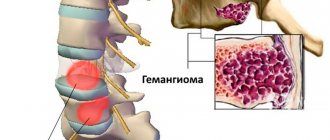
Hemangioma is a benign formation consisting of blood vessels. The occurrence of hemangioma is associated with venous deviation of congenital origin. Any organ and any tissue is susceptible to the formation of this tumor if there is a wide branched network of blood vessels there. Externally, a hemangioma is a flat or lumpy vascular tumor that can be purple or bluish in color.
This tumor develops in the first weeks of a person’s life, or in 30% of cases, a person is born with it. Girls are much more susceptible to the appearance of hemangioma than boys. Most often the tumor is localized on the face, neck and scalp. The most intensive growth of hemangioma occurs in the first few months of a person’s life, then its growth slows down or stops, and in some cases the process of reverse development may even begin. In some people, with age, the hemangioma begins to grow again, causing various complications.
Causes
To date, scientists cannot name the exact cause of hemangioma, but there are many assumptions about this. One of the theories for the occurrence of this tumor in humans is considered to be a viral-infectious factor that occurs in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is during this period of intrauterine development that the formation and establishment of a system of blood vessels occurs, and the influence of infection can change their properties, which subsequently leads to the formation of intraorganic or superficial hemangiomas.
Etiology and pathogenesis of capillary hemangiomas
Today, it is believed that capillary hemangioma is a hamartomatous proliferation (i.e., a nodular benign tumor-like formation representing a tissue developmental abnormality) of vascular endothelial cells. To date, no specific gene mutations or obvious hereditary characteristics have been found that would be 100% responsible for the appearance of hemangiomas.
In its development, hemangioma goes through 2 phases - proliferative and involutive. The proliferative phase usually begins 8–18 months after tumor manifestation and is characterized by progressive growth of the tumor. Histologically, it is characterized by an increase in the number of endothelial and mast cells, the latter stimulating further vascular growth.
The proliferative phase gives way to the involutive phase , which is characterized by gradual regression of the hemangioma. It exhibits a reduction in angiogenesis, apoptosis of endothelial cells, a decrease in the activity of mast cells and dilation of vascular channels. About 50% of all neoplasms undergo involution before the age of 5 years, and about 75% - before the age of 7 years.
Classification of hemangiomas
Depending on the location of origin, hemangiomas are divided into:
- Skin.
The most common type of hemangiomas (90% of cases). This tumor is located in the upper layer of the skin. If it is localized near the organs of vision or hearing on the face, on the back or in the perineum, urgent removal is necessary to avoid irreversible changes in nearby organs. - Hemangiomas of the musculoskeletal system.
Such a tumor grows very quickly and outstrips bone growth, which can lead to skeletal deformation. - Mucosal hemangiomas.
Formed on the mucous membrane: lips, tongue, genitals. - Hemangiomas of parenchymal organs
(kidneys, liver, brain, etc.). Such a tumor requires prompt removal in all cases, as it can lead to internal bleeding or damage to the organ in which the tumor formed.
Depending on the histological structure, hemangiomas are:
- Capillary or simple.
In this case, the tumor is characterized by a shallow location in the upper layers of the skin. This form is considered the initial stage of the disease and is characterized by the intensive formation of new capillaries, prone to sprouting into surrounding tissues. - Cavernous.
Hemangioma is born under the skin and consists of vascular cavities of various sizes and shapes, which are separated by a septum. In such cavities, blood clots form and blood clots form. - Racemose.
The tumor forms on the scalp or extremities. Very rare. Consists of writhing and intertwining vessels. - Combined.
This hemangioma is a transitional form from capillary to cavernous. It forms on the bones of the skull, intraorganic surfaces, frontal bone or skin. Most often develops in adults. - Mixed.
When the tumor is combined with other tumors: lymphoma, keratoma, etc.
The main types of the disease and its symptoms
Depending on the morphological characteristics, the following types of hemangiomas are distinguished:
- simple (capillary). It has clear boundaries, red or purple-blue color. It turns pale when pressed, and then restores the shade;
- cavernous (cavernous). Lumpy, nodular formation located subcutaneously. It is characterized by a soft elastic consistency, which is explained by the structure - inside there are cavities filled with blood;
- combined. It has a cutaneous and subcutaneous part. Clinical manifestations are characteristic of the capillary and cavernous type;
- mixed. A tumor with a complex structure, containing elements of vascular, nervous, connective and lymphoid tissues. Color, consistency and appearance vary depending on the fabrics included.
Tumors are single and multiple in nature, and can be small or large. In 95% of cases in pediatrics, simple forms are diagnosed. Symptoms of hemangioma appear only externally; rarely the patient complains of itching and discomfort in the affected area.
Treatment and examination of a child with hemangioma provides:
- pediatrician;
- surgeon;
- dermatologist.
Additionally, consultation with an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, urologist, dentist and pediatric gynecologist is indicated. In order to determine the depth of spread and evaluate the structure, an ultrasound scan of the affected area is performed. The complex evaluates the speed of blood flow in the tumor itself and the vessels supplying it.
The prognosis for patients is favorable. The tumor may regress on its own. A soft tissue tumor that does not have indications for surgical removal does not need to be eliminated. The decision on the treatment scheme or dynamic control method is always made by the doctor.
Are you experiencing symptoms of hemangioma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Why does hemangioma need to be treated?
The sooner a hemangioma is treated, the less consequences and residual effects can develop. This is due to the fact that the tumor can noticeably increase in a short period of time and grow into neighboring organs and tissues.
Treatment is indicated primarily for patients whose hemangioma is located in the following areas:
- In the respiratory system or near the respiratory tract;
- Around eyes;
- On the face with a risk of cosmetic defects;
- In the ear area;
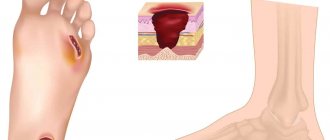
- If there are ulcers (ulcers). Ulcerations can be painful and lead to scarring, sometimes very rough and disfiguring, and the presence of ulcers can lead to infection and bleeding!
Answers to frequently asked questions
What does a hemangioma look like?
Externally, the tumor is a red or bluish spot that merges with the skin or rises above its surface. The size of the spot in diameter ranges from 1-2 cm to 10-20 cm. The tumor has different shapes. In children, temperature asymmetry appears; the defect is always warm to the touch.
Is it necessary to remove the hemangioma?
A skin hemangioma must be removed if it causes discomfort, itches or bleeds. It is necessary to remove the tumor if it is located in difficult places that are constantly rubbed by clothing.
Can a soft tissue tumor go away on its own?
It is not always necessary to remove hemangioma surgically. The tumor can regress on its own. There are several stages in the extinction process. It begins with the formation of a pale spot in the center of the tumor, then the shade changes and becomes normal towards the periphery. The process of disappearance is long, up to several years.
Why is hemangioma dangerous?
If treated incorrectly and untimely, complications may occur that pose a threat to human life and health:
- germination with subsequent destruction of nearby organs;
- destruction of bone and muscle tissue;
- spinal cord compression;
- ulceration of the tumor, infection;
- malignancy;
- development of pathologies of the vascular system;
- cosmetic defect.
Treatment of hemangioma with us
In our clinic, specialists remove hemangioma using the most effective method - laser irradiation, which removes the affected tissue layer-by-layer without compromising the integrity of healthy tissue. A dense crust forms at the site of laser exposure, which peels off on its own after 2-3 weeks.
Removal is carried out by selective absorption of the laser beam energy by the capillaries that make up the hemangioma. Selective absorption ensures minimal damage to the skin layers.
The laser allows you to remove hemangioma without leaving a scar on the skin. Hemangiomas of varying degrees require different numbers of procedures. Small superficial hemangiomas can most often be removed the first time. Larger, deep-seated hemangiomas may require more treatments spaced 1/2 month apart.
The consultation is conducted by specialists who have extensive experience in removing various benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue using laser and surgical methods.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Treatment methods
- Medicinal methods
- Surgical methods
- Hardware methods
Hemangioma (capillary hemangioma, capillary hemangioma) is a benign tumor that develops from hyperplastic vascular endothelium. It is often absent at birth, but appears in childhood and is characterized by progressive growth.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for removing hemangiomas:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
A feature of hemangiomas is the possibility of spontaneous involution, therefore the treatment tactics for these neoplasms are selected individually for each patient, based on the current state of the tumor and its dynamics. Spontaneous regression distinguishes hemangiomas from other vascular malformations, such as port-wine stains.
According to statistics, capillary hemangiomas occur in 1–2% of newborns, with about 50% of neoplasms forming on the head (often in the eye area) and neck. 30% of patients say that their parents or doctors recorded signs of hemangioma immediately after birth, but the majority note the onset of manifestation of this neoplasm at the age of 6 months. The ratio of men to women in the incidence of hemangioma is 1:3.
Zolotov Sergey Alexandrovich
- Candidate of Medical Sciences, surgeon, specialist in laser surgery.
- From 2003 to 2009 completed training at the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Russian National Research Medical University" named after. N.I.Pirogov Ministry of Health of Russia.
- From 2009 to 2011, he completed his residency at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution, Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology, specializing in Pediatric Surgery.
- In 2011, he completed training under the program of additional professional education of doctors in laser medicine at the State Scientific Center for Laser Medicine of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia. From 2011 to 2014, he studied full-time graduate school at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology.
He has extensive experience in removing various benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue using laser surgical methods.
More than 5 years of experience in surgery.
Benefits of laser removal
Treatment of neoplasms can be medicinal or surgical, involving sclerosis, cryodestruction or laser coagulation of blood vessels. Removal of hemangioma using a laser is used for tumors located on the surface of the skin. To carry out the procedure, a special vascular laser with a wavelength of 532 - 1064 nm is used. Its light energy is actively absorbed by hemoglobin in the blood, which leads to selective coagulation of the pathological vessel. The use of laser demonstrates not only high efficiency, guaranteeing complete cure, but also a number of advantages that are not available to other treatment methods.
- Non-contact exposure.
- No damage to the surface of the pathology and adjacent tissues.
- Bloodlessness of the procedure.
- Less traumatic, since only the vessels are affected.
- High level of sterility due to the bactericidal properties of laser radiation.
- Sighting accuracy of impact.
Removing hemangiomas with a laser takes a minimum of time: small single tumors are coagulated in 5 - 15 minutes; treatment of larger tumors requires a little more time. At the same time, only 3–4 procedures are enough to finally solve any problem.
Price list for medical services of the laser surgery department
Consultation
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Initial consultation | 2 000 |
Research
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Cytological examination | 500 |
| Histological examination | 2 800 |
Anesthesia
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Application anesthesia | 500 |
| Infiltration anesthesia | 500 |
| Conduction anesthesia | 1 500 |
Bandages
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Adhesive bandage | 300 |
| Aseptic dressing | 500 |
| Bandage with medicines | 1 000 |
Removal of formations using laser radiation
| Anatomical zone | Cost in rub. for 1mm in maximum diameter |
| Scalp | 500 |
| Hands, forearms, feet, legs | 500 |
| Neck, chest, abdomen, back, armpits, shoulders, hips, crotch | 600 |
| Forehead, temporal region, ears, postauricular region | 600 |
| Eyebrows, nose, nasolabial triangle, chin, cheeks, cheekbones, red border of lips | 700 |
| Lower upper eyelids | 850 |
| Ciliary edge of the eyelids | 1 000 |
| External genitalia - single elements* *per 1 mm. 600 rub. | 1 000 |
Removal of papillomas with a diameter of up to 2.0 mm
| Name | Cost in rub. for a unit |
| Neck, chest, abdomen, back, armpits, shoulders, hips, crotch | 300 |
| Lower upper eyelids | 500 |
| Ciliary edge of the eyelids | 1 000 |
Scar treatment
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Drug injection into the scar | 1 200 |
| Laser dermabrasion (resurfacing) per cm² | 1 200 |
Removal of vascular formations using laser radiation*
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Photodestruction of the vessels of the wings of the nose | from 5 000 |
| Photodestruction of cheek vessels | from 10 000 |
*exact cost depends on capillary density, repeated stage of vessel destruction minus 30%
Treatment of ingrown toenails using laser radiation
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Marginal resection of the nail plate | 6 000 |
| Removal of hypergranulations | 1 900 |
| Nail plate removal | 3 500 |
| Complex plastic surgery for ingrown toenails | 8 500 |
Removal of lipoma, atheroma
| Name | Cost in rub. |
| Lipoma removal | 18 000 |
| Removal of atheroma up to 5 mm | 6 000 |
| Removal of atheroma from 5 to 10 mm | 12 000 |
| Removal of atheroma more than 10 mm | 18 000 |
Modern methods of treatment
Some hemangiomas are diagnosed at birth or in early childhood (up to 5 - 10% of one-year-old children).
Hemangioma usually shrinks over time and in some cases may disappear. If it is small, stable and not causing any symptoms, it can be monitored with imaging studies every 6 to 12 months. There are no medications to treat liver hemangioma. Surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor if it is growing quickly or causing significant discomfort or pain. A technique called vascular embolization, in which the blood vessels supplying the hemangioma are closed, can slow or reverse its growth.
For what reasons does hemangioma appear?
Modern science has not fully elucidated the causes of pathological proliferation of endothelial cells. According to one version, hemangioma begins to grow during intrauterine development of the fetus under conditions of chronic oxygen starvation. According to another, the overgrown cells are residual embryonic cells. Another theory suggests that the neoplasm is formed under the influence of maternal infections in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. But these are just guesses, since the formation of hemangioma also occurs in babies who were born during a normal pregnancy, not complicated by infectious diseases.
It has been noted that pathology is observed more often in multiple pregnancies and in premature newborns.
Risk factors for the development of a benign tumor of this type include the mother’s age exceeding 40 years, as well as medical indicators: preeclampsia (protein in the urine, high blood pressure, swelling), threat of miscarriage, entanglement of the umbilical cord, inflammatory processes of the placenta, its abruption and presentation (when the embryonic organ is located as low as possible in the uterus, which makes childbirth difficult).
hemangioma on a child's face
Diagnostics of education
In exceptionally extreme cases, only by chance, liver hemangioma in a child or adult can be detected at an early stage. In the vast majority of cases, it is found when the size reaches serious volumes.
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver (may show a round tumor with clear boundaries);
- MRI of the biliary tract and liver (in addition to the outlines of the formation, it will also show its contents);
- MSCT of the abdominal cavity (layer-by-layer will demonstrate the boundaries and contents of the tumor).
When a tumor is detected, it is necessary to determine its qualitative characteristics. To confirm hemangioma, angiography of the celiac trunk is performed; static liver scintigraphy may also be needed. To determine the degree of benignity (malignancy) of atypical cells, hepatoscintigraphy is prescribed.
Along with this, clinical tests are carried out:
- liver tests;
- complete blood count, blood biochemistry;
- blood test for genetic markers.
Nutrition
Nutrition for liver hemangioma plays a significant role in getting rid of it. The patient is required to be prescribed a diet so as not to provoke a worsening of the situation (sharp proliferation of atypical cells).
A diet for liver hemangioma in adults and children involves excluding from the diet such foods as:
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol and low-alcohol drinks;
- any chocolate;
- egg yolks;
- hot spices;
- pears, melons;
- fresh bread.
You should limit your consumption of fatty, fried, smoked, and salty foods.
Instead, you need to focus on:
- low-fat fish;
- liver;
- dairy products;
- viscous porridge;
- vegetables;
- not sour fruits.
Vitamin B12 may be additionally prescribed.