Ear pain is a phenomenon that many people of different ages have experienced. Ear pain is accompanied by discomfort, strong, constant, unpleasant, exhausting sensations, and has a negative impact on sleep patterns and quality of life. For this reason, the question of how to get rid of it comes to the fore.
Practice shows that people experiencing ear pain make many mistakes, which increases the likelihood of complications and negative consequences. In such cases, an ENT doctor is needed. The specialist will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment appropriate for the specific case.
To do this, you can contact our clinic and receive high-quality medical services. Our prices for paid medical services are the most affordable in Rostov-on-Don, and the otolaryngologist provides consultations for both adults and children.
Therapy methods
Having found out why the patient has pressure on his ears, the doctor develops a treatment regimen.
It all depends on the true causes of the pathological process. For high blood pressure, which can cause severe headaches and stuffy ears, Captopril helps. Nootropic drugs are also used that strengthen the walls of blood vessels and normalize blood circulation: Vertizin, Disiron. Osteochondrosis requires complex treatment using ointments and creams (Diclac gel, Clodifen, Diclofenac), anti-inflammatory drugs, Noofen, which improves cerebral circulation, drugs that strengthen blood vessels, for example, Ginkgo Biloba. When the cause of the malaise is sinusitis, the patient is prescribed a procedure for clearing the nasal passages of accumulated pus, which is called “cuckoo”. In severe cases, the nasal septum is punctured or a Yamik catheter is inserted. In addition to treatment, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, for example, Zinnat, Amoxil, vasodilating drops, and herbal medicines.
Purulent otitis media is treated with antibiotics for both internal and external use. The patient drinks pills, drips medicine into his ears, and takes vitamins. In case of atherosclerotic changes, thinning medications (Aspirin) are prescribed, as well as drugs that reduce the risk of blood clots (Wobenzym). Migraine attacks cannot be cured, but they can be controlled with painkillers. It is important to take the pill at the very beginning of the headache, otherwise it will not help the patient.
How to get rid of ear congestion?
In a healthy person, the unpleasant feeling of congestion goes away quickly. In order for your hearing to return to normal, it is enough to drink water, suck a lollipop or chew gum. There is a special exercise that helps increase pressure in the middle ear:
- take a deep breath,
- pinch your nose with your fingers and close your mouth,
- exhale slowly.
If you hear a slight pop in your ear, there is no reason to panic: the eardrum has returned to its normal position. Sometimes the exercise needs to be repeated several times. However, it can only help if there is no infectious process in the ears, which has become the main cause of the problem.
Causes
Let's consider the possible reasons why there is pressure on the ears from the inside.
Migraine
Migraine is a dysfunction of the body of a neurological nature. Most often, migraine manifests itself in regularly occurring episodes of severe headaches that torment a person. The etiology of migraine has not been fully elucidated. Presumably, predisposing factors for migraine, which causes a feeling of pressure in the ears, are:
- genetics;
- neuroses;
- increased stress levels;
- overvoltage;
- eating certain foods that provoke the occurrence of this disease;
- drinking alcohol;
- weather dependence.
Migraine is not accompanied by any other deterioration of a person’s condition, as a rule: there have been no previous blows to the head, concussion, increased pressure in the blood vessels or eye diseases that radiate to the head.
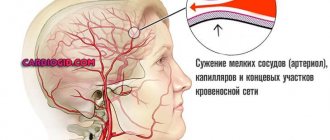
With migraine, there is a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain, their uneven expansion, and impaired perception of CO2. The risk of migraines increases if relatives suffer from high blood pressure.
Migraines are characterized by throbbing pain inside the head and pressing pain in the ear. As a rule, the pain is long-lasting, from four hours to three days. Most often, only one half of the head is affected, although, in severe cases, the entire head may hurt. With migraine, pressing pain is felt only in one ear on the affected side. Most often the pain is felt on the outside of the ear.
- Pressure in the ears: how it feels and how to get rid of it
Hypertension
Hypertension can cause a feeling of pressure in the ears. Arterial hypertension is characterized by a prolonged increase in blood pressure above the following units: siastolic - above 140, and diastolic - above 90 mmHg. There are many reasons for such a sharp change in pressure:
- taking dietary supplements;
- obesity;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- stress;
- overwork;
- loads that are not comparable with age;
- smoking;
- high blood sugar;
- menopause;
- hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of arterial hypertension are:
- sudden increase in blood pressure;
- loss of strength, change in complexion;
- perspiration;
- blurred vision;
- patients complain of pain in the back of the head;
- sudden anxiety may occur;
- heart rate increases;
- causeless fear arises;
- often dizziness, fainting;
- pain in the ears is of a pressing nature, with ringing or squeaking, tinnitus, hearing impairment - like deafness.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is another possible cause of ear pressure. This is a disease characterized by impaired metabolism of fats and proteins, resulting in deposits of cholesterol and some types of fats on the walls of blood vessels. Such deposits are called atherosclerotic plaques. The formation of atherosclerotic plaques leads to blockage of blood vessels, and, as a consequence, to disruption of blood flow to the organs.
Causes of atherosclerosis:
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- drunkenness;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- menopause;
- poor family history.
Atherosclerosis does not have the ability to develop in a specific organ, and if it has already appeared in the human body, it affects all the vessels of the body. Atherosclerotic plaques penetrate the endothelium of the vessel, and, having the ability to break away from the walls, can lead to rupture of the vessel and subcutaneous hemorrhages. In addition, a detached plaque can simply clog a vessel, completely blocking blood access to a certain human organ. Affecting the vessels of the head and neck, it gradually reaches smaller vessels - the vessels of the ear. By disrupting the blood flow to the ear, it leads to the ear tissue not receiving enough oxygen and necessary substances. The patient may feel that the head is bursting from the inside and the ears are blocked; there is a feeling that there is pressure in the ear.
Otitis
Otitis media is a disease of the hearing organ. There is inflammation of the outer, middle and inner ear. Most often, children are susceptible to otitis media, but adults suffer from it not much less often.
- Inflammation of the outer ear is usually associated with the appearance of a boil in the auricle. Bursting, pressing pain inside the ear in this case is explained by the development of purulent inflammation of the boil. In addition, a person may feel heat in the ears, pain when touching the ear, and tugging pain in the ear. It’s painful to sleep at the cause site, it’s impossible to touch, even straighten your hair. Discomfort persists until the boil breaks out. The inflammatory process can even spread to the eardrum, leading to hearing impairment.
- Inflammation of the middle ear may be purulent, or may not develop into this stage. A person can suffer from inflammation of the middle ear constantly (in chronic form), or temporarily, episodicly and acutely. It is characterized by fever, suppuration from the ear, pressing, bursting pain inside the ear and head. As a rule, otitis media is bacterial in nature. Bacteria can enter the middle ear through the nasal passage in the presence of sinusitis. The hematological route of infection is also possible - through the eardrum. Otitis media can develop with the flu, then bloody discharge will be observed from the ear. And also with scarlet fever, in which case the suppuration will be very profuse, and the pain in the ear will be very severe.
If you suspect that you are developing inflammation of the middle ear, you should immediately consult a doctor: in favorable cases, pus breaks through and exits through the ear canal. But there is a very high risk that the pus will not find a way out through the ear and will spread inside the head, which can lead to the development of meningitis or purulent damage to the brain tissue.
Reference. Inflammation of the inner ear is an inflammation of part of the hearing organ - the labyrinth. It is impossible to make such a diagnosis on your own. As with other types of ear inflammation, this disease is characterized by pressing pain in the ear.
Sulfur plug
Ear wax can also be a source of trouble for a person and lead to a feeling of pressure. As a rule, this symptom occurs without pain in the ear. Earwax is the result of wax accumulation inside the ear and leads to blockage of the ear opening. Poor hygiene and/or improper cleaning of the ear from accumulations of wax leads to compaction of wax residues towards the eardrum. In addition, predisposing factors for the formation of ear plugs may be an asocial lifestyle, working on the street or in dusty industries, and lack of awareness of the rules of personal hygiene. Surprisingly, wearing headphones, telephone headsets and hearing aids leads to the formation of ear plugs. Although everything is logical: physiologically, earwax partially falls out of the ear on its own in small particles. This happens when walking, chewing, talking. The use of the above devices closes the ear canal, and wax cannot find a physiological exit from the auricle.
- An adult's ear hurts: causes, what to do and how to treat at home
Forming in the ear, cerumen plugs the ear canal, disrupts the conduction of sound into the ear, and hearing decreases. Adjacent to the eardrum, it can cause inflammation and, consequently, the development of otitis media. The sad companions of wax plug are pain in the ear canal, inflammation, vomiting, headache and, of course, shooting pain inside the ear, pressing pain.
Other reasons
Other causes of pressure and pain in the ears may be a difference in atmospheric pressure. For example, during takeoff and landing of an airplane. Professional scuba divers often experience ear pain and discomfort due to water pressure and pressure differences at the top. They need to be especially careful, because with a sharp change in pressure they can get decompression sickness.
Why are my ears clogged?
Ear congestion can occur for a variety of reasons. The most common ones are:
- Sulfur plug. Earwax is produced to create a natural barrier against dust particles and water that can enter the ears. Sometimes, if the ear is not treated correctly, the sulfur becomes denser, creating a plug, and a feeling of stuffiness appears;
- Tubootitis, or inflammation of the Eustachian tube, which develops as a result of improper rinsing of the nose and long-term treatment of a runny nose;
- Allergic reactions that are provoked by seasonal or other external irritants;
- Otitis, when, in addition to congestion, there is acute pain in the inflamed ear;
- Chronic hearing loss, which causes a feeling of gradual ear fullness and decreased hearing levels;
- Foreign bodies of the external auditory canal and tympanic cavity.
- Among the causes of ear congestion there are also serious diseases, so this symptom cannot be ignored.
When is it due to nerves?
At the time of panic attacks or as they approach, patients often experience increased blood pressure, which can cause severe discomfort in the ears, temples and head. It is known that hypertension provokes the occurrence of severe spasms.
We recommend that you read: What is depersonalization?
Often, floaters appear before the eyes - various spots, stripes, dots.
Other accompanying symptoms include:
- tachycardia, interruptions, body tremors, fever or chills;
- respiratory disorders (shortness of breath, suffocation);
- frequent urination;
- pain, tension, tightness in the chest area;
- nausea, diarrhea;
- the appearance of red spots on the skin, “nervous” allergies;
- numbness of the limbs.
What is noise in the head like?
Tinnitus is nothing more than sounds from physiological processes that constantly occur in the body: breathing, heartbeat, blood flow in the vessels, muscle contractions, etc. The hearing of a healthy person does not perceive somatic noise. Normally, they are masked by external sounds. Noise and ringing in the head become audible when perception is heightened or when abnormal limits are reached.
Types of tinnitus:
- Constant monotonous noise. The sound is not loud, without a strong ringing. Most patients get used to monotonous tinnitus and stop paying attention to it until associated symptoms appear;
- Pulsating noise. The buzzing in the head occurs in paroxysms, and at the same time it can block the ears. Ripple appears when blood circulation is impaired. The patient cannot cope with the attack on his own;
- Ringing (whistle). This is one of the signs of hearing loss. It becomes difficult for a person to understand the words of other people and external sounds. To make out anything because of the whistle, you have to listen.
Diagnostic methods
When visiting a doctor, the patient must describe his symptoms in detail. This will narrow down the search for a possible disease. To make a diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental tests are prescribed, with the help of which the condition of the body is assessed, inflammatory processes, infections, metabolic disorders and other problems are identified.
If there is pressure on the ears and other symptoms bother you, the root cause can be determined using:
- What to do if you have a blown ear: symptoms and treatment at home
- ultrasound examination of the vessels of the cervical spine to determine the presence of circulatory disorders in the brain,
- biochemical blood test to determine cholesterol levels,
- magnetic resonance imaging,
- blood pressure monitoring,
- measuring intracranial pressure,
- x-ray of the spine,
- computed tomography with contrast agent to check the condition of the brain vessels.
After receiving the results of these procedures, the specialist can prescribe a course of treatment taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.