It is generally accepted that a threat to human health and life is posed by an increase in blood pressure, while its decrease remains without due attention. However, hypotension is also a problem. It is often much more difficult to defeat it than hypertension. First of all, it is worth understanding what upper and lower pressure show.
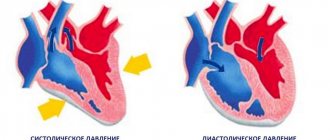
Upper pressure (or systolic) is also called cardiac pressure because it is recorded at the moment of contraction (systole) of the heart muscle. It shows how hard the heart pushes blood into the arteries. Lower diastolic is recorded during maximum relaxation (diastole) of the heart, and shows the blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels at this moment. The tone of blood vessels is responsible for the indicator of lower pressure.
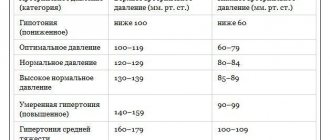
The optimal reading is 120/80 mmHg. Art. They may deviate slightly in one direction or another, but the difference between the upper and lower pressure should be 30-40 mm.
Lower pressure 60 mm Hg. Art., what does this mean?
Tonometry is an important procedure that gives doctors a lot of information about a person’s condition. When measuring blood pressure, the tonometer shows two main values - upper and lower.
Upper blood pressure is called systolic (cardiac). It shows the resistance of the vascular wall of the arterioles at the time of blood ejection by the heart muscle.
The lower blood pressure is called diastolic (renal). Its indicator is the force of influence of the liquid component of blood on the walls of blood vessels when the myocardium is relaxed.
The third significant indicator of tonometry is pulse pressure, which is the difference between upper and lower blood pressure.
The normal level of these indicators for people after twenty years of age is determined by WHO experts within the boundaries:
- 110 -139 mm Hg. Art. – upper blood pressure;
- 70 – 89 mm Hg. Art. – lower blood pressure;
- 40 units – pulse blood pressure.
Any deviations from these figures may be interpreted as an anomaly. Whether it indicates a disease or not is determined by the doctor based on a number of specific signs after an examination, taking into account the possible influence of negative factors.
Thus, 60 mmHg. Art. for diastolic pressure, this is a downward deviation. Indicators below the officially accepted ones are usually classified as hypotension.
If systolic and diastolic pressure levels are reduced for a long time, typical hypotension is diagnosed. When only the diastolic indicator is reduced, we are talking about isolated hypotension.
Hypotension is not always a pathology that requires correction. Sometimes it is a variant of the physiological norm, or is caused by objective physiological reasons, the elimination of which will lead to normalization of the condition.
Types of arterial hypotension
There are three types of arterial hypotension:
- physiological;
- pathological;
- symptomatic.
Low blood pressure as a physiological norm may be a congenital feature characteristic of a particular person due to his constitutional type. A similar situation is observed among professional athletes, residents of high mountain areas and tropical latitudes. Thanks to the decrease in pressure, the body adapts to physical activity and climate conditions. In this case we are talking about a compensatory function.
The pathological form of the disease is of two types: orthostatic and neurocirculatory. Orthostatic hypotension occurs when there is a change in body position when a person gets up after resting or sleeping. The neurocirculatory form is associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system. The patient may periodically experience low blood pressure or have hypotension, in which diastolic pressure is chronically low.
Symptomatic hypotension is secondary. Its causes are disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems, intoxication.
Physiological causes of diastolic hypotension
Hypotension with lower blood pressure readings of 60 mm Hg. Art. can be detected in both healthy and sick people. Experts call the physiological reasons causing the condition:
- Puberty. The hormonal characteristics of adolescents are accompanied by abnormalities in hemodynamics and heart rate. This leads to a typical or isolated form of hypotension, which occurs in thin, tall adolescents (usually girls).
- Advanced age. A slight decrease in indicators is explained by deterioration in the functioning of the heart and brain due to circulatory problems, which causes insufficient nutrition of tissues and organs.
- Changes in hormonal levels in women. A similar condition accompanies pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause. As a rule, it does not require drug correction. The exception is pathological menopause, accompanied by a serious deterioration in well-being.
- The body's need to adapt. Such hypotension is typical for professional athletes, workers in hazardous industries, and tourists visiting countries with an unusual climate.
A decrease in diastolic indicators in the above cases can occasionally affect general well-being, which requires special measures to be taken. But usually, it does not manifest itself in any way, therefore, the person feels quite healthy.
Feeling unwell due to decreased blood pressure is much more common. This is explained by the manifestations of diseases that cause hypotension.
Increased diastolic pressure
Increased lower pressure often goes unnoticed in the first stages. When manifestations of such pathology become frequent, the patient goes to the doctor. Lost time can negatively affect the prognosis of the disease, so you need to contact doctors at the first signs of this disease.
Pathological reasons:
- The kidneys are one of the most important organs involved in regulating blood pressure, so the slightest malfunction in this system will immediately affect the tonometer readings. Kidney diseases: chronic glomerulonephritis, narrowing of the renal artery, renal failure, congenital defects in the structure of the blood vessels of this organ.
- Heart defect or tumor in this area.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Hormonal disorders, especially in women during pregnancy or menopause.
- Pathologies of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands, which provoke increased synthesis of hormones that affect blood pressure levels.
- Vertebral hernias.
It should be borne in mind that increased lower pressure may be a variant of the norm, since this index can change several times a day. Physical activity or emotional stress will certainly affect the tonometer data, namely the lower numbers.
Signs:
- disturbance of consciousness;
- nosebleeds;
- visual impairment in the form of blurred vision;
- difficulty breathing;
- swelling of tissues;
- headaches that occur frequently and last a long time;
- signs of other diseases that caused an increase in this index.
Often, the manifestations of this disorder in the body are completely absent; a person may not suspect such a malfunction in the body for a long time. It is necessary for all people to measure their blood pressure at least once a year in order to timely record deviations in the tonometer data, on which their future health depends.
The danger of this situation is that manifestations of the disease may be absent for a long time, and the disease progresses more and more. Many people mistakenly believe that only high blood pressure poses a danger, but this is not true. With this pathology, the heart is under constant tension and relaxation almost never occurs. This leads to disruption of the blood supply to the organ, and then structural changes begin that cannot be reversed.
Every person needs to evaluate the importance of this indicator, because ignoring increased diastolic pressure for a long time significantly increases the risk of stroke, vein thrombosis, and heart attack.
In addition to drug treatment for this disease, you must follow some additional doctor's instructions.
Recommendations:
- balanced and proper diet;
- carefully regulate your daily routine, improve sleep, and get proper rest;
- reduce body weight if you are overweight;
- playing sports;
- taking medications and using traditional methods of therapy.
You can find out what low blood pressure means at an appointment with your doctor. If the doctor tells the patient about the importance of this indicator, then the person will take this situation seriously.
Pathological causes of decreased blood pressure
Some diseases and pathological conditions can become factors causing a decrease in diastolic pressure to 60 mmHg. Art. and below. Among them:
- kidney disease with insufficiency of renin synthesis (more often, this is typical hypotension);
- adrenal gland problems with insufficient cortisol synthesis (Addison syndrome);
- pathologies of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), pituitary gland;
- early period of a heart attack, stroke;
- TBI;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system, cervical muscles (fibrosis, myositis, intervertebral hernia);
- anemia;
- massive bleeding;
- tumors of different locations;
- cardiomyopathy;
- severe infections (tuberculosis, syphilis);
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (prolonged diarrhea, vomiting);
- mental instability (neuroses, depression).
Hypotension can occur as a consequence of prolonged use of drugs to lower blood pressure prescribed for hypertensive patients, diuretics. This especially often occurs due to self-medication or exceeding prescribed doses.
Questions and answers
Are there any contraindications
Autohemotherapy is contraindicated in certain diseases and conditions of the body:
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- acute period of colds and infectious diseases;
- period of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Can it be done at home?
The autohemotherapy procedure itself is simple and does not require any special equipment.
Therefore, it can be carried out both in the clinic and at home.
And it is better if in this case the procedure is carried out by a medical professional.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
A decrease in blood pressure is not always asymptomatic. Sometimes it is accompanied by unpleasant or painful symptoms that require consultation with a specialist. These include:
- prolonged throbbing headaches;
- dizziness, coordination problems;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- exhaustion;
- irritability, apathy;
- menstrual dysfunction;
- decreased sex drive;
- blurred vision;
- fainting;
- extraneous noises in the head or ears.
With a sharp drop in indicators to critical levels, a symptom complex very similar to the consequences of a stroke may occur:
- unilateral paresis (face, limbs);
- sensation of goosebumps;
- speech disorders;
- passing blindness (partial or complete).
This condition is considered an emergency. It requires immediate hospitalization of the patient and intensive care.
First aid at home
To get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of hypertension or pressure surge at home, you can take:
- One tablet of Capoten. Place it under your tongue and suck it slowly. Effect within 30-60 minutes.
- Corvalol – 40 drops diluted in a glass of water. The tonometer readings decrease within half an hour. Corvalol tablets are used only for long-term therapy.
- Valerian tincture. Use as directed or make your own. Pour a tablespoon of grated valerian root with a glass of boiling water and leave overnight. Strain, drink 1 tablespoon before meals.
- Motherwort. For 2 tbsp. motherwort requires 2 cups of boiling water. Pour in the grass and let sit for 15 minutes. You need to drink it three times a day before meals and at night.
These drugs and methods will help to immediately lower your blood pressure if it has not risen above 120 to 100. In other cases, first aid at home will not bring results and you will need to take medications, consult a doctor, or call an ambulance.
If there is a sudden increase in pressure, provide fresh air, unbutton your collar, apply a damp, cold towel to your neck, and take a comfortable sitting position.
What to do: treatment features
Treatment of hypotension with a lower pressure of 60 mm Hg. It is necessary only if your health deteriorates significantly or if unpleasant or painful symptoms appear.
The first step to recovery should be a visit to a general practitioner. He will be able to refer you to more specialized specialists - a cardiologist, endocrinologist, urologist, neurologist. You should also prepare to undergo detailed diagnostics and undergo laboratory tests.
To relieve the symptoms of hypotension, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease that caused it. To alleviate the condition, symptomatic drug therapy is prescribed. Can be used:
- analeptics;
- alpha adrenergic agonists;
- adaptogens;
Also prescribed are medications that include caffeine and can help in a very short time - Citramon, Caffetamine, Saparal. The drugs are recommended in limited dosages so as not to provoke the onset of hypertension.
To stabilize the level of lower pressure, physiotherapy may be recommended - massage, electro-, water- and magnetic therapy, aromatherapy.
In some cases, professional psychological help is necessary.