Types of bilirubin
Total bilirubin is divided into two parts - bound (conjugated) and free (unconjugated). They differ in their ability to dissolve in water.
Unconjugated bilirubin:
- It is formed in the spleen, which ensures the utilization of red blood cells. In the process of their destruction, bilirubin appears. Due to its inability to dissolve in water, free bilirubin is not excreted from the body by the kidneys.
- In the blood it interacts with albumin and in the liver it is converted into bound albumin.
- It accumulates in adipose tissue and, in excess, has a toxic effect on the body: it disrupts protein synthesis and negatively affects cellular respiration.
Conjugated bilirubin is water-soluble, formed in the liver, low-toxic, and practically harmless. The bound pigment is excreted in urine and feces.
How to normalize bilirubin metabolism
It is important to keep the level of the substance normal, but traditional methods are useless here. It is necessary to identify the cause of the pathology and undergo treatment with drugs, strictly following the doctor’s instructions. In case of liver disease, a man will have to go to hospital and adhere to a strict diet. If the concentration disorder is caused by blockage of the bile ducts with stones, they resort to surgery.
Although hereditary pathologies are not amenable to drug therapy, the man’s condition is maintained with periodic red blood cell transfusions. In case of severe genetic diseases, excision of the spleen is recommended.
Norm of bilirubin for men
Direct bilirubin makes up approximately 1/5 of the total pigment in the blood of men. Normal bilirubin levels are as follows:
- general - up to 20.5 µmol/l;
- bound - up to 4.2 - 4.5 µmol/l;
- unbound - up to 15.3-17.1 µmol/l.
In different laboratories, indicators of the normal amount of bilirubin in the blood may differ slightly: the error is 10-15%. The approximate ratio of unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin is 3:1, 4:1.
In men over 50 years of age, the concentration of pigment in the blood changes.
Normal bilirubin content in the blood of men of different age groups:
| 17-20 years old | 3.7 - 18 µmol/liter; |
| 21-30 years old | 3.8 - 19 µmol/liter; |
| 31 - 40 years 3.8 | 8.5 µmol/liter; |
| 41-50 years | 3.9 - 18.7 µmol/liter; |
| 51 - 60 years | 3.8 - 18.5 µmol/liter; |
| 61 - 70 years | 3.7 - 18.5 µmol/liter; |
| 71 years and older | 3.5 - 18.2 µmol/liter. |
The amount of bilirubin in the blood is a marker of changes in the body and allows for the timely detection and elimination of various diseases. This is what the change in pigment concentration indicates.
Questions for the doctor
Additional examination
Hello! Recently, my dad (he is 64 years old) was invited for a preventive examination at the clinic. Now the nurse called and said the bilirubin level was high. I myself noticed that his skin and eyes were somehow yellowish. But he himself has no particular complaints.
Tell me what additional examination should dad undergo in order to determine the reason for the poor analysis? After all, is bilirubin 60 in an adult man abnormal?
Expert opinion
Romanova Natalya, surgeon
Good day! Indeed, a BIL-T value exceeding 18.5 μmol/L is considered pathologically elevated. To find out the causes of the disease, I recommend that your dad take:
- Laboratory tests:
- UAC;
- OAM;
- additionally determination of fractions D-BIL, ID-BIL;
- scatological research;
- Instrumental tests:
- Ultrasound of the liver and gastrointestinal tract;
- according to indications - radiography.
The instructions written above are just the standard minimum; you may need something more. After receiving the results, be sure to show them to your doctor to draw up an adequate plan for diagnosing and treating the disease. Be healthy!
Increased bilirubin
Often indicates accelerated breakdown of red blood cells. An increase in bilirubin in the blood may be associated with cirrhosis of the liver, hepatitis, anemia, and diseases of the pancreas. Unconjugated bilirubin negatively affects the functioning and functionality of the nervous system. A high concentration of pigment indicates its accumulation in the body.
Bound bilirubin increases when:
- liver cirrhosis;
- gallstone disease;
- hepatitis;
- helminthiasis;
- drug intoxication;
- Rott syndrome;
- blockage of the biliary tract.
An increase in the concentration of unbound bilirubin is observed in the following diseases and conditions:
- Gilbert, Lucy-Driscoll syndrome;
- congenital or acquired anemia;
- typhoid fever;
- sepsis;
- syphilis;
- internal hemorrhages.
Exceeding the norm of bilirubin in the above diseases may be associated with impaired bile outflow, increased destruction of red blood cells, or deterioration in the processing of pigment in the liver.
Taking insulin, aspirin, and chloramphenicol can also cause an increase in bilirubin.
In addition, bilirubin increases due to alcohol abuse, tattooing, poor diet, and smoking.
Diagnostic features
Analytical studies are recommended when it is stated:
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin;
- clarification of excrement;
- darkening of urine.
If you detect at least one sign, you need to consult a doctor. He will prescribe a diagnosis.
Indications for examination
When is it recommended for adult men to undergo a medical examination:
- if cirrhosis, hepatitis, pancreatic diseases, or oncological processes are suspected;
- upon reaching old age;
- when diagnosing pancreatitis;
- after treatment;
- in cases of anemia, intoxication;
- during medical examinations and medical examinations.
The basis of the research is a blood test.
Analyzes and preparation for them
For the study, 5 ml of venous blood is taken. If pathology is suspected, a biochemical blood test is repeated. You should be properly prepared for the procedure.
Biomaterial is given on an empty stomach. Drinking coffee is not recommended. You can only drink still water. The day before laboratory tests, fried, fatty foods and alcoholic drinks are prohibited.
Signs of increased pigment in the blood
When the concentration of bilirubin in the blood increases, the following symptoms are observed:
- itchy skin;
- yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- hyperthermia;
- general weakness, headaches;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- discoloration of stool;
- change in urine color.
Skin color with increased bilirubin depends on the type of “jaundice”. Thus, adrenal jaundice is caused by the accelerated destruction of red blood cells and gives the skin a yellowish-lemon tint. Hepatic jaundice occurs when bilirubin metabolism is disrupted and gives a yellowish-saffron color. Subhepatic jaundice appears when there is a change in the transport of bile and is distinguished by a yellow-greenish tint.
Sometimes an increase in bilirubin has no clinical manifestations and is detected by chance during testing.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
Promoted?
Increased bilirubin in men and women is a common problem with which patients often consult a doctor. An increase in the concentration of BIL-T and its fractions always indicates ongoing pathological processes in the body. In this case, the liver, gallbladder, and blood system are most often affected.
So, let's look at the main causes of increased bilirubin in men and women:
- Hemolytic anemia is a type of anemia in which massive hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells occurs with the formation of a large amount of ID-BIL.
- Liver diseases that occur with damage to hepatocytes:
- Viral hepatitis A, B, C, D;
- Toxic (including alcoholic and drug-induced) hepatitis;
- Parasitic infestations.
- Diseases of the biliary tract, accompanied by a violation of the outflow of bile and its excretion into the gastrointestinal tract:
- Cholelithiasis;
- JVP;
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of the abdominal cavity).
Pathology is not always associated with the liver
To establish the exact cause of increased BIL concentrations, it is important to conduct a complete clinical, laboratory and instrumental examination. However, one can assume the nature of the pathology based on the indicators of bile pigment.
Table 3: Elevated bilirubin in women and men: causes and differential diagnosis:
| Analysis data | Character of jaundice | Possible reasons |
| ↑ BIL-T ↑ ID-BIL | Hemolytic | “Suprahepatic” problems – hemolytic anemia, parasitic diseases, spleen lesions. |
| ↑ BIL-T ↑ D-BIL | Parenchymatous | Direct damage to liver hepatocytes in hepatitis, cirrhosis, etc. |
| “Subhepatic” diseases are a violation of the excretion of bile from the hepatobiliary system. |
The photo shows a patient with severe jaundice (right)
Or demoted?
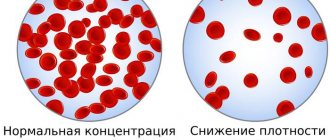
A decrease in the concentration of total bilirubin and its fractions is much less common in medical practice. It may be associated with various pathological processes in which the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood sharply decreases.
Among them:
- chronic renal failure;
- long-term drug intoxication (for example, during treatment with anti-tuberculosis drugs);
- exhaustion, cachexia;
- aplastic anemia;
- acute leukemia.
All these reasons lead to a decrease in the content of red blood cells and myoglobin in the blood
Nutrition to normalize bilirubin
To normalize bilirubin levels, men are advised to exclude salt from their diet and reduce the amount of meat and bread. Doctors also do not recommend eating the following foods:
- mushrooms;
- mayonnaise, mustard;
- lemon, onion;
- smoked products, sausages;
- seafood;
- canned foods;
- alcohol;
- products containing dyes or sweeteners.
You should eat small meals; you should not eat fast foods. Doctors recommend drinking more fluid - up to 2.5 liters per day. This includes not only water, but also green tea and unsweetened compotes.
List of allowed foods and dishes to normalize bilirubin levels:
- cottage cheese, milk;
- non-acidic fruits;
- chicken and quail meat, rabbit meat;
- soups with vegetable broth or milk;
- herbal infusions.
Traditional medicine recommends drinking beet juice, decoctions of various herbs, and motherwort.
What can you do to get this setting back to normal?
The first thing you should do if yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the eyeball appears is to consult a doctor. Only a specialist, based on the clinical manifestations of the disease, will be able to prescribe a number of additional examinations and establish a diagnosis.
Trust a specialist
Comprehensive treatment will be required to normalize BIL levels. It will require:
- combating the cause of hyperbilirubinemia – the underlying disease;
- correction of lifestyle and nutrition;
- as a supplement - the use of folk remedies.
The diet for high bilirubin in men and women deserves special attention. To reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract and the hepatobiliary system in particular, you will need to exclude from the diet:
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- fatty fried foods;
- too spicy food;
- smoked meats, marinades;
- fast food and other food “garbage”.
Don't overload your gastrointestinal tract
It is recommended to eat frequently (4-6 times a day), in small portions. The diet should include a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits - they are rich in fiber and pectin, improve digestion. Experts also recommend increasing fluid intake (mainly in the first half of the day). Cereals – buckwheat, oatmeal, rice – will also be useful.
Note! A diet for high bilirubin in women and men is only one element of auxiliary therapy. It cannot completely replace drug treatment.
It turns out that this bilirubin is so important. The sooner a person discovers signs of an increase in the concentration of bile pigment and undergoes an examination, the faster the indicators of BIL and its fractions will return to normal, and the disease - whatever it may be - will be defeated.