Causes of presyncope (why it occurs)
Let's first figure out what are the causes of presyncope. As mentioned above, a fainting state occurs due to the fact that the brain stops receiving the required amount of blood. But there are many other factors that can lead to this condition. The leading position among them is in intoxication of the body, which is caused by cancer and infectious diseases.
These include the following pathologies and diseases:
- intestinal infections of various etiologies;
- parasitic infection;
- thyroid diseases;
- viral hepatitis in acute or chronic form;
- hypotension;
- poisoning with chemical and toxic substances;
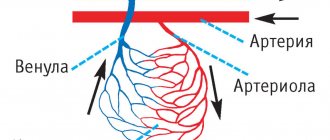
- various diseases of the cardiovascular system: arrhythmia, ischemic disease, heart failure.
The development of presyncope is promoted by dehydration, and pregnant women are often exposed to it. In these cases, an attack occurs due to insufficient blood volume necessary for normal functioning of the body.
There are other causes of fainting. These include: alcohol intoxication, tobacco addiction, congestion in the gallbladder, etc. The level of glucose in the blood is also one of the causes of pre-fainting. Since its increase or decrease can cause hypoglycemic fainting in a person. In this case, a complete examination of the pancreas is necessary, and consultation with a doctor regarding the necessary dietary therapy and level of physical activity. If these measures are taken on time, the development of such a serious disease as diabetes can be prevented.
The first signs of vascular complications and disasters
- hypertensive crisis;
- heart attack;
- transistor ischemic attack (TIA);
- stroke.
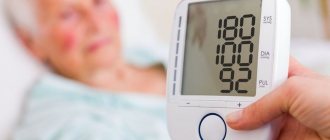
Symptoms of a hypertensive crisis:
- sudden onset within minutes or 1-3 hours;
- the blood pressure level is individually high (in one patient it is 240/120, in another – 130/90). This depends on the initial blood pressure level. If a patient has persistently low blood pressure, even a slight increase can cause a hypertensive crisis;
- presence of cardiac complaints (heart pain, palpitations);
- presence of complaints from the brain (headaches, dizziness, various visual impairments);
- the presence of complaints from the autonomic nervous system (chills, trembling, sweating, a feeling of a rush of blood to the head, a feeling of lack of air, etc.).
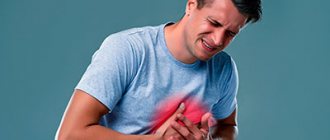
Symptoms of myocardial infarction:
- most common: pain and pressure in the chest,
Patients suffering from heart attacks may experience a variety of symptoms, such as:
- pain, feeling of fullness and/or squeezing in the chest;
- jaw pain, toothache, headache;
- shortness of breath;
- nausea, vomiting, general feeling of pressure in the pit of the stomach (upper center of the abdomen);
- sweating;
- heartburn and/or indigestion;
- pain in the arm (most often in the left, but can be in any arm);
- upper back pain;
- general painful sensation (vague feeling of malaise).
Symptoms of transistor ischemic as well as (TIA):
Typically, symptoms of transient ischemic attacks can last from a few minutes to an hour and include:
- feeling of weakness, numbness, tingling sensation in one half of the body;
- paralysis of arms or legs;
- visual disturbances (darkening of the eyes);
- loss of speech clarity;
These symptoms usually disappear completely within 24 hours, but may recur.
Symptoms of a stroke:
- sudden numbness or weakness of a certain part of the face, arm, leg (especially one-sided);
- sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes;
- sudden paralysis (usually one-sided);
- sudden dizziness or headache with nausea and vomiting;
- sudden difficulty speaking;
- difficulty swallowing;
- dizziness, loss of balance and coordination;
- loss of consciousness.
You can talk about an increased risk of stroke if:
- one or more of your blood relatives has had a stroke or myocardial infarction;
- you have been diagnosed with a tendency to microthrombosis;
- You suffer from arterial hypertension, angina pectoris, dyscirculatory encephalopathy;
- you have diabetes;
- you smoke or abuse alcohol;
- your lipid metabolism is disturbed (increased blood sugar and cholesterol levels), your body weight is significantly higher than normal;
- You have already had or currently have cerebrovascular accidents: neurocirculatory dystonia, transient ischemic attacks, hypertensive cerebral crisis.
How to prevent a stroke?
About half of strokes can be prevented. This is possible because many risk factors for stroke can be controlled. Here are these risk factors that can be prevented:
- High blood pressure (above 140/90 mmHg),
- Atrial fibrillation (a disease in which there is rapid chaotic contraction of the atria, resulting in blood clots in their cavities),
- Diabetes mellitus without adequate treatment,
- Increased cholesterol levels
- Smoking,
- Alcohol abuse
- Obesity,
- Disease of the carotid or coronary arteries.
To avoid vascular accidents, pay attention to your well-being in a timely manner. Get rid of risk factors (smoking, alcohol abuse, excess weight, physical inactivity). Monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
AND REMEMBER!
Regardless of the presence of complaints, once a year it is mandatory for everyone:
- undergo a fluorographic examination;
- measure blood pressure;
- visit an examination room (for women) and a urologist (for men);
- if you are over 40 years old, measure intraocular pressure, determine cholesterol and blood sugar levels, and undergo an ECG.
We wish you health and a long, interesting life!!!
Narab L.V.
Signs and symptoms of presyncope: dizziness, nausea
Symptoms of presyncope are characterized by sudden development, which is usually provoked by certain factors. A stuffy room, tight clothing, stressful situations, excessive physical activity, eating - all this can contribute to the onset of an attack.
The most characteristic symptom of presyncope is dizziness, which may be accompanied by nausea. This indicates disturbances in the functioning of the human autonomic system.
There is a certain risk group of people for whom the presyncope may be permanent. These are people suffering from hypotension (low blood pressure), chronic anemia (low hemoglobin level in the blood, less than 100 units), bradycardia (low heart rate, less than 40 beats).
Any of the described signs is a serious reason to see a doctor. But, since an attack of pre-fainting can occur at any time and in any place, it is necessary to have at least a general understanding of how to provide first aid to the victim or yourself at home.
Examination methods
If your eyes and head in the forehead area often hurt, you need to undergo an examination to determine the cause of this symptom. The initial examination is carried out by a therapist, then additional examinations are prescribed according to indications. They may include consultations with a neurologist, traumatologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, as well as a number of tests and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- general and biochemical blood tests - make it possible to determine inflammatory processes, acute and chronic diseases of internal organs;
- MRI, CT scan of the head - a method for detecting tumors, hematomas, pathologies of the structure of the brain;
- blood pressure measurement;
- determination of eye pressure, methods for diagnosing visual acuity.
The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment for diagnosing diseases that are accompanied by headaches. The ability to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as many years of experience of specialists, allow us to prescribe the most effective treatment in a timely manner.
What to do if you feel faint: first aid
All first aid techniques during a pre-fainting state are aimed at preventing the onset of full-fledged fainting. Let's look at all the necessary steps in detail.
- The first is to provide oxygen access to the room, and, if possible, take a comfortable position. Remove all objects that put pressure on the chest and neck (scarf, tight collar, tie). To better saturate the blood with oxygen, it is necessary to take rhythmic inhalations and exhalations. If the breathing process is difficult, ammonia will help. A sweet, warm drink in the form of tea also helps relieve an attack. If you suspect evaporation of harmful substances in the room or a gas leak, you should quickly leave the building and go outside.
- After the crisis has passed, the body must be provided with the required amount of fluid, which involves consuming at least 2.5 liters of water per day. Taking drugs such as Asparkam and Panangin will normalize the balance of electrolytes in the blood and ensure normal blood supply to all organs. And, of course, it is necessary to establish the cause of the pathology.
- If you have chronic fatigue syndrome, you must take the necessary vitamins and minerals and ensure all conditions for normal work and rest. In case of hypotension or anemia, the cause of this condition should be immediately determined. Since some pathologies require immediate medical attention.
Everything we talked about in this article needs to be known and remembered by every person. Because presyncope attacks develop suddenly, which can pose a serious threat to life. After all, at this moment a person can cross the roadway or drive a car. The most important thing when providing first aid to yourself or your loved ones is to prevent full-blown fainting from developing.
Primary appointment with a neurologist: 1850 RUR.
Sign up Online 5% discount when registering from the site
Consequences of lack of treatment
A headache in itself is an unpleasant occurrence. It can deprive a person of working capacity, lead to depression and generally reduce the quality of life. But, in addition to such consequences, it, acting as a symptom of the disease, can lead to severe or even life-threatening complications, in particular:
- brain hypoxia, which can be complicated by shortness of breath, dizziness, loss of consciousness and even coma;
- severe damage to the spinal roots, leading to paralysis;
- stroke;
- heart attack;
- cardiomyopathy;
- thromboembolism;
- pronounced decrease in immunity;
- an increase in the size of tumors and the formation of metastases, if they are malignant.
Headache treatment
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take a comprehensive approach to the treatment of headaches, depending on the identified cause of its occurrence. In each specific case, treatment is selected individually. Therapy includes relieving headache attacks and treatment during the inter-attack period. Neurologists use the following treatment methods:
- drug therapy with the latest drugs;
- acupuncture;
- psychotherapy;
- autogenic training;
- manual therapy (to relieve muscle tension during tension headaches).
Rehabilitation clinic specialists prefer to use gentle manual techniques. The rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital have the following innovative methods of non-drug treatment in their arsenal:
- biofeedback;
- various types of massage;
- kinesitherapy;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- laser therapy.
Doctors include effective medications in their headache treatment regimen. The variety of causes of headaches, which doctors at the Yusupov Hospital identify during a comprehensive examination, also determines individual approaches to the treatment of each individual patient in the neurology clinic, where there is a full arsenal of diagnostic and therapeutic assistance for headaches. If you have symptoms such as headache, nausea, weakness, make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Diagnostics
If headaches occur, you should consult a neurologist. At the initial appointment, the doctor will conduct a survey of the patient, during which he will find out the nature of the pain that bothers him, its location, severity, frequency and duration of persistence. The doctor will also be interested in what other symptoms are observed and whether there are factors that contribute to the occurrence of headaches.
After this, the doctor conducts an examination. At the same time, he assesses the degree of tension in the muscles of the neck of the head, palpates the spine, conducts a series of neurological tests, and measures blood pressure levels. To obtain a more complete picture of the patient’s health status, the following are prescribed:
- Ultrasound with Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and head;
- ECG;
- EEG;
- CT and/or MRI of the cervical spine;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine.
Based on the examination results, in the vast majority of cases it is possible to establish the cause of the headache. And this already accounts for 50% of success in the fight against it.