Formed blood cells perform basic functions that ensure the functioning of the body as such. The following structures can be found in liquid connective tissue:
- Red blood cells. They carry oxygen and transport carbon dioxide. Without these cells there cannot be normal tissue respiration.
- Leukocytes. White bodies. They act as a kind of protective structures, working to protect the body.
- Platelets. Red records. Provide blood clotting. Closing wounds.
Some laboratory indicators are based on artificial methods for assessing conditions. These include ESR. The abbreviation stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
ESR is a formal level that shows the onset and course of inflammatory, and less commonly, cancer and other pathological processes. There can be many options. In some cases, the speed increases due to natural reasons.
The underlying pathological process needs to be treated. The intensity of red blood cell sedimentation itself is not considered a disorder. This is a formal indicator, a feature that develops against the background of diseases.
When is a test ordered?
There are many reasons for diagnosis. As a rule, the study is carried out directly as part of a general blood test. If we talk about situations when the procedure is prescribed:
- Increased body temperature. Almost guaranteed to indicate inflammation of an infectious or autoimmune nature.
- Signs of a septic process. It doesn’t matter which one: from a simple cold to more complex disorders such as tuberculosis, herpetic conditions and others.
- Inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid and other forms of arthritis.
- Pain of any localization.
- Disturbances of the normal menstrual cycle.
- Pregnancy. The study is carried out as part of regular screening. The erythrocyte sedimentation reaction in women is the first to show inflammatory processes. They are destructive during gestation, as they can affect the child in the most negative way.
- Preventive examinations. As part of preventive diagnostic measures, inflammation and other abnormal conditions are excluded. Examinations are scheduled every six months or less often. Depends on the source data.
- Study of the dynamics of the pathological process against the background of treatment. Simply put, by the rate of cell sedimentation you can understand how the disease behaves, where to move next, and how to adjust the therapeutic course.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a natural reaction, but during inflammatory processes, oncology, and congenital anomalies, the cells stick together, forming complexes.
They have a higher density, so they naturally sink faster to the bottom of the test tube with the solution. The intensity of this process is used to assess the patient’s health status.
What does erythrocyte sedimentation rate show?
Based on diagnostic results and a general blood test, the following disorders can be identified:
- Any infections. From colds, ARVI to sexually transmitted diseases and others.
- Autoimmune disorders. Inflammatory conditions associated with changes in the activity of protective forces.
- Cancer, oncological processes.
- Disorders of the endocrine system. Quite rare, but a possible cause of change.
Be that as it may, ESR is a nonspecific indicator. Therefore, it is impossible to provide accurate information and make a diagnosis only in this way. Additional measures are required.
Treatment
Patients are often interested in the question: when can an increase in ESR be considered safe? A deviation of no more than 5 mm/h is considered acceptable. After 3–5 days, you should re-take the test in the same laboratory department.
Consistently high results with double repetition of the analysis require additional diagnostics (leukocyte formula, C-reactive protein, biochemical blood test, etc.).
After the doctor has made a final diagnosis, he selects treatment methods. Treatment of infectious inflammatory diseases begins with identifying the pathogen. If a bacterial nature is detected, a test is performed to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to known groups of antibiotics. After which preference is given to the antibiotic with the maximum effect on pathogenic bacteria.
When a fungal infection is detected, the most effective antimycotic drugs are similarly selected. Treatment of diseases of viral etiology consists of the use of a complex of drugs with antiviral and immunomodulatory activity. Mixed infection requires the use of several groups of drugs.
Tables of norms by age
The ESR norm for women is 3-17 mm/hour and practically does not change throughout life. Age data is presented in the table:
| Age (years) | ESR norm (mm per hour) |
| 0-15 | 3-17 |
| 15-25 | 3-16 |
| 25-35 | 3-15 |
| 35-55 | 3-15 |
| 55-70 | 3-15 |
| 70 and older | 3-15 |
In women after 50-60 years, the ESR norm may deviate upward, at the level of 1-2 mm, this is acceptable.
In pregnant women, the normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 20-25 mm/h. It is necessary to systematically monitor the woman’s condition so as not to miss pathologies.
Research methods
There are 3 main methods by which ESR blood tests are performed:
- according to Panchenkov, the essence is to collect the blood being tested (venous or capillary) into a sterile graduated capillary along with an anticoagulant (ratio 1 to 4) - a substance that prevents clotting. After which the capillary is fixed in a vertical position on a tripod. The height of the resulting translucent plasma column is measured “by eye” after 1 hour. The established value is the result of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The maximum value is 100 mm/h. The disadvantage of the technique is subjectivity when assessing the height of the column;
- according to Westergren, venous blood is mixed with an anticoagulant (4:1) and placed in special tubes with a scale from 0 to 200 mm. The test tubes are placed in a vertical rack, and the resulting column is measured after 1 hour. The technique is recognized internationally and is considered preferable compared to the Panchenkov method, since it allows you to expand the maximum permissible limit (up to 200 mm/h) and is characterized by greater sensitivity;
- capillary photometry, implemented on special analyzer devices. The process is fully automated. It was noted that insufficient mixing with the anticoagulant can lead to the formation of microclots of erythrocytes, which significantly distorts the data obtained. In automatic analyzers, due to the continuous mixing of the biomaterial with the anticoagulant, the formation of microclots is excluded. Measuring range capabilities from 2 to 120 mm/h. A direct correlation of the results of the method with the data of the Westergren analysis has been reliably established.
Reasons for the increase
Factors that increase the indicator are almost always pathogenic. Although, there are exceptions.
Infectious inflammatory processes
Various forms of septic conditions. It can be anything.
Three groups can be distinguished:
- Bacterial lesions.
- Disorders of the body under the influence of viral agents. For example, herpes, influenza, adenovirus and others.
- Fungal disorders. They are relatively rare.
The symptoms of the disorder depend on the specific case. As a rule, the following problems are always present:
- Increase in body temperature. Up to levels from 7 to 40 degrees and even higher. It all depends on the specific pathological process.
- Headaches, discomfort of other localization.
- Weakness, drowsiness. Signs of general intoxication of the body.
For the rest, you need to build on a specific diagnosis.
Treatment is specific, depending on the condition:
- Antibiotics are prescribed in loading doses.
- Antiviral drugs help fight infections.
- Fungicides fight fungi.
- To lower the temperature, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal origin are used.
Next - depending on the situation. The issue should be resolved by a specialized specialist or, at a minimum, a therapist.
Autoimmune inflammatory processes
Another kind of pathological condition. In this case, we are talking about a nonseptic lesion. That is, infectious agents are not involved here. The body itself reacts to a non-existent threat.
The immune system begins to attack the cells of its own body, the host. The process becomes cyclical and practically never ends if you don’t fight it. All that remains is to correct the symptoms.
Among the most common forms of the disorder:
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammatory process of the joints. Usually affects large structures. Be it knees, elbows or hips. Occurs in patients of different ages.
- Rheumatism. A destructive process affecting the myocardium. Characterized by systematic relapses and exacerbations.
- Lupus erythematosus. Generalized autoimmune inflammation.
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Damage to the thyroid gland. It occurs relatively rarely, but poses a huge danger to the body.
Treatment depends on the specific pathological process. ROS (erythrocyte sedimentation reaction) normalizes on its own, some time after the main therapy.
Glucocorticoids are prescribed. Prednisolone and more powerful analogues, if required. If ineffective, immunosuppressants are used.
They reduce the intensity of the reaction of the defense forces. That those that other drugs cannot be taken for a long time. Too dangerous for your health. Lots of side effects.
Oncological processes
Cancer almost immediately leads to an increase in ESR in women and not only. The more advanced the condition, the worse the health situation.
The speed increases gradually, not rapidly. Therefore, a violation can go unnoticed for a long time. It makes sense to conduct a thorough diagnosis in addition to a general blood test.
It doesn’t matter where exactly the tumor is located. What is more important is what stage it is at.
Symptoms of advanced cancer are specific. There are always common signs:
- Increase in body temperature. Due to the disintegration of the tumor and poisoning of the whole body.
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- Abnormally thin. Weight loss. Related to the same thing.
Recovery is carried out under the supervision of an oncologist. The goal is to remove the tumor. It is solved surgically by excising the abnormal structure.
Then, if appropriate, radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed to eliminate any remaining neoplasia and prevent it from growing again.
After quality treatment, the ESR decreases. Normalization is temporary until a relapse occurs (if there is one at all).
Endocrine diseases
The above pathologies are especially common. As for hormonal imbalances, this is a relatively rare cause of changes in ESR.
However, a woman’s body is more sensitive to fluctuations in the level of specific substances. Therefore, the reason is more common than in men.
Thyroid pathologies can cause disturbances in sedimentation rate. Among them are qualitatively different:
- Thyrotoxicosis. When there are too many substances. T3 and T4 are produced in excess and poison the entire body.
- Hypothyroidism. The opposite phenomenon. In this case, the concentration of hormones decreases.
Symptoms of pathological processes will be diametrically opposite.
For hyperthyroidism, this is:
- Loss of body weight.
- Protruding eyes.
- Weakness.
- Insomnia.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Cardiac dysfunction, tachycardia.
With insufficient production of substances, everything is exactly the opposite.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of an endocrinologist. To correct the increased amount of T3 and T4, iodine preparations and a diet low in this element are prescribed.
The reverse process is treated with substitutes, artificial forms of the hormone.
The task is complex, but can be solved under the guidance of a competent doctor. It may well be that secondary changes will develop. For example, a decrease in estrogen concentration.
In such a situation, other disorders also need to be treated. Otherwise, they themselves can lead to an increase in ESR. Here you need the help of an endocrinologist and gynecologist.
Poisoning, intoxication
Some toxic substances can lead to aggregation of red blood cells, their sticking together and death.
These include, for example:
- Salts of lead and other heavy metals.
- Vapors of chemical compounds, acids.
- Organic poisonous components.
In any case, urgent treatment in a hospital is needed. It is quite difficult to encounter poisons in natural conditions.
Violations occur especially often when:
- Working in hazardous industries. If a woman performs functions directly in the workshop.
- Consumption of food that has been fertilized with harmful fertilizers.
- Poisoning often occurs when using mushrooms that grow in questionable places. For example, in the area of disposal of lamps, waste, garbage.
Be that as it may, the patient is transported to the hospital. It is necessary to detoxify and restore the functioning of the body.
The ESR norm in women is restored within several weeks to an adequate 3-15 mm/h, and by this indicator one can judge the dynamics of the process and the quality of therapy.
Some forms of metabolic disorders
They should not be confused with endocrine disorders. Here we are talking about problems with metabolism.
Among the possible pathological processes:
- Amyloidosis. Deposition of a specific compound in tissues.
- Hypercholesterolemia. Especially its family types, when too many fats circulate in the body and they are not excreted normally.
There are other forms of pathological processes. The point is that they lead to a rapid increase in ESR rates. You need to fight the primary diagnosis in order to cope with the disorder.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of endocrinologists. The course depends on the specific diagnosis.
Use of certain drugs
From the point of view of the female body, estrogens are especially dangerous. You can find synthetic hormones in oral contraceptives.
Birth control pills are very difficult medications. They should be taken with caution and strictly in the prescribed dosage. Not for long, so as not to provoke violations.
Of course, few people follow these recommendations. As a result, a group of symptoms develops, in addition to an increase in ESR:
- Sudden changes in body weight. Usually, the weight increases.
- Mental disorders. Emotional instability, depression, irritability and aggressiveness. Other changes. Need help from a psychotherapist.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Reproductive disorders. It becomes impossible to conceive a child. This will continue until the hormones return to normal.
Changes in ESR are indicative, but not the biggest problem in the context of the situation. Treatment is carried out by endocrinologists.
The drug is discontinued and replacement therapy is prescribed.
Attention:
Hormonal levels, as a rule, do not return to normal on their own; this is very rare.
Natural causes
{banner_banstat9}
Not in all cases, the increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is due to pathologies. There are also normal factors. If they are affected, no special treatment is needed.
Physiological aspects include:
- Beginning of the menstrual cycle. Until the hormonal levels stabilize. In this case, it makes sense to notify the doctor about your condition. To prevent the results from being misinterpreted.
- Pregnancy. All phases of gestation are associated with an increase in ESR. It's quite normal. In addition, the further the process, the higher the indicator. There's no need to worry.
- Exercise stress. Any. Immediately after, for several hours, the level will be elevated. The norm of ESR in the blood of women will recover to 3-15 mm/l on its own, after a short time. This must be taken into account when preparing for examinations and blood donations.
- Stressful situations.
- Lack of fluid in the body. Leads to the same results. You need to make up for the deficiency and only then get tested. This factor should be taken into account when preparing for the study and adhere to the optimal drinking regime.
An increase in ESR in women in approximately half of the cases or slightly more is associated with pathological processes. Further, if the non-pathogenic nature of the changes is proven, you can look for natural factors.
What is ROE and its significance for the body
What is RO ESR (ESR)—erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The analysis is one of the main basic blood tests. A referral for examination is issued upon initial consultation with a doctor, before medical procedures or surgical interventions.
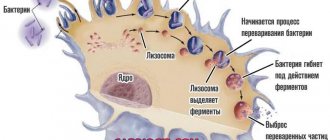
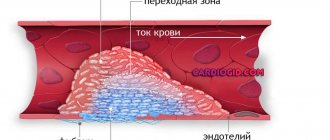
Laboratory essence of the method: healthy red blood cells precipitate slowly. Aggregated (glued) red blood cells have a greater mass and settle at a faster rate. Factors that indicate the activation of the immune response to pathology in the body lead to the sticking of red blood cells.
The erythrocyte sedimentation reaction is a nonspecific laboratory indicator that indirectly indicates pathological disorders in the body. Based on ROE, a final diagnosis cannot be made, but the direction of further research can be determined.
Reasons for the decline
{banner_banstat10}
This condition is less common. Among the provocateurs:
- Anemia of several types. Accompanied by changes in the concentration of red blood cells. The classic form that is dangerous in this context is the hemolytic variety.
It leads to immediate and rapid destruction of red blood cells. The rest begin to form complexes. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate decreases to significant limits.
- Excessive amount of fluid in the body. Overhydration. As a rule, it is associated with a violation of the water-salt balance. For example, if a person consumes too much sodium chloride. The so-called table salt.
There are other factors too. Another option is a psychological urge to drink a lot, diabetes insipidus, thirst. The correction is simple. The goal is to normalize the water regime.
- Lung pathologies. A low ESR in the blood of women is detected during inflammatory processes from pneumonia to tissue degeneration of a paired organ. The treatment is specific. The underlying disease must be eliminated. The ESR will return to normal on its own.
- Disorders of the digestive tract. Most often, stomach disorders: ulcers, gastritis.
- Liver diseases. Hepatitis, cirrhosis.
There are also genetic disorders. It’s difficult to fight them because you can’t radically influence the situation. All that remains is to work with the symptoms.
How to prepare
The duration of the analysis does not exceed 5-10 minutes. As a rule, the procedure is accompanied by slight pain and discomfort in the puncture area, but the discomfort passes very quickly. If capillary blood is needed, then before piercing the third or fourth finger of the left hand, the skin in this place is treated with an alcohol cotton ball. After this, using a special medical blade, a small incision is made on the fingertip (its depth does not exceed 3 millimeters). The resulting drop of blood is disposed of with a sterile napkin, after which the laboratory assistant proceeds to collect the biomaterial. Having collected the required amount, the wound surface is lubricated with an antiseptic, and a cotton swab with alcohol is applied to the puncture site.
If the analysis involves taking biomaterial from a vein, then the patient’s forearm is tightened with a medical tourniquet or strap, after which he must work a little with his fist (clench and unclench) for better vascular filling. The site of the intended puncture is treated with an alcohol wipe, after which a needle is inserted into the selected vessel, to which a test tube is connected to collect the released blood. Having collected a sufficient amount of biomaterial, the needle is removed, and a cotton swab with alcohol is applied to the wound.
To calculate ESR, an anticoagulant is placed in the biological material to prevent clotting. Then it is sent to a vertical container for 60 minutes. Since the specific gravity of red blood cells exceeds the weight of plasma, gravity forces them down to the bottom of the container. Because of this, 2 visible layers are formed in the test tube: the upper (colorless plasma) and the lower (erythrocyte accumulations). Then the laboratory assistant takes measurements of the top layer. The indicator corresponding to the mark between the red blood cells and the plasma zone on the test tube scale is ESR (indicated in mm/h).
Today there are 2 main ways to detect ESR:
- Panchenkov's method. The capillary is divided into exactly one hundred compartments, and later 5% sodium citrate is added to it to the “P” level. Then the capillary is filled with biomaterial up to the letter “K”. The resulting mixture is mixed and installed vertically. The assessment takes place after 60 minutes.
- Westergren method. Here, venous blood is used, mixed with sodium citrate 3.8% in a ratio of 4:1. It can be mixed with Trilot B followed by the addition of sodium citrate or saline solution in an amount of 4:1. The study is carried out in test tubes equipped with a 200 mm scale. The result is assessed after 60 minutes. This technique is used everywhere, and its main distinguishing feature is the type of test tubes and measuring scale used.
Despite the coincidence of the results of these methods, the Westergren method is famous for its greater sensitivity to exceeding the ESR indicator, and therefore it is considered highly accurate and informative.
Additional examinations if the ESR deviates from the norm
Supporting activities include the following methods:
- Oral interview with a person. It is necessary to identify complaints and symptoms of the alleged pathological process.
- Anamnesis collection. To determine the characteristic origin of the disorder. The issue is resolved quickly, right in the doctor’s office. But the results allow us to develop a further diagnostic strategy.
- Biochemistry of venous blood. To find specific markers of autoimmune inflammation, as well as other indicators like bilirubin.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract. To detect possible gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Serological tests, PCR, ELISA. Within the framework of these methods, infectious processes are studied.
- Chest X-ray.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones, specific sex substances (estrogens).
Usually this is enough.