Cortical atrophy of the brain is a devastating, irreversible change that most often affects people between 50 and 55 years of age, although there are cases of cortical atrophy in newborn infants. Pathological disorders, as a rule, manifest themselves in the frontal lobes of the brain, which are responsible for the thinking process, human behavior, and control. The disease progresses slowly with a gradual increase in the main symptoms, which ultimately leads to the emergence and development of senile dementia.
Causes of the disease
The main factor that leads to brain atrophy in 95% of cases is genetic predisposition. With age, the volume and mass of the brain decrease. This pathology is most pronounced in older women. Provoking external factors can aggravate the situation. Mutations in chromosomes and infectious processes during pregnancy can lead to congenital brain atrophy in a newborn. The main reasons for the development of the disease include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Diseases of the mother that are transmitted to the fetus through the placenta, trauma during childbirth, hypoxia.
- Poor blood supply to the brain due to changes in blood vessels and a decrease in their capacity.
- Insufficient mental stress, as a result of which the brain atrophies.
- The influence of alcohol, drugs and medications, which has a detrimental effect on the cortex and subcortical formations of the brain. Radiation exposure.
- Chronic anemia, which leads to insufficient saturation of brain cells with oxygen, which ultimately leads to ischemia and atrophy.
- Injuries, including those resulting from neurosurgical intervention, lead to compression of blood vessels, which affect brain tissue, which can cause the development of atrophy. Slow development of neoplasms, which also compress the vessels.
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases of the brain.
Factors that contribute to the development of pathology include: excessive smoking, chronic arterial hypotension, use of vasoconstrictor drugs, chronic alcoholism.
It is important to note that cortical atrophy of the brain is changes in the nervous tissue of the brain after its normal formation. Primary underdevelopment of the central nervous system during intrauterine development cannot be considered atrophy.
The development of pathology in the cerebral cortex in elderly people very often depends on the level of their mental load in youth. People who think a lot and are engaged in intellectual work are less at risk of developing senile dementia.
Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of the disease
Symptoms of cortical atrophy of the brain directly depend on the degree, site of damage and extent of the pathology. Cortical cerebral atrophy has five stages of development of the destructive process with its own characteristic features. It is also important to consider where exactly the harmful changes occur - in the cortex or in the subcortical zones. The first manifestations of the main signs of the disease depend on this. Depending on age and external factors, pathological changes may develop faster. The disease has the following stages of development:
- Grade 1 cortical cerebral atrophy usually occurs without any symptoms. From time to time there is a headache, weakness, and dizziness. This stage of the disease develops very quickly and moves into the next one.
- The second stage of pathology is characterized by the fact that a person becomes irritable, cannot calmly accept criticism, conflicts with the environment, and easily loses the thread of communication. Memory deteriorates, handwriting may change, old habits are forgotten and new ones are acquired. At the second stage of atrophy development, you can notice a disturbance in the coordination of movements and changes in gait. The patient may begin to copy other people, as his independence in thinking and movements is lost. The second stage should alert loved ones and encourage them to seek help from a specialist.
- Loss of control over behavior, sudden outbursts of anger, despondency are characteristic features of the third stage of the destructive process. Basic self-care skills are lost.
- In the last stages of the disease, a person reacts inadequately to the world around him, loses awareness of what is happening, and does not show any emotions.
A person in the last stage of pathology is often dangerous to society, and therefore such people may be isolated in a psychiatric or neurological clinic. The most famous pathology of the cerebral cortex is bihemispheric cortical atrophy (destructive changes occur in both hemispheres at once). This disease is better known as Alzheimer's disease. Another type of atrophic disease of brain tissue is Pick's disease, in which thinning of the cerebral cortex is observed. Its main symptoms include: inability to concentrate, increased distractibility, gluttony, hypersexuality. The pathology develops slowly, but progresses steadily. Unlike Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease is treatable when detected early in its development.
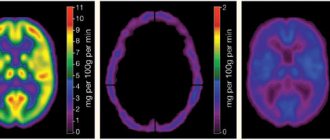
Pathological changes in the cerebral cortex and the degree of damage can be diagnosed using additional studies, as well as computer or magnetic resonance therapy, the indications for which are the main symptoms of a possible disease. Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and brain, and cognitive tests (to determine the stage of the pathology) are also performed. To identify neoplasms and lesions with structural changes, the patient undergoes X-ray examinations. The most accurate diagnostic method today is magnetic resonance therapy, which allows not only to identify pathological changes in brain tissue in the early stages of the disease, but also to monitor them over time.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, the signs of the disease are smoothed out. Those closest to him begin to notice in the patient: lethargy, apathy, indifference to everything. It is possible to display previously unusual sexual activity, while denying moral boundaries. Further death of brain cells is manifested by:
- impoverishment of vocabulary, difficulties in choosing words to express emotions, describe an event, an object;
- rapid deterioration of intellectual abilities;
- loss of self-criticism;
- loss of self-control in actions and behavior;
- deterioration of motor skills.
The characteristic features depend on which area has undergone destructuring. Destruction of cortical tissues is characterized by:
- slow thinking;
- speech changes, timbre is distorted;
- the skills of memorizing information are lost;
- fine motor skills are lost.
The death of the medulla oblongata is manifested by:
- respiratory dysfunction;
- digestive problems;
- disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- decreased immunity.
Damage to the cerebellum is accompanied by movement disorders: disturbances of balance, coordination, and muscle tone. Destruction of midbrain cells leads to loss of responses to external stimuli, intermediate - failure of the functions of thermoregulation and metabolism. All reflexes are lost when the anterior part of the GM undergoes destructuring.
When a large part of the neurons dies, the body loses its ability to maintain vital functions and death occurs. Necrotic changes in GM tissues are often caused by: chronic poisoning with toxins, TBI. The severity of the pathology depends on the location of the atrophy process and the stage of its development.
Instrumental methods are used to diagnose cerebral atrophy. CT allows you to identify areas of blood supply disturbance, vessels affected by a stroke, areas of hemorrhage, the presence of cysts, tumors in brain tissue. MRI makes it possible to evaluate pathological changes in all areas of the brain. Allows you to detect brain subatrophy - a precritical state, which significantly improves the prognosis of treatment. Allows you to identify the initial signs of pathology and a new diagnostic method - multislice tomography.
Methods for treating atrophic brain pathology
Cortical atrophy of the brain cannot be completely cured. The most important thing is to stop the progression of the pathology, which can be done with greater success at a young age than in older people. Therapy for atrophy, depending on the situation, can be carried out using the following medications:
- nootropics are used to improve nutrition of brain cells. In addition, these drugs help normalize the thinking process;
- the action of antioxidants is aimed at improving metabolism, slowing down the atrophy process, and counteracting oxygen free radicals;
- drugs to improve blood microcirculation.
In addition, if a person suffers from headaches, he is prescribed to take analgesics or anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. For increased excitability, irritation, and insomnia, sedative medications are indicated. The support of the patient’s relatives, their help and understanding is very important. It is undesirable for the patient to change the usual way of life; it is necessary to create the most calm and familiar environment for the person. Walking in the fresh air and feasible physical activity are very important. Daytime sleep is undesirable for a person with atrophic pathology of the brain. If the doctor allows, the patient may be prescribed a course of therapeutic massage to improve the patient's blood flow. If necessary, the treating specialist can prescribe sedatives, antidepressants, and tranquilizers. In cases where relatives are not able to cope with the patient on their own, due to his aggressive behavior, specialized nursing homes and boarding schools are provided for patients with impaired brain function.
The prognosis of people with cortical atrophy of the brain is far from rosy. The disease, one way or another, progresses at a slow or rapid pace, leading to irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex, personality degradation, which ultimately leads to death. The main factors that can stop the development of pathology in a patient are:
- positive psycho-emotional mood, complete absence of stressful situations;
- daily mental stress, working on your memory;
- eating healthy foods;
- complete cessation of habits harmful to the body, such as smoking, alcohol, and taking drugs;
- blood pressure control;
- daily walks, moderate physical activity.
Cortical atrophy
Usually this type of disease is observed in older people and appears due to senile changes. It affects the frontal lobes, but the disease can spread to other parts. Signs of the disease do not appear immediately, but the result is a decrease in intelligence and memory, and dementia. An example of the impact of such a disease is Alzheimer's disease. Usually diagnosed using MRI.
With the diffuse spread of the disease, blood flow is disrupted, tissue restoration is suffocated and mental performance is reduced. A disorder of fine motor skills of the hands and coordination of movements also appears; the development of the disease changes the lifestyle and leads to absolute incapacity.
The role of nutrition in the treatment of disease
Proper nutrition is very important to support the normal functioning of the brain and saturate its cells with all the necessary vitamins and minerals. A person diagnosed with cortical atrophy of the brain must necessarily include omega acids, unsaturated fats, and fat-soluble vitamins in their diet. It is necessary to remove everything fatty, fried, smoked and floury. Eating walnuts, fruits and vegetables has a good effect on brain nutrition. You should introduce fatty fish into your diet. Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle can stop the death of nerve cells and enable the patient to carry on with his usual life activities.
Treatment of pathology using traditional medicine
Brain atrophy is characterized by irreversible processes in the body that cannot be cured. However, with the help of traditional methods, it is possible to slow down the rate of development of pathological processes and improve the patient’s well-being. Herbal teas and tinctures are used with great success in the treatment of brain atrophy. Here are the best options for such fees:
- Take oregano, horsetail, motherwort and nettle in equal proportions. Pour boiling water into a thermos and leave overnight. Take 3 times a day;
- A tincture of young rye and chickweed, steamed with boiling water, can be drunk after meals in any quantity. This tea helps a lot after an injury.
- A tincture of viburnum, rosehip and barberry, steamed with boiling water and infused for 8 hours, is taken instead of tea in unlimited quantities, or with honey.
Preventive examinations, careful attitude towards one’s health, and strict adherence to the recommendations of specialists and the attending physician are very important for every person. This will help you maintain good health and live many more years of a happy and fulfilling life.
Multiple system atrophy
This disease is considered progressive. The occurrence of the disease includes 3 different disorders, combined with each other in different ways. But usually such atrophy manifests itself in the form of:
- parsionism;
- destruction of the cerebellum;
- vegetative disorders.
To date, the causes of this disease have not been identified. Diagnosis is made using MRI and clinical examination. Treatment includes supportive care and reduction of symptoms of the disease.