How can high blood pressure and low pulse be combined? People suffering from hypertension are sometimes surprised to find that their heart rate decreases when their blood pressure increases. As a rule, in this condition, the heart muscle, on the contrary, contracts more intensely. Medicines taken by hypertensive patients to lower blood pressure also reduce heart rate. Drugs that increase heart rate can cause a surge in blood pressure. What to do in such a situation and how can the indicators be normalized? What are these symptoms associated with? Are they a sign of pathology of the cardiovascular system?
What blood pressure is considered high?
When the heart muscle contracts, it pushes a portion of blood into the arteries. At this moment, the pressure in the blood vessels increases sharply, reaching its maximum value. This indicator is called systolic pressure. "Systole" translated from Latin means "contraction of the heart." Normal systolic pressure in a healthy person ranges from 110-130 mmHg. Art. Before the next heartbeat, the pressure in the blood vessels drops, reaching its minimum value. This indicator is called diastolic pressure. The normal value of diastolic pressure is 70-80 mmHg. Art.
A deviation from the norm of 5-10 units is quite acceptable. However, the blood pressure (BP) value is 140/90 mm Hg. Art. considered elevated. There is a widespread belief that blood pressure of 140/90 should not be considered elevated if a person feels great. This is actually a myth. This load on the vessels is quite serious. Another heartbeat can create tension that the blood vessels cannot withstand. Moreover, with age and due to negative factors, the walls of blood vessels become less elastic and less durable.
Diagnostics
Conducted by a cardiologist. In the absence of data for a purely cardiac process, a neurologist may be involved.
Approximate list of events:
- Oral interview and history taking. Objectification of symptoms, drawing up a clinical picture.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate. Blood pressure is normal, but heart rate drops. This is a typical but not required combination. The indicators exist separately.
- 24-hour Holter monitoring. Dynamic assessment of indicated vital levels over a 24-hour period. If necessary, it is prescribed repeatedly. It is considered the most informative methods of early diagnosis.
- Electrocardiography. Study of the functional activity of cardiac structures. Detects arrhythmias and other disorders.
- Echocardiography. Used to visualize defects and anatomical defects.
- MRI as needed
- EEG.
- Assessment of neurological status using routine methods. Including testing basic reflexes.
- General blood test, biochemical, hormones. In case of metabolic disorders or deviations in the level of specific substances, an endocrinologist is involved.
This is enough for early diagnosis.
What heart rate is considered critically low?
The average pulse rate in a healthy person ranges from 60-80 beats per minute. Preschoolers have a higher pulse - about 100 beats. Healthy newborns may experience a heart rate of up to 140 beats per minute.
Doctors consider a heart rate of 50 beats per minute to be pathologically low. This value may be a sign of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
To identify the causes of a critical decrease in heart rate, you need to consult a cardiologist. Most often, a decrease in heart rate causes low blood pressure. But other reasons are quite possible. For example, dysfunction of the heart, its damage or disturbances in the functioning of other systems and organs.
A decreased heart rate can accompany many insidious and dangerous diseases. Low heart rate is a dangerous condition in which the body experiences oxygen starvation. First of all, the brain suffers from lack of oxygen.
A decrease in heart rate below 30 beats per minute can cause a short-term cessation of heart function. Without immediate medical attention, a person may die.
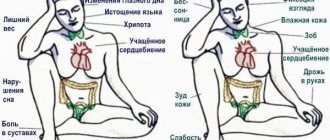
Signs of high blood pressure with a low pulse
If the pulsation rhythm is slightly reduced, the person will only feel signs of high blood pressure. The patient may complain of headache, tinnitus, shortness of breath, fever, facial flushing, and nausea.
He may not be aware of the decreased heart rate. In this case, it is possible to detect a weak pulse only by measuring pressure using an electric tonometer, which automatically detects the pulse.
If the pulse rate is reduced significantly, below 50 beats per minute, the patient may feel dizzy. He may lose consciousness.
Symptoms of bradycardia
Manifestations of bradycardia are caused by a lack of blood supply to vital organs: the brain, heart and lungs. Bradycardia can manifest itself (Fig. 4):
- decrease in blood pressure;
- presyncope and loss of consciousness;
- dizziness, headache;
- rapid fatigue;
- chest pain;
- shortness of breath and poor tolerance to any physical activity;
- pale skin.
Figure 4. Symptoms of bradycardia. Source: MedPortal
Why does high blood pressure cause low heart rate?
There are several reasons that cause a condition in which a person’s blood pressure rises and the heart rate slows down:
- Various pathologies of the heart muscle.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system, thyroid diseases and hormonal imbalances negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Taking medications with side effects or drugs to treat hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- The period of adaptation of a hypertensive patient to a changed temperature regime. This condition can also cause excessive fatigue during intense mental workload. This is a temporary phenomenon and goes away on its own.
Heart pathologies
- Sick sinus syndrome. The sinus (or sinoatrial) node is the part of the heart that regulates its activity by producing impulses. If the production of the latter is disrupted, the heart rhythm changes and contractions become irregular. Such disorders are more often detected in older people. Although there are cases of diagnosing pathology in children and adolescents. The cause of the disease may be trauma to the nervous system caused by exposure to negative factors of various origins. Cardiac dysfunction occurs in the case of the development of certain cancers, as a result of long-term use of medications that cause changes in water and electrolyte balance, due to hemorrhage in the brain. Pathology can be caused by surgery, inflammatory processes and autoimmune diseases. Malfunctions of the sinus node in children most often appear as a result of its autonomic dysfunction. There are often cases when, with age, heart function in adolescents normalizes without treatment.
- Endocarditis. It is an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart - the endocardium. It can be caused by other diseases, such as rheumatism. Endocarditis can be triggered by surgery or allergies. There are infective endocarditis. The causative agents of the latter are fungi, bacteria and sometimes viruses.
- High blood pressure with a low heart rate can be a sign of heart disease - a defect in the heart muscle. It may be congenital or acquired. Heart defects can appear after endocarditis or as a result of trauma.
- Heart block is diagnosed when the passage of electrical impulses to the heart is disrupted. This happens when the impulse meets an obstacle. It may be blocked or delayed. Depending on this, the blockade can be complete or incomplete. It can also be congenital or acquired.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia as a complex of symptoms characterizing dysfunction of the heart and cardiovascular system.
Treatment of bradycardia
Not all bradycardia requires treatment. Only a doctor can determine the need for treatment by excluding physiological causes of a decrease in heart rate.
Conservative treatment
For conservative treatment use:
- anticholinergics - drugs that prevent the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart;
- adrenaline analogues - drugs that stimulate heart rate;
- antiarrhythmic drugs.
Treatment is carried out with tablets and injections. Their doctor can prescribe them occasionally during attacks and for a long time.
Surgery
In cases where conservative treatment is ineffective or there is damage to the conduction system of the heart, surgical treatment is indicated - installation of an electrical pacemaker (pacemaker). This is an electronic device that is implanted subcutaneously in the left subclavian region and sets the necessary rhythm to the heart through electrodes (Fig. 5). The pacemaker not only stimulates impulses to contract the heart, but also controls its natural electrical activity.
Figure 5. Installation of a pacemaker for bradycardia. Source: MedPortal
Treatment with folk remedies
To treat bradycardia at home, infusions of herbs are mainly used, which reduce the tone of the parasympathetic nervous system, increase myocardial contractions, and maintain blood pressure. These are Chinese lemongrass, tartar, immortelle, yarrow, walnuts, a mixture of lemon, honey and garlic and others.
Important! Treatment with folk remedies should be carried out very carefully and only after consultation with a doctor. It is possible with mild degrees of bradycardia (heart rate of at least 40), in the absence of complications and manifestations such as fainting, shortness of breath, dizziness, chest pain.
What do we have to do
First of all, you need to find out whether the indicators are random. To find out, you need to take several measurements in a row, then repeat the procedure twice more during the day.
If there are doubts about the functionality of the device for measuring blood pressure, you need to take repeated measurements using another device.
If the indicators are confirmed, it is necessary to find out the reasons for this condition. Since it can be caused by various diseases, many of which are serious and dangerous, you should immediately visit a doctor.
If there is a low pulse with high blood pressure, and the person’s condition is serious, you should call an ambulance. While waiting for the doctor to arrive, it is better for the patient to lie down. If possible, you can put mustard plasters or a warm compress on the collar area, lower back or calves.
You should not take any medications. Perhaps it was the drug intake that provoked this condition. Taking the dose again can seriously worsen the situation.
A cardiologist will prescribe an electrocardiogram and blood pressure monitoring or perform Holter monitoring of the heart muscle. The patient will also undergo an ultrasound examination of the heart, echocardiography, and bicycle ergometry.
Simultaneously with the study of the functioning of the cardiovascular system, the patient will undergo a blood test to determine hormone levels. An ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland will be performed.
The doctor will review your medical history and previously prescribed treatment. Perhaps the reason for the appearance of this condition was incorrectly selected therapy.
Depending on the results of the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
How dangerous is the condition?
The consequences of the pathological process are varied.
- Heart failure. Asystole is the first thing a patient risks encountering when bradycardia develops. A fatal complication occurs not so much as a result of a decrease in the frequency of contractions, but as the main cause of this condition.
There is a decrease in myocardial contractility, the intensity of blood ejection into the large and small circles weakens. Insufficient nutrition affects the tissues of the heart, the process is aggravated by myocardial ischemia.
Attention:
The likelihood of asystole does not depend on the severity of bradycardia, therefore, equal attention to all patients is necessary.
- Heart attack. If the above process takes a different path and ischemia reaches a critical point, acute necrosis of the heart muscle will develop. Mortality compared to other diseases is almost 70%; even timely first aid and treatment do not guarantee survival.
- Stroke. This time ischemic brain damage. As a result of weakened hemodynamics, cerebral structures receive a small amount of nutrients and oxygen.
The danger of the condition is not only the probable death from damage to vital centers, swelling and other complications.
Even if therapy is started in a timely manner, the risk of neurological deficit is high. How it will manifest itself—impaired speech, hearing, vision, or other means—is not known.
- Pulmonary edema. Weakening of gas exchange leads to the formation of effusion in the tissues between the alveoli. The liquid compresses the structures. The amount of oxygen delivered decreases. In addition to suffocation itself, there is an inferiority of cellular respiration.
Preventing fatal complications is a priority goal of therapy, along with eliminating symptoms and etiological factors.