Author Diana Gavrilova
08/06/2019 15:19 (Updated: 03/18/2021 19:33)
Health
Every time the human heart beats, blood is released from the muscle pump and passes through 96,000 km of blood vessels. A network of tubes connects every cell in the body that depends on blood. The vital fluid delivers essential nutrients, removes waste, fights infections and heals wounds.
Why is human blood red?
Science knows that different living organisms on the planet have different blood colors.
However, in humans it is red. Why is blood red? This question is asked by both children and adults.
The answer is quite simple: the red color is due to hemoglobin, which contains iron atoms in its structure.
What makes blood red is hemoglobin, which consists of:
- From a protein called globin,
- The non-protein element heme, which contains the ferrous ion.
There are four hemes in hemoglobin molecules.
Their number is 4 percent of the total mass of the molecule, and globin accounts for 96 percent. The main effect in the activity of hemoglobin belongs to the iron ion.
Ferrous oxide makes blood red.
The metal that promotes the reproduction of red blood cells is continuously produced by the human body.
Nitric oxide, in turn, plays an important role in regulating blood pressure.
Types of blood
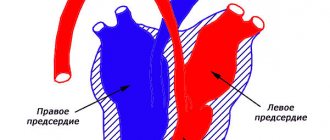
| Arterial | Venous |
| Rich in oxygen, comes from the heart. A bright scarlet hue distinguishes arterial blood from venous blood. | Gives oxygen to organs and returns to the heart. The dark red tint is a distinctive feature. What makes this blood dark is the carbon dioxide that fills it. |
Specialists
| 5.0 330 reviews | Balyura Elena Vladimirovna Andrologist Experience 32 years Doctor of the first category Admission from 3180 rub. |
| 4.3 134 reviews | Larina Tatyana Lvovna Andrologist Experience 29 years Doctor of the highest category Admission from 2500 rub. |
| 4.3 669 reviews | Vorotnikova Irina Valentinovna Andrologist Experience 45 years Admission from 1900 rub. |
Compound
Blood is a rapidly renewing connective tissue that continuously circulates throughout the human body.
It was possible to find out what gives the red color, but its elements turn out to be no less interesting. What elements give it this color is an equally interesting aspect.
Blood contains:
- Plasma. The liquid is light yellow in color, with its help the cells in its composition can move. It is composed of 90 percent water, with the remaining 10 percent made up of organic and inorganic components. Plasma also contains vitamins and microelements. The light yellow liquid contains many beneficial substances.
- Formed elements of blood cells. There are three types of cells: white blood cells, platelets and red blood cells. Each type of cell has certain functions and characteristics.
Leukocytes
These are white cells that protect the human body. They protect it from internal diseases and foreign microorganisms penetrating from the outside.
Leukocytes
This is a white element in color. Its white tint cannot be ignored during laboratory tests, so such cells are identified quite simply.
White blood cells recognize foreign cells that can cause harm and destroy them.
Platelets
These are very small colored plates whose main function is coagulation.
Platelets
These cells are responsible for ensuring that the blood:
- It coagulated and did not flow out of the body,
- Coagulates quite quickly on the surface of the wound.
Red blood cells
More than 90 percent of these cells are in the blood. It is also red because red blood cells have this hue.
Red blood cells
They carry oxygen from the lungs to peripheral tissues and are continuously produced in the bone marrow. They live for about four months, then are destroyed in the liver and spleen.
It is very important for red blood cells to carry oxygen to various tissues of the human body.
Few people know that immature red blood cells are blue, then acquire a gray tint and only then turn red.
There are quite a lot of human red blood cells, which is why oxygen reaches peripheral tissues so quickly.
It is difficult to say which element is more significant. Each of them has an important function that affects human health.
What else is prescribed with this study?
Humoral immunity (immunoglobulins IgA, IgM, IgG, IgE, circulating immunocomplexes, complement components C3, C4)
17.51. Ven. blood 8 days
2,580 ₽ Add to cart
Immune status (screening) (Phagocytic activity of leukocytes, cellular immunity, total immunoglobulin IgE, immunoglobulins IgA, IgM, IgG)
27.960. Ven. blood 3 days
5 680 ₽ Add to cart
Total immunoglobulin IgE
17.2. Ven. blood 1 day
410 ₽ Add to cart
Cellular immunity (T-lymphocytes, T-helpers, T-cytotoxic cells, Immunoregulatory index, B-lymphocytes, NK-T cells, NK cells, Leukocyte formula)
17.50. Ven. blood 3 days
4 160 ₽ Add to cart
Serum paraprotein typing using immunofixation
50.28.2181 Ven. blood 14 days
3,380 ₽ Add to cart
Explanation for the child
Children often ask questions regarding the components of the human body. Blood is one of the most popular topics of discussion.
Explanations for children should be extremely simple, but at the same time informative. Blood contains many substances that differ in function.
Consists of plasma and special cells:
- Plasma is a liquid that contains useful substances. It has a light yellow tint.
- The formed elements are erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets.
The presence of red erythrocyte cells explains its color. Red blood cells are red by nature, and their accumulation leads to the fact that a person’s blood is exactly this color.
There are about thirty-five billion red cells that move throughout the human body in the blood vessels.
Oximeter readings
Blood oxygen saturation level ( SpO2 ) is the ratio of hemoglobin containing oxygen to the total amount of hemoglobin in the blood, measured as a percentage. Here is the range of variation of this parameter: 95% and above – normal 90-94% – I degree, a dangerous level may indicate a health disorder. 75-89% Grade II, extremely dangerous, low blood oxygen saturation, may indicate a serious health disorder. Less than 75% – III degree, hypoxemia. Less than 60% – IV degree, hypoxemic coma.
Pulse oximeter. Measurement result 99%!
Top of page
Why are veins blue
The veins carry burgundy blood. They are red, like the color of the blood that flows through them, but not blue. The veins only appear blue.
This can be explained by the law of physics about the reflection of light and perception:
When a ray of light hits the body, the skin reflects some of the waves and looks light. However, it transmits the blue spectrum much worse.
The blood itself absorbs light of all wavelengths. The skin gives a blue color for visibility, and the vein is red.
The human brain compares the color of the blood vessel against the warm tone of the skin, resulting in blue.
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry (optical spectroscopy) is a method of research and analysis of substances based on measuring absorption spectra in the optical region of electromagnetic radiation.
Spectral analysis
Optical spectroscopy originated in 1802 with the discovery of Fraunhofer lines - dark lines in the spectrum of the Sun, which were described by Joseph Fraunhofer (a German physicist and optician) in 1814 .
In the 60s of the 19th century Gustav Kirchhoff (German physicist) showed that these are absorption lines caused by the presence of various gases in the solar atmosphere, and that a specific line is associated with each gas. In 1853, Anders Jonas Angström (Swedish astrophysicist) compared the emission lines of gases with various chemical elements, which laid the basis for a new method of obtaining information about the composition of substances - spectral analysis .
Joseph Fraunhofer, Anders Jonas Angström, Gustav Kirchhoff.
Absorption spectrum
The absorption spectrum of an object depends on its molecular composition. The Bouguer-Lambert-Beer law is the basic law that describes the absorption of light by a medium. It relates the intensities Il of light passing through a layer of medium with thickness l and the initial light flux I0 .
where kλ is the absorption rate of the substance. For solutions of absorbing substances in non-absorbing solvents, the absorption index can be written as: where: X λ is a coefficient characterizing the interaction of a molecule of an absorbing substance with light of wavelength λ , C is the concentration of the dissolved substance.
Spectrophotometer
The common features of all spectrophotometers are: a light source, a monochromator, a cuvette compartment with a sample, and a recording detector.
Spectrophotometer
The light source is most often mercury or halogen lamps. A monochromator is a device for selecting a narrow part of it (1-2 nm) from the entire emitted spectrum. Monochromators can be built on the basis of light-separating prisms or on the basis of a diffraction grating. Also, some devices may additionally use sets of light filters. The cuvette compartment can be equipped with mechanisms for thermostatting, mixing, and adding substances directly during the measurement process. For studies of small volumes of substances, cellless technology can be used, when the sample is held due to the forces of surface tension of the liquid. The detector converts the light signal into an electrical signal for subsequent processing.
Top of page
a pulse oximeter is used to measure oxygen in the blood at home . To measure, a pulse oximeter is placed on the tip of your index finger. The device measures oxygen levels in both oxygenated arterial blood and oxygen-depleted (deoxygenated) venous blood. And the measurement results are presented as the ratio of these values as a percentage, that is, in SpO2 . To measure these two different types of blood, the device uses light sources of two different frequencies: an infrared light source and a red light source. Infrared frequency is used to measure oxygen-rich blood (arterial blood). The red frequency is used to measure desaturated (oxygen-poor) venous blood. If the highest absorption coefficient is in the infrared range, this means a high degree of saturation (oxygen saturation). And if the highest absorption coefficient is in the red range, then this means a low degree of saturation (oxygen saturation).
Blood of a different color in various living creatures
Not all living organisms have red blood.
The protein that gives this color in humans is hemoglobin, contained in hemoglobin. Other living beings have other fat-containing proteins instead of hemoglobin.
The most common shades besides red are:
- Blue. Crustaceans, spiders, mollusks, octopuses and squids boast this color. And blue blood is of great importance for these creatures, as it is filled with important elements. Instead of hemoglobin, it contains hemocyanin, which contains copper.
- Violet. This color is found in marine invertebrates and some mollusks. Typically, such blood is not only purple, but also slightly pink. The blood of young invertebrate organisms is pink. In this case, the protein is hemerythrin.
- Green. Found in annelids and leeches. The protein chlorocruorin is close to hemoglobin. However, iron in this case is not oxide, but ferrous.
The color of blood varies depending on the protein it contains. Whatever the color of blood, it contains a huge amount of useful substances necessary for a living organism. Pigment is important for every organism, despite its diversity.
References
- Encyclopedia of clinical laboratory tests / ed. WELL. Titsa. - M.: Labinform, 1997. - P. 213-215, 223-226.
- JVaillant, A., Jamal, Z., Ramphul, K. Immunoglobulin. In: StatPearls, 2021.
- Sathe, A., Cusick, J. Biochemistry, Immunoglobulin M. StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
- Histology (introduction to pathology) / ed. E.G. Ulumbekova, Yu.A. Chelysheva. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 1997. - P. 528 – 530.
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A., Fausto, N. et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2014. - 1464 p.
Unusual vaginal bleeding – when to contact a gynecologist?
If unusual bleeding occurs, you should make an appointment with your gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an interview and order an examination to determine the type of bleeding.
You will have to answer questions about your last menstrual cycles, how much bleeding you have had, and whether blood stains appear on your bed linen. Information indicating the pharmacological treatment and gynecological procedures being carried out is important for the doctor. Issues related to sexuality, forms of contraception used and possible sexually transmitted infections are important.
The doctor will also perform a gynecological examination. During the examination, the gynecologist uses two fingers to check the condition of the organs, determining the size of the uterus and its sensitivity to touch. The doctor also uses a speculum to gently open the vagina and examine the cervix.
During a gynecological examination, a smear of the vagina and cervix is performed. This sample is then sent to a laboratory to determine whether the discharge is the result of an infection. After receiving all the results, the gynecologist, in collaboration with the patient, decides on the need for further tests, including ultrasound.