Good day!
My name is Khalisat Suleymanova - I am a herbalist. At the age of 28, I cured myself of uterine cancer with herbs (read more about my experience of recovery and why I became a herbalist here: My story). Before being treated using traditional methods described on the Internet, please consult with a specialist and your doctor! This will save your time and money, since the diseases are different, the herbs and treatment methods are different, and there are also concomitant diseases, contraindications, complications, and so on. There is nothing to add yet, but if you need help in selecting herbs and treatment methods, you can find me at my contacts: Khalisat SuleymanovaInstagram page: instagram.com/fitoterapevt1
Telephone: 8
Email: [email protected]
I consult for free.
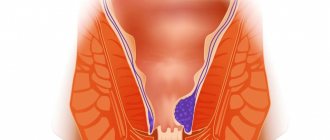
There are a large number of diseases that bring discomfort to a person. These may not only be aesthetic problems. The list of such diseases includes hemorrhoids. Not only adults, but also children are susceptible to it. At this time, there are a large number of different drugs to solve this problem. Their use depends on the degree of complexity and the wishes of the patient. The most extreme option is surgical intervention. But some people recommend the use of ASD 2 for humans in the treatment of hemorrhoids.
Anatomy of the rectum and perianal region, functions of the obturator apparatus
The rectum and anal canal are the final sections of the digestive tract. The immediate tasks of the rectum are the accumulation, formation and excretion of intestinal contents and gases. The functions of the anal canal are unique: a system of nervous reflexes and a complex muscle complex provide one of the most important functions of the body - control of bowel movements, as well as differentiation of the composition of intestinal contents without the need for conscious assessment and subsequent “smart” control of evacuation. In other words, a healthy person most of the time does not think about what kind of contents are in the rectum, whether it is necessary and whether it is possible to retain it in a given situation. All this is controlled unconsciously, thanks to multi-level neuromuscular self-regulation of the holding process.
The approximate boundary between the rectum and the anal canal on the side of the mucous membrane (lumen) of the intestine is formed by the so-called dentate line. There are vertical folds on it, alternating with depressions - crypts. The ducts of the anal glands open into the crypts. The mucus produced by these glands facilitates the sliding of intestinal contents as they pass through the anal canal. Circumstances such as trauma, swelling of the mucous membrane due to defecation disorders, chronic intestinal diseases can lead to inflammatory changes in the crypts and anal glands.
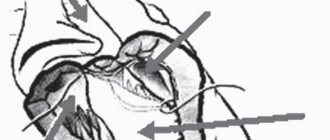
Outside the mucous membrane there is a complex of muscles - these are the sphincter muscles mentioned above, which provide the function of retention and excretion. There are internal and external sphincters. The internal sphincter forms the so-called resting tone, uninterruptedly ensuring the tightness of the anal canal. Its regulation and reduction occur unconsciously, that is, without our will. The external sphincter surrounds the internal one and consists of several layers (portions). Its reduction occurs due to our volitional effort (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the rectal sphincters
What is a fistula
A fistula is a pathological, normally non-existent, passage in the form of a tube connecting the lumen of a hollow organ with the external environment or the lumen of another organ. A rectal fistula, a kind of “tunnel,” connects the lumen of the rectum with the skin of the perineum, buttocks or (rarely) other hollow organs, sharply reducing the patient’s quality of life. This pathological process can involve a large portion of sphincter muscles, which initially characterizes such a fistula as complex and does not allow for “minimally invasive” treatment. In such a situation, a careful assessment of the degree of involvement of muscle structures and planning of special techniques for economical excision of the fistula with subsequent plastic closure of the resulting defect are required.
Important! Such operations must be performed by expert surgeons with extensive experience in such interventions, otherwise the likelihood of relapse (recurrence of the disease) increases several times.
Fistulas have the following structure:
- internal opening: it is usually the affected anal crypt (that is, the most terminal part of the gland duct). The crypt is connected by a duct to the anal gland, located in the space between the sphincters. It is the inflammation of this gland that in the vast majority of cases leads to the development of the disease (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Stages of fistula formation: a) - anal gland with an excretory duct, b) - inflammatory process in the gland, with a forming abscess (abscess) c) - formed fistula tract.
- fistula tract, which can be tortuous, have cavities and branches
- external opening: but most often located on the skin of the perineum near the anus (Fig. 3), sometimes in the vagina or urethra (urethra).
Important! If you have the slightest suspicion of a rectal fistula, you should immediately consult a specialist. If treatment is untimely or inadequate, the disease can be complicated by acute inflammation and additional purulent leaks, which significantly worsens the prognosis!
However, it also happens that the fistula tract ends blindly in the pararectal (peri-rectal) tissue, tissues of the perineum, buttocks, that is, it has only an internal opening of the fistula, which opens from the mucous membrane of the rectum and has no “exit” to the outside.
Figure 3. External opening of the fistula
Description and types of medicine
ASD is the result of research by the famous Russian scientist Alexei Vlasovich Dorogov. Initially, it was developed as a drug that has the ability to protect a living organism from radiation exposure.
Having invested a lot of time and effort, the scientist presented the fruit of his labors - ASD. This remedy improves the state of the body's immune system, activating defense mechanisms and restoration of tissue cells.
The fraction is of organic origin, made by sublimation of tissues with the transformation of vapor into liquid - condensation. Meat and bone residue is used as raw material, so the product itself has a somewhat unpleasant aroma. But this in no way detracts from its effectiveness and does not reduce the restorative effect.
The experts did not stop at one product; later both fraction 2 and 3 appeared. There are differences between them - ASD 2 has the ability to dissolve in alcohol, water and fat, so it can be used both as an external preparation and for internal use. ASD 3 is used exclusively locally.
These products are used in a variety of medical fields, including proctology, as they have a number of effects:
- fight the inflammatory process;
- strengthen the body's immune system;
- disinfect;
- get rid of bacterial and other infectious pathogens;
- eliminate tumor formations.
How to use ASD for hemorrhoids depends on what stage the disease is in and what tissues are damaged.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=PabDbjYuaqM%3Ffeature%3Doembed
When treating inflammation of hemorrhoids, ASD fractions 2 and 3 are used.
Candles. In modern medicine, for this delicate illness, medications are more often used in the form of suppositories, and this also applies to this remedy. ASD suppositories for hemorrhoids have a number of advantages:
- they are easy to use and convenient to use;
- it is difficult to find a form of the product with a more accurate dosage of the active substance;
- absorption of the drug occurs immediately in the blood circulation, without affecting the liver tissue.
An antiseptic in the form of suppositories is less allergenic than a drug in a more traditional form, but this applies to any means.
Treatment of hemorrhoids ASD 2 in the form of suppositories is cheaper than using conventional drugs, since suppositories have a targeted effect on the affected area. In most cases, when the use of ASD 2 suppositories is recommended, treatment includes a 20-day course of therapy. For the first 10 days, the drug is taken twice a day, then the dosage is reduced. If necessary, therapy may be repeated.
Suppositories are popular in the treatment of hemorrhoids, but the use of the product involves several more methods, and which one is necessary in a particular case is decided by the doctor.
Microclysters. Dorogov’s antiseptic stimulant No. 3, as already noted, is an exclusively external remedy; it is used in the form of microenemas.
To do this, the fraction is mixed with camphor oil. The resulting mixture is drawn into a syringe, the needle is removed and the tip is lubricated with cosmetic Vaseline or a small amount of baby cream. The tip of the syringe is carefully inserted into the anus and its contents are squeezed out. After which it is taken out. It is better to carry out the manipulation before going to bed. The duration of treatment is a week and a half.
Oral administration. An antiseptic stimulant is often used in complex therapy, that is, it is taken orally and topically at the same time. This is due to the fact that the product has a positive effect on the functioning of the digestive system. And as you know, when the functions of the gastrointestinal tract are disturbed, difficulties with defecation arise - chronic constipation, they are to a greater extent responsible for the development of inflammatory processes in hemorrhoids.
To eliminate a common and unpleasant pathology with the help of ASD 2, the use of the drug is recommended according to the standard scheme, which was developed by the author of the drug himself, Academician Dorogov:
- the fraction is dissolved in a certain amount of cool, pre-boiled water (the dosage is determined individually);
- drink the solution 2 times a day, always on an empty stomach, half an hour before meals;
- this scheme is followed for 5 days, followed by a 3-day break;
- then follows the second approach, maintaining the previous dosage;
- treatment should be continued until the unpleasant symptoms disappear.
How common is rectal fistula?
The incidence in European countries is about 10-25 people per 100 thousand population. Mostly people of working age suffer from rectal fistulas. Men get sick 2-3 times more often than women.
Important! This disease, being benign, can dramatically reduce a person’s quality of life. A serious and most common complication of inadequate treatment of perianal fistulas is impaired holding function due to damage to the muscular apparatus of the anal canal.
Causes of fistulas
If you experience symptoms characteristic of a rectal fistula, in the vast majority of cases the cause for this was an inflammatory process in the anal gland (Fig. 2). In turn, inflammation of the gland is usually preceded by microtrauma of the anal canal. The cause of such injury is most often excessive irritation and/or trauma to the anal canal when too hard stool passes through the anal canal during constipation or, conversely, during diarrhea. Relatively rare causes of so-called specific fistulas of the anal canal and rectum are inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), tuberculosis, rectal tumors, and the consequences of radiation therapy of the pelvic organs. Inflammation of the gland is accompanied by the development of an abscess (ulcer) in the soft tissues of the perineum and is usually characterized by severe pain, which forces the patient to consult a doctor. Timely and correctly performed opening of the abscess leads to rapid relief of the condition, however, according to modern data, about half of all abscesses are accompanied by the subsequent formation of a fistula and require repeated intervention.
It is this repeated intervention that is aimed at radically getting rid of the fistula and requires not only an extremely thoughtful approach to the choice of treatment tactics, but also extensive surgical experience on the part of the surgeon.
Important! Opening an abscess is a relatively simple operation, but if performed incorrectly, it is at this stage that the muscular complex of the anal canal is most often damaged, which leads to disruption of the function of controlling intestinal contents!
If your visit to the doctor is postponed, the abscess may open on its own with the release of pus, after which your health usually improves and the pain in the perineal area decreases sharply. Symptoms may subside or disappear completely for a period of several weeks or months to many years. Despite the improvement in general well-being, spontaneous opening of an abscess is a relatively unfavorable scenario, because in this case, there is no complete evacuation of the contents of the purulent cavity, but only part of the purulent discharge occurs through the formed hole, which can soon close again. Proper treatment of an abscess consists of creating adequate drainage by creating a sufficient hole, evacuating the contents, rinsing the abscess cavity with antiseptic solutions and, if possible, removing the inflamed gland that is causing the inflammation.
Important! Sometimes, in the hands of an expert surgeon, with the relative simplicity of the fistula tract, radical excision of the fistula at the stage of surgical opening of the abscess is possible, but performing this intervention is extremely dangerous in the hands of an insufficiently experienced specialist and today is not recommended in most international recommendations.
When an abscess spontaneously opens, the likelihood of a return of the acute disease increases and the process becomes chronic with the formation of a fistula. A long course of the disease with periodic exacerbation leads to scarring of the surrounding tissues and, most importantly, the sphincter muscles responsible for the holding function. In addition, in conditions of constant inflammation, a relatively simple fistula can give rise to additional passages and leaks, which significantly complicates subsequent treatment.
Timely consultation with a doctor at an early stage of the disease can reduce the likelihood of developing a fistula and such dangerous complications of the inflammatory process as pelvic phlegmon. Therefore, even minor symptoms that do not significantly affect the quality of life require attention and evaluation by a qualified specialist.
How does fraction 2 of ASD work for hemorrhoids?
In antihemorrhoidal therapy, the second and third fractions of ASD can be used. But ASD 2 is still used more. In this case, the most convenient dosage form is rectal suppositories with ASD 2 for hemorrhoids.
Candles with ASD 2 have several advantages:
- fixed dose ASD 2;
- ease of use;
- direct therapeutic effect on the affected area of the rectal canal;
- low risk of adverse reactions;
- complexity of action;
- relatively inexpensive compared to a number of traditional means.
Suppositories with ASD 2 have several advantages: a fixed dose of ASD 2, ease of use, direct therapeutic effect on the affected area of the rectal canal.
ASD of the second fraction exhibits such therapeutic effects for hemorrhoids as:
- antiseptic;
- venotonic;
- angioprotective;
- anti-inflammatory;
- immunomodulatory;
- antitumor.
What types of fistulas are there?
Traditionally, rectal fistulas are classified according to their location relative to the sphincter muscles. In accordance with this, intrasphincteric, subcutaneous-submucosal, intersphincteric, transsphincteric, suprasphincteric, extrasphincteric fistulas are distinguished (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Types of fistulas
- Extrasphincteric fistula
- Low transsphincteric fistula
- Subcutaneous submucosal fistula
- Suprasphincteric fistula
- Intersphincteric fistula
The fistula tract can be located at a short distance from the edge of the anus and occupy no more than 1/3 of the lower part of the sphincter muscles - then they speak of a low (simple) fistula, or go high up, crossing a significant portion of the muscle complex - these are high (complex) fistulas. The complexity of the fistula is determined not only by the degree of muscle involvement, but also by the presence of swelling, active inflammation, and the presence of scarring around the fistula.
Subcutaneous-submucosal fistulas are the simplest fistulas. Simple fistulas also include intra- and intersphincteric fistulas. The fistulous tract in this form is usually straight, without streaks or cavities, and involves a minimal number of muscle fibers, thus not disrupting the function of the sphincter. Intersphincteric (intrasphincteric) fistulas pass through the internal sphincter into the intersphincteric space and then extend to the perineum. The external sphincter is not involved. As a rule, such fistulas are also simple and do not pose any difficulties for surgical treatment.
Transsphincteric fistulas of the rectum are more common than extrasphincteric fistulas and can affect more extensive layers (portions) of the sphincter complex. In this case, the fistula tract involves both external and internal sphincters.
Important! Tortuous fistula tracts, purulent cavities in the peri-rectal tissue, scarring in the surrounding tissues (including the sphincter) are more common if the fistula is located high in relation to the sphincter.
Suprasphincteric (from supra - above (lat.)) fistulas, starting in the intersphincteric space, rise upward and cross the muscular structures of the anal canal at its highest point, thus involving the entire obturator apparatus.
With such fistulas, high blind branches can form, which can sometimes be identified through the wall of the rectum.
In 3-5% of cases, extrasphincteric fistulas occur, in which the fistula tract goes around the external sphincter, and the internal opening of the fistula is low, in the area of the crypts. These fistulas are characterized by the formation of a tortuous course, streaks, and cicatricial changes.
In addition, additional fistula tracts may extend from the main fistula tract in various directions, and along the fistula, cavities with accumulation of mucus, pus, and necrotic (destroyed) tissues may form.
If the patient has already undergone surgery to eliminate a rectal fistula, and the symptoms of the disease resume after some time, the fistula is called recurrent.
Important! Treatment of recurrent and postoperative fistulas should be carried out only in specialized clinics and only by experienced surgeons!
Symptoms of the disease
- the presence of a small, painless wound - an external fistula opening on the skin of the perineum or buttocks.
- purulent, mucous or bloody discharge from the fistula opening
- itching, burning, feeling of fullness and discomfort in the fistula area.
- the presence of an internal opening of the fistula, detected upon examination of the mucous membrane of the anal canal (in approximately 30% it is not possible to find the internal opening during examination)
With an incomplete fistula, skin manifestations may be blurred or absent, and symptoms can vary from mild discomfort, a feeling of tightness or fullness, the presence of a lump in the anus, to discharge from the rectum.
When the disease worsens, a painful thickening is observed in the area of the external opening on the skin, the pain is often pulsating, bursting in nature. This may be accompanied by an increase in temperature and general weakness - these are the symptoms of acute abscess or paraproctitis.
Important! Acute paraproctitis should be opened as early as possible, in a surgical hospital!
Sometimes patients mistake the painful process for an exacerbation of hemorrhoidal disease and begin self-medication, which in no case should be done until the correct diagnosis is established!
Which doctor should you contact if symptoms occur?
If you or your loved ones have the described complaints, you should contact a coloproctologist as soon as possible, who, after consultation and examination, will establish a preliminary diagnosis and determine further tactics and urgency of treatment, or, if in doubt about the diagnosis, a list of necessary additional studies.
If surgery is required, you will be offered hospitalization in a hospital, where, after assessing the results of the studies, which, as a rule, do not take much time and are easy to perform, the operation will be performed.
What studies should be performed in preparation for surgical treatment?
Before the operation, you need to perform a number of standard tests, however, if the disease worsens with the formation of an abscess, the operation is performed for emergency reasons, so waiting for test results should not delay surgical treatment.
In addition to general clinical standard laboratory tests, if a complex fistula or deep-seated abscess is suspected, a number of additional diagnostic procedures may be needed: MRI of the pelvis, ultrasound examination of the pelvis and perineal tissue.
As a rule, the external fistula opening is detected during examination, the internal one - during digital examination of the rectum or anoscopy. However, in some cases - with recurrent, complex fistulas - there is a need to trace the fistula tract along its entire length, evaluate its relationship with the structures of the perineum, and determine the presence of additional tracts or leaks. Today, only MRI of the pelvic organs has this capability, due to its high specificity and sensitivity. That is why this study is the main method for diagnosing complex rectal fistulas.
To objectively assess the functional state of the sphincter (that is, how well it contracts and performs its function), in some cases it is necessary to perform anorectal manometry. The indications and need for it in your case will be determined by your attending physician.
In addition, the patient is usually asked to fill out a special questionnaire, the results of which can be used to determine the degree of continentness (retention of solid and liquid stools and gases) before surgery.
In women, it is often necessary to conduct a vaginal examination to exclude communication between the fistula tract and the vagina when the fistula is located anteriorly.
To exclude other diseases of the colon (in patients over 45 years of age, in cases of colon cancer in relatives, in the presence of two or more fistula tracts), a colonoscopy may be necessary.
Contraindications for use
When used correctly and in accordance with the dosage, ASD is safe and does not cause side effects. It is prescribed with caution for chronic kidney diseases. Before starting treatment, you should consult your doctor and make sure there are no allergic reactions. Alcohol in any quantity is contraindicated while taking the drug.
To treat hemorrhoids, you can use ASD fractions 2 and 3. The drugs are effective not only against the pronounced signs of this disease, but also have a general strengthening effect. To obtain results, treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor in compliance with the recommended dosages.
Treatment
The only radical treatment for rectal fistula is surgery. The purpose of the operation is to eliminate the fistula and simultaneously preserve the function of the sphincters. These are two mandatory conditions that must be met during treatment. Once the diagnosis is established, your attending physician will tell you about all treatment options for this disease, their risks and the effectiveness of each method, and will also indicate which type of treatment is optimal in your case.
The type of fistula and the degree of involvement of the sphincter in the pathological process determine the choice and extent of surgical intervention.
In case of a low location of the fistula tract, affecting no more than 1/3 of the height of the sphincter apparatus (subcutaneous-submucosal, intersphincteric, low transsphincteric fistulas without additional leaks), the fistula tract is removed within healthy tissues with dissection of a small volume of sphincter fibers, which are then sutured (Fig. 5). For the most low-lying fistulas, an effective method is simple dissection of the fistula.
Figure 5. View of the postoperative wound after excision of the fistula with suturing of the sphincter. Marked stitches on the muscles
With this type of surgical treatment, after excision, a virtually painless wound defect is formed, which heals with the formation of a barely noticeable scar. When using this surgical intervention, cure occurs in 92-97% of cases.
For high or recurrent fistulas, the use of the above method of dissecting the fistula is unacceptable due to the risk of developing incontinence of intestinal contents or gases as a result of damage to a large volume of muscle mass. Instead, the fistula tract is cut out in the form of a tube within healthy tissue. In this case, a defect is formed in the wall of the rectum, which is closed with a small section of the mucous-submucous membrane of the intestine, the so-called plastic surgery with a displaced flap (Fig. 6).
Figure 6. Schematic illustration of the operation using a repositioned flap.
Another relatively low-traumatic method for the sphincteric apparatus is the method of ligation of the fistula tract in the intersphincteric layer - LIFT (ligation of intersphincteric fistula tract), proposed in 2007 by the Thai surgeon A. Rojanasakul. During this operation, the area of the fistula is excised through a small access in the projection of the intersphincteric space, the remaining areas of the fistula are bandaged. With this technique, there is no damage to the sphincter, the soft tissue defect is insignificant, and the wound heals faster. However, only the author of this technique was able to achieve outstanding treatment results with a cure rate of up to 94%. Modern world statistics indicate the effectiveness of this operation at the level of 60-70%.
Features of the use of Dorogov antiseptic
As noted earlier, ASD fraction 2, the use of which is permitted only on the initiative of a physician, is used for external or internal therapy. To ensure maximum convenience for the consumer, the medication is produced in four different forms, namely in the form of suppositories, lotions, microenemas and for oral administration.
Candles
https://youtube.com/watch?v=rUKFuftm22U%3Fenablejsapi%3D1%26autoplay%3D0%26cc_load_policy%3D0%26iv_load_policy%3D1%26loop%3D0%26modestbranding%3D0%26rel%3D1%26showinfo%3D1%26fs%3D1% 26playsinline%3D0%26autohide%3D2%26theme%3Ddark%26color%3Dred%26controls%3D2%26
ASD 2 suppositories are used for a simultaneous therapeutic and prophylactic course for hemorrhoids, as well as for eliminating swollen lumps in the anal ring.
To use suppositories, you must stop taking alcohol-containing products a week before the start of the course. Before using as directed, you need to cleanse the intestines with an enema. After using the restroom, thoroughly rinse the genitals and affected area with warm water. Then introduce suppositories with ASD.
The therapeutic course of this type of remedy is exactly three weeks with one administration in the morning and evening.
Lotions
Initially, the digestive tract should be cleansed through bowel movements or an enema. Afterwards, wash the genital area and anal ring, preferably with a hygiene product.
Lotions are made as follows: cotton wool or gauze is soaked with a product produced in liquid form. A thoroughly moistened cloth should be applied to the affected area for half an hour. Manipulation is performed 2 times a day. The therapeutic course is 21 days.
It is worth noting that the use of lotions allows you to quickly stabilize the patient’s condition, eliminate the newly formed lump and improve the condition of varicose hemorrhoidal veins.
Microclysters
This method implies the elimination of provoking causes and symptoms at the developmental stage, as well as the restoration of the natural regeneration of damaged veins in the anus.
To administer a microenema, you need to perform appropriate hygiene procedures, then rinse the anus without using auxiliary cosmetic or antibacterial products. For procedures, use only cool water.
At the end of the hygiene procedures, you need to take a syringe (it is recommended to use a tool with two cubes), collect one and a half milliliters of camphor oil and half a milliliter of ASD 3. By the way, this is the only methodology that uses the third fraction.
By pulling back the syringe plunger, you need to mix the collected products. It is recommended to shake the syringe for a minute.
The needle is used only when collecting funds into the instrument; it is not necessary for the procedure.
It is recommended to lubricate the back hole with petroleum jelly and place the cannula (the head on which the needle fits) completely into it. After this, slowly inject the medicine.
Microclysters for hemorrhoids are carried out no more than once a day, preferably before bed. The therapeutic course is two weeks, but, based on the symptoms of the disease and the patient’s condition, the time of use of the drug can be extended for another week.
After introducing the solution into the rectal canal, you must remain on your side or back for half an hour so that the medication does not leak out of the anus.
Oral administration
The methodology implies a complex effect on hemorrhoids. Oral administration allows you to simultaneously eliminate symptoms and provide complete treatment that has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the digestive tract. Promoters of this treatment method are convinced that during the therapeutic course, varicose hemorrhoidal veins will begin to shrink until they return to their original state.
The method of application is very simple. Every day, before the first meal, you need to take 30 drops of ASD 2, diluting the drug in a quarter glass of boiled water. Be sure to cool the water before mixing. The therapeutic course is two weeks of 6 days with a break of two days. The product should be used based on the doctor's recommendation.
Suppositories, microenemas or oral medications are prescribed by the attending physician after appropriate diagnosis. In case of an overdose or an incorrectly constructed therapeutic course, uncontrollable consequences may occur that can worsen the condition of the body, which will lead to the need for additional treatment.
Treatment of complex fistulas should be divided into 2 stages
At the first stage, a drainage ligature is installed into the fistula tract - a thin, almost invisible suture material (Fig. 7). The main goals of this stage of treatment are: the formation of a direct fistula tract around the ligature, drainage of possible leaks, reduction of the inflammatory process, prevention of self-closure of the external opening for constant drainage of inflammatory and/or purulent discharge.
Figure 7. Drainage ligature
At the second stage, after the acute inflammation subsides (4-6 weeks), the main surgical treatment is performed - excision of the fistula.
Important! Two-stage surgical treatment provides conditions under which radical surgery becomes possible with minimal complications.
Currently, in the treatment of rectal fistulas, various biological materials based on connective tissue (Permacol), fibrin glue, and collagen paste are widely used, which are introduced into the fistula tract, tamponing it. These methods have a lesser effect on the rectal closure apparatus; their use does not lead to the formation of a massive wound defect. However, the rate of disease recurrence is significantly higher than radical surgery.
Promising modern methods for treating fistulas are endoscopic (VAAFT) and laser (FiLaC) technologies for removal of affected tissue. These technologies practically eliminate the possibility of damage to the sphincter apparatus, however, today, the effectiveness in leading clinics in the world does not exceed 50-60%.
Anesthesia and pain relief after surgery
The vast majority of surgical interventions for rectal fistulas are performed under subarachnoid or, as it is also called, spinal anesthesia. It refers to regional anesthesia methods that block the transmission of nerve impulses in a specific part of the body. A distinctive feature of any method of regional anesthesia is the minimum number of complications, in particular from the cardiovascular system, respiratory system, and brain. At the same time, you are conscious or, at your request, are in a superficial medicated sleep (sedation).
In the case of subarachnoid anesthesia during perineal surgery, the blockade of the nerve impulse occurs at the lumbosacral level. In our clinic, anesthesiologists and resuscitators prefer to perform a “saddle” block, which provides ideal anesthesia of the perineum with virtually no motor block, i.e. with preservation of motor function. If necessary, anesthesia can be supplemented with intravenous sedation. All this ensures maximum comfort for the patient and ideal working conditions for the surgeon.
If you are constantly taking a number of medications, for example, antihypertensives, those that affect blood clotting, or others, be sure to inform your anesthesiologist-resuscitator about this a few days before surgery.
Surgical interventions on the perineum can also be performed under general anesthesia.
After the operation, you will be prescribed pain relief as planned for several days, which can be easily done at home using tablets. These include local anesthetic drugs, intravenous analgesics and, in case of severe pain, potent drugs.
Use during pregnancy
Another important contraindication is that the antiseptic Dorogov stimulant of the second fraction is strictly prohibited for use by pregnant, nursing mothers and women planning to conceive. This measure is due to the fact that the active ingredient in meat and bone meal can cause significant harm to the baby or fetus located in the mother’s womb, while weakening the female body.
If hemorrhoids occur in pregnant or lactating women, experts recommend using a similar drug or refraining from treatment, using maintenance medications that are safe for the baby’s health.
How to behave after surgery?
After the operation, you will remain in the hospital for 1 to 5 days, depending on the complexity of the operation. You will be prescribed, if necessary, antibacterial therapy and dressings with wound-healing ointments will be performed. After surgery, you may need to hold stool to allow the wound to heal.
Your doctor will teach you how to care for the wound, and it is extremely important to follow these recommendations strictly. One of the important recommendations is to irrigate the wound with a stream of water 3-4 times a day for the purpose of mechanical cleaning and periodic medical monitoring of proper healing in the direction “from the bottom of the wound.” After training, as a rule, you will be able to perform dressings yourself at home.
Microclysters with ASD 3
Microenemas with ASD 3 help relieve the inflammatory symptoms of hemorrhoids, and also accelerate the healing of anal tears.
Microenemas with ASD 3 help relieve the inflammatory symptoms of hemorrhoids, and also accelerate the healing of anal tears.
Before microenemas, bowel movements and hygienic toileting of the anus with cool water without soap are mandatory.
Then fill the syringe with one and a half milliliters of camphor oil and half a milliliter of ASD 3.
Pulling back the syringe plunger slightly, shake the well-filled solutions. The syringe is used without a needle!
Lubricate the cannula of the syringe with petroleum jelly, insert it into the anus and inject the contents into the rectal canal.
Microclysters with ASD 3 are recommended to be performed once a day at night for 7-10 days. After the procedure, you need to lie down for 30-40 minutes so that the medicine does not leak out of the anus.
What complications can there be after surgery?
Currently, with the availability of standardized technology and an integrated approach to the diagnosis and treatment of rectal fistulas, unpleasant consequences are minimized. However, it should be noted that the risk of complications always exists.
The most serious complication after surgery for rectal fistulas is the development of anal incontinence. The risk of its occurrence is especially high during repeated interventions, when the anatomy is significantly changed and the holding function may be initially compromised. It is worth noting that when operations are performed by an experienced specialist who performs this type of intervention on an ongoing basis, the risk of incontinence is practically absent.
In addition, bleeding may develop both in the early postoperative period and several days after surgery. The nature and severity of the complication are determined only after examination. Stopping bleeding is usually possible in a dressing room. In some cases, repeat surgery may be required.
In addition, when treating complex and recurrent fistulas, due to pronounced scar changes, the sutures fixing the mucomuscular flap may diverge, which leads to inflammation in the wound and requires repeated interventions.
What is the likelihood of the disease returning?
The risk of disease relapse with complex, high fistulas is slightly higher than with simple intrasphincteric fistulas and depends on the type of fistula, its location, and the presence of previous surgical interventions. Treatment of recurrent fistulas is a particularly difficult task for a coloproctologist. Previous operations on the anal canal create gross cicatricial deformities, changing the anatomy and significantly impairing the function of retention, and a long course of the disease or inadequate previous treatment can lead to the formation of additional streaks and passages. In such conditions, planning of surgical intervention should be carried out after a full examination.
The success of the upcoming surgical intervention largely depends on a comprehensive assessment of the available data using various diagnostic methods and a mandatory conversation with the surgeon. An important factor is also the implementation of surgical intervention in a specialized hospital, where this type of treatment is based on world research data, their own many years of experience and is carried out by specialists who have successfully completed training and courses to improve their skills in treating this disease.
Important! The skill of a coloproctologist is judged all over the world by the ability to correctly operate anorectal fistulas, since since the existence of proctology, the treatment of fistulas has been and is now perhaps the most difficult section of diseases of the anorectal zone!
Description of the drug
On the shelves of pharmacies you can find a huge number of drugs for the treatment of hemorrhoids - since this problem is very common, new ways to solve it are being developed, both with the help of drugs and alternative medicine.
One of these methods is the treatment of hemorrhoids using a solution of ASD fraction 2: an antiseptic stimulant of animal origin. Despite the low prevalence of the drug, it has obvious advantages over a number of other means of scientific medicine - its high effectiveness and minimal risk of side effects on the body have been experimentally proven. The benefits of fraction ASD 2 for medical use were revealed during clinical experiments - the drug helps treat a large number of diseases: asthma, eczema, infertility, etc.
There are many different drugs to treat hemorrhoids
Why do you choose us?
Part of the Perm State Medical University named after. I.M. Sechenova Clinic of Coloproctology and Minimally Invasive Surgery is an example of a new generation of medicine, harmoniously combining the deepest fundamental knowledge, honed skills, a modern multidisciplinary approach and attentive attitude to any category of patients.
KKMH is a guarantee that the surgical interventions performed within our walls correspond to the most current ideas about colorectal surgery. This includes our own department of anesthesiology and intensive care, whose employees ensure a smooth course of the operation and the early postoperative period and treat seriously ill patients. This is an “open intensive care unit”, where you can not only find out the most complete information about the condition of a loved one, but also be with him during a difficult time for him.
The doors of our Clinic are open to patients who were denied treatment in other hospitals due to the complexity of the surgical intervention or the neglect of the process. Elderly patients, patients with a “bouquet” of concomitant diseases (so-called comorbid) are an area of our special interest. The presence in the hospital of such highly professional specialists as a cardiologist, pulmonologist, urologist, etc. allows us to treat patients of any age and with any concomitant diseases.
KKMH is a dynamically developing team of specialists who sincerely and deeply love their work, who are continuously learning and teaching others, who are interested in keeping you healthy.
Oral administration of ASD 2
When taken orally, ASD 2 has a complex effect on hemorrhoids, since the drug eliminates not only the symptoms of the disease, but also normalizes intestinal function and metabolism in the tissues of the anorectal area, increases the tone of the hemorrhoidal veins, etc.
When taken orally, ASD 2 normalizes intestinal function.
In the morning, half an hour before meals, take 30 drops of ASD 2, diluted in ¼ cup of boiled and cooled water. The course of treatment in this case is 13 days (5 days each with a break of 3 days).
Treatment for ASD 2 or ASD 3 should be prescribed exclusively by your doctor. Incorrect selection of the dose of the drug can negatively affect the general condition and even aggravate hemorrhoids.
Only a doctor knows the characteristics of your body and the course of the disease, so he can foresee possible adverse reactions and the outcome of treatment.