When should you take a VLDL cholesterol test (including triglycerides)?
- Assessment of lipid metabolism in the body;
- High level of total cholesterol in the blood (in the absence of lipid profile results);
- Assessing the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases associated with atherosclerosis, obesity and/or type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- Taking medications that disrupt the metabolism of fats in the body;
- Dynamic monitoring of patients receiving lipid-lowering therapy (drugs that lower the concentration of cholesterol in the blood).
Reference values:
Units of measurement: in CELT - mmol/l, alternative units mg/100 ml; mg/dl;
conversion factors: mg/dl x 0.0259 = mmol/l
Reference values: 0.26 -1.04 mmol/l
Reasons for the increase:
- Metabolic diseases are hereditary and acquired.
- Lipid metabolism disorders due to liver and kidney diseases, obesity, endocrine disorders, alcohol abuse, diabetes.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Third trimester of pregnancy.
Reasons for the decline:
- Hereditary low cholesterol levels.
- For serious liver diseases.
- Oncology.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Arthritis, arthrosis.
- Deficiency of B vitamins or folic acid.
- Burns.
- Period of acute infectious diseases.
- COPD
Detailed description of the study
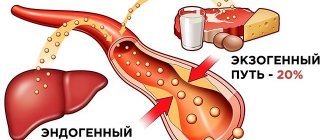
Cholesterol (CS, cholesterol) is an organic steroid compound that is found in every cell of the human body. Cholesterol is a structural component of cell membranes. It also produces hormones, bile acids and vitamin D. Most cholesterol molecules are synthesized in the liver (>50% of the total), the rest enters the body as part of animal fats (meat and dairy products).
Cholesterol is a fat-soluble molecule, so it cannot circulate in the blood on its own. In this regard, its transport is carried out as part of the shell of specific proteins - lipoproteins (LP, lipoproteins). These are complex proteins that contain lipid compounds, including cholesterol. Lipoproteins are divided into several subtypes based on density:
- HDL - high density lipoproteins;
- LDL - low density lipoproteins;
- VLDL - very low density lipoproteins;
- IDL - intermediate density lipoproteins;
- Chylomicrons.
This laboratory test evaluates the concentration of VLDL cholesterol and triglycerides (TG) in the blood. TGs are reserve fat molecules that are used by the body as an energy reserve during fasting, excessive physical activity and other situations.
VLDL are formed in liver cells and are the main drugs that transport triglycerides in the blood, 55% of their total mass is TG. The level of cholesterol in VLDL is about 7%.
Entering the bloodstream, VLDL gradually loses triglycerides in its composition and is successively converted into LDLP and LDL (“bad cholesterol”). The latter is a key lipoprotein that transports cholesterol in the blood.
The concentration of VLDL and TG in the blood can be increased by many factors. These may include: a high-fat diet, alcohol abuse, physical inactivity, overweight or obesity, and a family history of high cholesterol and/or triglycerides.
The study of VLDL and triglyceride levels allows you to evaluate the metabolism of lipids (fats) and cholesterol in the body. Based on these indicators, the attending physician can judge the risk of developing various diseases - arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, atherosclerosis, obesity, diabetes - and also select the optimal plan for the prevention and treatment of these pathologies.
The best material for determining the concentration of the studied organic compounds is venous blood. For this laboratory analysis, capillary blood (from a finger) is used. Indications for this diagnostic method may be:
- Large area burns;
- Small or hard-to-reach veins;
- Excessive obesity;
- Proven tendency to thrombus formation in venous vessels;
- Age up to 7 years.
In the absence of the above conditions, it is strongly recommended to study VLDL and TG levels in venous blood.
Analysis value
VLDL is a fairly aggressive type of cholesterol. This means that if the norm is exceeded, it can be deposited on the walls of blood vessels, forming atherosclerotic plaques. They, in turn, lead to various vascular diseases and increase the risks of stroke and heart attack.
Cholesterol is produced in sufficient quantities in the human body - this happens in the liver. Additionally, it can be obtained from food - there is a lot of it in meat products and fatty dairy products. The level of cholesterol and lipoproteins of all types also depends on hereditary predisposition.
Normally, VLDL enters the blood plasma from the liver in small quantities. There should be as much of it as needed for the transport of triglycerides (this is another function of VLDL). After 10-12 hours, VLDL disappears or turns into other types of lipoproteins.
If for some reason the concentration of VLDL increases, then the risk of developing atherosclerosis, diabetes, and kidney disease increases.
Read completely
Very low density lipoprotein cholesterol - 400 rubles.
Urgent analysis - 800 rub.
Deadlines
Normal – 1 day.
Urgent – 1.5 – 2 hours.
Taking blood from a vein is paid separately - 300 rubles.
(If several tests are performed simultaneously, the service for collecting biomaterial is paid once)
Indications for the study
- As part of the diagnosis of diseases associated with impaired fat metabolism.
- To assess risks and screen the current state of the cardiovascular system.
- As part of preventive examinations in adulthood.
Material for analysis
Blood serum.
Preparing for the study
- Strictly after a long overnight fast, on an empty stomach.
- It is important to avoid physical and emotional stress for some time before the test.
- Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Important Notes
Material for research Capillary blood.
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood. Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications)! According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible: in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
General information
The amount of VLDL serves as an indicator of the level of harmful cholesterol and lipid metabolism. Excess cholesterol is deposited on the walls of blood vessels. First, plaque forms on them, and over time plaques form. Excess cholesterol can also have a negative effect on triglyceride transport. The test results are assessed taking into account the clinical picture and data from other studies.
Cholesterol refers to substances without which the body cannot function normally. At the same time, its excess is dangerous to health. This substance is necessary for the construction of cell membranes, the synthesis of certain hormones, and the formation of fatty acids. Lack of cholesterol leads to disruption of these processes. Cholesterol, which is necessary for the functioning of the body, is produced by the liver. This substance is also absorbed from food. An increase in its level is observed if a person constantly eats too much animal fat, as well as in the presence of a hereditary predisposition.
References
- Francois, M., Baigent, C., Catapano, A. et al. 2021 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk, 2021. - Vol. 41(1). — P. 111-188.
- Arthur, C., John, E. Physiology Review, 2015.
- Severin, E.S., Aleynikova, T.L., Osipov, E.V. and others - M.: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2008. - 364 p.
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A., Fausto, N. et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2014. - 1464 p.
Indications for the study
Periodic lipid testing is recommended for all adults. This makes it possible to timely identify violations and take the necessary measures. The period between studies should be no more than 5 years. In some cases, it is recommended to undergo examination more often. It is recommended to take a blood test for VLDL cholesterol annually or several times a year if the patient is at risk for the development of vascular and heart pathologies. The risk of their development is increased in smokers, patients suffering from high blood pressure, diabetes, and increases with age. Measurement of indicators can be carried out directly or performed using a calculation method.
Complexes with this research
Lipidogram.
Diagnostics of atherosclerosis Analysis of pathologies of lipid metabolism and the risk of heart and vascular diseases 1,500 ₽ Composition Fitness monitoring Examination for choosing physical activity and monitoring the condition of the body 6,890 ₽ Composition
Metabolic profile 6,010 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 29,710
- Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 29,130
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 34,230
Hyperlipoproteinemia - symptoms and treatment
Diet
If the patient has no symptoms, then treatment begins with a special diet.
Correction of nutrition can reduce cholesterol levels by 5–10%. Recommended:
- Eat less animal fat (up to 30% of daily calories).
- Include vegetable oils in your diet: sunflower, olive and cottonseed (up to 25–30 mg per day). They are a source of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which normalize cholesterol metabolism.
- Eat fewer foods rich in cholesterol: liver, kidneys, brains, fatty meats, egg yolks, mayonnaise, fatty sauces.
- Do not fry the meat, but boil it, but avoid very rich broths.
- Eat no more than 40–50 g of sugar per day, limit consumption of sweets, cakes, pastries, sugary drinks and fruit nectars. Excess sugar contributes to the development of atherosclerosis.
- Drink freshly squeezed juices from apples, oranges and carrots 1-2 times a week.
- Do not indulge in strong tea and coffee, as they can increase blood pressure, cause palpitations and insomnia.
- Eat no more than 3–5 g of salt per day.
- There are more vegetables, fruits, cereals (especially rolled oats) and wholemeal products.
- Eat fish twice a week, steaming or grilling it.
- Season salads with olive oil, lemon juice, herbs and spices [3].
It is important to remember that cholesterol not only comes from outside, but is also formed in the body. Therefore, you should not completely give up foods containing fats.
Drug treatment
For cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease and a high risk on the SCORE scale, cholesterol-lowering medications are indicated. However, in some cases, patients even at moderate risk may require drug therapy. It will help reduce the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis.
To correct the level of atherogenic lipids, drugs are taken for a long time, most often for life. When LDL levels are reduced, the risk of cardiovascular disease decreases by 30–40% [9].
Groups of drugs for the treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia:
- statins;
- fibrates;
- inhibitors of cholesterol absorption in the intestine;
- bile acid sequestrants;
- PCSK9 enzyme inhibitors;
- n-3 fatty acids [8].
Statins
Statins (Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Pitavastatin) are the most effective drugs for lowering cholesterol. They block the enzyme that is involved in its formation and thereby suppress the production of cholesterol in the liver. Statins reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglycerides (TG).
Statins prevent the development of atherosclerosis of the coronary and cerebral arteries, and with long-term use they reduce the size of plaques in the vessels. These drugs are necessary for patients with hyperlipoproteinemia and atherosclerosis for the prevention of myocardial infarction and stroke.
Before you start taking statins, it is necessary to determine the lipid profile, and also check the condition of the liver based on the content of liver enzymes (ASAT, ALAT) in the blood. Statins are used in safe dosages until target LDL levels are achieved. The dosage depends on the patient's cardiovascular risk.
To assess the safety and effectiveness of the prescribed dose, a month after starting treatment, it is necessary to re-test the lipid profile, AST and ALAT. The effect appears within the first week from the start of treatment. After two weeks it is 90% of the maximum effect. The greatest effect is achieved by the fourth week and then remains constant.
If the target LDL level is reached and the drug does not adversely affect the liver, then the statin at this dosage is used for a long time. The lipid profile, ASAT and ALAT are monitored every 3–6 months. When liver enzymes increase above three norms, the drug is no longer used.
Target levels for lowering LDL cholesterol depend on cardiovascular risk [7].
| Cardiovascular risk | Lower LDL |
| High | ≥ 50% of baseline to 1.4 mmol/l |
| Moderate | 2.6 mmol/l |
| Short | 3.0 mmol/l |
In addition to lowering cholesterol, statins have a positive effect on the condition of the inner lining of the arteries, stabilize atherosclerotic plaques and improve blood flow.
Statins are generally well tolerated, but some patients experience side effects such as muscle pain. The drugs should be taken under the constant supervision of a doctor, their dose should be adjusted in a timely manner or used in combination with other medications.
Fibrates
Fibrates (Fenofibrate) stimulate the activity of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase and thereby accelerate the breakdown of lipoproteins. They reduce not only cholesterol, but also triglycerides (TG). These are the drugs of choice for patients with diabetes, who most often have elevated TG.
Inhibitors of cholesterol absorption in the intestine
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors (Ezetimibe) are used as second-line therapy in combination with statins. They are prescribed if it is not possible to reduce lipoprotein levels to target levels, as well as if it is impossible to take statins [5].
Bile acid sequestrants
Sequestrants (Cholestyramine, Colestipol) are ion exchange resins that prevent bile acids from being absorbed in the intestine. Depletion of these acids activates their synthesis from cholesterol in the liver. Used in patients with cholestasis.
Taking drugs in this group often causes side effects: flatulence, stool retention, nausea, pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, which limits their use.
Monoclonal antibodies
PCSK9 inhibitors (Alirocumab, Evolocumab) are monoclonal antibodies that bind to LDL receptors in the liver and stimulate the breakdown of lipoproteins. They are administered subcutaneously, usually once every 2 weeks or once a month, depending on the drug. Prescribed to patients with a very high risk of cardiovascular disease and when it is impossible to take statins [7].
N-3 fatty acids
To reduce the level of triglycerides and lipoproteins (especially VLDL), you can take eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. The exact dosage is determined by the doctor [8].
It is important to prescribe lipid-lowering therapy on time to prevent the development of atherosclerosis and its complications.