Complexes with this research
Male anti-aging diagnostics Monitoring of key indicators in men aged 40+ 13,520 ₽ Composition
Fitness monitoring Examination for choosing physical activity and monitoring the condition of the body 6,890 ₽ Composition
Metabolic profile 6,010 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 12,280
- Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 29,130
- Stress complex 4,360 RUR
- Healthy interest RUB 4,350
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 34,230
Calculation of the atherogenic index
The atherogenic coefficient is an indicator that reflects the degree of risk of developing heart and vascular disease.
In the development of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels, not only an increase in the total amount of cholesterol in the blood is important, but also the ratio between “bad” and “good” cholesterol. This is what the atherogenicity coefficient reflects. It is calculated using the following formula: KA = (total cholesterol - HDL)/HDL .
The optimal atherogenicity coefficient is 2-3.
Detailed description of the study
Cholesterol (C) is a complex molecule that includes lipids (fats) and a polycyclic alcohol. This substance is necessary for humans, therefore it is synthesized by liver cells. In addition, some of the cholesterol comes from eating foods that contain animal fats.
The human need for cholesterol is dictated by its important role in many biological processes. This substance serves as a substrate for the formation of sex hormones (in both women and men) and bile acids, and is involved in the metabolism of vitamin D and the formation of cell membranes.
Once in the blood, cholesterol combines with special molecules - lipoproteins, in which they are delivered to organs and tissues, and can also be transported from cells back to the liver. Depending on the type of such compounds, cholesterol fractions are distinguished; their totality is designated as the lipid spectrum.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) carry cholesterol into tissues, including arteries, which creates the preconditions for the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. Because of this, LDL-C is often labeled as “bad” or “harmful.” The higher the LDL level, the higher the risk of cardiovascular diseases and their complications: coronary heart disease, heart attack, cerebrovascular accident.
In contrast to LDL, cholesterol found in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is classified as “good” or “useful.” The advantage of HDL is that it transports lipids from blood vessels and organs back to the liver. Adequate HDL levels are essential for maintaining cardiovascular health.
To avoid the development of atherosclerosis, the ratio between total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol must be maintained at a certain level. This indicator is called the atherogenic index/coefficient (AC).
An increased atherogenic index means that there is an imbalance in the metabolism of fats in the person being examined, with a predominance of the “bad” cholesterol fraction. Low KA is associated with sufficient presence of HDL cholesterol in the body. It should be noted that the analysis does not show the reason for the identified changes.
The study serves as a complement to the standard biochemical blood test. It can be considered as one of the basic and easily accessible tools for predicting cardiovascular risk. Using the data obtained, your doctor will decide whether to lower your cholesterol levels.
Increased atherogenicity coefficient, what to do?
If the results of laboratory tests reveal a high coefficient, this indicates that the body produces predominantly “bad” cholesterol. Despite the lack of evidence about the direct and main role of fatty alcohol in the formation of cardiovascular diseases and pathologies, it is not worth the risk. Measures should be taken immediately to normalize the indicator.
You can do this in two ways:
- Change your lifestyle and diet.
- Start taking specialized medications.
Lifestyle
The increase in the index is due to a number of reasons:
- Presence of bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse, drug use). Psychoactive substances “inhibit” normal fat metabolism and disrupt fat synthesis.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Physical inactivity leads to stagnant processes. Fats and fatty complexes are synthesized too actively.
From this we can conclude that to normalize the index you need:
- Lead a more active lifestyle. Strong physical activity can normalize the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and lipid metabolism. A healthy person is recommended to do 4 sessions during the week, 35-40 minutes each. If you have a history of diseases, you should consult a doctor to exclude contraindications and select the optimal physical activity regimen.
- Give up bad habits.
Diet
It is advisable to limit consumption or completely avoid the following foods:
- Sausages;
- Fatty fermented milk products (sour cream, cream, butter);
- Products rich in trans fats (margarine, palm oil spreads, etc.)
On the contrary, you should include in your diet:
- Fish. Cod, hake, flounder and others. Frying should be avoided, giving preference to boiling.
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts). Nuts contain monosaturated fatty compounds and can reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
- Fruits vegetables. Especially beets. Potatoes are not recommended.
- Chocolate and green tea.
- Garlic.
- Cereals.
As well as other products containing fats of vegetable rather than animal origin.
Read more: How to lower cholesterol at home, without drugs?
Taking medications is another way to reduce the atherogenic index. However, statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs) have many side effects and should be taken strictly on the advice of a doctor and in a very limited number of cases.
References
- Kukharchuk, V.V., Ezhov, M.V., Sergienko, I.V. and others. Clinical recommendations of the Eurasian Association of Ardiologists (EAA) / National Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis (NOA) for the diagnosis and correction of lipid metabolism disorders for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis. Eurasian Journal of Cardiology, 2021. - T. 2. - P. 6-29.
- Quispe, R., Elshazly, M., Zhao, D. et al. Total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratio discordance with LDL-cholesterol and non-HDL-cholesterol and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in primary prevention: The ARIC study. Eur J Prev Cardiol., 2021. - Vol. 27(15). - P. 1597-1605.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are the most important source of energy for cells; they are derivatives of glycerol. Triglycerides enter the human body with food, then they are synthesized in adipose tissue, then in the liver and in the intestines. The level of triglycerides in a person’s blood directly depends on age. To diagnose atherosclerosis, as well as many other diseases, triglyceride analysis is used. Plant seeds, liver and adipose tissue contain triglycerides, which are an essential part of human food.
Blood calcium is elevated, other tests have been taken - how to decipher them?
Of course, deciphering a blood test is the prerogative of the attending endocrinologist, and independent study of one’s blood test can lead the patient to diagnostic errors, however, within the framework of this article, we will give some information about the possible results of a laboratory examination for elevated blood calcium. Use the information obtained with caution and remember that it is not a substitute for consultation with a medical specialist.
So, possible options for laboratory results and their interpretation.
Blood calcium is increased, parathyroid hormone is increased, phosphorus is decreased, calcitonin is normal, calcium in daily urine is increased
– most likely, we are talking about primary hyperparathyroidism and the presence of a parathyroid adenoma. Additional examination is necessary using ultrasound of the thyroid gland and neck, scintigraphy of the parathyroid glands with technetril, and in some cases, computed tomography of the neck. It is treated surgically (endoscopic surgery through an incision about 2 cm long is possible in a specialized center).
Parathyroid hormone is elevated, calcium is normal, phosphorus is normal, calcitonin is normal
– with a high degree of probability we are talking about secondary hyperparathyroidism due to a banal deficiency of vitamin D in the blood. It is treated by taking vitamin D and calcium. It is important to exclude a laboratory error associated with an underestimation of the level of ionized calcium in the blood (it is better to retake the test for ionized calcium in a specialized laboratory of the endocrinology center).
Calcium in the blood is increased, parathyroid hormone is normal, phosphorus is normal, calcitonin is normal
– a neuroendocrine tumor that produces PTH-like peptides or forms lytic metastases in the bone should be suspected. Examination and treatment depend on the type of tumor detected.
High calcium in the blood (usually slightly increased calcium is observed), parathyroid hormone is moderately increased, phosphorus is normal, calcitonin is normal, calcium concentration in daily urine is reduced
– we can talk about a rare familial disease, the so-called familial benign hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. This disease is accompanied by a change in the sensitivity of cellular receptors to parathyroid hormone and impaired calcium excretion in the urine. Does not require treatment and is not dangerous. Often, inexperienced doctors diagnose primary hyperparathyroidism in such cases and refer the patient to unnecessary surgery to remove a non-existent parathyroid adenoma.
Ionized calcium is increased, total calcium is normal, parathyroid hormone is increased
– we are usually talking about parathyroid adenoma.
Ionized calcium is elevated, total calcium is below normal
– laboratory error must be excluded. The analysis should be re-taken in a specialized laboratory.
Ionized calcium in the blood is increased, parathyroid hormone is increased, calcitonin is increased
– the patient should be suspected of having both a parathyroid adenoma and medullary thyroid cancer. Together, these two diseases indicate a high probability that the patient has type IIA multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome - a rare hereditary pathology transmitted in the family and leading to the development of three dangerous tumors: medullary thyroid cancer, parathyroid adenomas (usually multiple), pheochromocytoma (tumor adrenal gland, which produces adrenaline or norepinephrine). Urgent consultation with an endocrinologist or endocrinologist surgeon is required!
Calcium in the blood is elevated during the first test, I want to retake the test - what is the best way to do this?
If you want to check whether your blood calcium is really elevated and are going to take a second blood test, follow some important rules that will help the second test be as accurate as possible:
1. a blood test should be taken only in a specialized laboratory using high-quality equipment;
2. a blood test must be taken only on an empty stomach;
3. if you are taking vitamin D or calcium supplements (or combination medications with vitamin D and calcium), stop them at least 2-3 days before your blood test; the entry of calcium from the drug into the blood can lead to an increased calcium level in the blood - of course, in this case a falsely elevated calcium is detected.
Apolipoproteins
- Apolipoprotein A1 is a protein that plays a specific role in lipid metabolism and is also the main protein component of HDL. Activates enzymes that unload cholesterol from tissues into HDL particles and allow them to be recognized by liver receptors and bind to these receptors. Apolipoprotein A1 concentration can be measured directly and tends to fall and rise with HDL levels.
- Apolipoprotein B is the main protein in all lipoproteins, with the exception of HDL. Reflects the danger of developing atherosclerotic lesions, thus being its marker. In addition, apolipoprotein B plays a major role in the recognition and binding of LDL by special receptors located on the membranes of almost all cells of the body, in addition to red blood cells and cells of the nervous system.
Should I raise
If the atherogenicity index is low, this is very bad, because 100% it warns of the possibility of developing many serious diseases, a significant increase in the risk of addiction to alcohol or drugs. From this point of view, it is necessary to pay attention to the following symptoms, which correspond to reduced SA:
- Severe loss of appetite;
- muscle weakness;
- fatty stool (steatorrhea);
- sudden mood swings;
- decreased sexual activity;
- decreased sensitivity to touch;
- enlarged lymph nodes for no apparent reason.
All these are indications for biochemical analysis. Detection of a reduced atherogenic index requires correction. It looks like you can heal yourself by increasing your daily intake of animal fats. However, this is a dangerous misconception. One wrong step and you will face deadly complications due to your perceived health. Only a doctor can prescribe appropriate therapy. If you have low blood pressure, you should first contact an endocrinologist, then a cardiologist, nutritionist and therapist.
Today there is no special medicine to increase cholesterol. The solution is a diet that will inhibit (or ideally prevent) the decline. The rules are quite simple:
- Total taboos on alcohol, cigarettes and drugs;
- introduction to the diet of seafood, fatty seafood, offal, pork, beef, lamb, fatty cheese, eggs in all varieties, butter, olives, olive oil;
- to neutralize LDL (“bad” cholesterol), vegetables and fruits in unlimited quantities, greens - everything that contains vitamin C (a natural antioxidant) is a must.
Movement is another way to normalize lipid metabolism. Normal cholesterol is the primary concern of the doctor and the patient.
Reasons for the decline
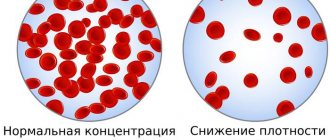
A reduced atherogenicity coefficient is a very rare phenomenon, but not dangerous; on the contrary, the risks of lipid deposition and the development of atherosclerosis are minimal.
If we talk about the reasons:
- Sports lifestyle. Or systematic physical activity at a level close to the peak of your own strength. If the patient follows nutritional recommendations, intense exercise will only be a plus. Under no circumstances should you deliberately overwork and exhaust yourself. You won't get much benefit from this.
- Systematic use of statin drugs. If a person has been undergoing treatment for a long time, there is nothing unusual in a reduced atherogenic index.
- Finally, the same thing is possible with a long-term strict diet. And not only. Supporters of a healthy lifestyle, vegetarians of various kinds are practically out of the risk zone. Because they get less cholesterol from outside.
A low atherogenic index, not reaching the average norm, is a good result, there is nothing dangerous about it. Against.