The essence of the Dopplerography method of uteroplacental blood flow
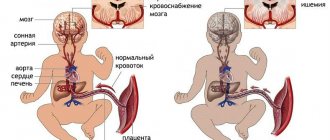
The newly formed fetal blood supply system supplies nutrition not only to the unborn baby, but also to the placenta - the protective membrane. Not only the physical protection of the fetus depends on the completeness and timeliness of blood supply. Good blood supply affects:
- the ability of the placenta to prevent the penetration of toxins;
- the baby's development in the following weeks;
- the ability of the mother's body to neutralize toxins.
Doppler ultrasound (DPM) is a study using a conventional ultrasound machine. The essence of the technique is to use the Doppler effect: when reflected from moving objects (red blood cells), ultrasound waves change their frequency. The device records the received data and displays an image of the blood flow on the screen. An experienced doctor, based on research, determines whether there are deviations in the functioning of the blood supply system, and how dangerous they are.
Blood flow disorders during pregnancy
General information
Blood flow is responsible for the movement of blood through the vessels of the circulatory system. During pregnancy, blood flow in the vessels of the unborn baby, the umbilical cord, and the uterus is examined. Fetal Doppler is a subtype of ultrasound diagnostics that allows you to evaluate the characteristics of blood flow in the vessels of the child, uterus and placenta. Based on this study, the doctor can judge whether the baby is suffering from a lack of oxygen. The doctor can find out information about at what level the vascular pathology occurred (in the uterus, placenta or umbilical cord). Doppler measurements are carried out together with ultrasound.
Vascular examination during pregnancy
Using Doppler ultrasound , it is possible to assess blood flow in the fetal vessels. Doctors examine:
- aorta;
- pulmonary trunk;
- carotid arteries;
- arteries of the brain;
- liver vessels.
The most valuable information is about blood flow in the uterine arteries and umbilical cord arteries. Examining these vessels. The doctor learns about how the placenta develops. You can also find out whether the fetus has enough oxygen and nutrients.
Blood flow disorders during pregnancy
Impaired blood flow is characterized by an increase in the diastolic component of the blood flow rate. An increase in cerebral blood flow is a compensatory centralization of fetal circulation during intrauterine hypoxia. In the fetus, hypoxia is characterized by the redistribution of blood to the blood supply to vital organs:
- cerebral hemispheres;
- myocardium;
- adrenal glands
Characteristic of an asymmetric form of fetal growth retardation.
Increased ASC is also a pathological sign. An increase in SDO in the internal carotid artery may mean:
- intrauterine infection;
- pathology of the central nervous system.
Based on an analysis of the results obtained, many pregnant women were prescribed timely therapy: both medication and lifestyle correction. This helped keep the desired pregnancy healthy.
Causes of blood flow disorders during pregnancy
- circulatory disorders in the uterus can be caused by:
- increased blood pressure;
- pneumonia;
- intrauterine infection;
- hypoxia.
For correct diagnosis in obstetric practice, three-dimensional ultrasound images are used. With the help of this modern diagnostic method, there is a prospect of diagnosing retroplacental bleeding and assessing cardiac malformations by monitoring blood flow. The method is indispensable, as it helps to see devections even in the smallest vessels.
Treatment and prevention of blood flow disorders during pregnancy
In the modern world, there are opportunities for early detection of obstetric complications, so correction can be made at an early stage, avoiding problems with blood circulation in the future. A pregnant woman should remember that her emotional states are transmitted to the child. In order for the fetus to develop without complications, it is necessary to create the correct diet with a maximum of vitamins, macroelements, carbohydrates, proteins and fats. If a pregnant woman is not bothered by swelling, then fluid intake should be at least 1-1.5 liters. in a day.
It is important to monitor changes in body weight, since by the end of pregnancy the weight gain should not exceed 10 kg. There are risk groups that require the use of drug prophylaxis, which promotes the interaction of the body systems of the fetus and mother and prevents dysfunction of the uteroplacental circulation. Timely adjusted methods of labor management and drug therapy will help to significantly reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality . But a high risk of severe neurological complications cannot be ruled out.
Indications and contraindications for diagnostics
The basis for Dopplerography of uteroplacental blood flow are several groups of factors:
- Diseases of a pregnant woman: diabetes mellitus, hypertension, collagen vascular diseases, preeclampsia (increased blood pressure after 20 weeks), kidney disease, Rh sensitization (Rh difference between spouses).
- Diseases and malformations of the fetus: growth retardation, causeless oligohydramnios or dropsy, premature ripening of the placenta, discrepancy between fetal weight and gestational age, heart defects, etc.
- Other reasons: abdominal injuries, age more than 35 or less than 20 years, pathological type of cardiotocogram, postmaturity, unsuccessful previous pregnancies, entanglement of the fetal neck with the umbilical cord.
The doctor has the right to prescribe DPM for any condition of the pregnant woman or fetus that causes fear for the life of the unborn child. The study is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment for uteroplacental insufficiency and the threat of late miscarriage.
Violation of fetal blood flow
General information
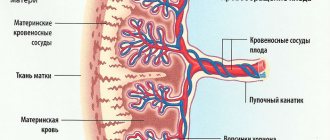
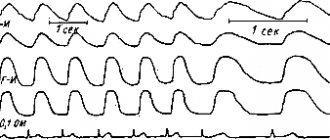
The bloodstream of the placenta includes two closely interconnected, but not interconnected, blood flow systems: fetal and placental. The Doppler effect is based on a change in the frequency of a sound wave depending on the speed of the observed emitter. In our case, it is a change in the frequency of the reflected ultrasonic signal from an unevenly moving medium - blood in the vessels. Changes in the frequency of the reflected signal are recorded in the form of blood flow velocity curves (BVR). A change in normal KSK indicators is a nonspecific manifestation of many pathological conditions of the fetus, and in many cases preceding the appearance of clinical symptoms; it is important that this also applies to the main pathological conditions during pregnancy, namely:
- NWRP;
- fetal hypoxia;
- gestosis.
Hemodynamic disturbances in the functional system “mother-placenta-fetus” are the leading pathogenetic mechanism of disturbances in the condition and development of the fetus during various complications of pregnancy. Moreover, in the vast majority of observations, hemodynamic disorders are characterized by the universality and uniformity of changes, regardless of the condition of the fetus and the etiopathogenetic factor.
Classification of fetal blood flow disorders
First degree: disturbance of fetal-placental blood flow, not reaching critical values and a satisfactory state of fetal hemodynamics (impaired blood flow only in the umbilical cord artery).
Second degree: compensated disturbance of fetal blood flow (disturbance of the actual hemodynamics of the fetus). A decrease in the maximum speed of blood flow through all valves of the fetal heart in 50% of cases, for the left sections - to a lesser extent. The predominance of the right parts of the fetal heart remains. Pathological spectrum of blood flow in the aorta and/or internal carotid artery of the fetus. Primary changes in the blood circulation of cerebral vessels are much less common (non-placental type of fetal hypoxia). The second degree does not last long and quickly turns into the third degree. Third degree: critical state of fetal blood flow. The functional predominance of the left parts of the heart over the right is a deeper restructuring of intracardiac hemodynamics associated with the centralization of blood circulation. Increased fetal hypoxia - a decrease in transvalvular blood flow by 10.3% for the valves of the left sections and by 23.3% for the right ones. Functional insufficiency of the tricuspid valve in 66.7% of cases (regurgitation flows). Aorta - decrease in diastolic blood flow to its absence (69.6%). Reduced resistance of the internal carotid artery in 57.1% of cases. The combination of simultaneous disorders in the aorta and in the internal carotid artery is more common than in degree 2 disorders (14.3% and 42.3%, respectively).
Stages of fetal blood flow disorders
It is possible to compensate for disturbances in fetal blood flow in various stages, more in the first stage, less in the second. In the third stage, decompensation of fetal hemodynamics occurs. Perinatal losses:
- 1 degree of disturbance of fetal hemodynamics - 6.1% of cases;
- 2nd degree - 26.7%;
- 3rd degree - 39.3%.
Neonatal intensive care:
- 1st degree - 35.5%;
- 2nd degree - 45.5%;
- 3rd degree - 88.2%.
An increase in SDO (peripheral resistance) is a high risk factor for complications in the neonatal period. The most common cause of increased SDO is intrauterine infection. Prolonged spasm of cerebral vessels plays an important role in reducing compensatory capabilities, which leads to disruption of adaptation processes in the early neonatal period.
Treatment of fetal blood flow disorders
Under the influence of therapy, it is possible to improve hemodynamics with mild gestosis . At the same time, circulatory disorders in the utero-placental link are less susceptible to positive dynamics than in the fetal-placental link, which can be explained by the development of morphological changes in the vessels of the uterus due to gestosis. At the same time, normalization of blood flow in 40% of cases in the umbilical cord artery suggests a possible functional nature of changes in fetoplacental hemodynamics.
However, in severe cases of gestosis, fetoplacental hemodynamics did not change significantly after treatment. The appearance of “zero” or retrograde blood flow in the umbilical cord artery, indicating an extreme degree of fetal suffering, dictates the need to abandon therapy in favor of emergency delivery.
Timely correction of the tactics of pregnancy and childbirth, drug therapy, carried out taking into account Doppler indicators, can reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality, but do not exclude a high risk of developing severe neurological complications in the early neonatal period.
A Doppler study conducted in women with grade 3 hemodynamic impairment in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system allowed us to establish the ineffectiveness of the therapy for placental insufficiency. With conservative management of labor, perinatal mortality was 50%. There were no perinatal losses during delivery by cesarean section A comprehensive Doppler assessment of the blood flow of the uterine artery and umbilical cord artery can be considered as an objective indicator of the severity of gestosis, regardless of its clinical manifestations. The outcome of pregnancy and childbirth is determined not so much by the nosological affiliation as by the degree of hemodynamic disturbance in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system. Timely correction of the tactics of pregnancy and childbirth, drug therapy, carried out taking into account Doppler indicators, can reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality, but do not exclude a high risk of developing severe neurological complications in the early neonatal period.
With gestosis, pathological SSCs are detected in 75% of cases. In severe forms of gestosis, changes occur in parallel in the umbilical cord artery. In hypertension, the accuracy of predicting adverse perinatal outcomes during pregnancy significantly exceeds the accuracy of clinical tests (BP, creatinine clearance, urea).
Features of Doppler testing
The examination procedure is absolutely safe and is almost no different from a regular ultrasound:
- The patient lies on the couch on her back and exposes the abdominal area.
- The doctor applies a special gel to the pregnant woman’s skin to improve image quality.
- The specialist first examines the general condition of the uterus and fetus for possible abnormalities.
- After this, the doctor turns on the Doppler function and examines the condition of the area of \u200b\u200bthe circulatory system of interest: the aorta, cerebral arteries, etc.
- The results are automatically entered into a special section of the program and analyzed.
If there are deviations, this is immediately visible on the screen. The duration of the procedure is from several minutes to half an hour. The time depends on the volume of the area requiring inspection and the level of qualification of the specialist.
There are no contraindications to the procedure - this is a safe ultrasound examination method, which has been confirmed by many years of clinical trials.
Consequences of violations identified during the inspection
Timely diagnosis detects the emergence and development of pathological conditions at the earliest stages. The accuracy of examinations largely depends on the doctor’s experience and the availability of modern equipment.
When referring for Dopplerography of uteroplacental blood flow, the procedure must be completed without fail. Otherwise, negative consequences are possible:
- abnormalities in child development;
- fetal death;
- increased likelihood of miscarriage;
- low birth weight of the child;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
The good health of the unborn child is the most important incentive for a happy life for most people. Correct implementation of DPM can detect the presence of developmental disorders in the early stages - and respond in a timely manner.
The Harmony clinic has everything you need to carry out Doppler measurements: qualified doctors, modern equipment, affordable prices and first-class service. If you want the procedure to be guaranteed to be not only accurate, but also safe for the baby, then come to us!