When is resuscitation necessary?
The onset of clinical death of the patient is accompanied by the absence of pulse, breathing and pupillary reaction to light. Unless caused by serious injury or other life-threatening illnesses, the condition is reversible. The optimal time for resuscitation is no more than five minutes after death. If assistance is provided later, there is a risk of developing severe complications from the central nervous system and other internal organs.
Assistance to a person who develops clinical death should be provided in accordance with a specially developed resuscitation program. The main tasks here include restoration of blood circulation, respiration of brain cells and functions of the central nervous system. Possessing knowledge of the basics of SRL and practical skills in this area gives a real chance of saving a person’s life.
Indications for use
When a patient develops clinical death, it is necessary to use a basic set of actions, which in many cases helps bring the patient back to life. To do this, it is important to know the symptoms of this condition. All signs of death are divided into primary and secondary. In the first case, we are talking about the following manifestations in humans:
- absence of pulse in the area of large vessels (asystole);
- unconsciousness (coma);
- lack of constriction of the pupils in bright light (mydriasis);
- lack of breathing in the victim (apnea).
Apnea is confirmed by complete immobility of the chest. To understand that there really is no breathing, you should lean towards the patient and listen. Another option is to hold a mirror to his mouth. If there is weak breathing, it will fog up.
To verify asystole, you need to find the carotid artery. In other places, it is quite difficult to feel the pulse, since in unconscious patients the systolic pressure often drops to 60 mmHg. Art. To palpate the carotid artery, place your middle and index fingers in the middle of the neck, then move them left or right to the cavity. Here the pulse is clearly felt. If it is absent, we are talking about the onset of clinical death.
The reaction of others when a person’s heart stops must be immediate.
To determine mydriasis, you need to open the victim's eyelid. If the pupil does not constrict when exposed to light, this indicates an acute lack of blood and oxygen supply to the brain tissue.
Among the secondary signs, paleness of the skin, loss of muscle tone, and complete absence of reflexes should be noted. If the above-described manifestations are detected in the patient, cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be started immediately.
Negative effects of drugs
Medicines that cause cardiac arrest are used for treatment. In rare cases, deliberate overdose causes death. This must be proven to the judicial and investigative authorities. When prescribing medications, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, weight, diagnosis, and warns about a possible reaction and the need to see a doctor again or call an ambulance.
Overdose occurs when:
- non-compliance with the regime (taking pills and alcohol);
- deliberately increasing the dose (“I forgot to drink this morning, so I’ll take two at once”);
- combination with traditional methods of treatment (St. John's wort, shepherd's ears, self-prepared tinctures of lily of the valley, foxglove, adonis);
- carrying out general anesthesia against the background of continuous medication use.
The use of St. John's wort herb should be very limited; its potency is comparable to antitumor cytostatics
The most common causes of cardiac arrest are:
- sleeping pills from the group of barbiturates;
- narcotic drugs for pain relief;
- groups of β-blockers for hypertension;
- medicines from the group of phenothiazines prescribed by a psychiatrist as a sedative;
- tablets or drops of cardiac glycosides, which are used to treat arrhythmias and decompensated heart failure.
It is estimated that 2% of asystole cases are drug related.
Only a specialist can determine which medications have the most optimal indications and have the least accumulation and addiction properties. You should not do this on the advice of friends or on your own.
When is resuscitation contraindicated?
Primary resuscitation of patients according to the new standard is carried out with the aim of saving the patient’s life. Further professional assistance is provided in a hospital setting by qualified specialists. If the death occurs as a result of a long-term course of various pathologies in a person that cannot be treated, the feasibility and effectiveness of life-saving measures are called into question. Such diseases include cancer, severe heart failure and other conditions incompatible with life.
In addition, there is no chance of saving a life if the following symptoms develop:
- body cooling;
- formation of cadaveric spots;
- cloudiness and dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- the appearance of the cat's eye phenomenon;
- muscle hardening.
These signs indicate the onset of biological death that cannot be resuscitated.
If there are signs of biological death, resuscitation is not carried out
Important! It is advisable to carry out resuscitation actions only in the event of clinical death that is not caused by serious degenerative processes in the patient.
CPR in patients with hypothermia
Attention. It must be remembered that patients whose death occurred as a result of hypothermia, or the dying process was accompanied by the development of hypothermia (for example, drowning in cold water), require longer (at least 60 minutes) resuscitation measures. Moreover, hypothermia must be eliminated during resuscitation.
Use active warming if body temperature < 32°C. Defibrillation is not effective until body temperature rises to 30-32°C.
Algorithm of actions
According to new standards of resuscitation, assistance to a person should consist of the following stages:
- Determining symptoms, calling an ambulance.
- Performing indirect cardiac massage.
- Artificial respiration.
- Defebrillation.
- Application of intensive care methods.
- Drug treatment of asystole and other conditions.
The algorithm of actions is carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the American Heart Association. For convenience, each of the stages of assistance is designated by letters - A, B, C, D, E. Let's consider each of them in more detail:
- Airway (A) – restoration of airway patency. The procedure is performed using tracheal intubation. The purpose of the event is to eliminate a life-threatening violation;
- Breathing (B) – artificial maintenance of a person’s respiratory function. Here the mouth-to-mouth technique is used. To prevent infection, it is recommended to use an Ambu bag;
- Circulation (C) – performing indirect massage of the heart muscle to ensure restoration of blood circulation throughout the body;
- Disability (D) – determination of neuralgic status, assessment of the victim’s vital functions;
- Exposure (E) – assessment of the patient’s external signs, relief of life-threatening conditions.
Help should be provided in compliance with all recommendations
The CPR standards described above are designed for physicians. People who provide first aid need to have knowledge and skills in carrying out the first three points.
Rules for ensuring the safety of the patient and resuscitator before the ambulance arrives. To increase the effectiveness of resuscitation actions and the safety of all participants in the process during the provision of assistance, the following recommendations should be adhered to:
- During CPR, the victim and the person performing resuscitation must be in a safe environment. People often need help after an accident on the road or in factories. All actions are carried out away from the road or dangerous equipment;
- when performing resuscitation, you need to call passers-by or neighbors, since the presence of several people will facilitate and speed up the procedure;
- If you can’t feel the pulse, you can’t focus on it. It is necessary to evaluate the patient's other vital functions (breathing, pupil reaction to light);
- the pupils stop responding to light only a few minutes after the heart stops. This nuance should be taken into account without wasting precious time.
Help must be provided in a safe environment
The sooner help is provided to the patient, the greater the chance of saving his life, preventing the death of brain cells, and, therefore, avoiding serious complications.
First aid for various types of body damage
Wound.
When providing first aid in case of injury, the following rules must be strictly observed.
It is forbidden:
- wash the wound with water or any medicinal substance, cover it with powder and lubricate it with ointments, as this prevents the healing of the wound, causes suppuration and contributes to the introduction of dirt from the surface of the skin into it;
- remove sand, earth, etc. from the wound, since it is impossible to remove everything that contaminates the wound;
- remove blood , remnants of clothing, etc. from the wound, as this can cause severe bleeding;
- Cover wounds with duct tape or webbing to prevent tetanus infection.
Need to:
- the person providing assistance should wash their hands or lubricate their fingers with iodine;
- carefully remove dirt from the skin around the wound, the cleaned area of skin should be lubricated with iodine;
- open the dressing package in the first aid kit in accordance with the instructions printed on its wrapper.
When applying a dressing, you should not touch with your hands the part that should be applied directly to the wound.
If for some reason there is no dressing bag, you can use a clean scarf, cloth, etc. for dressing). Do not apply cotton directly to the wound. Add iodine to the area of the tissue that is applied directly to the wound to obtain a spot larger than the wound, and then place the fabric on the wound;
- contact a medical organization as quickly as possible, especially if the wound is contaminated with soil.
Bleeding.
Internal bleeding.
Internal bleeding is recognized by the appearance of the victim (he turns pale; sticky sweat appears on the skin; breathing is frequent, intermittent, the pulse is rapid and weak).
Need to:
- lay the victim down or give him a semi-sitting position;
- ensure complete peace;
- apply “cold” to the suspected site of bleeding;
- Call a doctor or medical professional immediately.
It is forbidden:
- Give the victim something to drink if there is a suspicion of damage to the abdominal organs.
Technique for performing resuscitation measures
Without medical education and special skills in performing resuscitation actions, only three assistance techniques can be used. These include precordial stroke, indirect massage of the heart muscle, and artificial respiration. In the ambulance and in the hospital, doctors have access to such types of resuscitation as fibrillation and direct cardiac massage. In combination with these procedures, the necessary medications are used.
Precordial beat
This method is a substitute for the cardiac fibrillation procedure. It is advisable to perform it within the first few seconds after cardiac arrest. In this case, the actions of the resuscitator should be as follows:
- If the situation allows, place the patient on his back; the surface should be flat. If the pulse cannot be felt in the area of the carotid artery, the technique should be started immediately.
- Two fingers are placed in the chest area, in the area of the xiphoid process. The blow is delivered with a hand bent into a fist, slightly above this area.
- If there is no further pulse, the person providing assistance should begin chest compressions.
Precordial beat helps start the heart
Important! Precordial shock is not used to resuscitate patients under 8 years of age. This can only make the situation worse due to injury.
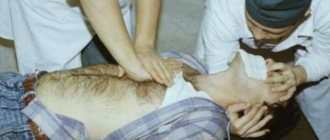
Chest compression
Another name for this resuscitation technique is indirect cardiac muscle massage. To perform the procedure correctly and effectively, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- The victim must lie on a stable surface. This will help prevent the body from shifting during the massage;
- it does not matter which side the resuscitator will be on during the session. Here attention should only be paid to the correct placement of the hands. They should be in the lower part of the sternum;
- the hands are joined with a lock or placed one on top of the other in the area 3–4 cm above the xiphoid process. Pressure is applied only with the palms, there is no need to work with fingers;
- chest compression is performed using the resuscitator’s body weight. Since each person has his own body weight, during the session you need to make sure that the chest is not pressed through more than 5–6 cm. If the pressure is stronger, you can injure the victim.
The hour interval between shocks should not exceed 1–2 seconds. The duration of the pressure itself is less than a second. In addition, it is important to take into account the age characteristics of the patient.
Indirect massage of the heart muscle is carried out with two palms
If we are talking about resuscitation of an infant, pushes are carried out with a finger, not with a palm. Palm compression is performed at an older age of the child. The chest compression procedure is considered effective when a pulse appears in the patient.
Artificial respiration
Before performing artificial ventilation, you should make sure that there are no foreign objects in the mouth that would interfere with normal breathing. For this, the patient is placed on his back, with his head thrown back as far as possible. Under your neck you need to put a rolled up towel or a roller from any available items. After this, the person providing assistance should perform a test breath through the mouth. If the victim’s chest does not rise, you need to examine the mouth and remove foreign objects.
After eliminating obstacles to artificial respiration, the algorithm for performing it is as follows:
- Inhalations are performed through the mouth. At the same time, the resuscitator must cover the nose of the unconscious person. This will ensure that air gets into the lungs.
- When performing the procedure, you need to monitor whether the victim’s sternum rises.
- The amount of air inhaled should be about 1 liter. About 12 breaths should be taken in 60 seconds. There should be a break of at least 5 seconds between them.
If the patient's celiac cavity swells during inspiration, you should be wary. This phenomenon may indicate air entering the stomach.
Artificial respiration ensures life support until doctors arrive
Important! Artificial respiration is most effective when combined with indirect massage of the heart muscle. This type of assistance should be performed by two people.
Causes of cardiac arrest
Among the causes, one can distinguish directly cardiac (cardiac) and external (extracardiac).
The main cardiac factors are:
- myocardial ischemia and inflammation;
- acute obstruction of the pulmonary vessels due to thrombosis or embolism;
- cardiomyopathy;
- high blood pressure;
- atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis;
- rhythm and conduction disturbances due to defects;
- development of cardiac tamponade with hydropericardium.
Extracardiac factors include:
- oxygen deficiency (hypoxia) caused by anemia, asphyxia (suffocation, drowning);
- pneumothorax (the appearance of air between the layers of the pleura, unilateral compression of the lung);
- loss of a significant volume of fluid (hypovolemia) due to injury, shock, persistent vomiting and diarrhea;
- metabolic changes with a deviation towards acidosis;
- hypothermia (hypothermia) below 28 degrees;
- acute hypercalcemia;
- severe allergic reactions.
Pneumothorax of the right lung sharply shifts the heart to the left, with a high risk of asystole
Indirect factors that influence the stability of the body’s defenses are important:
- excessive physical stress on the heart;
- elderly age;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- genetic predisposition to rhythm disturbances, changes in electrolyte composition;
- suffered electrical trauma.
A combination of factors significantly increases the risk of cardiac arrest. For example, drinking alcohol in patients with myocardial infarction causes asystole in almost 1/3 of patients.
Helping a patient in a hospital setting
After the victim is transported to the hospital, resuscitation continues using techniques such as direct cardiac massage, defibrillation and the use of medications.
Direct cardiac massage
This type of resuscitation care is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. The technique is carried out like this:
- the doctor dissects the person’s sternum, which provides direct access to the organ;
- A rhythmic heart massage is performed to restore blood flow to the vessels of the whole body.
The effectiveness of massage depends on many factors, among which are the time of death, the professionalism of the doctor, and the reasons that led to cardiac arrest.
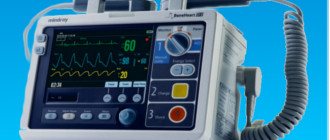
Defibrillation
This method involves the use of special equipment - a defibrillator. With its help, doctors apply electric current to the heart. This procedure is effective in severe conditions in patients with disorders such as ventricular fibrillation, supreventricular and ventricular tachycardia. If a complete cardiac arrest occurs, the method is considered inappropriate.
Defibrillation is performed in a hospital using special equipment
Use of medications
When performing resuscitation, the doctor injects the necessary medications into the patient’s vein or trachea. Intramuscular injections have low effectiveness and are used extremely rarely.
The following means are most often used to save human life:
- Adrenaline is most effective in cardiac arrest;
- Sodium Bicarbonate – Used to help patients with hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) and metabolic acidosis.
Depending on the type of disease and the symptoms developed in a person, many other medications are used. Among them it is necessary to highlight anticoagulants, antihypertensive and hypertensive drugs, tranquilizers and others.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, according to new standards, is a series of measures aimed at bringing the victim out of clinical death. The main measures during the provision of assistance include artificial respiration and chest compression. After hospitalization, the decision on the type of resuscitation actions is made by doctors on an emergency basis, depending on the patient’s condition.
Main types of cessation of cardiac activity and mechanisms of their development
The causes of cardiac arrest according to the developmental mechanism are hidden in a sharp violation of its functional abilities, especially excitability, automatism and conductivity. The types of cardiac arrest depend on them. Cardiac activity can stop in two ways:
- asystole (in 5% of patients);
- fibrillation (in 90% of cases).
Asystole is a complete cessation of ventricular contraction in the diastole phase (during relaxation), rarely in systole. An “order” to stop can come to the heart from other organs reflexively, for example, during operations on the gall bladder, stomach, and intestines.
With reflex asystole, the myocardium is not damaged and has fairly good tone.
In this case, the role of the vagus and trigeminal nerves was proven.
Another option is asystole in the background:
- general oxygen deficiency (hypoxia);
- increased carbon dioxide content in the blood;
- shift of acid-base balance towards acidosis;
- altered electrolyte balance (increase in extracellular potassium, decrease in calcium).
These processes taken together negatively affect the properties of the myocardium. The process of depolarization, which is the basis of myocardial contractility, becomes impossible, even if conductivity is not impaired. Myocardial cells lose active myosin, which is necessary to obtain energy in the form of ATP.
With asystole, hypercalcemia is observed in the systole phase.
Cardiac fibrillation is an impaired communication between cardiomyocytes in coordinated actions to ensure overall myocardial contraction. Instead of synchronous work causing systolic contraction and diastole, many separate areas appear that contract on their own.
The contraction frequency reaches 600 per minute and above
In this case, the ejection of blood from the ventricles is affected.
Energy expenditure is significantly higher than normal, and effective reduction does not occur.
If fibrillation affects only the atria, then individual impulses reach the ventricles and blood circulation is maintained at a sufficient level. Attacks of short-term fibrillation can end on their own. But such ventricular tension cannot provide hemodynamics for a long time, energy reserves are depleted and cardiac arrest occurs.