Pregnant women and their families usually expect one answer from an ultrasound examination - what is the sex of the child. For an obstetrician-gynecologist, a research method is necessary to promptly identify impaired blood flow during pregnancy and abnormal fetal development.
The management plan and delivery tactics depend on this. To understand the mechanisms of the disorder, it is necessary to consider the capabilities of the circulatory system between mother and child.
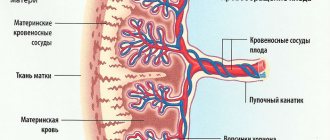
Structure of the uteroplacental blood flow
Mother and child are connected not only by the placenta, but also by a complex system of blood vessels. Therefore, all joint blood circulation is usually divided into levels that cannot exist in isolation, but work only in combination.
- The central part of the system is the placenta. It ensures the “absorption” of products from the maternal blood through the villi that have grown deep into the wall of the uterus. At the same time, the blood of mother and child does not mix. Several rows of special cells form a hematoplacental barrier, which is a serious obstacle to substances unnecessary for the fetus. Through it, the waste blood returns to the mother's venous system.
- The second part of the blood flow consists of the branches of the uterine arteries. If before pregnancy in the female body they are in a collapsed state and are called spiral, then from the period of 1 month they lose the muscle layer that can cause spasm. And by four months, the arteries transform into full-fledged trunks, filled with blood and heading to the placenta area. It is this mechanism, useful for feeding the fetus, that can turn out to be fatal during uterine bleeding: the walls of the vessels can no longer contract.
- The vessels in the umbilical cord form the third pathway of blood flow. There are 2 arteries and a vein here. They connect the baby with the placenta and form the fetal-placental circle. Reduced blood flow at this level causes the most severe damage to the fetus.
Features of blood circulation between mother and child during pregnancy
Disturbance in the blood flow of the placenta causes a lack of nutrition and oxygen in the child and causes his death.
The state of placental-uterine blood flow requires close attention during pregnancy. To assess his condition, routine diagnostics are carried out, and preventive and therapeutic measures are taken. The work of blood circulation between mother and baby is based on the functioning of the umbilical artery, veins, and placenta. The uterine arteries are able to contract, blocking the flow of blood due to the thickness of the muscle layer they have. This structure of the uterine arteries is designed to reduce blood loss during menstruation.
During pregnancy at 4-5 weeks, during the gestation of the egg, the muscle layer in the arteries disappears under the influence of hormones. At 16 weeks, another transformation of the arteries occurs, during which they open to constant filling with blood.
What happens in the arteries:
- connection of two flows of different directions;
- diffusion of substances necessary for a growing baby;
- enrichment of the fetal bloodstream with oxygen and beneficial substances brought by the maternal circulation.
Part of the work of blood circulation falls on the arteries and veins of the umbilical cord. Blood flows through the arteries to the baby, and through the veins it returns to the placenta. Violation of the fetal-placental blood flow leads to inhibition of the growth of the child’s organs and poses a threat to his health.
How is placental circulation disrupted?
Poor blood flow associated with the placenta is called placental insufficiency. It can occur at any stage of pregnancy in two forms.
Acute appears suddenly, even during childbirth, and does not depend on the duration of pregnancy. The fetus falls into a state of hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), which threatens its death.
The main pathological mechanisms of this condition:
- premature placental abruption;
- heart attack due to thrombosis.
Chronic often complicates the course of pregnancy after 13 weeks. Symptoms appear in the third trimester. The mechanism of formation is early aging of the placenta due to the deposition of fibrin on the villi.
As a result of changes in the structure of chorionic villi (placental tissue), the functioning of the hematoplacental barrier ceases, metabolic processes between the maternal body and the fetus are disrupted
Negative consequences in such conditions, depending on the degree of violation, can lead to inevitable death of the fetus.
Degrees of impaired blood flow
In the joint violation of fetoplacental and uteroplacental blood flow, 3 degrees are distinguished.
I - changes are compensated, do not threaten the fetus, affect only the uteroplacental blood flow, the child develops normally. Depending on the level of changes, there are:
- degree Ia - disturbance of uteroplacental blood flow is limited to one of the uterine arteries, all hemodynamic parameters are stable, within normal limits;
- degree Ib - blood flow is disrupted at the level of communication between the fetus and the placenta due to the vessels of the umbilical cord; enough blood flows through the uterine arteries.
If minor changes in the first stage were not detected and the woman did not receive treatment, then after 3-4 weeks, second-degree disorders occur.
II - blood flow in the uterine and umbilical arteries changes.
III - indicators are critical, reverse blood flow in the arteries is possible.
Causes of blood flow disorders during pregnancy
Various reasons can cause disruption of uteroplacental blood flow. These include common maternal diseases:
- pathology of the neuroendocrine system (diabetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, changes in the hypothalamus region of the brain stem);
- lung diseases (emphysema, bronchial asthma);
- disorders in the cardiovascular system caused by developmental defects, the consequences of hypertension, a tendency to hypotension;
- renal pathology (chronic nephritis, pyelonephritis, especially in the stage of renal failure;
- anemia (anemia) associated with deficiency of iron and vitamins;
- conditions accompanied by increased blood clotting contribute to increased thrombus formation in the vessels of the placenta;
- acute and exacerbation of chronic infectious processes cause corresponding inflammation in the placenta, vascular edema and reduction in blood flow; in the first trimester this can result in miscarriage.
Pathology of the uterus creates local conditions for inadequate blood flow:
- any changes in the layers of the uterus (myometrium, endometrium);
- malformations (for example, “bicornuate”, “saddle-shaped” uterus);
- underdevelopment (hypoplasia);
- tumor formations from muscle tissue (fibroids), especially in a primiparous woman over the age of 35; at a younger age, small fibroids help compensate for blood flow.
The causes of insufficient blood flow include unfavorable conditions during pregnancy in the following cases:
- multiple births;
- Rhesus conflict;
- preeclampsia;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- pathological placenta previa.
The risk of impaired blood flow occurs when:
- previous abortions;
- maternal smoking, alcoholism and drug addiction;
- constant nervous environment associated with social or everyday unsettlement;
- violation of proper nutrition of a woman.
Therapy
If the fetus does not receive enough blood, it will develop hypoxia. When such a condition is detected, gynecologists must respond immediately and offer the girl the most appropriate treatment regimen, which will be based on simultaneous action on several stages of pathogenesis.
Initially, medications are selected that have the ability to improve the process of blood microcirculation, for example, it could be Actovegin or Pentoxifylline. Particular attention is paid to maintaining good blood flow in the vessels and stabilizing blood pressure.
For this purpose, medications based on hydroxyethyl starch are prescribed, including: Stabizol, Infucol, Voluven, ReoHES, Venofundin. These drugs act as an osmotic solution of starches, due to which the liquid does not leave the lumen of the blood vessels. It is best to take them during gestosis, since this way you can avoid the occurrence of edema and stabilize blood flow.
To relieve arterial spasm, medications with a vasodilating effect are prescribed. Eufillin, No-shpa or Magnesia are often prescribed (the drugs are best used in injection form). Hypoxia can also be prevented or eliminated by eliminating uterine tone. To do this, a woman will have to take Magnesia, Ginipral or vitamin B6.
It is not enough to eliminate hypoxia, it is also necessary to prevent the likelihood of complications, so Tocopherol, Ascorbic acid and Chophytol are introduced into the therapeutic complex. Some patients are injected intravenously with a 5% concentration of glucose solution, which makes it possible to remove toxins from the body.
To improve the condition of the placenta and saturate it with phospholipids, Essentiale is prescribed. To improve cellular nutrition, Cocarboxylase is prescribed, and if pregnancy occurs in a woman who has a history of uterine fibroids, taking Curantil will be useful.
When carrying a child, a woman must be prescribed a study of uteroplacental blood flow using Doppler ultrasound. As medical practice shows, it is this diagnostic method that makes it possible to identify all deviations, even minor ones; accordingly, doctors have the opportunity to start therapy in a timely manner and stabilize the condition of the pregnant woman.
Types of chronic placental insufficiency
Depending on the development of consequences for the fetus and the ability of the mother’s body to adapt, 4 forms or stages of chronic placental insufficiency are distinguished:
- compensation - the mother’s body fully protects the fetus by improving blood flow through other pathways, and the child does not feel a lack of oxygen, develops normally, is born on time and develops well;
- subcompensation - the mother is not able to fully compensate for the lack of nutrition, and the fetus lags behind in development, there is a risk of complications and congenital defects;
- decompensation - accompanied by a complete disruption of the adaptation mechanisms, normal pregnancy is impossible, the fetus develops serious defects that are incompatible with viability, and death in utero is very likely;
- critical - due to severe changes in the structure of the placenta, further gestation of the fetus is impossible, inevitable death occurs, any treatment is ineffective.
Complications
Violation of uterine blood flow during pregnancy is a very serious pathological condition. If it is present, specialists often diagnose fetal growth retardation syndrome, which manifests itself in the insufficient weight of the child. If the electrolyte composition of the blood is disturbed, the occurrence of tachycardia, bradycardia and arrhythmia cannot be ruled out.
When the blood circulation process is disturbed, the fetus develops hypoxia. Source: beremennostnedeli.ru
The acidity level of the biological fluid may also change, the hormonal levels will not correspond to the norms, and the amount of fat depots decreases sharply. All this, in most cases, can provoke spontaneous abortion, and in a severe situation, intrauterine fetal death cannot be ruled out.
What degrees of blood flow disturbance does placental insufficiency cause?
A comparison of clinical manifestations and ultrasound examination results made it possible to distinguish 3 degrees of blood flow disturbance between mother and fetus.
The first is characterized by minimal changes at the uteroplacental level, provides a “reserve” of time of about a month for treatment and full recovery without consequences, there are 2 types:
- Ia - only the uteroplacental blood flow is reduced, with the fetal-placental blood flow unchanged. It manifests itself as a delay in fetal development in 90% of cases.
- Ib - fetal-placental circulation suffers, but the uteroplacental circulation remains normal. Delayed formation and development of the fetus suffers somewhat less (in 80% of cases).
The conclusion is issued after examining all components of the fetal blood flow
The second is that the disorder occurs both at the level of the uterine and umbilical vessels; hypoxia can be fatal to the fetus.
Third, blood circulation indicators are at a critical level, and it is even possible that the direction of blood flow is reversed (reverse).
For clinicians, such a classification provides an opportunity to accurately determine the level of disorders and choose the most appropriate treatment tactics.
Why blood circulation may be impaired
Causes of fetoplacental insufficiency (impaired blood circulation between mother and child):
- Low placentation (attachment of the placenta to the wall of the lower parts of the uterus or “presentation”). The thin muscular layer of the lower uterus is not able to provide sufficient blood flow to the fetus. If there is no migration of the placenta (advancement in the upper part of the uterus), the situation threatens to worsen the pathology.
- Late toxicosis of pregnant women. It affects the small vessels of the uterus, which disrupts blood circulation.
- Drop in hemoglobin level or anemia. This condition causes an accelerated heartbeat in the mother, altering the normal blood circulation in the uteroplacental circle.
- Incompatibility of the Rh factors of the blood of mother and baby, causing anemia in the fetus and immune conflict.
- High blood pressure in the mother due to heart problems, swelling, stress.
- Pathology of the umbilical arteries , for example, the presence of only one umbilical artery.
- Multiple pregnancy , requiring more nutrients.
Some maternal diseases contribute to the spread of pathology, in particular:
- Acute infections, the pathogens of which are capable of penetrating the placenta;
- Uterine defect (“bicornuate” uterus, having a septum in the middle dividing it into two halves). Fetal development occurs in only one of them. The threat is posed by the compression factor of the growing fetus and the disruption of blood flow to it. In such situations, a disturbance of uteroplacental blood flow on the left, grade 1a or on the right, often occurs.
- Diabetes. It affects the walls of the uterine vessels.
- Deviations of the uterine epithelium (endometriosis).
- Uterine tumors. The size of a benign tumor (fibroid) determines how much the fetus will suffer from insufficient blood supply. The larger the fibroids, the higher the risk of failure. Hormonal changes caused by pregnancy stimulate the growth of tumors. The presence of this disease requires constant monitoring of the uterine blood supply.
Symptoms of impaired blood flow
If the impaired blood flow is compensated, then the woman does not feel any abnormalities, but learns about them only after the examination.
Pronounced manifestations occur in acute form and chronic decompensation:
- the motor activity of the fetus increases sharply or completely disappears (at 28 weeks, normal development is accompanied by ten movements per day), this symptom requires immediate contact with an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- a slow increase in abdominal circumference, detected during monthly examination and measurement in the antenatal clinic (associated with excessive formation or lack of amniotic fluid);
- late toxicosis;
- high blood pressure;
- large weight gain;
- swelling in the legs;
- the appearance of protein in the urine.
The most dangerous thing is bleeding from the vagina. This sign can be regarded as beginning placental abruption. You must not delay in providing medical care.
What does the mother feel and what does the doctor determine during the examination?
Hypoxia stimulates fetal motor activity.
At an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, the doctor listens to the fetal heartbeat and pays attention to high frequency, arrhythmia or bradycardia. This necessitates referral for Doppler examination.
A pregnant woman pays attention to increased movements, tremors
Diagnostics
The most complete picture of blood circulation between the uterus and the fetus is obtained through Doppler ultrasound, which is performed on all women three times during pregnancy.
The technique allows:
- measure blood flow by the speed of movement of the formed elements;
- determine its direction in arteries and veins;
- record changes before clinical manifestations.
The effect is based on the properties of ultrasonic wave reflection and is completely safe for the child and mother.
All changes are recorded on the monitor, measured with special sensors, and can be photographed in the required format.
By comparison with normal indicators, a conclusion is made about the degree of pathology. Violations can be detected at any level, in the vessels:
- umbilical cord,
- uterus,
- fetus
The doctor has time to prescribe treatment and check it at the next examination.
A type of Doppler ultrasound is Doppler ultrasound. It is prescribed for:
- maternal concomitant pathology;
- suspected premature aging and disruption of the placental barrier;
- signs of high or low water;
- preliminary data on intrauterine growth retardation, the formation of congenital malformations of the fetus;
- presence of genetic diseases in the family;
- clinical symptoms of fetal hypoxia.
The examination can reveal:
- thinning of the placenta;
- increase in growth area;
- intrauterine infection.
The method of long-term inpatient monitoring of the degree of fetal hypoxia allows you to see the results of using medications
Classification
These deviations have varying degrees of damage and development. Mainly the following are distinguished.
| Failure of blood flow 1a degree | Accompanied by the presence of abnormalities in the uterus and placental arrangement of blood vessels. The fruit is not affected. At this stage, the pathology is not significant. Therefore, it can be easily eliminated. After timely diagnosis, you should definitely undergo a routine examination |
| Violation 1b degree | The child’s condition with this pathology remains satisfied. But the risk of danger increases |
| Development of stages 2 and 3 of the disease | Severe abnormalities in all systems. Serious complications can lead to fetal death |
Treatment of pathology
The possibility of maintaining pregnancy with the help of conservative treatment remains with the degree of impaired blood flow Ia and b. The second degree is considered borderline, the third requires urgent surgical delivery.
Treatment takes into account the pathogenesis of disorders. To achieve results it is necessary to influence all links:
- In case of mild disturbance of microcirculation, Chofitol (with a mineral-herbal composition) is prescribed, in more severe cases - Actovegin, Petoxifilin.
- If a mother’s tendency to form blood clots and disrupt the aggregation properties of blood is detected, then drugs such as Curantil, Trental are indicated. They can improve blood flow through the vessels.
- If low blood pressure is detected, Venofundin, Stabizol, ReoHES are used.
- Vasodilators - No-spa, Eufillin in injections - eliminate spastic contraction of blood vessels.
- It is recommended to reduce the tone of the uterus with the help of Magnesia, the drug Magne B6, this acts as an antihypoxic way to improve blood flow.
- A group of vitamins with antioxidant action eliminates negative consequences (vitamin E, ascorbic acid).
Medications are prescribed by a doctor. If necessary, the woman is offered hospitalization. This allows:
- provide bed rest;
- Constantly monitor the progress of pregnancy.
If there is an effect of conservative treatment, the woman independently carries to term and gives birth to a child. If there are no results, doctors may decide to perform an early cesarean section. In the third stage, only surgical delivery is indicated.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of any pathologies during pregnancy, including impaired blood flow, pregnant women need to avoid negative emotions, physical strain and stressful situations. It is important to eliminate bad habits. You need to monitor your diet, include cereals, fruits, herbs, vegetables and nuts in your daily diet.
Regular walks in the fresh air and exercise for pregnant women will be useful. You need to sleep on your left side. Comfortable conditions during night and day rest will be provided by the U-shaped pillow for pregnant and lactating women “Body Pillow”.
It should be noted that if the blood flow is disrupted and the woman is 32-40 weeks pregnant, she should go to the hospital. You cannot neglect the usual rules, because this can lead to dire consequences. If an unexpected situation occurs, you must immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital.
This article should be an ABC for every pregnant woman and useful for their husbands. Be careful during pregnancy, take care of yourself and pay attention to the slightest deterioration in your health!
Repost this article on social networks, let your friends get acquainted with detailed information so that they know what to do in unusual situations! Take care of yourself and see you again in the next articles!
Sincerely, Katherine Grimova, mother of a wonderful daughter!
What to do to prevent blood flow disorders?
Gynecologists urge women at risk to prepare themselves for pregnancy in advance and prevent unplanned conception.
Choosing the right body position while sleeping helps fetal blood flow
If you are already pregnant, it is recommended:
- avoid emotional and physical overload;
- eliminate bad habits;
- organize nutritious meals for the pregnant woman;
- monitor daily walks and stay in a ventilated room;
- do special gymnastics for pregnant women, yoga exercises;
- control body weight, carry out monthly weighing and measurement of abdominal circumference;
- It is considered more beneficial to sleep on the left side; this position reduces pressure on the inferior vena cava, which runs to the right of the uterus, but in some cases, with stagnation in the kidneys, sleeping on the right side improves the outflow from these important organs.
Modern diagnostic methods and approaches to the management of pregnant women make it possible to prevent severe disorders. However, many possibilities depend on the woman herself and her desire to have a healthy heir.
Impaired blood flow during pregnancy: causes of pathology
An ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound helps to identify deformities in the fallopian tube, artery or placenta of a pregnant woman. It allows you to detect problems associated with blood vessels and calculate the rate of nutrients and oxygen supplied to the child.
Placental insufficiency in pregnant women is a common occurrence, so every expectant mother needs to learn why blood flow is disrupted and what this may be associated with.
The following reasons are known in medical practice:
- pregnancy at a very early or too late age;
- little time has passed from the last birth to the current pregnancy;
- toxicosis in the later stages of pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- kidney pathologies;
- formations in the uterus of various nature;
- an intrauterine infectious disease is diagnosed;
- there have been abortions or miscarriages in the past;
- development of more than one fetus is observed;
- lack of iron in the body of a pregnant woman;
- atypical location of the placenta;
- Rh factor incompatibility;
- blood clotting disorder.
The causes and consequences of placental insufficiency are interrelated.
Main symptoms of the disease
Depending on the type of blood flow disorder, various symptoms may appear. Compensated placental insufficiency does not manifest itself in any way during pregnancy, so it is only discovered during an ultrasound scan. In the acute and decompensated form, changes appear in the baby’s movements: he moves either too much or very little. In this case, it is important to monitor this indicator (the fetus should move at least 10 times per day).
Additional signs may include slow abdominal growth, lack or excess of amniotic fluid. You won’t be able to monitor this on your own, so you need to visit a doctor to monitor changes in measurements. It happens that impaired blood flow accompanies gestosis - late toxicosis during pregnancy. The existing symptoms may include increased blood pressure, sudden weight gain, swelling, and protein excretion in the urine.
The most dangerous sign of placental insufficiency is the appearance of blood from the birth canal associated with placental abruption. In this condition, only emergency medical help will help.
Treatment methods for different degrees of pathology
The first degree of the disease involves taking medications that improve blood circulation. Doctors will also conduct Doppler measurements and cardiotocography (heartbeat) of the fetus in dynamics. Research should be carried out 1-2 times every 7 days. If the dynamics are positive, the woman will continue to carry the baby until it is born. If the indicators worsen, it is necessary to conduct daily examinations to prevent irreversible changes and perform an emergency caesarean section in time. With normal fetal development, childbirth can occur naturally.
Stage 2 blood flow disorders during pregnancy can also be treated. Usually the same drugs are used as in the first case, but the woman will be offered hospitalization. Doctors will monitor changes in the body and, if necessary, carry out early delivery.
The third degree cannot be treated in any way, since irreversible consequences begin to appear. In this case, specialists do not risk the child’s life and prescribe an emergency operation.