Rh factor
During scientific research in 1940, an antigen was found in the blood of macaques, which later received the name Rh factor. It is hereditary and depends on race. Those people who have this antigen in their blood are Rh positive, and if it is absent, they are Rh negative.
Transfusion compatibility:
- Rh negative is suitable for transfusion to people with Rh negative;
- Rh positive is compatible with any Rh blood.
If you use Rh-positive blood for a patient with a Rh-negative category, then special anti-Rhesus agglutinins will be produced in his blood, and with another manipulation, red blood cells will stick together. Accordingly, such a transfusion cannot be carried out.
Any transfusion is stressful for the human body. Whole blood is transfused only if the loss of this biological fluid reaches 25% or higher. If less volume is lost, blood substitutes are used. In other cases, transfusion of certain components, for example, only red blood cells, is indicated, depending on the type of lesion.
Blood donation
Blood donation is the voluntary donation of blood or its components for further use.
The World Health Organization and donor societies in different countries point out that blood transfusions save many human lives.
Donor blood is vital:
- Women who have lost a large amount of blood during childbirth.
- People who suffered as a result of accidents, received injuries, lost a lot of blood during any accidents and disasters.
- Cancer patients.
- For blood diseases, which include leukemia, hemophilia, aplastic anemia.
- For complex diseases with a chronic course.
- During a bone marrow transplant operation.
- For many surgical interventions, including cardiac surgery, endoprosthetics, and other complex operations.
Thus, it becomes completely clear that modern medicine cannot do without blood transfusions.
Unfortunately, a considerable number of prejudices, fears and peculiar myths have formed around blood donation, which, as a rule, have nothing behind them.
Myth #1: Donating blood is harmful to the donor.
In fact. If a person is healthy, then donation does not cause him the slightest harm. In addition, this procedure stimulates and activates hematopoietic processes, which brings considerable benefits to the person. This is an absolutely safe procedure. The blood losses incurred by the donor are physiological and are quickly restored by the body. Regular donation prevents atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, gout, and helps maintain normal weight. In addition, periodic blood renewal has a rejuvenating and immunostimulating effect.
Myth No. 2. By donating blood, you can get some kind of infection.
In fact. The procedure is completely safe, since all equipment at the donor points is completely sterile, only disposable needles and syringes, as well as blood transfusion systems are used, and the packages are opened immediately before the procedure so that the donor can see the unsealing process. After blood collection, used syringes and needles are destroyed (disposed of).
Myth No. 3. The donor procedure is very painful.
In fact. The blood donation procedure does not bring any pain, except for one thing - a puncture of the skin and vein on the inside of the elbow. The strength of the sensations during this short-term impact is comparable to a gentle pinch, and the process of blood sampling itself is absolutely painless.
Myth No. 4. Very few people need donor blood, so there is no point in donating it.
In fact. Any person may need the help of donors and blood transfusions. Medical statistics confirm that every third inhabitant of the planet has been forced to resort to blood transfusion at least once during his life.
Myth #5: It takes a long time to donate blood.
In fact. The blood donation procedure takes about fifteen minutes, a little longer is required to donate blood components (platelet or plasma) - these procedures can last from half an hour to an hour and a half.
Myth No. 6. Most often, what is needed is not blood of the 1st or 2nd group, but of rare groups, so this is exactly the kind of blood that should be donated.
In fact. Blood of any group and with any Rh factor is constantly in demand.
Myth No. 7. Smokers cannot donate blood and be donors.
In fact. If a smoker donates blood, he should not smoke for an hour before the blood donation procedure and for at least an hour after the procedure.
Myth No. 8. Donating blood is a very tiring procedure, after which a thorough rest is necessary.
In fact. After the blood sampling procedure, you should sit quietly for a quarter of an hour and on this day you should not engage in heavy physical work.
Myth No. 9. To restore lost blood and not feel the loss, you should eat nutritious food in large quantities both before and after the procedure.
In fact. At least a day before donating blood, you must avoid fatty and spicy foods, as well as fried and smoked foods. Eggs, dairy products including butter, dates and chocolate are not recommended at this time. Suitable foods before donating blood are cereals and pasta cooked in water, bread and crackers, vegetables, fruits (except bananas). Suitable drinks include mineral water, compotes, juices, fruit drinks and sweet tea. After donating blood, meals should be regular and nutritious (a full five meals a day is best) - this eating regimen is necessary for at least two days.
Attention! Blood should not be donated on an empty stomach.
Myth #9: Some people claim that donating blood will make you fat.
In fact. People who donate blood do not gain weight from this procedure, but can gain weight because they do not adhere to the recommendations about the need for enhanced nutrition for two days after donating blood, continuing to eat in an enhanced mode even when there is no longer any need for it.
Myth No. 10. Donation can ruin your appearance, and your complexion can especially suffer.
In fact. People who donate blood regularly always have a healthy complexion because the blood is constantly renewed. And blood renewal, in turn, is an excellent prevention of various diseases of the cardiovascular system, immunity and the entire immune system, as well as prevention of the gastrointestinal tract, including the liver. As a result, donors have a very good and healthy complexion, and their skin becomes completely clean and radiant.
Myth No. 11. Donation harms the body because the body loses blood.
In fact. Evolutionarily, the amount of blood in the human body is slightly higher than necessary. It is very useful for a person to sometimes “change the reserve volume” of blood, so donation is also useful for the donor himself.
Myth No. 12. Donation cannot be considered normal, because with any blood loss and any bleeding, the blood must be stopped as quickly as possible, and donors constantly lose up to half a liter of blood.
In fact. Donation can be regarded as a kind of training for the body - a donor has a better chance of coping with significant blood loss, since his body knows how to restore blood loss and is more ready for this than a person who has never donated blood. It is known that the blood balance in a normal situation can be restored to its original state in about four weeks, however, when the situation is critical, the donor’s body will be more adapted to react to blood loss.
Myth #13: Donating blood regularly can be addictive.
In fact. If blood is donated by a person who is completely healthy both physically and mentally, then no negative consequences occur even after donating blood multiple times.
Myth #14: People are best matched with blood from a donor of the same ethnicity.
In fact. The cellular composition of blood is the same in all people and does not depend on nationality. Blood is suitable not depending on the nationality of the donor, but depending on the group (one out of four) and on the Rh factor, which can be positive (85% of cases) and negative (15% of cases). The recipient (the person receiving the blood transfusion) is suitable for donor blood that has the same group and Rh factor as the recipient's blood, and nationality does not matter, as does gender, race or religion.
Myth No. 15: Along with blood, some characteristics of the donor, such as beliefs or habits, can be transferred to the recipient.
In fact. Blood does not contain information about religion, political beliefs, musical preferences, or any habits, so none of the above is transmitted through blood. However, blood can tell about bad and dangerous habits, such as drug addiction, alcoholism or alcohol abuse, smoking, and infectious diseases. That is why the donor must be completely healthy.
Myth No. 16. The Church has a negative attitude towards donation.
In fact. Christianity, Islam and Judaism consider donation to be a desire to save the life of a neighbor and regard it as the embodiment of mercy, therefore they bless blood donation.
How to prepare for donating blood?
Only a person who has no contraindications for donation and who is 18 years old at the time of donating blood can become a donor, but the donor’s age should not exceed 60 years. The donor's weight should not be less than 50 kg.
If donating blood goes according to plan, then it is highly advisable to first (a day or two before) donate blood for a test, during which the blood type, Rh factor, level of hemoglobin, red blood cells and other components, as well as the possible course of hidden chronic diseases, are clarified. Immediately before donating blood, body temperature and blood pressure are measured.
The final decision on the possibility of donating blood is made by a transfusiologist immediately before the procedure.
In order to properly prepare for a planned blood donation, several conditions must be met.
- Do not use aspirin or any painkillers three days before the blood donation procedure.
- Avoid drinking any alcohol, including low-alcohol drinks, two days before donating blood.
- Refuse fatty foods, as well as meat and dairy foods in favor of cereals, baked goods and fruits - at least 12 hours before donating blood, and preferably a day before.
- Donors cannot donate blood on an empty stomach, so you must have breakfast with approved foods.
- Smokers should not smoke for at least an hour before the blood collection procedure.
Attention! You can donate whole blood no more than five times within one year - the intervals between blood donations must be at least 60 days. Platelet and plasma donations are allowed more frequently, but are not recommended more than once a month as the body takes time to fully recover.
Absolute contraindications for blood donation:
- AIDS/HIV
- Any viral hepatitis, regardless of whether it is acute, chronic or only mentioned in the anamnesis.
- Tuberculosis at any stage.
- Any cancer at any stage.
- Any blood disease and/or any abnormalities in the composition of the blood identified during biochemical analysis.
Temporary contraindications for blood donation:
- ARVI, after complete recovery from which at least a month must pass.
- Tooth extraction and other surgical dental procedures, after which at least ten days must pass.
- Vaccinations, after which, depending on the type of vaccine, should take from ten days to one year.
- Acupuncture procedures, tattooing or piercing of any part of the body - at least a year must pass after these procedures.
- Pregnancy in any trimester, as well as breastfeeding, must pass at least a year after birth, and at least three months after the end of lactation.
- Menstruation and the week after it ends.
Attention! It is better not to plan blood donation during periods of strong emotional stress or significant physical activity.
No one can know when he, his child, his loved one, his parents or his friend will need blood. In today's world, no one is immune from accidents, illnesses and other unforeseen situations. Someone knows their donor and is grateful to a specific person, while others received salvation from a blood bank, where nothing is indicated except the group and Rh factor. And who should we thank in this case? And how to do this? The best gratitude is to donate blood, which will also save someone’s life, and then there will be one less tragedy on the planet. Thanks to your blood, thanks to you!
Physiotherapist Elena Mikhailovna Khveskovets
How to determine blood type
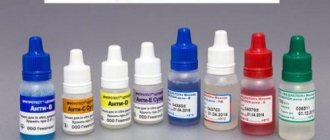
To determine the blood group during transfusion, standard serum is taken and the blood being tested is dripped into it. This serum contains certain antibodies. The blood reaction occurs with antigens in the red blood cells. They are either similar to antibodies in serum or they are not. Red blood cells in different blood groups agglutinate with a certain serum, that is, they accumulate into a small mass.
- Example: to detect the third (B) and fourth blood group (AB), serum containing anti-B antibodies is used.
- For the second (A) and fourth (AB), serum containing anti-A antibodies is prepared.
- Blood group 1 (0) does not cause any reactions with any serum.
Blood group test
Indications and contraindications for transfusion
Blood transfusion is indicated for almost all types of cancer, which are accompanied by dangerous changes in hematopoiesis. The main indications for supporting the body with donor blood:
- lesions of the red bone marrow, spleen, kidneys, disrupting the process of hematopoiesis;
- blood transfusion with low hemoglobin in oncology;
- blood loss during surgery;
- bone marrow damage due to chemotherapy, radiation treatment;
- internal bleeding;
- vomiting of a constant nature, which leads to a lack of substances necessary for hematopoiesis;
- Blood transfusion is required for blood cancer.
The procedure has a number of contraindications:
- allergy to blood components;
- serious heart problems;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- bronchial asthma;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- stage III hypertension.
Life-threatening conditions require transfusion if there are contraindications. At the same time, preventive measures are taken to prevent the development of complications.
Blood compatibility
The most important criterion for choosing a donor for a patient is group compatibility of blood during transfusion. To answer the question why there is no blood compatibility, you need to know that there is no universal group for everyone, but a special table will help you choose the right one, which shows the blood groups that are suitable for everyone:
Blood compatibility chart
- For example, a person of the first group is an ideal blood donor; it is suitable for all other groups; the fourth is a universal recipient.
- The first group (0) can be transferred to all other groups without any problems, but it can only receive its own, the first.
- The second (A) is suitable for the second and fourth, but can accept its own and the first.
- The third (B) is a donor for its own and the fourth group and accepts only the third and first.
- The fourth blood group (AB) is an ideal recipient; it accepts all blood groups, but only the fourth is suitable as a donor.
In addition to human blood groups, there is another important criterion by which the donor and recipient are matched to each other. Great importance is attached to the Rh factor or antigen. It can be positive and negative, they are incompatible.
For example, if blood is transfused from a blood donor with a third blood group and a negative Rh factor to a patient with the same group with a different Rh factor, the patient’s native plasma sticks to the donor’s red blood cells, causing an incompatibility reaction. In medicine, this process is called an agglutination reaction and leads to death. The number of antigens in blood plasma is also determined by different systems.
History of the 4th group
The opinions of scientists regarding the relatively recent appearance (no earlier than the 11th century AD) of the 4th Civil Code are divided. But there are three main theories:
- Mutation of the 2nd and 3rd groups into the 4th as a result of the mixing of races: Indo-European and Mongoloid, which were characterized by individual characteristics that appeared during a long evolutionary process. This mixing began recently, which explains the youth of the fourth group.
Mixed marriage of Indo-European and Mongoloid races
- Another version: the emergence of the 4th group is associated with humanity’s opposition to viruses that threatened the complete destruction of the earth’s population. The response to such attacks was the development of appropriate antibodies that combine A and B.
- According to the third theory, the young fourth group was formed as a defense for the body during the evolution of the culture of eating. As food processing methods became more complex, the need arose to combine antigens A and B, which should protect the body from unnatural food preferences.
Disagreements regarding the truth of the theory of the origin of the 4th group still exist in the scientific community. But there is unity regarding the rarity of this blood.
Interesting! Carriers of different HAs have characteristic agglomerations. The first and second groups are characteristic of the inhabitants of Africa and Europe, and the third - of Asia and Siberia. The 4th GC is characteristic of the inhabitants of Southeast Asia, Japan and Australia. Traces of AB (IV) were found on the Shroud of Turin.
Blood compatibility for conceiving a child
Before pregnancy, planning a child needs to be approached wisely. Reproduction specialists advise parents to determine blood compatibility in advance. The child’s inheritance of a certain set of qualities from each partner will depend on this, and checking Rh compatibility will help protect against hemolysis during pregnancy. If a woman is Rh-, and a man is Rh-positive, a Rh-conflict arises, in which the body perceives the fetus as foreign and begins to fight, actively producing agglutinins (antibodies) against it.
- What disability group is given for grade 3 knee gonarthrosis?
Rhesus conflict poses a danger not only for the expectant mother. Hemolytic disease can occur when positive and negative red blood cells react in the fetal bloodstream. Ottenberg's rule can determine whether conception will be successful based on blood type:
- it will help protect the couple by finding out what diseases can arise during conception and pregnancy;
- establish an approximate scheme of combination of a set of chromosomes during the formation of a heterozygote;
- guess what Rh factor the child may have;
- determine height, eye and hair color.
Compatibility table of blood groups and Rh factor
The ratio of the blood type of the father and mother determines the possible inheritance of qualities and genes by the child. Incompatibility does not mean the inability to get pregnant, but only indicates that problems may arise. Knowing in advance is better than finding out when it's too late. It is better to check with your doctor which blood groups are incompatible for conceiving a child. Compatibility table of blood groups and Rh factor:
| Blood type | 0(I)Rh+ | 0(I)Rh- | A(II)Rh+ | A(II)Rh- | B(III)Rh+ | B(III)Rh- | AB(IV)Rh+ | AB(IV)Rh- |
| 0(I)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| 0(I)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| A(II)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| A(II)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| B(III)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| B(III)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| AB(IV)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| AB(IV)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
The probability of a child inheriting the Rh factor:
| Dad | Mother | Baby |
| Positive | Positive | 75% positive 25% negative |
| Positive | Negative | 50/50 |
| Negative | Positive | 50/50 |
| Negative | Negative | Completely negative |
How are donors' blood tested?
For oncology, you can do a blood transfusion that has undergone a thorough examination for infections, group membership, and Rh factor. If necessary, additional testing is carried out for other group antigens. To completely protect patients from infections, the following measures are taken:
- Before donating blood, the donor answers a questionnaire. He is obliged to talk about possible cases of infection recently. If there is the slightest suspicion of infection in a donor, he is not allowed to donate;
- the donor is examined by doctors and undergoes tests. People who have abnormal test results (abnormal bilirubin, increased white blood cells, high liver enzymes, etc.) are excluded from taking the test;
- After collection, the blood is examined for parenteral infections. If they are absent, she is divided into factions and sent to a six-month quarantine to check the donor again. He could have had infections that were not detected by laboratory methods because they were at an early stage of development.
Blood group compatibility
In the 20th century, the idea of transfusion arose. Blood transfusion is a useful procedure that restores the total volume of blood cells; plasma proteins and red blood cells are replaced. The compatibility of the blood groups of the donor and recipient during transfusion is important, affecting the success of the blood transfusion. Otherwise, agglutination will occur - a fatal gluing of red blood cells, resulting in the formation of a blood clot, which leads to death. Blood compatibility for transfusion:
| Blood type | Recipients | Which ones can you transfuse from? |
| 0(I) | I, II, III, IV | I |
| A (II) | II, IV | I, II |
| B(III) | III, IV | I, III |
| AB(IV) | IV | I, II, III, IV |
First
The first blood group is considered to be the foundation of human civilization. Our ancestors developed the habits of excellent hunters, brave and persistent. They are ready to spend all their strength to achieve their intended goal. Modern first-bloods need to be able to plan their actions in order to avoid rash actions.
Main character traits:
- natural leadership;
- extroversion;
- better organizational skills.
Strengths:
- strong digestive system;
- physical endurance;
- increased ability to survive.
Weaknesses are considered:
- Types of arthrosis and their degrees for which a disability group is given
- increased acidity (risk of peptic ulcer);
- predisposition to allergies, arthritis;
- poor clotting;
Second
City dwellers. Evolution moved forward and people began to engage in agriculture. When plant protein became the source of human energy, the vegetarian second blood group arose. Fruits and vegetables began to be used as food - the human digestive system began to adapt to changing environmental conditions. People began to understand that following the rules increases their chances of survival.
Main character traits:
- communication skills;
- constancy;
- composure.
Strengths:
- good metabolism;
- excellent adaptation to change.
Weak sides:
- sensitive digestive system;
- weak immune system.
Third
People with the third blood group are called nomads. It is difficult for them to experience an imbalance within themselves, in the team. It is better to live in mountainous areas or near water bodies. They suffer from a lack of motivation because their bodies produce large amounts of cortisol when they are stressed.
Main character traits:
- flexibility in decisions;
- openness to people;
- versatility.
Strengths:
- strong immunity;
- tolerate changes in diet well;
- creative.
Weak sides:
- Is disability allowed for arthrosis of the knee and other joints?
- susceptible to autoimmune diseases;
- lack of motivation and self-confidence.
Fourth
Holders of the rarest, fourth blood group occurred as a result of the symbiosis of the second and third. A bohemian, easy life is what characterizes its representatives. They were tired of everyday decisions and devoted themselves to creativity. The total number of people with such a group is only 6% on the planet.
Main character traits:
- mysterious;
- individual.
Strengths:
- resistant to autoimmune diseases;
- resist allergic manifestations.
Weak sides:
- fanatics, capable of going to extremes;
- Drugs and alcohol should be avoided.
Division of blood into groups
Blood is a liquid connective tissue that contains blood cells - red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes. It is the presence of certain antigens on the membranes (shells) of red blood cells that is the factor according to which the blood is divided into 4 groups. These are protein and carbohydrate compounds called agglutinogens and agglutinins.
The division of blood into groups is classified according to the AB0 system. To have an idea about the antigenic characteristics of erythrocyte membranes, you need to know that blood is characterized by the presence of α and β agglutinins, and erythrocytes - A and B agglutinogens. One red blood cell can contain only one of the α or A elements (β or B, respectively). Therefore, only 4 combinations are obtained:
- 1st group (0) contains α and β;
- Group 2 (A) contains A and β;
- Group 3 (B) contains α and B;
- Group 4 (AB) contains A and B.
Carriers of the 1st group make up the majority - 41% of humanity, and the 4th - a minority - 7%. Not only what kind of blood can be transfused depends on belonging to the group, but also the physiological characteristics of the body (in particular, the gastrointestinal tract), and psychological traits.
Important! You can inherit the fourth blood group from parents who have the second, third or fourth HA, that is, those whose erythrocyte cell membrane contains antigens A and B. Therefore, if one of the parents is a carrier of the first group, the child will never have AB (IV ).
Blood groups
Video on the topic: