Date of publication: 04/06/2017
until January 31
You get 10% cashback when purchasing a gift certificate More details All promotions
Blood or arterial pressure is the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels. It is determined by the volume of blood that the heart pushes out per unit time, and the strength of the vascular response resistance. Pressure creates conditions that allow blood to reach organs and supply them with oxygen and the nutrients it transports. It is believed that a person’s blood pressure is normal when the heart copes with its pumping function and the blood vessels remain elastic and strong.
Lower and upper blood pressure
In a healthy person, the heart muscle contracts 60 to 80 times per minute at rest. With each contraction, the heart pumps another portion of blood into the arteries. Accordingly, the maximum blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels is recorded at the moment of contraction of the heart muscle. Between contractions, the heart muscle relaxes. At the time of such rest, blood pressure is at its lowest.
The highest reading is called systolic or upper pressure. The name comes from the word “systole” - the stage of contraction. The lowest pressure reading is called diastolic (from the word “diastole” - the stage of relaxation). Systole and diastole are stages of the normal cardiac cycle.
Pressure readings are traditionally recorded in millimeters of mercury. When measuring, the upper pressure indicator is always indicated first, and the lower pressure indicator second.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
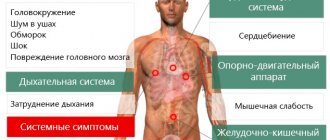
Most doctors consider chronic low blood pressure to be dangerous only if it causes noticeable signs and symptoms, such as:
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Fainting
- Dehydration and unusual thirst
- Lack of concentration
- Blurred vision
- Cold, clammy, pale skin
- Rapid breathing
- Fatigue
- Depression
A single deviation from normal blood pressure readings is not a cause for concern unless you are experiencing any other symptoms.
What pressure is considered normal?
Several factors simultaneously influence blood pressure:
- condition of the heart muscle;
- condition of the walls of blood vessels;
- the presence of deposits on the walls of blood vessels;
- person's age;
- human body type;
- a person’s lifestyle and physical activity;
- external factors, for example, region of residence.
If we summarize all these points, we can conclude that the “ideal” blood pressure is determined very individually. Of course, doctors have a standard of 120/80, but this does not mean that absolutely all people will feel good at this pressure. For example, the normal pressure indicator for petite women is 110/70, for athletes who are constantly exposed to physical activity - 130/80. A normal person may have slightly lower or higher blood pressure, and even the slightest changes will be immediately noticeable.
However, there are also extreme limits that doctors consider critical. For example, if the pressure reading is 140/90 and at the same time it tends to increase, then this is a sign of arterial hypertension. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor, and if your general condition suddenly worsens, call an ambulance.
To bring the blood pressure back to normal, the doctor may prescribe medication. In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to change your lifestyle and eating habits: give up smoking, alcohol, fatty, heavy foods.
Extremely low blood pressure, for example 90/60, indicates that the organs are not receiving enough nutrition: the brain activity of such a person is reduced, and there is a risk of oxygen starvation. Such indicators may indicate concomitant diseases: vegetative-vascular dystonia, anemia, adrenal insufficiency, etc.
What does systolic blood pressure indicate?
Any deviations of indicators from the norm indicate malfunctions in the functioning of one or another body system. Both values or only one of them can increase or decrease. For example, an increase in systolic pressure occurs when:
- Overactive thyroid gland – thyrotoxicosis, when the thyroid gland secretes too many hormones;
- Severe anemia, when the type of blood circulation changes;
- Slowing of the pulse - bradycardia, ineffective operation of the aortic valve, when the upper pressure increases due to increased blood release;
- A decrease in the elasticity of the aorta, an increase in the density of its walls - most often the cause is atherosclerosis of a large vessel in old age.
An increase in only the upper pressure without changes in the lower is called systolic arterial hypertension. But such a deviation does not always indicate a disease. So, with significant sports loads, an increase in upper pressure is also observed, and this is not considered a deviation from the norm.
Age norms for blood pressure
Blood pressure levels can change throughout life. Sometimes this is due to a person moving to another region: the body adapts to new external conditions, so the pressure can decrease or increase within 10 points. However, in most cases, changes in blood pressure are affected by age.
With age, the walls of blood vessels become less elastic, and their internal space decreases due to various deposits and “plaques”. The response resistance from the vessels weakens, and the blood stretches their walls more strongly.
With age, a person's blood vessels become clogged and narrowed.
However, experts advise not to make serious allowances for age when measuring blood pressure. In a healthy person, it is permissible to increase blood pressure with age by 10–15 mmHg. If there is a sharp jump in pressure, then this is not due to age, but rather to the development of a disease of the cardiovascular system, which is dangerous to ignore.
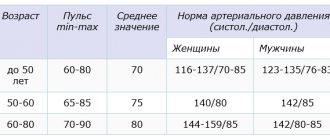
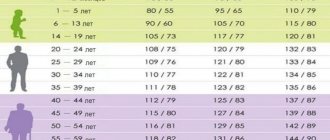
Average age-related blood pressure norms in young men are slightly higher than in women, which is explained by greater muscle mass. However, with age, the rates for both sexes become approximately the same. Changes in indicators with age can be presented in the following table.
Indicators of upper and lower pressure depend on the age and gender of the person
Doctors recommend measuring blood pressure regularly and monitoring its levels starting at age 30. From the age of 40 years and over, measuring blood pressure should become a daily procedure.
What you need to know about diastolic pressure?
The diastolic pressure indicator characterizes the degree of resistance of blood vessels and their permeability to blood. The health of the vascular system is determined by two main factors: the elasticity of their walls and the functioning of the kidneys. The human body contains a large amount of fluid; without its circulation, metabolism is impossible, and blood plays a crucial role in this process. It passes through the kidneys, which act as a kind of filter, regulate water-salt balance and remove toxins from the blood along with urine.
With this mechanism, an increase in diastolic pressure is usually associated with a violation of the removal of fluid from the body, an increase in its volume and an increasing load on the walls of blood vessels. If lower blood pressure exceeds normal levels for a long time, the risk of heart attacks and strokes increases. If it decreases for a long time, problems arise with the supply of oxygen to tissues and organs. Because of this, dizziness and fainting occur, especially during physical activity.
The causes of low diastolic pressure may be bleeding, prolonged hunger and dehydration, allergies with anaphylactic shock. The indicator decreases with insufficient production of the hormone renin, which regulates vascular tone. The decrease also occurs due to stress, fatigue and tuberculosis.
Blood pressure measurement
Modern devices for measuring pressure are either mechanical or electronic. When using a mechanical pressure gauge, a phonendoscope is required, with which you can hear the beginning and end of the stages of systole and diastole.
Blood pressure is measured while sitting or lying down. In order for the readings to be accurate, the pressure gauge should be at the level of the person’s heart, and the cuff should be approximately 2 cm above the elbow. Air is pumped into the cuff, causing compression of the blood vessels and the disappearance of the pulse, and then slowly released. The point at which clearly visible pulse beats appeared is noted as an indicator of upper pressure, and the point at which these beats disappear is noted as an indicator of lower pressure. An electronic pressure gauge works without a phonendoscope; in this case, indicators of upper and lower pressure, as well as pulse, are recorded automatically and displayed on the screen.
The availability of modern devices for measuring blood pressure and the ease of their operation allow everyone to regularly monitor this important vital sign of their own body and take timely measures if such a need arises.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Characteristic symptoms of hypertension and hypotension
At the first stage of hypertension, pressure surges up to 159/99 mm Hg occur. Art. Most often, malaise occurs after severe overwork or stress. Patients note an increase in heart rate and headaches, weakness, and increased nervous excitability.
At the second stage, the following symptoms include: deterioration of sleep, nosebleeds, pain in the heart, severe headaches. Blood pressure rises to 160–170/100–109 mmHg. Art.
The third stage of hypertension is a serious disease that irreversibly affects the entire human body. This stage is characterized by cardiac dysfunction, chronic renal and heart failure, heart attack, and angina.
Important! If at the first stage the patient’s condition can be corrected and the disease goes away almost without a trace, but stages 2 and 3 of hypertension are practically not curable. The goal of the doctor and his patient is to monitor the condition and regularly take antihypertensive drugs that can stabilize the patient’s well-being for some time.
Low blood pressure manifests itself differently. A person suffers from headaches, which are localized in the temporal region, loss of strength, drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, and fainting. Symptoms worsen during weather changes, magnetic storms, and during acclimatization.
Both hypertension and hypotension require treatment. What it will be like and how long it will last depends on the patient’s health condition. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the treatment regimen drawn up by the doctor, without independently increasing or decreasing the dosage of drugs.
Conclusion
The optimal difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is 70
is 40 mmHg. But a slight deviation of 10 units up or down is also within acceptable limits.
blood pressure prevention
If the pressure changes by 20 more or less, and you feel normal, most likely there was an incorrect pressure measurement. If your health really gets worse, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In case of difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
is sixty or more, this is the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases. In this case, you must constantly consult your doctor. To make an appointment with our specialist, leave a request on the website or call.
How to measure
To obtain accurate results, pressure must be measured correctly (you can learn about methods for measuring blood pressure in this article). Its value depends on many factors, namely physical and emotional stress. Therefore, ideally you need to measure it in the morning, without getting out of bed. In other cases, you may need to rest for about 10 minutes before the procedure. The tonometer should be at the level of the heart, and the arm in the cuff should be placed horizontally at the same level. To obtain a more reliable result, you need to measure blood pressure 2-3 times with a short interval and calculate the average value. Together in blood pressure, the pulse is measured.
A tonometer is used to measure blood pressure. There are mechanical (mercury and aneroid) and electronic (semi-automatic and automatic) devices. In mechanical dial models, air is pumped into the cuff manually, the tones are listened to using a phonendoscope, and the result can be seen on the dial.
The choice of tonometers today is wide - from old mercury devices to compact electronic
The oldest are mercury tonometers, which are practically not used today. They are bulky and require skill to use and careful handling, as there is a risk of damage to the flask. Modern mechanical tonometers are compact and more convenient to use. In general, mechanical instruments are considered durable, reliable and accurate. The big plus is that their work and results are not affected in any way by interference, such as conversation, moving a hand, and others.
Electronic devices are very easy to use and do not require any skills. The air is pumped by a device for automatic ones and manually for semi-automatic ones. The results (upper blood pressure, lower blood pressure and pulse) are displayed on the display. They are intended, rather, for measuring blood pressure at home. As a rule, they are not used in medical institutions.
Norms by age
Previously, it was believed that normal blood pressure could increase with age. If for young people it should be 120/80, then for a person over 60 years old a value of 150/90 was allowed. Today, doctors say that there are no age-specific blood pressure standards for adults. Normal blood pressure is the same for everyone, with the exception of children.
High blood pressure is more common in older people
What is the importance of diastolic blood pressure
Diastole refers to an indicator that includes two important factors:
- The first one determines the tension or relaxation of the capillary line. With strong compression, the diastole will be higher, which indicates a malfunction occurring in the cardiovascular department, a high risk of hypertensive syndrome. When the level is reversed, a drop in diastolic blood pressure is observed.
- The second indicates the degree of relaxation of the heart muscle during diastole. If the data is bad, the issue is related to the lack of normal rest and the heart working hard. Regular overloads over time provoke various pathological changes against the background of wear and tear.
Recorded changes should not be ignored. A timely visit to the clinic will allow you to catch the disease in the early stages, avoiding its severe course and many complications.
Some numbers
There are more than 95 thousand kilometers of blood vessels in the body of a healthy adult. More than seven thousand liters of blood are pumped through them every day. The size of the blood vessels varies from 25 mm
(aortic diameter)
to eight microns
(capillary diameter).
Down with atherosclerosis!
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common vascular diseases. It is characterized by the formation of fatty plaques on the walls of the arteries. Find out how to prevent atherosclerosis.