Heart rate is considered one of the main indicators of the state of the cardiovascular system and the body as a whole. The heart rate level is a dynamic value: it changes every second, but is always within certain limits.
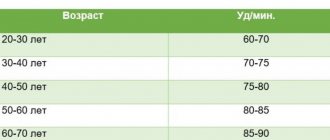
The boundaries that are considered reference have long been named by both the World Health Organization and national cardiology communities. These are considered numbers in the range from 70 to 80 beats per minute, plus or minus, depending on the cardiological concept or “school”.
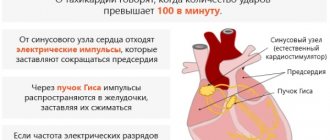
How adequate is a level of 110-115 beats per minute at rest? According to the generally accepted classification, this is moderate tachycardia, which approaches pronounced tachycardia in frequency.
This condition does not bode well for the patient: if bradycardia in many cases occurs as a result of the influence of physiological factors: fatigue, overabundance of medications, climate change, everything is much more complicated here.
Statistics speak directly: 70-80% of cases of accelerated heart rate are the result of pathology. And already within this system, cardiac problems account for about 60% of situations. That is, most people with tachycardia are patients with severe pathologies in latent or early forms.
Natural Factors to Increase Heart Rate
There are not many of them. It is possible to distinguish a pathogenic process from a relatively harmless condition through diagnosis.
If no organic pathologies are identified, it makes sense to work through the problem with a neurologist and psychotherapist.
Interesting:
You can try to distinguish one from the other based on the clinical picture: with physiological deviations there are almost no symptoms, and if there are, they are short-lived.
What are we talking about:
- A stressful situation that develops over a long period. For example, the moment before an exam or a public speaking. The body mobilizes and produces more specific hormones: catecholamines and corticosteroids. Hence tachycardia and increased blood pressure, as well as other autonomic symptoms. No treatment is required, everything returns to normal after the stressful situation ends.
- Psychological overload, nervous breakdown or shock. It develops like a snowball; the body simply cannot stand it. The pressure jumps sharply, the heart rate rises to significant levels, up to 110-150 beats per minute, the patient falls into a stupor or completely loses consciousness for a short period. Autonomic manifestations are obvious, clearly visible even to a person without medical education: tachycardia, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, pallor of the skin, sweating, affective manifestations (laughter, tears, inhibition of thinking, anger or irritability). Therapy is carried out with sedatives or tranquilizers until the condition stabilizes.
- Too much tonic. This can be either harmless coffee or cocaine with heroin, which also cause persistent tachycardia. The difference is in the duration of the effect: when consuming the first, the heartbeat continues for 2-4 hours, while drugs cause persistent deviation for 12-24 or more hours, and we are not talking about the effect of opiates, but as a result of the influence of harmful impurities of homemade street psychoactive substances . Treatment in the second case is urgent, with detoxification and neutralization of the harmful effects.
- Moving to a damp or humid climate. At the same time, it is not necessary to move anywhere; unfavorable weather conditions can come on their own. This is especially noticeable in the summer months in regions with a harsh continental climate. The entire central zone of Russia is like this. Heavy weather is difficult to bear, you need to move less, drink more and better not go outside.
- Nightmares. They differ from other processes in their short duration. Autonomic symptoms cease to exist as quickly as they appeared. Within 2-5 minutes. No specialized medical care is required.
In 30% of cases, a pulse of 110 means that there are physiological deviations as a result of the subjective controlled actions of the patient himself or the influence of external stimuli. Correction is almost never required.
Forecast
In the absence of cardiac pathologies, the outcome is favorable. In people who have had a mild or moderate coronavirus infection, the condition usually returns to normal within 1–2 months. In case of severe COVID-19 or the presence of complications, the rehabilitation period is lengthened; when the unpleasant manifestations pass, it is impossible to say for sure. It is still difficult to give detailed forecasts due to the lack of the required volume of statistical data and the variability of the flow.
To make an appointment with a specialist at the Leto clinic, call tel. 8(969)060-93-93.
Pathological factors
They occur much more often. Possible diseases include:
- Diabetes. Systemic endocrine condition. Requires lifelong therapy. In the early stages, it is difficult to identify; there is often a latent course: the patient can walk with the problem for years; it is discovered by chance or when it is too late for a total correction. You need to pay attention to the following manifestations: sudden attacks of hunger, tremors (shaking hands), pallor, weakness in the legs, fainting. Objectively, glucose does not always increase; you need to examine the sugar curve throughout the day. The heart and blood vessels suffer “for company”, diabetes affects all organs and systems.
- Problems with blood circulation in the brain. The result of osteochondrosis and compression of the arteries feeding the cerebral structures. The normal regulation of cardiac activity at the level of the central nervous system is disrupted. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist.
- Hyperthyroidism. Excessive production of thyroid hormones as a result of poor nutrition, natural factors, and the development of tumors. Accompanied by increased body temperature, headaches, shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, inability to sleep, bulging eyeballs, changes in the relief of the neck (goiter), and mental disorders of a depressive-affective nature. Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
- Hypercorticism. Another pathology of the same profile. The concentration of adrenal hormones, primarily cortisol, only increases. Secondary Itsenko-Kushang disease occurs with sudden weight gain, uneven fat deposition, destruction of the spine and entire skeleton, and mental problems. Often results from a tumor of the adrenal gland or pituitary gland. Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist and neurosurgeon.
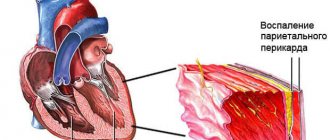
- Violations from the heart itself. As a result of irritation of the third reflex zone of the organ, the heart rate accelerates. The assessment is carried out by a cardiologist. Despite the variety of diseases, their symptoms are almost the same: chest pain of a pressing nature, radiating to the arms and back, shortness of breath even at rest, especially after physical activity, sweating, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, pallor of the dermal integument, fatigue, arrhythmias ( not only by type of tachycardia). Mandatory electrocardiography is carried out, and, if possible, stress tests.
- Vascular diseases. First of all, atherosclerosis, with narrowing or blockage of the lumen by cholesterol plaque. Lipid deposits grow radially, along the entire diameter of the blood supply structure, making it more difficult for blood to overcome resistance. That's why the heart speeds up. This is the only visible symptom. Another, less obvious one is increased blood pressure.
- Panic attack, affective disorders. Psychotherapeutic problems.
A pulse of 107-112 beats per minute is the result of hemodynamic and endocrine pathologies. Often in the system. Therefore, treatment is carried out under the supervision of a group of doctors of different profiles.
Physiological reasons
An elevated heart rate can occur for various physiological reasons. In this case, there are no serious threats to human health. Most often, an increase in indicators is noted during intense physical activity that does not correspond to the age and capabilities of a particular person. For example, the heart rate increases in people without adequate physical training after climbing stairs or lifting a heavy load.
Mental stress also causes a high heart rate. This condition is often noted by students when preparing for serious exams or by employees of enterprises before signing important documents. The cause of an increased heart rate against the background of normal blood pressure can be any stressful situations and an unstable emotional situation. In such cases, the occurrence of internal anxiety, sleep disturbances, and in severe cases, panic attacks occur.
Other common physiological causes:
- Climatic conditions. In particular, heat is often a provoking factor. Against this background, the concentration of oxygen in the blood decreases, so the heart begins to pump hematological fluid through the vessels faster in order to prevent hypoxia.
- Drinking large quantities of drinks that have tonic properties. First of all, these include tea and coffee.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs. Against the background of addictions, vasoconstriction and impaired blood flow occur. This increases the load on the cardiovascular system.
What can you do at home?
Quite a bit. This level of tachycardia is difficult to correct on your own, but it’s worth a try. The main thing is to strictly follow the recommendations and not skip steps:
- Take 1 tablet of Karevdilol or, better, Anaprilin. They should stabilize within 10-15 minutes.
- Secure the result by drinking herbal preparations (motherwort or valerian), phenobarbital (Corvalol, Valocordin).
- You can replace sedatives with folk recipes: 1 tablespoon of a mixture of lemon and honey or 1 glass of tea with St. John's wort, chamomile, peppermint and the same motherwort and valerian.
After 30 minutes everything should return to normal. If this does not happen, you should try to lower your heart rate with a breathing exercise. Inhale, 5 seconds, exhale the same amount. And so on for 10 minutes.
All this time you need to lie down and move less. Loosen tight clothing constricting your neck and remove jewelry.
If there is no effect, or if the pulse starts to jump, call an ambulance to resolve the issue on the spot or in a hospital.
Attention:
A heartbeat of 110 beats per minute requires drug correction in the hospital if the phenomenon lasts more than 30 minutes. or the presence of accompanying manifestations.
Expected duration of attack
The duration of a pulse increased to 110 beats per minute depends on its cause:
- the heartbeat as a result of the fever will return when the body temperature returns to normal;
- rapid pulse caused by blood loss is corrected after intravenous administration of solutions or blood components;
- in case of pathology of the thyroid gland, it is necessary to suppress its synthesis of excess thyroid hormones;
- a rapid pulse caused by excessive coffee consumption or the effects of medications is restored after about an hour, when the active substances begin to be eliminated from the body;
- in case of heart or lung diseases, increased heart rate persists for a long time, including at rest.
Symptoms requiring an ambulance call
There are quite a lot of them, you should pay attention to the following signs of problems with the heart:
- Chest pain of a pressing type, radiating to the arms or back.
- Breathing problems. Dissatisfaction after inhalation, even at rest. The frequency of movements increases, the phenomena of hypoxia also increase.
- Dizziness.
- Cephalgia (headache). Pulsating in time with the beat of the heart.
- Fatigue, drowsiness for no apparent reason. Decreased performance.
- Weakness in the legs, inability to navigate in space.
- Visual impairment.
- Decreased hearing.
In these cases, an ambulance must be called to correct the condition and possible transportation to a hospital for diagnostics.
If there is at least one of these manifestations, the issue of saving life will already be resolved:
- Acute headache in the back of the head, accompanied by neurological symptoms.
- Blindness.
- Facial distortion.
- Paralysis of half the body, paresis of the limbs.
- Inability to speak normally.
- Complete lack of orientation in space.
110 beats per minute at rest is already grounds for calling an ambulance. Adequate regulation of heart rate occurs in a matter of minutes, if not faster. Otherwise, a pathological process takes place.
Diagnostics
It is carried out in an outpatient or inpatient setting. Everything goes faster in the hospital. Patient management is the prerogative of the cardiologist. As needed, third-party specialists are involved: neurologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist.
Sample list of studies:
- Oral assessment of health complaints.
- Anamnesis collection. Often doctors neglect the moment. But this is the most important procedure. You need to take the initiative into your own hands and tell as much as possible about the problem and its possible origins.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate. It is carried out using an automatic device or the “old-fashioned” method, using a watch and a stethoscope. Which is not so accurate.
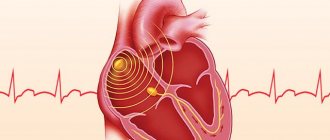
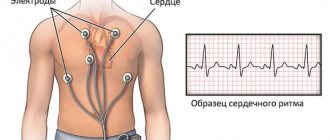
- Electrocardiography. Basic technique. Gives an idea of the nature of functional abnormalities in the work of the heart. It is also possible to differentiate between the types of arrhythmias, the main thing is that the doctors have enough experience.
- Echocardiography. It shows only gross changes, therefore it has minimal information content.
- Blood tests (hormones, biochemistry and general), urine tests.
- Examination of neurological status.
- Angiography.
- CT and MRI.
Depending on the nature of the process, tachycardia should be differentiated into:
- Sinus.
- Supraventricular.
- Ventricular
Based on the results, a therapeutic course is prescribed.
Treatment options
Determined by the type of pathological process. However, these are subtleties.
The approximate diagram is always the same:
- Use of medications.
- Using folk recipes.
- Surgical correction.
- Lifestyle changes.
Drug treatment
Several groups of drugs are indicated:
- Cardiac glycosides to normalize organ activity. Lily of the valley tincture.
- Beta blockers. Reduce the sensitivity of specific receptors to adrenaline and other substances: Carvedilol, Anaprilin.
- Calcium channel blockers. They prevent blood vessels from narrowing, normalizing blood pressure and, at the same time, heart rate. Diltiazem and Verapamil.
- Herbal sedatives. Motherwort and Valerian.
- Tranquilizers. Calm the nervous system and inhibit its activity. Diazepam and analogues.
- Potassium and magnesium preparations (Magne B6, Magnelis, Asparkam). Prescribed to nourish the heart muscle.
Using folk recipes
Only as a help. Not the main method at all.
- Honey with lemon (a tablespoon 2 times a day or more).
- Chokeberry tincture (200 g of berries per 400 ml of vodka or alcohol, take 2 teaspoons 2 times a day).
- St. John's wort, motherwort, valerian, mint, chamomile in tea form. 100 g of mixture per 300 ml of water. A glass 1 time per day or more, as needed.
Surgery
For congenital and acquired defects of a muscular organ, tumors, advanced stage atherosclerosis, thrombosis, destruction of the atria, persistent tachycardia (installation of a pacemaker). They resort to this technique in extreme, hopeless cases.
Lifestyle change
- Quitting smoking and alcohol.
- Normalization of sleep (8 hours per night).
- Drinking regime: 1.8 liters per day.
- 2 hours of walking during the day.
Diet optimization
Can:
- Vegetables, fruits (especially potatoes, apricots, bananas, apples and carrots).
- Lean meat and broths, soups.
- Cereal porridge
- Natural sweets.
- Nuts.
- Eggs.
- Dairy products.
- Oils (butter and vegetable).
- Kissels, berry decoctions.
- Coarse bread.
- Fish.
It is forbidden:
- Canned food.
- Semi-finished products.
- Chocolate.
- Tea.
- Coffee.
- Energy.
- Fast food.
- Salt over 7 grams per day.
- Muffins, fried pies and similar products.
- Fat meat.
Cooking method: boiling, steaming, baking. Frying, especially in oil, is prohibited or strictly limited. It is necessary to observe the principle of fractionalization: more often is better, less. You can’t eat at all at night (2-3 hours before bedtime).
Treatment tables No. 3 and No. 10 are shown, with limited amounts of salt and liquid. You can create a menu yourself or contact a nutritionist. The approximate one is already ready, all that remains is to adjust it.