I would like to immediately make a reservation that I am against treatment over the Internet, since each patient is individual and there are no absolutely universal treatment regimens for this or that ailment.
Therefore, if you are in a metropolis or in a place where there is a relatively free access to medical services, then in case of any pronounced malfunction in the body that cannot stand waiting for an outpatient doctor’s consultation, I recommend that you do not self-medicate, but call “112” or “03” "and call a doctor or at least ask for advice on what to do in a given situation.
In this article we will discuss how, relatively safely, to reduce increases in blood pressure and heart rate at home.
The following recommendations are addressed to patients who do not have the “03” service nearby, or you know in advance that it will take a very long time to get to you...
What actions should I take?
Scheme No. 1
Increased blood pressure above 140 mm Hg. Art. with normal heart rate (<80 beats per minute):
- Take 1 tablet of Captopril (Capoten) 25 mg and place it under the tongue.
- We wait 1 hour. Ideally, within an hour the pressure will return to normal or be slightly lower than usual, there is nothing to worry about, since on average the effect of Captopril goes away within 4 hours after administration.
- If after 1 hour the pressure has not decreased or decreased less than 10 mm. Hg Art., then add 1 tablet of furosemide inside (not under the tongue); Within 1-2 hours, almost any increase in pressure will decrease.
Scheme No. 2
Increased blood pressure above 140 mm. Hg Art. when the pulse increases (>80 beats per minute)
We take Metoprolol (Egilok) 50 mg and put it under the tongue, for a faster effect, you can crush it with 2 dry tablespoons, wait 1 hour, then events can develop according to 2 scenarios:
- Scenario 1: a decrease in heart rate along with blood pressure - this is ideal.
- 2nd scenario: the pulse became, for example, 65 per minute, and the pressure remained as it was, for example, 160 mmHg..., in this case, we simply apply scheme No. 1 (i.e. capoten 25 mg under the tongue -we wait an hour, etc.)
Each of the drugs has contraindications and, as a rule, there are many of them, which is why there are doctors who can, without Wikipedia, select the optimal regimen for the patient, but we are now talking about situations in which it is not possible to receive this medical care.
Pulse and pressure: what is it?
First, it’s worth understanding what blood pressure is. This term refers to the force with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels, which is why it is also called blood pressure. Several factors influence blood pressure:
- The ability of the heart to contract with a certain force, providing the necessary release of blood into the vessels;
- Properties of the blood itself - the higher its density and coagulability, the slower the movement through the vessels;
- The elasticity of the vascular walls - over time they wear out and lose their ability to withstand significant loads. This is why hypertension often develops in old age;
- Atherosclerosis, which reduces the elasticity of the walls;
- A sharp dilation of blood vessels or their narrowing - this happens with hormonal imbalances, serious nervous shocks;
- The work of the endocrine glands, which determine hormonal levels.
Blood pressure depends on gender and age.
To find out the normal blood pressure, you can use a special table that shows normal values for different age periods:
| Age | Lower limit of normal | Upper limit of normal |
| 16-20 years old | 100/70 | 120/80 |
| 20-40 years | 120/70 | 130/80 |
| 40-60 years | 140/90 | |
| Over 60 years old | 150-90 |
The older a person is, the higher the blood pressure level, which is considered normal for him. This is due to age-related changes that occur in the heart, blood vessels, and other organs and systems.
When you absolutely cannot capoten (captopril):
- Pregnancy (if you are pregnant and are prone to increased blood pressure and/or pulse, including other pathologies, then you, in principle, are not recommended to travel far from qualified medical care or at least very clearly understand the advice of your doctor in such situations). If there are no options to call the medical service, then you need to replace Capoten with Dopegit 250 mg. inside, not under the tongue. The standard maintenance dose of Dopegit® is 0.5-2 g/day in 2-3 doses, without further use of furosemide.
Increased blood pressure and pulse during pregnancy is, in general, a separate topic for conversation.
Captopril has other contraindications, such as severe dysfunction of the liver and/or kidneys, severe stenosis of the renal arteries, allergies (Quincke's edema), various valve stenoses, and electrolyte changes. But with a rare or one-time dose, severe harm will not occur, except for allergies (for example, Quincke's edema), but it is not realistic to predict here, the main criterion for allergic reactions is, precisely, the second time of taking the substance that causes the allergy, since the so-called sensitization or, in other words, the production of antibodies to this substance (this will not manifest itself in any way externally), but repeated exposure to the irritant provokes a number of allergic reactions, for example, urticaria, anaphylaxis, Quincke's edema, etc.
The timing of parameter measurements matters.
YES. Measure your pulse and blood pressure only while you are at rest. Data obtained during or after physical activity reflect the work of the heart and blood vessels under load: an increase in indicators in this case is a natural process. To get accurate information and calculate averages, take measurements periodically throughout the day.
Which indicator needs to be monitored more often depends on your health. Patients with atrial fibrillation need to regularly monitor their pulse rate, while those who suffer from certain other heart diseases need to monitor their blood pressure. To get a complete picture of your health, we recommend measuring both parameters.
When is furosemide strictly forbidden?
- Renal failure with anuria (complete absence or urine output less than 50 ml per day)
- Pregnancy
- A pronounced disturbance of the outflow of urine of any etiology (including unilateral damage to the urinary tract), note: in the presence of kidney stones (if there is a history of urolithiasis), but at the time of increased blood pressure there are no signs of renal colic - furosemide is not contraindicated
- Decompensated mitral or aortic stenosis
- Severe electrolyte imbalance (including severe hypokalemia and hyponatremia)
- Severe liver failure, hepatic coma and precoma
Low performance is always a problem.
NO. Don't rely only on optimal values. For some, a heart rate of 40-50 beats per second is a serious problem, and for some healthy young people it is a sign that they are in good shape. Low blood pressure is a little more complicated, especially in people with heart disease and the elderly. However, if the decrease is abnormal, you will feel weak and dizzy. The numbers themselves do not have much meaning, what is important is how you feel under these parameters.
When is it absolutely forbidden to take metoprolol (egilok)?
- AV blockade of the II and III degrees, sinoatrial block, in other words, pauses in heart contraction, usually more than 2 seconds (the presence of these abbreviations in your diagnosis or in the conclusion on the ECG and/or 24-hour monitor)
- severe sinus bradycardia (heart rate less than 50 beats/min)
Also note: metoprolol, unlike, for example, anaprilin, is allowed for bronchial asthma in small dosages.
And also, even in the presence of the above contraindications, but during an attack of severe tachycardia, above 100 beats per minute. (for example, with Tachy-Brady syndrome), anyway, B-blockers are often used, in particular metoprolol.
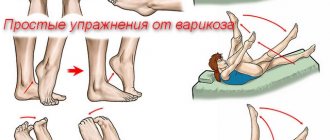
How to measure your pulse
The pulse can be measured manually or using special devices. In the first case, you need to put your fingers on the places where the blood pulsation is most clearly felt:
- To the wrist;
- To the area near the ear;
- To the inside of the elbow;
- In the groin area;
- Below the knee.
Use a stopwatch to time 1 minute and count the number of beats. You can measure the number of beats in 15 seconds and multiply by 4, or in 30 seconds and multiply by 2.
Fitness bracelets and heart rate monitors allow you to obtain more reliable data. Such devices are convenient to use during sports training, walking, jogging. The fitness bracelet displays current information about your heart rate; some models allow you to save information in memory or in an application on your smartphone for later analysis.
The chest strap of the heart rate monitor allows you to get the most accurate results when measuring heart rate, which are comparable in accuracy to an ECG. Measurements are made using highly sensitive sensors. The devices can calculate the average and maximum heart rate and transmit the results to the application, which makes it possible to study the effect of different levels of load on the body.
Unconventional methods of treatment
Folk remedies based on the use of medicinal herbs and plants will help increase heart rate and stabilize blood pressure.
Natural medicines from yarrow, peppermint, and lily of the valley will help raise the level of pulse contractions
You can achieve an increase in myocardial contractile activity using the following recipes:
- Lemon-garlic mixture. To prepare, you need to squeeze the juice from 5 lemons, then chop half a head of garlic, add 2 tbsp. l. honey, mix thoroughly. Leave for 24 hours, take 1 tsp. 4 times a day before meals.
- Radish juice. Remove the top of the vegetable, take out a small amount of pulp so that a cavity is formed. Add 1 tbsp to the well. l. honey, leave for 2-3 hours. Take the resulting nectar 3 times a day.
- Nut mixture. In a container, mix 1 glass of sesame oil, 500 g. chopped walnuts and 1 tbsp. Sahara. Place the sliced lemon in a separate container and pour boiling water over it. Combine the components, mix together, leave for about 24 hours in a place inaccessible to sunlight. Take 3 times a day.
The ratio of heart rate and pressure is an important diagnostic criterion in assessing the condition of a hypertensive patient, so some disorders may indicate the development of concomitant diseases. In some cases, a minor deviation is a physiological process or the body's reaction to certain medications. The course of the pathology depends on the cause of occurrence and the functional state of the vascular and cardiac systems. Timely diagnosis will help normalize the patient’s condition and slow down the progression of the disease.
Symptoms
Patients with constant rapid heartbeat complain of lack of air, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and constant weakness. The pulse rate reaches 130 beats per minute.
Paroxysmal tachycardia usually begins suddenly. The pulse rate reaches 200 beats per minute and higher - sometimes it’s even difficult to count. Patients may complain of palpitations (the heart is pounding, jumping out of the chest), dizziness, shortness of breath, darkening of the eyes, a feeling of fear, chest pain, and may faint. The attack may also end suddenly.
By what signs can a deviation be identified?
Every hypertensive person has the concept of “working” pressure, which means pressure indicators at which the general condition is within normal limits. This indicator is individual for each person, since it can be either normal or elevated (135/100). However, a slight excess of the norm can cause a number of uncomfortable sensations. A short-term and slight acceleration of the heart rate does not provoke pronounced symptoms, but is accompanied only by the occurrence of tinnitus and uncomfortable feelings.
A prolonged attack of high blood pressure and high pulse is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Throbbing headache localized in the temporal and occipital region.
- Dizziness with concomitant loss of coordination of movements.
- Visual impairment (darkening, flickering “flies” before the eyes).
- Cardiac dysfunction (irregular rhythm, feeling of rapid heartbeat).
- Increasing shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air.
- Unreasonable muscle weakness, a feeling of trembling throughout the body.
- Nausea followed by vomiting.
The severity of symptoms depends on the state and sensitivity threshold of the autonomic nervous system, as well as on the stage of hypertension. Thus, an increase in cardiac activity can lead to the development of heart failure and angina.
Pathological causes of the disorder
The development of the pathological form of the disease is associated with functional changes in the functioning of the heart, kidneys, thyroid gland or the presence of infectious agents in the body. The attacks are longer and are not caused by physiological factors.
The group of main pathologies that cause increased heart rate and increased blood pressure includes:
Can there be a fever with high blood pressure?
- Hypertensive crisis of the first type (sympatho-adrenal crisis). When the regulation of the autonomic system is disrupted, the body's normal reaction to stimuli is disrupted, which is associated with diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Arterial hypertension of various etiologies. It is observed in cases of hormone imbalance, renal failure, and vascular regulation disorders.
- Hyperthyroidism. An increase in sympathetic activity occurs when the metabolism of thyroid hormones is disrupted. The pathology is characterized by sinus tachycardia, provided that foci of ectopic activity remain in the myocardium.
- Hypercorticism. The pathological condition is caused by hormonal imbalance due to excessive activity of adrenal hormones. The disease is characterized by a mechanism of increased automatism of the sinus node.
- Diseases of neurogenic and psychogenic nature. Minor positive or negative emotions provoke tension in the nervous system. Cardiovascular neurosis causes increased heart rate as a result of dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system with increased sympathetic nerve activity.
In cases where an increased pulse is diagnosed with increased pressure, the risk of developing vascular complications increases, which can cause rupture of blood vessels in the brain or heart. This pattern affects people aged 45 to 55 years, so the higher the pulse and blood pressure, the higher the risk of negative consequences.
Diagnosis and treatment
Since a rapid pulse can have different causes, in order to carry out the correct treatment of tachycardia at normal pressure it is necessary to undergo diagnostics. To do this, you should visit a cardiologist.
First, the doctor talks with the patient to collect anamnesis. Blood pressure must be measured during the examination to confirm compliance with standard indicators. After this, electrocardiography is prescribed. This study is considered the most informative when it is necessary to determine the causes of tachycardia. Additionally, if necessary, other specialized studies may be prescribed according to existing indications.
Now in practice, various methods are used to treat tachycardia at home in accordance with the diagnosis. Therapy is always prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis, taking into account the patient’s condition. The main goal is to eliminate the diagnosed pathological process in the body.
For symptomatic treatment to reduce the pulse, special medications are prescribed. They can now be bought in pharmacies at an affordable price. In severe cases, surgical treatment is indicated.
The doctor will help you in the future
The doctor must decide what to do next. Be sure to consult a doctor. The sooner first aid is provided and the cause of the disease is determined, the more effective the treatment process will be. The main task is to find and eliminate the cause of tachycardia.
Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis, prescribe medications if necessary, and, if necessary, recommend surgical treatment.
For any form of tachycardia, the treatment complex includes physical therapy (physical therapy), dietary, balanced nutrition, dosed walking, proper sleep, and elimination of factors causing the disease. It is definitely recommended to give up bad habits, not self-medicate and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Providing self-help
What to do if there is a sharp increase in heart rate against the background of high blood pressure? In this situation, you should contact a specialist to clarify the diagnosis and identify the root cause of the disorder. However, functional etiological factors can also cause tachycardia, for which first aid can be provided independently.
First you need to determine the source causing the violation. The patient is recommended to rest, have a good night's sleep, and also have a fasting day that excludes fatty, spicy, and sweet foods. To prevent worsening of the pathology, caffeine drinks, smoking and alcohol should be avoided.
Algorithm for providing assistance:
- Remove constrictive clothing and provide fresh air.
- Take a horizontal position or half-sitting with support under your spine.
- Take sedatives (Persen, Validol, Fitosed, motherwort tincture).
- To lower your blood pressure, take the prescribed antihypertensive pills (Captopril, Captopress, Enap).
- Use a breathing technique with deep inhalation and slow exhalation.
- Massage the area of your eyeballs and temples if you have a headache.
Important! Monitor indicators every 30 minutes. If the use of therapeutic measures does not have the desired effect, then a medical team should be called.
What happens in the heart
Most often, such a pulse occurs in paroxysms and reflects the development of supraventricular tachycardia. What kind of rhythm disturbance is this:
- with supraventricular tachycardia, the heart rate ranges from 140 to 220 per minute (usually in the range of 160 to 180 per minute);
- the source of electrical signals is not the usual sinus node, but a cluster of cells between the atria and ventricles; therefore, the atria are excited retrogradely (from bottom to top), and their contractility is impaired;
- due to the “bifurcation” of the atrioventricular node into 2 paths, with this arrhythmia the impulse quickly circulates through the resulting loop, constantly stimulating the ventricles with a frequency of 140 per minute and higher;
- little blood enters the ventricles, and just as little of it is thrown into the aorta, so the body experiences a pronounced lack of blood circulation.
Another reason why the pulse can be in the range of 140 – 150 or more is the tachysystolic form of atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation. With this disorder, the muscle fibers of the atria contract irregularly, as if twitching, with a very high frequency (up to 450 per minute). Only a portion of these signals are carried to the ventricles.
The tachysystolic form is said to occur when the number of heart contractions during atrial fibrillation exceeds 100 per minute.
When it increases to 140 per minute, a pulse deficit often occurs. This is a discrepancy between heartbeats and palpable pulse waves, since some of them are “empty”; very little blood is thrown into the aorta at this time.