Does vasospasm occur in children?
A little person does not know how to talk about his feelings.
He is afraid of everything unusual. Angiospasm in infants is caused by violations of the mother's regimen during pregnancy (smoking, drinking alcohol), difficult childbirth, and the use of vacuum extraction. Even moderate trauma to the cerebral vessels causes changes in the baby’s behavior: increased anxiety, crying, poor appetite, sleep disturbance, decreased weight gain.
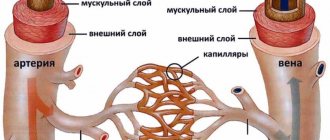
Clinical signs of vasospasm depend on the area of the lesion, the location of the narrowed vessels, and the possibilities for the development of collateral blood supply. With age, the child develops its own protective mechanism, and the tone of the vascular wall is restored.
In adolescence, a breakdown is possible due to school overload and hormonal imbalance. Angiospasm of cerebral vessels is manifested by increased fatigue in class, short-term headaches with dizziness, and decreased vision. A diagnosis of neurocirculatory dystonia is usually made.
You can learn in detail about how vasospasm of peripheral and central vessels manifests itself in adults on our website in the article “Symptoms of vascular spasms.”
Causes of cerebral vasospasm
In addition to stress and unfavorable ecology, other factors also influence the disease, for example, insomnia and chronic fatigue, overstrain of the nervous system, strong emotions, and lack of headwear during the cold season.
Vascular angiospasm can cause the following pathologies:
- Osteochondrosis;
- Aneurysm;
- Damage to the structure of the arteries;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Improper functioning of the endocrine system;
- High pressure;
- Oncology.
Treatment
Treatment of vasospasm is aimed at:
- elimination of the main cause of spasm (inflammation, increased thrombus formation, atherosclerotic process, hypertension);
- restoration of nervous regulation of arterial tone;
- relieving symptoms of temporary ischemia of organs and tissues;
- preventing the development of more severe diseases.
Bad habits are the beginning of many diseases.
For any localization of vasospasm, it is necessary:
- stop smoking and alcohol abuse;
- organize the correct work and rest schedule;
- remove excess weight;
- exclude from food foods that increase blood cholesterol;
- engage in vigorous physical exercise.
- medications from the group of calcium antagonists (Verapamil, Nifedipine) are indicated; they help relax the vascular wall.
With spasm of the coronary vessels (Prinzmetal's angina), Nitroglycerin and Isoket aerosol help relieve attacks. If attacks occur frequently, then long-acting nitro drugs are prescribed.
We recommend reading the article:
Effective tablets for brain vessels
- Cerebral vascular spasm: causes, symptoms and treatment
Cerebral symptoms are relieved with antispasmodic drugs (Papaverine, No-shpa). Angiospasm of cerebral vessels must be distinguished from vertebral artery syndrome, which also causes similar temporary signs of impaired blood supply to the brain. However, the main reasons lie in the disrupted structure of the vertebrae or the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta and the artery itself. Manifestations occur when moving the head, bending, turning.
Therapy for vascular lesions of the lower extremities includes taking antispasmodics and drugs that improve nutrition of the tissues and muscles of the legs (Nicotinic acid, Depo-padutin).
Great importance is attached to the possibilities of physiotherapy. Procedures such as electrophoresis with novocaine, lidase, paraffin and ozokerite applications, mud therapy, contrast douches, radon and hydrogen sulfide baths help maintain the patient’s motor activity.
Surgical treatment is necessary when conservative therapy is unsuccessful. It consists of using a series of novocaine blockades of sympathetic nodes to eliminate the spasmodic effect of Raynaud's syndrome, spasm of the arteries of the legs.
Diagnostic methods
To most accurately identify abnormalities in the activity of cerebral vessels, a specialist will carry out diagnostic procedures:
- duplex scanning of brachycephalic and intracranial arteries - allows for a comprehensive examination of the structure of the vessels, the speed of blood flow in them, as well as the presence of atherosclerotic and thrombotic deposits;
- MRI - the most accurate diagnosis;
- radiography with contrast if it is not possible to perform an MRI.
The full amount of information obtained after the above diagnostic procedures allows the specialist to make an adequate diagnosis.
Prevention
Preventing any spasm requires adherence to a regimen and dietary restrictions.
According to WHO, abuse is defined as the single consumption of more than 60 ml of alcohol by men (150 ml of vodka, 0.5 liters of wine, 1.3 liters of beer), for women - more than 50 ml (125 ml of vodka, 0.4 liters of wine, 1.1 l beer) even once a month.
And no more
Treatment of hypertension and atherosclerosis helps to avoid the occurrence of additional symptoms that intensify the underlying disease.
Many doctors advise patients over 40 years of age to take a daily dose of a blood thinner (Cardiomagnyl, Cardiasc).
- Why is a study of the blood vessels of the brain and neck performed?
Intraocular injections
Intravitreal injections are the injection of a drug directly into the eye cavity (into the vitreous body). Such injections are performed for hemorrhages (partial hemophthalmia), wet form of macular degeneration, retinal edema, the appearance of newly formed vessels and other serious eye diseases.
In our clinic, intravitreal injections are performed by ophthalmologists with extensive experience in complex intraocular injections in sterile procedure rooms, in compliance with appropriate medical protocols. Such therapy for retinal pathologies, using effective medications, allows one to preserve visual function and also achieve a significant improvement in visual acuity.
Lucentis
The active component of the drug is ranibizumab, a substance that suppresses excessive angiogenesis (the formation of pathological blood vessels), which is characteristic of age-related macular degeneration. In addition, it helps relieve macular edema, normalizing the thickness of the retina. The drug quickly penetrates completely into the layers of the retina, reducing the size of the lesion, preventing possible hemorrhages and further progression of the growth of newly formed vessels with a pathological wall. More about Lucentis >>>
Eilea
The active substance of Eylea is aflibercept. Its action is aimed at inhibiting the progression of age-related macular degeneration (wet form). In addition, it has the ability to act effectively and safely in reducing visual acuity in the case of diabetic macular edema and edema caused by retinal vein occlusion.
The innovative drug Eylea has a long-lasting effect, so injections can be performed less frequently than with Lucentis, which is much more convenient for patients. More about Eylea >>>
Ozurdex
It is used in cases of macular edema caused by occlusion of the retinal veins. The drug is produced in the form of a thin implant in the form of a rod, which is inserted into the vitreous body. The implant contains the potent steroid dexamethasone, which begins to be released inside the vitreous in small portions. This innovative method of dosed delivery of a medication to the affected area significantly increases the duration of action of the hormone, which can last up to six months. Read more about Ozurdex >>>
Parabulbar and intravitreal injections are performed under sterile conditions
Drug therapy for vasospasms
Vasospasm of cerebral vessels is quite amenable to complex treatment - the impact should be exerted both directly on the very cause of the disorder, and on the diseases that preceded it.
General recommendations:
- give up bad habits - abuse of tobacco, alcohol, drugs;
- carry out timely sanitation of foci of chronic infection - visit the dentist, treat sinusitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis;
- adjust your diet - eat more fruits and vegetables so that your body receives beneficial vitamins and microelements;
- get a good night's sleep;
- walk more in the fresh air - go out into the countryside, take walks in the nearest forest park.
Courses of special medications that can improve blood circulation help eliminate vasospasm. Specialists individually select the optimal drug therapy regimen:
- nootropics - promote the expansion of small and large veins, due to which more blood with nutrients flows to the nerve cells, and also increase the overall tone of the vascular wall;
- angioprotectors – increase blood circulation in arterioles;
- sedatives - herbal or synthetic based, help calm excited nervous structures, which also has a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels;
- vitamin therapy – saturation of brain tissue with vitamins, especially subgroup B.
In addition to medications, experts recommend physiotherapeutic procedures, reflexology courses, and hydrotherapy. To consolidate the achieved success - reducing the number of attacks of vasospasms, you should undergo sanatorium-resort treatment.
Providing quick help to yourself
A full treatment course should only be prescribed by a neurologist. If there is a deterioration in health caused specifically by cerebral vasospasm, the following measures can be taken at home:
- wash with cool distilled water;
- lie down in a darkened room, place an orthopedic pillow under your head;
- drink 25-30 drops of valerian;
- if there are no contraindications, take an analgesic or antispasmodic tablet;
- conduct a self-massage session;
- Drink slowly in small sips of warmed water with a drop of honey.
If you cannot cope with the attack on your own, then it is not recommended to delay consultation with a specialist.
Complications of mesenteric thrombosis
- Gangrene of the intestine. If the blood flow to the intestines is completely blocked, then its death develops.
- Perforation. The dead section of intestine may rupture. As a result, the contents of the intestines spill into the abdominal cavity, causing an infectious process in the peritoneum (peritonitis).
- Scar changes in the intestinal wall. Sometimes these dangerous complications do not develop, but the damaged intestinal wall is replaced by a scar, causing narrowing of the intestinal tube and the development of intestinal obstruction.