, infarction in the placenta area, and hemorrhage. Capable of causing the death of a child.
- Chronic - occurs more often, develops from the second trimester, but manifests itself only in the third. Changes in the placenta are in the nature of premature aging; fibrin is deposited on the surface of the villi. Permeability is sharply reduced, which provokes fetal hypoxia.
Against the background of the development of chronic placental insufficiency, the following stages can be distinguished:
- compensation - the course is favorable, since the protective mechanisms of the mother’s body are triggered and compensate for the baby’s missing nutrition, the treatment is effective, the child is born on time, healthy;
- subcompensation - the mother’s body is not able to fully compensate for the “unprofitable” blood supply to the fetus, full treatment is necessary, the child may be born with complications and lags behind in development;
- decompensation - the pathology develops rapidly, compensatory mechanisms are insufficient, the fetus’s heart activity is disrupted, intrauterine death is possible;
- critical stage - characterized by pronounced structural changes in the placenta, which disrupts its functions, therapy cannot change the condition of the fetus, death is inevitable.
What parameters are used to examine uteroplacental blood flow?
In order to decide on further actions, the doctor compares the results obtained with the results of the norm, guided by a number of parameters:
- resistance index;
- pulsation index;
- systole-diastolic ratio.
Each of the parameters is calculated using a specific formula. Calculations are carried out for at least three cardiac cycles, after which the average indicator is determined, obtaining the most objective value.
The examination of the uterine arteries is carried out on both sides and is normal; the difference in indicators can be minimal. As the fetus grows, blood flow increases, and therefore the uterine arteries dilate. Their diameter becomes ten times larger. If it remains at the same level, the fetus will suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Such violations may be unstable, which will certainly be reflected in the results of studies conducted on different days. If changes in parameters are observed on both sides, this is a sign of BMD disturbances; on the one hand, this is an indicator of impaired functioning of the kidneys and liver.
Degrees of impaired blood flow
In the joint violation of fetoplacental and uteroplacental blood flow, 3 degrees are distinguished.
I - changes are compensated, do not threaten the fetus, affect only the uteroplacental blood flow, the child develops normally. Depending on the level of changes, there are:
- degree Ia - disturbance of uteroplacental blood flow is limited to one of the uterine arteries, all hemodynamic parameters are stable, within normal limits;
- degree Ib - blood flow is disrupted at the level of communication between the fetus and the placenta due to the vessels of the umbilical cord; enough blood flows through the uterine arteries.
If minor changes in the first stage were not detected and the woman did not receive treatment, then after 3-4 weeks, second-degree disorders occur.
II - blood flow in the uterine and umbilical arteries changes.
III - indicators are critical, reverse blood flow in the arteries is possible.
Features of DPM of uteroplacental blood flow
The pattern of ultrasound examination and Doppler testing for the patient is no different. The procedure is performed transabdominally, with the pregnant woman lying on her back or side. The diagnostician applies a medical gel to the area being examined, which allows for better visualization. It eliminates the presence of air between the ultrasound scanner sensor and the surface of the skin and ensures their tight contact.
Sometimes the study is performed transvaginally. It is prescribed if you need to obtain a detailed image. The process uses sensors whose power is sufficient to provide visualization of vessels located at a distance of no more than 10 cm. The sensor is inserted directly into the vagina and thus a scan is carried out.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The Doppler ultrasound method most accurately helps to make the correct diagnosis and identify the level of impaired blood flow. The method is highly sensitive and very informative. Shows even small changes in the first stage before clinical manifestations. An important advantage is safety for the fetus and the expectant mother.
Using Dopplerography, it is possible to examine blood flow through arteries and veins, obtain a color graphic image, and measure fetal hemodynamics.
This plays a significant role in predicting the course of pregnancy and creates conditions for making decisions on treatment measures.
Indirect diagnostic methods include:
- computed tomography,
- Ultrasound.
The methods allow us to identify lack of fetal weight and placental dysfunction. These signs may be evidence of the development of hypoxia.
Diagnostic methods
Dopplerography can provide the most reliable and complete information about this pathology. This diagnostic procedure is based on the use of ultrasonic waves and is completely safe for the expectant mother and baby. Using the procedure, signs of circulatory disorders are diagnosed, such as a decrease in diastolic velocity, an increase in the resistance index, and a dicrotic notch in the blood flow curve. The table provides information on how this pathology is diagnosed.
| Diagnostic method | Type of study | Purpose of the event |
| History taking | Analysis of the patient’s complaints, correlation of abdominal circumference with standard indicators corresponding to the gestational age | Making a preliminary diagnosis, developing a plan for further action |
| Physical examination | Auscultation | Determination of fetal heart rate |
| Laboratory research | Blood analysis | Determination of the amount of estrogens, progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin |
| Instrumental studies | Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs | Determining the size of the fetus and the condition of the placenta |
| Cardiotocography | Study of the child’s heart function | |
| Dopplerography | Assessment of the intensity of blood flow, determination of the state of intraplacental circulation, flow speed and direction of blood in the vessels of the uterus and umbilical cord |
What does the mother feel and what does the doctor determine during the examination?
Hypoxia stimulates fetal motor activity.
At an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, the doctor listens to the fetal heartbeat and pays attention to high frequency, arrhythmia or bradycardia. This necessitates referral for Doppler examination.
A pregnant woman pays attention to increased movements, tremors
Impaired blood flow during pregnancy: causes of pathology
An ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound helps to identify deformities in the fallopian tube, artery or placenta of a pregnant woman. It allows you to detect problems associated with blood vessels and calculate the rate of nutrients and oxygen supplied to the child.
- pregnancy at a very early or too late age;
- little time has passed from the last birth to the current pregnancy;
- toxicosis in the later stages of pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- kidney pathologies;
- formations in the uterus of various nature;
- an intrauterine infectious disease is diagnosed;
- there have been abortions or miscarriages in the past;
- development of more than one fetus is observed;
- lack of iron in the body of a pregnant woman;
- atypical location of the placenta;
- Rh factor incompatibility;
- blood clotting disorder.
The causes and consequences of placental insufficiency are interrelated.
Treatment of disorders
Establishing the degree of impaired uteroplacental blood flow is necessary for choosing pregnancy management tactics.
- It is believed that it is possible to maintain a pregnancy in the first degree (a and b); treatment will also help.
- The second degree is considered borderline, requiring constant monitoring; the effectiveness of treatment is unlikely.
- In the third degree, urgent delivery using surgical methods is required.
Treatment options are aimed at all parts of the pathology:
- to improve microcirculation, use Pentoxifylline, Actovegin;
- to support low blood flow speed and pressure in the vessels, Stabizol, Venofundin, Infucol are used (synthesized on the basis of a starch solution, capable of retaining fluid in the vessels);
- vasodilating drugs such as Eufillin, No-shpa eliminate spasm of medium and small arteries;
- by reducing the tone of the uterus, it is possible to influence vascular spasm, reduce the degree of hypoxia, use magnesium sulfate, Magne B6, Ginipral;
- antioxidants eliminate the effects of hypoxia, destroy decay products, prescribe Tocopherol, combinations of vitamin E and ascorbic acid, Chophytol;
- Essentiale has a protective effect by increasing the level of beneficial phospholipids in the blood and improving liver function;
- Curantil is prescribed during pregnancy against the background of uterine fibroids; a positive effect on microcirculation and the prevention of thrombosis has been established.
Obstetricians continue to use Cocarboxylase in practice, which cardiologists have abandoned. But gynecologists consider the drug effective for restoring tissue respiration.
Incubators are used for the treatment and care of newborns as indicated.
Preventive measures
Patients who are at risk of developing this disease need to carefully prepare for pregnancy. Spontaneous conception in this case can turn into a tragedy for the couple.
For those women who are already pregnant, to prevent deterioration of uteroplacental blood flow, it is necessary to follow a number of rules:
- Avoid stress.
- Eat properly. Food must contain the required amount of proteins and vitamins.
- Completely quit smoking, incl. passive, and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Take walks in the fresh air every day.
- Regularly ventilate the living space.
- Avoid excessive physical activity. Preference should be given to yoga, swimming, and gymnastics for pregnant women.
- Monitor your body weight. Weigh yourself regularly and measure your abdominal diameter.
- Sleep on your left side. If the stomach is on the left for a long time, the load on the inferior vena cava, located to the right of the uterus, is reduced. However, sometimes with renal congestion, sleeping on the right side solves this problem.
- Pass all scheduled examinations.