WHAT IS UV RADIATION?
Ultraviolet (UV, UV) radiation is electromagnetic waves with a length from 100 to 400 nm, emitted by the sun and other stars, physiotherapeutic devices, bactericidal lamps and, to a lesser extent, fluorescent lighting devices and electric welding machines. Limited use is used in physiotherapy UV radiation range from 390 to 180 nm, which has the following effects on the human body:
- long UV waves (UVA) with a length from 390 to 320 nm - stimulate the production of melatonin pigment in the skin, have an immunostimulating and photosensitizing effect. Long-range UV rays can provoke the formation of skin cancer - melanoma.
- medium ultraviolet waves (UVB) with a length of 320 to 280 nm - have an antirachitic effect (stimulates the production of vitamin D3), improves the absorption of the vitamin. C and vitamin E synthesis, improves blood flow in tissues (erythema-forming effect).
- short ultraviolet waves (UVC) with a length from 280 to 180 nm - have pronounced bactericidal properties, the ability to improve metabolism and correct blood clotting.
For general ultraviolet irradiation, devices with a quartz-mercury arc lamp are used, emitting the entire spectrum of UV rays. Such rays, when exposed to the body, are almost completely absorbed by the epidermis of the skin, penetrating to a depth of 0.6 mm to the superficial capillary network and nerve endings.
Features of physiotherapeutic treatment of sexually transmitted infections
Treatment of diseases occurs due to the influence of physical factors:
- heat;
- cold;
- electromagnetic or laser irradiation;
- direct or alternating electric current;
- mechanical impact.
Physiotherapeutic treatments for sexually transmitted infections that have already proven effective:
- cryotherapy;
- laser radiation;
- radio wave radiation, for example, from the Surgitron apparatus;
- exposure to electric current (electrical stimulation).
The specialists of the URO-PRO clinic have extensive experience in treating diseases using physiotherapy; you can make an appointment with us for a consultation right now by filling out the online form on the website. Do not delay treatment; timely diagnosis will help avoid the development of more serious diseases.
HOW DOES UFO AFFECT A CHILD'S BODY?
When a child's skin is exposed to UV rays, the process of absorption of light energy (quanta) by atoms and molecules of biological tissues and substances occurs. The energetic impact of UV rays initiates the formation in tissues of more complex biological molecules, the formation of molecules with new physicochemical properties and the breakdown of protein molecules with the release of a large number of biologically active substances, such as histamine, acetylcholine, heparin, prostaglandins, kinins, etc. the substances have a local effect - aseptic inflammation occurs, which manifests itself in the form of local redness and slight swelling of the skin (erythema). This erythema forms within 3-12 hours after irradiation and lasts up to 3 days. Also, biologically active substances formed as a result of irradiation are carried through the bloodstream throughout the body, causing functional changes in all organs and systems. Also, the formation of biologically active substances and direct exposure to UV rays stimulates nerve endings in the skin, creating a flow of nerve impulses that cause activation of reflex zones and the central nervous system as a whole.
Due to the mechanisms described above, the following effects are realized during general UV irradiation (UVR):
- immunomodulatory effect.
- potentiation of the formation of vitamin D2, D3 optimizes the synthesis of vitamin A.
- anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect.
- desensitizing effect (the body's sensitivity to allergens decreases).
- stimulation of metabolism and local blood supply.
- improvement of cerebral circulation.
- detoxification effect.
- normalization of blood clotting processes.
- increase in hemoglobin level.
- improvement of the functional state of the cardiorespiratory system.
Galvanization
Galvanization is a technique of electrotherapy, during which the patient’s body is exposed to a constant low-voltage electric current. Galvanization is applied locally to affected areas and reflex segmental areas, and there is also a method of general galvanization.
Dermatologists traditionally use several galvanization methods:
- local - to foci of inflammation;
- intranasal;
- general according to Vermeule;
- galvanization of the collar zone according to Shcherbak;
- four-chamber galvanic bath;
Indications
Galvanization is indicated for patients with:
- neurodermatitis;
- other itchy dermatoses;
- scleroderma or nodular vasculitis;
- psoriasis or lichen planus;
- keloid scars.
Contraindications
Galvanization is not recommended for:
- eczema, dermatitis and pyodermitis;
- stage 3 hypertension;
- feverish condition;
- oncological diseases.
IN WHAT CASES IS UFO FOR CHILDREN RECOMMENDED?
General UV irradiation is used:
- for the prevention and treatment of rickets in children, pregnant and lactating women.
- for the treatment of mastitis in newborns, navel weeping, limited forms of staphyloderma and exudative diathesis, pneumonia, rheumatism.
- in order to increase the overall resistance of the body, for hardening.
- treatment of pustular diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
- for skin diseases.
- in chronic sluggish inflammatory processes.
- for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs and respiratory system, for bronchial asthma.
- for gastritis, gynecological diseases
- to stimulate hematopoiesis.
- when compensating for ultraviolet deficiency (sun starvation).
- for metabolic disorders.
- for inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system, bones and joints.
- for neuralgia and myalgia.
Device "Darsonval"
"Darsonval" is a device with a wide range of uses. This device is used in the treatment of diseases in the field of cosmetology, dermatology, surgery and neurology.
Indications for use
- prevention of skin aging;
- acne treatment;
- treatment of pimples and acne;
- reduction of sebum secretions and the number of propion bacteria;
- reducing the development of staphylococci;
- prevention of baldness or hair loss;
- treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and alopecia;
- psoriasis treatment;
- treatment of allergic conditions, itching or eczema, etc.;
- treatment of herpes of various etiologies and localizations;
- elimination of postoperative edema, keloid scars;
- treatment of neurodermatosis and various atopic skin conditions;
- improving metabolism, relieving swelling;
- treatment of lymphostasis.
The Darsonval device improves blood circulation, due to which tissues are actively nourished, they are supplied with oxygen, and biochemical metabolic processes are also activated.
Contraindications
The use of this technique is contraindicated if you have bleeding and bleeding disorders, malignant tumors or individual intolerance to current. Treatment with the Darsonval apparatus is not recommended for patients with epilepsy or tuberculosis.
The list of contraindications also includes cases such as:
- the patient has a pacemaker;
- pregnancy;
- pronounced forms of rosacea;
- hirsutism;
- feverish condition;
- thrombophlebitis or cardiac arrhythmia.
CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR UV irradiation
General contraindications for ultraviolet irradiation include:
- severe chronic renal and liver failure.
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- individual hypersensitivity to UV rays.
- systemic connective tissue diseases.
- malaria.
- mental illnesses.
- porphyria, thrombocytopenia.
- ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- decreased blood clotting ability.
- strokes and myocardial infarctions.
- neoplasms.
Equipment
Hemorrhagic vasculitis in children and adults
The source of UV radiation for therapeutic use is gas-discharge lamps made of quartz glass that transmits UV rays. Based on the area of the emitted spectrum, irradiators are divided into integral and selective.
Integral irradiators emit rays of the full UV spectrum. Such irradiators are high-pressure fluorescent lamps such as mercury-quartz arc lamps (QQVs) of varying power, corresponding to the digital index of the lamp. The lamp is a quartz tube with tungsten electrodes soldered into the ends. The air has been pumped out of the tube; it is filled with mercury vapor and a small amount of inert argon gas. When the current is turned on, an arc discharge occurs in the mercury vapor. The presence of argon makes it easier to light the lamp. Its normal combustion mode is established 10-15 minutes after switching on.
The emission spectrum of a mercury-quartz lamp contains a large amount of UV rays, as well as visible light of predominantly blue and green colors and a small amount of IR rays.
PREPARATION FOR UFO SESSIONS
No special preparation is required for UVB sessions, however, the child’s skin should be dry and clean, and there should be no creams or ointments on it. Before the procedure, the skin in the area of the procedure is examined to exclude the presence of hemangiomas, lipomas and other neoplasms.
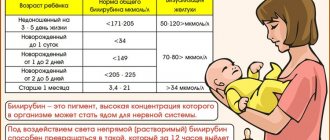
Before starting procedures, the child’s individual radiation biodose is always calculated using a biodosimeter to determine the procedure time, or averaged biodose values are used. One biodose is the minimum time of ultraviolet irradiation of the skin, causing the appearance of the least intense erythema within 24 hours. The following types of UV radiation doses are distinguished:
- suberythemal (0.5 biodose);
- small erythema (1-2 biodoses);
- medium (3-4 biodoses);
- high (5-8 biodoses);
- hypererythemal (more than 8 biodoses).
During sessions, patients' eyes are protected with special safety glasses.
Reviews from doctors and patients
Most patients note a positive effect after 5-6 sessions of ultraviolet irradiation. Ultraviolet cleaning relieves the symptoms of many diseases, improves body tone and overall well-being. However, some patients who fully relied on the procedure and refused traditional treatment did not get rid of their problems.
Therefore, ultraviolet radiation should be combined with taking medications, and not considered a panacea for all diseases.
Doctors share the same opinion - many of them recommend undergoing the procedure to speed up the healing process .
But it is important to remember that official medicine has not yet recognized the Ural Federal District. It will not be possible to undergo the procedure in public medical institutions - UFO is performed in private clinics at the patient’s expense.
There are skeptics among the medical staff who deny the benefits of the procedure, but even they agree that when performed correctly, ultraviolet irradiation of blood is absolutely harmless.
HOW IS THE UV IRRADIATION PROCEDURE PERFORMED?
With ultraviolet irradiation, exposure can be made both to the entire body (general UV irradiation) and to a separate part of it (local UV irradiation). For local irradiation, suberythemal and erythemal doses are used, and individual areas of the body can be irradiated in turn. Depending on age, the maximum area of body surface irradiation during local exposure is strictly limited. With local ultraviolet radiation, the impact area ranges from 50 square meters. cm in newborns up to 300 sq. cm in school-age children. One area of skin can be exposed no more than 3-4 times per course of treatment, except for purulent wounds, bedsores and mucous membranes, which are allowed up to 10-12 impacts. A repeated course of treatment is prescribed no earlier than after 1 month.
With general irradiation, the first irradiation sessions begin with a reduced biodose: weakened and premature children begin to be irradiated with 1/10–1/8 of the biodose, older ones - with 1/4 of the biodose. UV irradiation is prescribed every other day (3 times a week), gradually increasing the daily dose to 1 1/2-1 3/4 biodoses, maintaining it until the end of the course. There are 3 treatment regimens - basic, accelerated and delayed, according to which the biodose is determined depending on the procedure number. UV irradiation time ranges from 10-15 minutes to half an hour. The course of treatment is up to 25 irradiations and can be repeated after 2-3 months.
If it is necessary to use an erythemal dose of UV irradiation, perforated oilcloth is used to soften the effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin.
Indications
UV irradiation of the pharynx and nose is necessary to eliminate the manifestations of unpleasant symptoms in various diseases. It is used in the following cases:
- Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. The procedure is performed after washing the sinuses. The action of ultraviolet rays is aimed at the mucous membrane of the nasal passages.
- Salpingootitis. This disease is a consequence of acute rhinitis. When treating a disease, tube-quartz affects the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx, as well as the nasal passages. Separately, irradiation of the external auditory canal can be performed.
- Chronic tonsillitis. The action of the rays is directed to the palatine tonsils using a tube that has an oblique cut.
- ORZ. The treatment method is used at the very beginning of the development of the disease. The pharynx and nose are irradiated.
- Flu. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the procedure is not performed. It is prescribed after all acute symptoms have subsided to prevent the development of complications. The places where ultraviolet rays are exposed are the throat and nose.
- Angina. The procedure is prescribed in the first days of the development of the disease. In this case, the patient should not have purulent plaque or high temperature. When the disease is in catarrhal form, further complications of angina can be prevented. The procedure is also relevant during the recovery period, after clearing pus from the tonsils. This allows for faster recovery.
- Acute rhinitis. Tube-quartz is prescribed both at the beginning of the development of the disease and during its subsidence. This allows you to exclude a secondary type of infection, as well as avoid various complications. The throat and nose are irradiated.
- Sinusitis and sinusitis. The method is relevant only for the catarrhal form of the disease. When performing it, it is important that there is no pus; it is also prescribed during the recovery period.
- Adenoids. With the help of ultraviolet irradiation, you can remove swelling and disinfect the mucous membranes. Helps avoid the development of inflammation.
- Rhinitis. The method is very effective for all forms of bacterial rhinitis. It actively eliminates inflammation, suppressing pathogenic microflora.
Ultraviolet therapy is also effective in the treatment of otitis media, pharyngitis, tonsillitis and other ENT diseases.
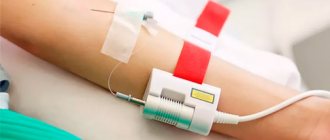
Blood plasmapheresis
Blood plasmapheresis is a method of modern medicine, which is used for the treatment and prevention of various diseases, stimulation of the body's defenses, healing and rejuvenation. The membrane plasmapheresis method is based on the separation of blood into fractions using a plasma filter consisting of many porous track membranes. Pores (holes) in the membrane allow blood plasma to pass through and retain formed elements. Thus, during the passage of blood through the plasma filter, plasma containing antigens, antibodies, circulating immune complexes, inflammatory mediators, excess fibrinogen, cryoglobulins, bacteria and their toxins, tissue and cell breakdown products is removed, and the formed elements are returned to the vein with adequate replacement various infusion media (crystalloids, colloids, donor plasma, albumin).
| The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of plasmapheresis is associated not only with the mechanical removal of toxic substances, but also with the general reaction of the body to exfusion. When blood loss occurs, mechanisms for activating the body's defenses are triggered: the sympathoadrenal system is activated, metabolic processes between water sectors change, tissue protein, iron reserves and other plastic materials are mobilized, hematopoiesis is stimulated with the acceleration of cell maturation in the bone marrow. Blood dilution with a preservative, hemodilution with infusion media, and deplasmization of erythrocytes and other cells are also important. |
Blood plasmapheresis provides:
- increasing the functional activity of hematopoietic, phagocytic and immunocompetent cells,
- immunocorrection and improvement of blood microcirculation,
- anti-inflammatory effect,
- removal of decay products of tissues and cells (during hemolysis, myoglobinemia), microbes, toxic substances, including those associated with proteins.
It is very important that one vein is used to operate the system, and the system is not disconnected during operation. This protects the patient from infection and increases the safety of the procedure as a whole.
Membrane plasmapheresis is characterized by a number of advantages: absence of injury to blood cellular elements, good tolerance of the procedure even by elderly and seriously ill people, guarantee against infection, use of one vein, sterility and disposability of all materials used.