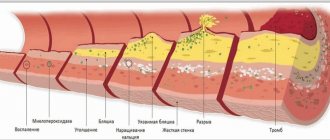
The prothrombin index is a diagnostic indicator that demonstrates the speed and quality of blood clotting. The calculations are based on the proportional ratio of the time required to change the properties of the plasma and the period taken as the conventional norm.
Next, based on the calculation results, a certain percentage is obtained, which becomes the desired value. Adequate levels are determined by age, but in general, there are no significant differences between years.
The prothrombin index (abbreviated PTI) is used in the practice of hematologists for early examination and detection of various forms of diseases and coagulopathies.
Treatment is not always necessary. Transient types of disturbance are possible. Next, corrective measures are prescribed as needed. Strictly under the supervision of doctors.
The role of prothrombin in the body
The protein prothrombin acts as one of the blood coagulation factors (second factor (FII). The compound takes part at a certain stage of regulating the rheological properties of liquid tissue (its fluidity).
By nature, it is a precursor of another enzyme, thrombin. But it does not have all the properties of its own conditional metabolite. If we talk about functions, they will be like that.
Ensuring normal clotting
This task is solved only when some damage is present. Internal or external, it does not matter in the context of the situation. Under natural conditions, when everything is in order, coagulation factors are in an inactive state. That is, they do not function and do not make themselves known in any way. As soon as the need for them arises, specific processes begin.
Prothrombin and its enzymatic metabolite behave in an identical manner. As soon as bleeding begins, substances, also in addition to those mentioned, provide a rapid change in the properties of the liquid connective tissue, which leads to a decrease in the rate of bleeding, and then to its cessation.
The process does not occur in isolation; another factor, platelet aggregation, also plays a major role in it. These two physiological phenomena form the basis and bring the condition back to normal. Otherwise, a person would die from a simple cut.
However, problems also arise with an increase in the activity of prothrombin and coagulation factors in general. Hypercoagulation begins, the blood becomes too viscous. Specific clots (thrombi) appear, they block the channel and clog the vessels.
This could end extremely badly. Therefore, the function is launched only when the named indicator is within acceptable limits. Not elevated and not below normal.
Indirect regulation of inflammation processes
The second function is less noticeable and not so obvious. To a greater extent, this property is inherent in thrombin, but its predecessor also has a certain potential in this area.
Control over the phenomenon occurs bilaterally. Both strengthening and weakening. Depending on the current physiological state of the body.
Both tasks are solved in parallel, dynamically. That is, at the moment when the situation, the patient’s condition, requires it.
Preparing for the test
The most accurate result of a screening test is obtained if the patient follows all the conditions for taking the test.
Blood sampling traditionally takes place in the morning.
In this case, you must follow some rules:
- Eight-hour fasting before taking material;
- Refusal to take any liquid other than water on the day of blood donation (alcohol, black or green tea, and coffee have a particularly negative effect on the objectivity of the test result);
- Discontinuation of any medications associated with changes in blood clotting properties no later than 1-2 weeks before the test. It is ideal to carry out the analysis before starting their schematic intake, if possible;
- Notifying the treating or supervising specialist about taking medications if it was not possible to complete their course in a timely manner;
- Avoid heavy physical activity and conflict situations (or other psycho-emotional stress) the day before the test;
- Limit fatty and fried foods a few days before the test.
It is important to limit smoking at least 1-2 hours before taking blood for analysis.
Indications and rules for taking the test
There are many reasons for prescribing such diagnostics and checking the prothrombin index. These are not only diseases, but also specific cases. To be more specific.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Damage to the largest gland in the human body. It is based on the death of tissues and hepatocyte cells. Necrosis.
Depending on the type of pathological process, we are talking about an acute or chronic variant of the course.
- In the first case, there is no point in the examination at all. Because everything is developing so rapidly that the essence is obvious and there is no time left for additional activities. We urgently need to act.
- In the second case, it makes sense to regularly check the prothrombin index, since PTI directly indicates the quality of liver function.
This makes it possible to monitor the dynamics of the condition, identify progression, and even evaluate the quality of the treatment provided.
It must be said that thrombin is a substance produced in the liver. Hence this diagnostic possibility. Based on the results, it is worth talking about complete, sub- and decompensation of cirrhosis. And act according to the situation.
Preparation for surgery
As a rule, doctors do not limit themselves to a standard coagulogram. If major surgical treatment is planned, it makes sense to conduct a more in-depth study.
This will allow you to obtain information about the patient’s condition, plan possible negative scenarios and prepare for hemostasis during surgery.
The question of necessity is determined by the doctor. It is also possible to prescribe diagnostics after a standard coagulogram if there is reason to doubt the completeness of the results.
Vitamin K or C deficiency in the body
In both cases, destructive processes begin. In the first, a change in the condition of blood vessels and arteries is observed, in parallel with a deviation in the rheological properties of the blood, with an increase in the activity of specific enzymes.
In the second, a disease known as scurvy manifests itself. It provokes massive bleeding, disruption of the strength and elasticity of connective tissue (hence the notorious symptoms such as loosening and loss of teeth, etc.).
The prothrombin index changes in parallel with the progression of the pathological process, immediately. Therefore, using this indicator, violations can be diagnosed in a timely manner.
Monitoring the state of the blood during systematic use of specific drugs
Anticoagulants and other medications. Screening is carried out on a regular basis to detect abnormalities. They do not always occur, but when they develop there is a high probability of complications, even fatal.
The risk of blood clots increases as you take the drugs. It is quite difficult to assess them in advance.
The prothrombin index varies within significant limits. In the high-risk zone are persons who are initially prone to the development of pathological processes in the circulatory system.
Pregnancy
Gestation is a significant risk factor for patients. In the process, a change in hormonal levels is observed. The elasticity and strength of blood vessels, the rate of production of coagulation factors, in particular prothrombin and its metabolite, depend on the concentration of estrogen.
The values do not always deviate and health problems do not begin in all cases. Diagnostics is more a measure of prevention, screening and verification, rather than a specific identification of a pathology that the doctor suspects.
It is enough to take the test once every 2 months. More often as needed and at the discretion of the doctor.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
The communication here is two-way. Patients with a history of similar problems are highly likely to experience changes in the rheological properties of the blood.
However, the processes are often secondary and provoked by the same factors. That is, both a violation of the prothrombin index and cardiovascular pathologies themselves manifest for identical reasons. This must be taken into account when diagnosing.
It makes sense to prescribe an examination for proven blood pathologies. As a screening method, assessing the dynamics of the disorder.
Prothrombin time
What is a coagulogram?
A coagulogram is a special study of a patient’s blood sample in a laboratory setting, which can be used to qualitatively and informatively monitor the functioning of hemostasis. This is a complex biosystem that is responsible for maintaining blood fluidity, maintaining a number of processes aimed at stopping bleeding, as well as the timely dissolution of dense blood clots.
The study of hemostasis is also called a hemostasiogram.
In order to maintain basic body functions, blood must be:
- Moderately liquid in order to maintain the ability to transport oxygen and nutrients through vessels to tissues and organs, remove decay products and toxins from the body, maintain the functioning of the immune system, and regulate body temperature;
- Moderately viscous to quickly close holes in large and small vessels in case of traumatic and other types of damage.
In cases where blood clotting is reduced to critical levels, bleeding can lead to massive blood loss and even death of the body.
If we are talking about excess thickness and increased coagulability, there is a high probability of blood clots forming. They can block the most important vessels and cause problems such as thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
A coagulogram is a very important analysis. A properly functioning hemostasis system prevents life-threatening blood loss, as well as the formation of blood clots and blockage of the vascular bed with blood clots, which can lead to unpredictable consequences and even sudden death.
Coagulogram – assessment of blood clotting. Based on the results of the analysis, hidden and obvious pathologies of the body can be detected. Venous blood is used as biological material for research.
This is a complex study, because it is necessary to evaluate each blood parameter separately and analyze all indicators as a whole.
Types of analysis
During the coagulogram, a huge number of parameters are studied. Each of them is important and is responsible for a specific hemostasis function.
Today there are two types of coagulogram:
- Simple;
- Extended.
A simple hemostasiogram helps confirm or refute the presence of problems in the blood clotting system. With the help of this analysis, the doctor can understand where exactly the deviation from the norm is located. If a specialist suspects the presence or development of a pathology, an extended coagulogram is prescribed.
Detailed analysis can also be called quantitative. It implies not only the fact of qualitative changes, but also the definition of specific indicators in numbers.
During a complete coagulation analysis, a number of blood clotting factors are taken into account. Deviation of any indicator from the norm can lead to serious problems for the entire body. Therefore, a simple coagulogram is considered as indicative - it does not provide specific data.
A detailed hemostasiogram is carried out both according to the indications of a specialist to diagnose a number of diseases, and as a standard procedure - before operations, during pregnancy, when taking anticoagulants.
Decoding the prothrombin test according to Quick: table
| Age (years) | Norm (%) |
| Until 6 | From 80 to 100 |
| From 6 to 12 | From 79 to 102 |
| From 13 to 18 | From 78 to 110 |
| From 19 to 25 | From 82 to 115 |
| From 26 to 45 | From 78 to 135 |
| From 46 to 65 | From 78 to 142 |
Table of norms by age
The normal level of PTI in the blood ranges from 50 to 150% according to INR and 75-142% according to Quick. Gender does not matter; the indicators will be the same for women and men; they change only with age and during pregnancy.
When interpreting diagnostic results, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the organism. Minimal deviations in one direction or another are possible.
| Age | Indicator in percentage (%) |
| Birth before the end of the first day | 60-140 |
| 1 month | 60-120 |
| Up to 1 year | 55-100 |
| 1-6 years | 70-150 |
| 6-15 years | 50-145 |
| 15-18 years old | 55-150 |
| After 18 years and before biological death | 71-140 |
As mentioned earlier, survey results are usually presented as percentages. This is the so-called INR or international normalized ratio.
Its essence is in the proportional calculation of the prothrombin time of a particular subject and an indicator that is generally accepted as adequate in general, multiplied by one hundred.
It is possible to use an absolute indicator in seconds, but this technique is used less frequently.
Norms during pregnancy
During gestation, the maximum upper limits are slightly higher, which is due to the need to more actively “displace” blood through the vessels in order to get rid of fetal waste products.
Typically, the prothrombin index in such patients is considered according to Quick. Normally, it ranges from 75 to 142%, and in pregnant women the level is defined as 98-152%. Plus or minus. Depending on the case.
Deviations should be considered as a potential disorder; only by proving the opposite can one calm down. Otherwise, there are no differences.
During the entire gestation period, the prothrombin index is approximately identical and does not change within significant limits.
Decoding INR
The international normalized ratio is a classic technique. Only one test tube is used, which reduces accuracy, but at the same time allows for rapid research.
The indicator, in contrast to the more detailed method (according to Quick), deviates insignificantly. At least not to the extent that the changes are critical and do not allow clinically correct conclusions to be drawn. That's why this variation is used more often.
The INR can be calculated as a percentage or as a coefficient. The first option was discussed in the table above, and in the latter case it is determined by a decimal fraction, and the range from 0.82 to 1.15 is considered normal. For diseases of the cardiovascular system and lungs, it is possible to increase the level to 3.0.
Content
- Blood clotting process
- Prothrombin time indicators
- Determination of prothrombin time according to Quick
- Methodology for studying prothrombin time
- Indications for prescribing prothrombin time analysis
- Prothrombin time indicators during pregnancy
The coagulation and anticoagulation systems of the blood determine the continuous flow of blood in the vessels, thereby ensuring all the vital functions of the body.
The anticoagulant system keeps the blood fluid, while the coagulation system prevents possible bleeding by forming blood clots.
Reasons for the decline
Taking into account the observed shifts, the formal prothrombin index is normally determined by the limit of up to 150%. This also includes some errors during the examination and individual characteristics of the body. Anything less clearly indicates problems.
PTI in the blood decreases as a result of the influence of pathological factors:
- Congenital anomalies in which insufficient fibrin protein is produced. This substance is involved in the binding and aggregation of platelets, its activation is provided by coagulation factors. With pathologies of this kind, the prothromboin index decreases. Depending on the nature of the process and the body’s ability to compensate for the violation.
- Congenital diseases, all forms of coagulopathies.
- Liver disorders. Which are not associated with the destruction of its tissues. These are mainly functional disorders. They are difficult to diagnose using routine tests such as ultrasound. Scintigration is required, laboratory tests may be performed.
- Often, a decrease in the prothrombin index is detected in the process of taking drugs to influence the rheological properties of the blood. Be it Aspirin and its analogues based on acetylsalicylic acid or modern medications for thinning. Especially often, abnormal results are obtained after finishing taking thrombolytics, which have an even more aggressive effect on fluid connective tissue.
- DIC syndrome.
- Other drugs also have a negative effect on the blood. For example, laxatives due to the active removal of fluid from the patient’s body.
It is not recommended to use nicotinic acid for a long time, as well as drugs to suppress the patient’s immune system. Methotrexate is especially aggressive.
Hormonal drugs and anabolic medications manifest themselves in the same way. If problems are detected, the course of therapy should be reconsidered.
If the deviations are purely laboratory in nature and do not manifest themselves objectively, moreover, there is no such tendency, it is possible to continue treatment.
A low prothrombin index indicates excessive blood thinning and prolonged clotting; spontaneous bleeding of varying degrees of intensity is possible.
Relevance of the analysis
A prothrombin time test is performed to monitor dynamics during anticoagulant treatment, diagnose the causes of bleeding, and identify a tendency to form blood clots.
The study is recommended before surgical treatment of patients (including minor interventions in vascular surgery).
Our specialists prescribe a screening test for prothrombin time for the following diseases (or suspicions of them):
- PE (pulmonary embolism);
- Myocardial infarction;
- Deep vein thrombosis;
- Infarction of the intestines and kidneys;
- DIC syndrome;
- Pre-infarction state or micro-infarction.
In addition, it can be included in the range of diagnostic measures to identify oncological pathologies, severe chronic liver diseases, and polycythemia.
A coagulogram is included in the standard package of preoperative studies. It is also used to determine the causes of bleeding of various locations and etiologies (in particular, internal).
Reasons for the increase
If the prothrombin index is elevated, this is evidence of excessive activity of proteins and enzymes that ensure normal coagulation. This phenomenon occurs less frequently. The main danger is the increased risk of blood clots.
There are relatively few formation factors:
- Malignant processes in the body. Cancerous tumors of any location. Mainly those that affect the bone marrow, liver, and organs of the digestive tract. Less often others.
Also large neoplasias or decaying structures in advanced stages. When the body is forced to clot blood faster due to massive destruction of abnormal tissue in order to prevent death.
- Allergic reactions. The phenomenon is temporary. It is necessary to eliminate the body's inadequate immune response as quickly as possible. Deviations in indicators for chronic diseases of this type are especially noticeable.
- Deficiency of vitamins C and K.
- Lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. The intestines, since the absorption of nutritional compounds is impaired, also the stomach. The liver stands apart. It is responsible for the normal synthesis of coagulation factors. Any deviations can cause illness. Diagnoses such as cirrhosis and structural abnormalities are especially dangerous.
- A high prothrombin index occurs in dysbacteriosis, when the balance of beneficial and opportunistic microflora is disturbed in the direction of increasing the amount of the latter. The decay processes slow down, and the evacuation of feces is disrupted. This leads to the release of toxins into the blood, poisoning the entire body. These poisons have the property of activating prothrombin indirectly. The reason is not so obvious, but no less dangerous.
When assessing the results and searching for pathological processes, it is necessary to take into account possible deviations of reference values in the specific laboratory where the study took place.
Influence of external factors on test results
The study result may be unreliable not only when taking indirect anticoagulants or coagulation inhibitors. Even food sources can affect it, especially those enriched with the stimulator of prothrombin production, vitamin K.
The following foods consumed in large quantities may affect the analysis result:
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Soya beans;
- Green tea;
- Green leafy vegetables;
- Cabbage;
- Beef, veal, pork liver.
The following medications can reduce prothrombin time:
- Oral contraceptives;
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone);
- Concentrates of prothrombin complex factors;
- Barbiturates;
- Hormone replacement therapy drugs;
- Thyroid hormones;
- Antibiotics (some types);
- Androgens;
- Anabolic steroid;
- Antidiabetic agents;
- Antiarrhythmic drugs;
- H2 receptor antagonists (prescribed to patients with ulcers and gastritis);
- Laxatives and diuretics.
Tell your specialist if you are taking homeopathic medications or dietary supplements.
Additional examinations
{banner_banstat9}
Auxiliary techniques are used to confirm the diagnosis and identify the causes of deviations from the norm. That is, the primary disorder. An approximate list of procedures is as follows.
- Ultrasound of the liver. Necessary for identifying organic disorders. It is most actively used as a routine technique.
- Scintigraphy is also used. This is already a method of functional research. When there are no structural changes, at least at first glance.
- MRI of the digestive tract is available upon request.
- Blood biochemistry, general analysis.
- ECG, ECHO-KG.
In most cases, this is enough.