It’s not for nothing that hemorrhoids are called “the problem of the century.” Both residents of villages engaged in heavy physical labor and residents of large cities who lead a sedentary lifestyle near a computer suffer from a painful illness. Poor nutrition, frequent constipation, prolonged standing, hereditary factors, failure to properly observe the rules of intimate hygiene - all this can cause the disease.
Treatment of hemorrhoids may include conservative therapy and surgery. In order to avoid surgery, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment. The treatment process includes a whole range of measures, including proper nutrition and moderate physical activity. Modern pharmaceutical companies produce a wide range of drugs.
One of the popular and effective remedies is Troxerutin for hemorrhoids. The drug has a number of unconditional advantages, but is also associated with some limitations. For this reason, the drug is not used as self-medication, but is used according to indications.
Pharmacology
The medicine helps relax the smooth muscles of internal organs. After taking it, there is an improvement in the tone of the walls of blood vessels, they become less distensible, as a result of which blood stagnation disappears, the likelihood of edema decreases, and the severity of inflammatory processes decreases.
Capsules for oral administration are easily excreted from the stomach. The maximum concentration of the active element occurs 3-7 hours after administration. The second peak occurs approximately 28 hours later. The drug leaves the body completely within a day. Most of it is excreted by the liver, and a small part is excreted by the kidneys.
When the gel is applied locally, the constituent elements do not leak into the blood, but they still penetrate into the tissue adjacent to the skin.
Instructions for use
To begin with, let’s highlight the main advantages of Troxerutin Vetprom:
- angioprotective effect;
- anti-edema effect;
- venotonic effect;
- antioxidant effect;
- combating the inflammatory response;
- active participation in regeneration processes;
- strengthening the walls of blood vessels;
- accelerating the elimination of metabolic products;
- no toxic effects.
Troxerutin is used not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of hemorrhoids
In what cases is it used
Taking the drug is advisable in the following cases:
- varicose veins (including when carrying a child);
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- haemorrhoids;
- tissue swelling;
- influenza, measles, scarlet fever;
- vascular effects resulting from radiation exposure;
- high permeability of capillary walls.
After surgery on the veins, it can be taken for preventive purposes.
How to take capsules correctly
The tablets must be taken with food. The capsule cannot be chewed or dissolved; it must be swallowed whole with water. The permissible dose is 1 tablet three times a day. If the drug is taken as an auxiliary medicine, then you need to take 2 tablets per day. The duration of the therapeutic course is 20-28 days. Only a doctor can extend the course of treatment.
Depending on the manufacturer of the drug, there may be minor differences in the instructions for use. Taking Troxerutin Zentiva capsules is similar to the regimen described above, while Troxerutin Vramed in the first days of therapy should be taken 1 capsule no more than 3 times a day, after which switch to maintenance therapy, taking 1 tablet per day.
Troxerutin-MIC involves administering the drug intramuscularly or intravenously. One injection will require 0.5 active substance. The procedure should be carried out every other day. The course must include at least 5 injections. After the injections, you can begin treatment with tablets.
Reviews about Troxerutin
Tatyana, 56 years old I have been suffering from hemorrhoids for a very long time, the disease has already become chronic. During exacerbations, I use rectal suppositories and ointments as directed by the doctor. At my last appointment with the proctologist, the doctor advised me to take Troxerutin capsules. He explained to me that the drug eliminates the very causes of hemorrhoids, reducing its manifestations. I took one capsule twice a day and after about a week the exacerbation passed. The doctor advised me to take the capsules for another three weeks, only once a day.
Lyudmila, 47 years old I treat hemorrhoids with Troxerutin gel. The doctor explained to me that gel alone is not enough, you need to change your lifestyle and normalize your diet. I really like the gel because it is quickly absorbed and does not leave stains on clothes. The drug really helps. Some time after application, discomfort in the anus disappears, itching and burning become less pronounced. As I understand from the instructions, Troxerutin is a safe remedy that does not have a toxic effect on the body. I am pleased with the result and recommend it to everyone. Troxerutin will definitely help!
Larisa, 39 years old I have been suffering from hemorrhoids for a very long time, I have already tried many medications, but I settled on Troxerutin. This is a drug that really helped me. I took the capsules orally and also lubricated the hemorrhoids with gel. I felt the effect of the drug the very next day, when the symptoms of hemorrhoids became much less. I didn’t experience any side effects, the hemorrhoids went away, and for six months now they haven’t bothered me. The doctor advised me to take a preventative course over time.
Troxerutin is a drug for hemorrhoids in action. The product is available in various dosage forms - both for oral administration and for local use. Troxerutin fights not only the clinical manifestations of hemorrhoids, but also eliminates the etiological mechanisms of the disease, providing a venotonic and angioprotective effect. The drug normalizes blood microcirculation and eliminates congestion.
You will feel the result within a few days. It is worth remembering that Troxerutin has a number of side effects and contraindications, so before starting treatment, you should carefully study the instructions. If you want to quickly cure hemorrhoids and avoid unpleasant complications, then do not delay your visit to the doctor, and when the first alarming symptoms appear, get examined!
How to take Troxerutin gel
The drug in the form of a gel is intended for local application. It should be applied to the problem area 2 times a day (morning and evening). The ointment should be distributed in a thin layer over the entire damaged area, without affecting healthy skin. You need to rub the product in with smooth massaging movements until the gel is completely absorbed.
The permissible dose depends on the size of the problem skin, but should not be more than 2 g. When the ointment is applied, a bandage should be applied to the surface of the skin.
The drug in the form of an ointment, regardless of the manufacturer, has a similar treatment regimen.
Side effects
The drug is well tolerated by patients, but in rare cases, unwanted complications may occur:
- headache;
- allergic reactions in the form of rash and peeling;
- dyspeptic disorders, stool disorders;
- dermatitis;
- skin redness.
In case of overdose, the following reaction is possible:
- rush of blood;
- excitation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- redness of the skin.
If unpleasant symptoms occur, you should stop using the product and report the incident to your doctor.
Contraindications
Contraindications include:
- hypersensitivity to the constituent substances of the drug;
- chronic gastritis in the acute stage;
- stomach ulcer;
- children under 15 years of age;
- lactation period;
- 1st trimester of pregnancy.
Use with caution in case of kidney problems (if long-term treatment is necessary).
Indications for use
The range of applications of Troxerutin is quite wide; it is used for venous insufficiency, injuries accompanied by edema and hematomas. When treating hemorrhoids, the remedy is part of complex therapy.
Pain in the anorectal area, the presence of hemorrhoids, constipation caused by inflammation of the anal veins - all this is an indication for the use of Troxerutin.
The drug is a vasoprotective agent that has the following effects on the body:
- improvement of tissue trophism;
- normalization of blood microcirculation;
- reducing the fragility of blood vessels and improving their elasticity;
- elimination of inflammation, swelling and hematomas.
Troxerutin is effective even when complications occur or the process becomes chronic. The drug is sometimes prescribed for venous insufficiency. The product is also used in the postoperative period to remove hemorrhoidal cones.
Troxerutin is not prescribed in the first trimester of pregnancy
special instructions
The drug in one of its forms can be used as part of a complex treatment. In case of vein thrombosis, parallel use of appropriate medications is allowed.
Shelf life: capsules – 5 years, gel – 2 years from the date of production.
Store in a dark place. Storage temperature for gel is 10-15 degrees, for capsules - 17-25 degrees.
Sold in any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.
Manufacturers assure that the drug is absolutely harmless. It is prescribed to people who are overweight, as well as to the fair sex who wear high-heeled shoes. The medicine is recommended for people whose work requires constant standing.
To achieve maximum effect, you need to use gel and capsules from the same manufacturer. In the absence of contraindications, it is best to use Troxerutin together with ascorbic acid for a more pronounced effect.
Modern methods of treating hemorrhoids
Etiology
Hemorrhoids (from the Greek haimorrois) literally mean “bleeding.” This disease, known since time immemorial, is still explained ambiguously and sometimes contradictorily, which fully reflects the level of our knowledge about it. Most researchers recognize that the sources of bleeding are cavernous formations, which under normal conditions are formed during intrauterine development.
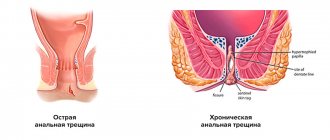
The first group of hemorrhoidal formations, the defeat of which leads to the formation of external hemorrhoids, is located at the exit from the anal canal, in the subcutaneous tissue.
The second group of cavernous formations, located in the submucosal layer of the rectum, above the dentate line, is the source of the development of internal hemorrhoids.
There are anastomoses between the external and internal cavernous formations, the functional purpose of which is not entirely clear, if only because with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, as a rule, external rather than internal nodes thrombose. Along with the external and internal sphincter, the cavernous plexuses are part of the obturator apparatus of the rectum. Their ability to increase in volume due to filling with blood allows for an ideal sealing of the intestine. Indirect evidence of this assumption is the ordered arrangement of hemorrhoidal formations around the circumference of the intestine; it corresponds to 3, 7 and 11 o'clock. Unfortunately, this delicate mechanism is very vulnerable and there are many reasons for this. The immediate cause of hemorrhoids is a violation of the blood supply to the cavernous veins, which can be caused by increased arterial blood flow, but more often by a slowdown in venous outflow. The dilated vein forms a “bag of blood”, which is called a hemorrhoid. In recent years, much attention has been paid to studying the condition of the ligamentous apparatus of the submucosal layer of the rectum, the violation of which leads to the prolapse of internal hemorrhoids. Therefore, from the point of view of modern pathophysiology, both variants of the development of the disease should be considered not only as equivalent, but, possibly, as complementary.
Prevalence . Data on the prevalence of hemorrhoids are very contradictory; for example, in Russia this figure ranges from 130–145 cases per 1000 adults [1]. Statistical data provided by foreign researchers is only about 4.4% [2, 3]. The inconsistency of the indicators is most likely due to the difference between morbidity and negotiability, which is indirectly confirmed by data from examinations of US residents, which stated that 80% of people who had hemorrhoids did not complain [4].
Classification of hemorrhoids . The classification was proposed by the State Scientific Center of Coloproctology [1]. It includes the symptoms of the disease, its clinical manifestations and anatomical changes. According to the course of the disease, chronic and acute types of hemorrhoids are distinguished. In shape - internal, external, combined. The chronic course of internal hemorrhoids is divided into 4 stages. It should be emphasized that the clinical symptoms of the disease correspond to the morphological changes occurring in the longitudinal muscle, which fixes cavernous formations in the submucosal layer of the rectum.
In the first stage: bleeding and discomfort are clinically noted, hemorrhoids do not fall out of the anal canal, the vascular pattern of the mucous membrane is enhanced, anatomically - changes in the longitudinal muscle are insignificant.
In the second - bleeding, prolapse of nodes, itching, mucous discharge; prolapsed nodes are automatically reset into the anal canal; histologically in the fibromuscular framework there is unexpressed dystrophy, the number of elastic fibers predominates.
In the third - bleeding, prolapse of nodes, anal itching, mucous discharge. Prolapsed hemorrhoids require manual assistance to reposition them into the anal canal; At the same time, morphological changes in muscle tissue indicate a loss of elasticity, which proves the predominance of dystrophy processes.
In the fourth - bleeding, itching, discomfort, incontinence of the anal sphincter, severe pain; constant prolapse and inability to manually reduce hemorrhoids into the anal canal; which corresponds to complete degeneration of the fibromuscular framework that holds the nodes in the anal canal.
Complications of hemorrhoids . The most common complication of hemorrhoids is thrombosis of hemorrhoids. As a rule, the lesion occurs in the external nodes and quite often thrombosis is the first manifestation of the disease. Precipitating moments for the development of thrombosis most often include pregnancy, childbirth, long air travel, lifting heavy weights, and acute stool disorders. If patients seek help in the first 2 days from the onset of the disease, an enlarged bluish (at an early stage) hemorrhoid, covered with skin and partially mucous, is easily visually detected. More often, the appearance of a node is accompanied by pain, especially intense if two or more nodes are affected. If the size of the node is significant (usually more than 2 cm) with pronounced tension in the mucosal tissue, an area of necrosis appears on it; after rejection of the latter, bleeding develops, sometimes parts of the blood clot may partially come off and the size of the prolapsed formation may decrease significantly. The skin part of the node becomes swollen and hyperemic. Clinically, as a rule, in this case, the patient notes a decrease in pain. Digital examination should begin with examination of the wall of the anal canal opposite to the thrombosed node, which makes the examination more gentle. A digital examination can reveal signs of thrombosis of the internal hemorrhoid. Examination of the anal canal using instruments is carried out only by proctologists.
More rare complications include the formation of a hematoma with a sharp increase in pressure and damage to the wall of the venous vessel. If an internal hemorrhoid prolapses, it may become strangulated. If necrosis of the internal node occurs, massive bleeding is possible, so the patient should be shown to a proctologist. In the event of strangulation of several prolapsed nodes or the occurrence of stool disorders, a purulent process may occur in the perirectal tissue.
Differential diagnosis
Clinical manifestations of hemorrhoids do not differ in the specificity of symptoms. In case of acute hemorrhoids or its complications, these are acute paraproctitis, anal fissure, cryptitis, rectal prolapse. In the case of chronic hemorrhoids, the development of a tumor of the rectum or anal canal should first be excluded. The group of patients who have been suffering from hemorrhoids for a long time, who have come to us due to increased bleeding or unstable stools, is of particular concern in terms of oncological diseases. In case of any treatment of a patient with hemorrhoids to a therapist or general practitioner, it is necessary to refer him for a consultation with a proctologist.
Conservative treatment
The choice of treatment method is usually determined by the stage of the disease or the nature of the complications that have developed.
A special diet for patients with hemorrhoids is not required, except in certain cases. For thrombosis of hemorrhoids, a protein-vegetable diet with a high fiber content and the exclusion of fried and spicy foods, spices, and alcohol is recommended. In patients with concomitant diseases of the colon (irritable bowel syndrome, diverticular disease or nonspecific colitis), the diet should be aimed at normalizing stool. In case of thrombosis of hemorrhoids, accompanied by constipation, patients should be prescribed microenemas to cleanse the intestines. Patients leading a sedentary lifestyle, without exacerbation, should be recommended to play sports, with the exception of weightlifting and cycling. Patients should pay special attention to performing hygienic measures. During the acute period of the disease, it should be recommended to take a cool shower 2-3 times a day and always after stool, and it is necessary to wash not only the skin of the perineum and anus, but also the anal canal itself. In cases where water procedures are not available, the use of special wet sanitary napkins should be recommended.
Systemic drugs . In the conservative treatment of hemorrhoids, one of the leading roles belongs to drugs containing bioflavonoids (diosmin and hesperidin). The use of the latter in the treatment of hemorrhoids is traditional, but with the creation of modern biotechnologies it was possible to obtain Detralex, a micronized drug, which made it more bioavailable and increased the effectiveness of treatment by about 30%. Bioflavonoids have several properties: first of all, they are able to increase venous tone, enhance lymphatic drainage, reduce vascular fragility and improve microcirculation. First of all, the listed qualities make it necessary to use Detralex in the event of thrombosis of hemorrhoids. The drug is prescribed 2 tablets 3 times a day for the first four days, then 1 tablet 4 times for up to 7 days. In addition, Detralex is able to reduce and prevent the development of hemorrhoidal bleeding and exacerbation of hemorrhoids. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to take the drug for up to 6 months, 2 tablets per day. The use of micronized bioflavonoids (the source of which are natural sources, for example, red grape seeds) is possible even during pregnancy, although not for a long time (up to 7 days). The drug is well tolerated and rarely causes allergic reactions. To date, the drug “Phlebodia 600” has been successfully used, which has a prolonged effect, which allows it to be taken once a day. In patients with thrombosis of hemorrhoids, accompanied by severe pain, it is possible to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics, but it is extremely difficult to assess the effectiveness of their effects, so the question of their use should be decided individually in each specific case.
Local therapy . Local treatment is prescribed to relieve inflammation and analgesia. Among the drugs of the first group, we can recommend Posterisan Forte ointment (or suppositories of a similar name). The drug contains a suspension of E. coli culture and hydrocortisone. E. coli metabolites can enhance local immune responses, accompanied by the release of cytokines, especially intraleukin-1. In addition, a suspension of bacterial culture causes the formation of specific immunoglobulin A, which forms a delicate film on the intestinal mucosa, acting as a local protective barrier. Hydrocortisone, which is the second component of the drug, helps to quickly suppress inflammation and accelerates the processes of tissue regeneration induced by a suspension of Escherichia coli culture. The drug is administered rectally 2 times a day; in case of severe inflammatory process, for example, in patients with nonspecific colitis, the frequency of administration can be increased taking into account the frequency of stool. The maximum duration of treatment does not exceed three weeks. If it is necessary to continue therapy, it is possible to use Posterizan suppositories or ointments containing exclusively a suspension of bacterial culture.
Among the drugs that have a complex effect, we recommend Relief Advance suppositories. The composition includes 10% benzocaine, which has a rapid analgesic effect, in addition, shark liver oil containing fat-soluble vitamins, free fatty acids, squalene and alkylglycerol, which are powerful reparants, which allows them to be recommended even for use in the postoperative period in patients who underwent surgery for hemorrhoids. The frequency of administration is 3–5 times a day. The drug is highly effective, well tolerated and rarely produces adverse reactions.
Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
External hemorrhoids . In addition to conservative treatment of thrombosed hemorrhoids in the first 24–48 hours, until inflammatory changes in the skin part of the node occur, surgical intervention is possible. It is usually performed under local anesthesia and involves removing the hematoma or thrombotic masses, although there is an opinion that it is necessary to remove the entire node along with the affected vein [5]. This tactic is justified in the presence of one (less often two) large nodes or in severe pain. Unfortunately, such operations can not be performed often, because the majority of patients consult a doctor already in the presence of severe inflammation, which sharply intensifies the pain syndrome that existed until that moment. Surgical removal of large external nodes is justified in case of difficulties arising with hygiene, persistent anal itching or after previous thrombosis, although in recent years many patients have turned to a proctologist for aesthetic reasons.
Internal hemorrhoids . Currently, there is a fairly large selection of minimally invasive treatments, used mainly for isolated internal hemorrhoids of stages I–II. True, sometimes the indications for their use can be expanded, mainly in elderly and senile people with severe concomitant diseases. Minimally invasive interventions include: infrared photocoagulation, latex ring ligation and, finally, transanal ligation under Doppler control. The first two of these methods have long been used in clinical practice, and their strengths and weaknesses are well known, so we will dwell in more detail on the last method.
Ligation of hemorrhoidal arteries under Doppler control . The essence of the method is based on the fact that Doppler examination reveals the distal branches of the superior hemorrhoidal artery, supplying blood to the internal hemorrhoids. The necessary equipment is an electronic unit and an anoscope with a Doppler sensor. The method can be used for stages I–III of the disease. The procedure can be carried out in a hospital within one day. The procedure lasts 20–40 minutes, does not require general anesthesia, restrictions on physical activity for about two weeks. Temporary disability is not required for patients. There are no problems with stool in the early postoperative period.
Operation Longo . Prolapse of the mucous membrane of the anal canal with internal hemorrhoidal plexuses, caused by damage to the muscular and ligamentous apparatus of the latter, is accompanied by a disruption of their blood supply and a change in the anatomical relationships between the external and internal nodes. This prerequisite served as the basis for the creation of the Longo operation, which involves tightening the prolapsed mucosa, restoring the anatomical position of the hemorrhoidal plexuses and normalizing their blood flow. The Longo method has been used in clinical practice since 1993, in our country for the last 5 years. The intervention is performed with a disposable set of instruments. The operation is indicated for stages II–IV of hemorrhoids. In our opinion, the advantages of this procedure are most convincing for circular prolapse of nodes. The operation can be performed under conduction or local anesthesia.
Advantages of the method; the duration of the operation is 10–20 minutes, the hospitalization period does not exceed one day, the pain syndrome is well relieved without the use of narcotic analgesics, there is no need for dressings, the patient can return to work in 5–10 days.
Bipolar coagulation of hemorrhoids using the LigaSure device . A modern alternative to classical hemorrhoidectomy is the method of bipolar coagulation of hemorrhoids, which is successfully used in stages III–IV of the disease. The method is based on the principle of bipolar coagulation using a modernized generator equipped with a feedback unit that allows tissue differentiation. In this case, the usual burn of the tissue does not occur, but welding occurs due to the polymerization of its own collagen and instead of the usual scab, the wound is covered with a collagen film. The intervention can be performed under spinal or epidural anesthesia. The intervention technique is simple. The reliability of polymerization guaranteed by the method makes it possible to coagulate vessels up to 7 mm in diameter. The duration of the operation is about 20 minutes. The duration of postoperative treatment is determined by the size of the wound defects of the anal canal. Pain syndrome in the postoperative period is less pronounced than during traditional surgery.
Literature
- Vorobyov G.I., Shelygin Yu.A., Blagodarny L.A. Hemorrhoids. M.: Publishing house "Mitra-Press", 2002. 192 p.
- Johanson JF, Sonnenberg A. The prevalence of hemmhoroids and chronic constipation // Gastroenterology. 1990, 98; 380–386.
- Bayer I., Myslovaty B., Picovsky BM Rubber Band ligation of hemorrhoids: covenient and economic treatment // J. Clin. Gastroentrol. 1966; 23:50–52.
- Haas PA, Haas GP, Schmaltz S., Fox TA Jr. The prevalence of hemorrhoids // Dis. Colon Rectum. 1983; 29: 435–439.
- Corman MI Colon and Rectum surgery, 3rd ed.Philadelphia, Pa: JB Lippincott. 1993: 54–115.
K. E. Mayat , Candidate of Medical Sciences European Medical Center , Moscow