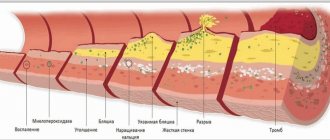
Heartbeat
The human pulse is a rhythmic oscillation of blood vessels that corresponds to the contractions of the heart. That is why the condition of the heart muscle is judged by their frequency. For example, the pulse can be used to characterize the strength and rhythm of the heartbeat and even the condition of the vessels through which blood flows. If the pulse loses its rhythm - it either becomes too fast, or slows down, or even begins to respond at irregular intervals - doctors begin to worry and check the patient for heart pathology, susceptibility to stress, or hormonal imbalances. Often, such failures can be a response to excessive coffee consumption.
Related article: My heart skipped a beat. When an arrhythmia becomes deadly Pulse indicators depend on many different criteria. For example, its frequency and even strength will be determined by a person’s age, exposure to environmental factors, and physical activity. The pulse also depends on the gender of a person: according to statistics, women knock more often than men. Children's heart rate will be significantly faster than adults'. This is especially true for babies.
As a rule, changes in the number and force of impacts are determined by various pathological processes. But there are a number of physiological reasons that can slightly reduce or speed up the heartbeat. So, for example, among them:
- Meals. After eating, a person’s heart rate often increases
- Inhalation height. Here the pulse also accelerates somewhat
- Changing body position, like physical activity, leads to an acceleration of the rhythm
- An increase in room temperature causes the heart to contract more often, because the blood thickens and more strength and energy is required to pump it
- Dream. Activity slows down during this time
In all these cases, if there is no pathological component, the pulse returns to normal quite quickly: 15 minutes is enough.
When might metrics be wrong?
Measuring your pulse does not always reveal accurate data. Violations can be observed in the following cases:
- prolonged exposure to frost, sun or near fire;
- after eating food and hot drinks;
- after consuming tobacco and alcohol products;
- after sexual intercourse within 30 minutes;
- after taking a relaxing bath or massage;
- during periods of feeling very hungry;
- during menstruation (in women).
We comply with the standard
According to the norm determined by the World Health Organization, the pulse is 60-80 beats per minute. It should be understood that this value is individual for each person. And for some, the pulse at night at rest reaches only 38 beats per minute: this is the norm. During exercise, the number of heartbeats can increase to 250.
Article on the topic
Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences Amiran Revishvili: “Arrhythmia must be controlled” The appearance of a high pulse, which is constantly recorded, usually indicates that something is wrong with the heart. Pathological tachycardia is noted when there is:
- Heart diseases, including various defects
- Nervous system lesions
- Pathologies in the endocrine system
- Tumors
- Infectious problems
It also happens that an increase in heart rate is affected by ordinary and, to many, seemingly harmless anemia. In fact, a lack of iron has a rather negative effect on the functioning of the heart, because it deprives it of the required amount of oxygen. As a result, he has to knock faster and harder in order to provide the body with normal living conditions.
A slowing heart rate is also not a pleasant situation. If the number of heartbeats is below the bar of 60 beats per minute, then this may also indicate various disorders. A decrease in heart rate indicates:
- Myocardial infarction
- Inflammation of the heart muscle
- Intoxication of the body
In older people, bradycardia (this is what a slow pulse is called) occurs against the background of increased intracranial pressure, ulcers, hypothyroidism, etc. If organic damage to the heart is noted, the pulse will be about 50 beats per minute.
Article on the topic
Pocket doctor. What gadgets count heart rate, steps and calories?
Forecast by heart rate
“For a long time, the normal pulse rate was actually considered to be 60-80 beats per minute,” says cardiologist, professor, vice-rector for regional development and head of the Department of Hospital Therapy No. 1 of the Moscow State Medical and Dental University Yuri Vasyuk. “But recently large studies have been conducted in which hundreds of thousands of people were observed over several decades. As a result, it turned out that in healthy people the optimal heart rate is 55–60 beats/min. If the heart beats faster or slower, it increases the risk of a number of cardiovascular diseases.
Article on the topic
Dangerous cough. What atypical symptoms indicate a heart attack? A study of heart rate in diseases of the heart and blood vessels has shown that the higher it is, the higher the risk of heart attacks, strokes and other cardiovascular complications, including death from such diseases. Therefore, increased heart rate began to be officially considered an independent risk factor. Now a rapid heart rate is on a par with other risk factors for cardiovascular disease - smoking, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes, high salt intake, etc.
As a result, scientists have revised the heart rate norms, and today it is believed that in patients with coronary heart disease, the pulse should be less than 70 beats/min, with arterial hypertension and chronic heart failure - less than 80 beats/min. If it is higher, the risk of complications and death increases significantly. Therefore, getting your heart rate below these values is one of the goals of treatment, as is reducing high blood pressure, cholesterol and other risk factors.
There is an explanation for these effects. The faster the pulse, the shorter the diastole - this is the time the heart muscle rests between heart contractions. It is in diastole that 90–95% of the blood flows to it. The lower the contraction frequency, the longer the diastole and the more oxygen the heart receives.
With arterial hypertension, the heart's need for oxygen increases, because it works with increased load, pushing blood into narrowed peripheral arteries. Because of this, hypertrophy of the heart muscle develops, and it requires even more oxygen and nutrients.
There is a hypothesis according to which any heart is programmed for a certain number of contractions. Accordingly, the lower the heart rate, the longer it can actively work. But it is confirmed only for heart rate in the range from 55 to 70–80 beats/min, and a decrease below 55 has the same unfavorable effect on the prognosis as an increase of more than 70–80 beats/min.”
Off the beat. How to restore heart rhythm Read more
How to measure
The traditional method of measuring pulse is to place two fingers on a person's neck or wrist. It is worth understanding that for various problems, the pulse can appear in unexpected and varied places. So, if a person has aortic valve insufficiency - this is a situation when the valve leaflets do not close completely - the pulse can be viewed through the pupils of the eyes. If there are problems with blood vessels, if there is a failure in the communication between veins and arteries, the veins may pulsate. If blood pressure increases, you can feel the pulse in the abdomen.
You can also feel the pulse in the foot, groin, armpit and forearm. Learning to feel your pulse yourself is not that difficult. This can help save a person’s life, because you can describe to the doctor the strength and speed of heart contractions even at the stage of calling an ambulance. Naturally, if a person has problems with the pulse, he should not expect that the problem will solve itself, and there is also no need to practice self-medication. In such a situation, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to determine the source of the problem and cope with the situation.
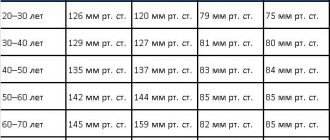
| Person's age | Average heart rate (beats per minute) | Minimum allowable heart rate (beats per minute) | Maximum allowable heart rate (beats per minute) |
| Newborn babies up to 1 month of age | 140 | 110 | 170 |
| Children from 1 month to one year | 132 | 102 | 162 |
| Children 1-2 years old | 124 | 94 | 154 |
| Children 4-6 years old | 106 | 86 | 126 |
| Children 6-8 years old | 98 | 78 | 118 |
| Children 8-10 years old | 88 | 68 | 108 |
| Children 10-12 years old | 80 | 60 | 100 |
| Teenagers 12-15 years old | 75 | 55 | 95 |
| 15-50 years | 70 | 60 | 80 |
| 50-60 years | 74 | 64 | 84 |
| 60-80 years | 79 | 69 | 89 |
How to determine pulse correctly
Most specialists measure the pulse at the wrist artery. This is due to the fact that the wrist artery passes close to the surface of the skin. In the marked place it is very convenient to independently detect and count the pulse. You can even do this for yourself.
The artery is felt on the left arm, since it is closer to the heart, and therefore the shocks of the artery walls are more distinct. You can measure the pulse on your right hand. It is only necessary to take into account that in this case it may be felt out of sync with the heartbeats and be weaker.
Ideally, the pulse in both arms should be the same for an adult. In practice, it varies. If the difference is large enough, then the cause may be problems with the cardiovascular system. If this is discovered, then it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist.
In order to correctly count the pulse, you need to turn your left palm up. It is better to place your hand on a horizontal plane at chest level and bend your wrist slightly.
If you grab your wrist from below with your right hand, the middle finger of your right hand will feel shocks in the area of the bend of the wrist of your left hand. This is the radial artery. It feels like a soft tube. You need to press it lightly, which will allow you to better feel the shocks. Then count the number of pulsations for a minute.
This will be the pulse. Some people count their pulse for 10 seconds and then multiply it by six. We do not recommend this method, since when counting beats per second, the error increases, which can reach large values.
It is not recommended to determine the pulse using your thumb, as it is less sensitive. You can miss the impulse from the heartbeat, which also leads to errors in the calculations.
"Broken heart"
The heart is one of the strongest muscles of the human body, but even the heart cannot always cope with the misfortunes that befall a person. In difficult circumstances, our “engine” has its own self-defense system. Thus, one of the heart conditions may be stress cardiomyopathy, characterized by a sharp and severe decrease in the activity of the heart muscle. This syndrome is often confused with myocardial infarction.
Stress cardiomyopathy (as the name suggests) is most often caused by severe emotional distress, which is why it is also called “broken heart syndrome.”
Unlike a myocardial infarction, there is no blockage of the coronary arteries, but the release of adrenaline helps protect the heart from overstimulation, paradoxically “pausing” the heart.
Silence of the heart
The average adult's heart beats 72 times a minute, 100 thousand times a day, 36 million times a year, and 2.5 billion times throughout a lifetime.
However, the heart beats rhythmically, which means that in addition to beats, there are also pauses in the cycle. So, if you add up all the pauses between heartbeats in one average human life, it turns out that our heart is “silent” for about 20 years. It is also interesting that the heart stops when you sneeze.
Another fact that cannot be explained from the standpoint of physics. Fluid can flow from higher to lower pressure, but in our body this law is constantly violated. When measuring pressure in the aorta and femoral artery simultaneously, blood from the aorta, where the pressure is lower, flows into the femoral artery, where the pressure is higher.
Heart and ecology
Recent research from Harvard Medical School, the results of which were published in the journal Science Dayly, has proven that one of the most negative factors for heart function is poor ecology.
The study examined medical data from 107,130 women from 1986 to 2012. Analysis of the data (comparing geographic location) showed that in 523 cases of sudden cardiac arrest, living within 50 meters of a road increased the risk of such death by 38% compared to living 500 meters from the road.
Thus, today we can already say that it is possible to reduce the likelihood of coronary heart disease - just move to the village.
Heart in weightlessness
NASA recently conducted a study that yielded very interesting results. It turned out that in a state of weightlessness the heart not only weakens and decreases in volume, but also... becomes rounder. During the experiment, NASA cardiologists studied the hearts of 12 astronauts working on the ISS.
Analysis of the images showed that in conditions of weightlessness the heart is rounded by 9.4%. However, upon returning to Earth, the heart returns to its normal shape within six months and resumes “earthly” activity. To imagine the decrease in heart activity, it is enough to say that lying on a bed for a month and a half is equivalent to working in zero gravity for a week.
Heart energy
The heart is the main worker of the human body. If we draw an analogy, the faucet in the kitchen must be turned on for more than 40 years in order to pass as much water as the amount of blood pumped through the heart of a person with an average life expectancy.
Every day, the heart spends so much energy pumping blood that it would be enough to drive a truck more than 30 kilometers. During life, the heart produces an amount of energy comparable to the energy expended by a spacecraft when flying to the Moon and back.