Do not self-medicate. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor.
This test has some distinctive features from other methods used to study the clotting time of the main biological fluid of the human body. For example, such a blood test involves the use of capillary blood, while others involve the study of venous material.
It is also worth noting that no specific preparation is required from patients. However, there are several factors that influence the determination of blood clotting in this way.
These include:
- age category - in infants, as a result of the lack of certain substances and features of the functioning of internal organs, the indicator may be increased, that is, coagulation will take longer;
- poor nutrition, namely, insufficient intake of vitamins and nutrients into the body provokes a decrease in coagulation;
- Excessive physical activity also negatively affects the period of time that should be spent on clotting.
Why is the rate of blood clotting determined, what does this indicator mean?
A coagulogram is important for assessing the state of hemostasis. This functional system is an evolutionarily developed protective reaction of the body aimed at preventing lethal blood loss due to vascular damage.
Hemostasis is a sequence of physiological processes that ensure a sufficient volume of hematological fluid for normal life and maintain it in an optimal state of aggregation.
Blood clotting according to Sukharev (the norm is estimated as the time interval between the collection of biological material and the beginning of its thickening) is determined for:
- making a diagnosis;
- clarification of the clinical picture;
- many other therapeutic purposes.
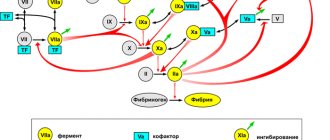
The coagulation mechanism is associated with physiological reactions and the chemical composition of the molecular plasma fraction of the hematological fluid. The leading role in the blood clotting process is assigned to fibrinogen, a colorless protein contained in the blood that is broken down by thrombin.
The process is automatically activated when the vascular walls are damaged. As a result, fibrin is formed - a high-molecular protein compound of a non-globular type. The substance is the finest insoluble thread-like structures that form a dense network.
A complex of biological transformations is aimed at the formation of clogging blood clots. They have a compacted structure that stops bleeding and heals wounds. The more platelets the material taken for laboratory analysis contains, the higher the coagulability of the hematological fluid.
Such diagnostic information characterizes the functional state of the hematopoietic system and is required:
- before operations;
- in the treatment of numerous diseases;
- to control gestation.
Interesting Facts
Poor blood clotting - treatment and symptoms.
How to treat poor blood clotting Such a rare and life-threatening genetic disease as hemophilia (blood clotting disorder) causes serious harm only to the male half of the population. A woman can only be a carrier of this gene with pathology, but the disease itself does not affect her health in any way.
There are several names of diseases associated with disturbances in the number of platelets in the blood and their activity:
- Absolutely any deviations in these indicators are called thrombocytopathy.
- If the level of platelets in the blood is low, then this pathology is called thrombocytopenia.
- If the level of such a main component of blood as platelets is higher than normal, then this is the disease thrombocytosis.
- When impaired functional activity is detected, the disease is called thrombasthenia.
At Harvard University, a group of scientists and students discovered an interesting relationship between the amount of fibrinogen (a protein that is produced in the liver and converted into fibrin, the basis for clot formation during the activation of the blood clotting process) and the number of human contacts in society. Based on the research results, it was concluded that the narrower the circle of contacts with people, the higher the level of fibrinogen. And this, in turn, causes irreparable harm to health, especially detrimental to the cardiovascular system. Therefore, communicating with other people is beneficial not only for mental health, but also for physical health!
Some private laboratories provide the service of taking biological material for blood clotting testing directly at home, i.e., you do not need to go to the laboratory yourself. This is very convenient for disabled people, elderly people and small children.
What is the essence of Sukharev’s method?
A coagulogram is a preventive measure to prevent complications with an increased risk of massive blood loss or thrombosis when prescribing drugs that affect the rheological properties of hematological fluid.
Blood clotting according to Sukharev
Sukharev's test involves the use of capillary biological material obtained by piercing the skin of the terminal phalanx of the finger with a scarifier.
The blood is placed in a laboratory vessel, alternately tilting it in opposite directions at an angle of 40°. Simultaneously with the start of the hematological test, a stopwatch is started, counting the time until the biomaterial clots.
The analysis is considered extremely simple, well established, and widely applicable. It allows you to obtain an informative hemostatic picture about the time interval of coagulation.
The test does not determine the chemical composition of the blood or provide data on physiological reactions. The main advantages of such analysis are speed, simplicity and availability in any laboratory.
The vessel is tilted in a given monotonous rhythm without sudden movements or shaking the contents of the test tube. According to Sukharev’s method, the beginning of coagulation is considered to be the cessation of free movement of biological material inside the vessel.
To automate the process, a special apparatus called a Panchenko tripod is used. The first drop of blood released from the finger is blotted, since it contains particles of the epidermis that distort the measurement result. The rheological properties of the following portions of biological material are studied.
Blood clotting according to Sukharev (the norm is determined by the beginning of the formation of fibrin protein) is necessary:
- to assess the effectiveness of therapy;
- for injuries;
- for hemodynamic disorders;
- in case of hepatobiliary dysfunctions, fibrin is produced by liver cells.
The indicator plays an important role in the interpretation of the coagulogram by the attending physician. Coagulation time according to Sukharev’s method is used to predict ischemic conditions, the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Diagnostics
Regardless of what symptoms appear, first of all you need to contact a general practitioner - a therapist or a pediatrician (for children).
In addition, you may need to consult specialists such as:
- hematologist – required;
- gastroenterologist;
- oncologist;
- nephrologist;
- medical geneticist;
- immunologist
The rate of blood clotting is determined by performing a biochemical blood test.
The procedure must be carried out taking into account the following rules:
- You need to donate blood in the morning - at least 8 hours must pass between the last meal and the procedure;
- one day before the LHC test, it is necessary to exclude from the diet fatty, fried foods, alcoholic beverages, excessive physical activity and taking medications (in consultation with the attending physician);
- You need to undergo the procedure in a calm emotional and physical state.
If the patient is on a diet or taking any medications that cannot be stopped, the doctor should be notified before undergoing LBC.
Rules for donating blood
Indications for testing
The time interval for blood clotting is determined in preparation for surgery on internal organs.
The following pathologies are considered indications for a hematological test:
- drug, chemical or alcohol intoxication of the liver;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- stomach ulcer;
- gastritis;
- erosive-perforative processes in the intestines;
- varicose deformation of venous beds;
- tendency to thrombosis;
- diabetes;
- endocrine disorders;
- metabolic and metabolic disorders.
This study is prescribed before using anticoagulant drugs.
Determination of blood clotting is indicated for women:
- For menstrual irregularities. The test is prescribed as part of differential diagnosis.
- Before childbirth. Diagnostic information about the rheological properties of blood allows you to avoid numerous complications.
- For the procedure of artificial abortion. Surgical intervention is traumatic and associated with massive blood loss.
- Before a caesarean section. Determination of hemostatic characteristics plays a significant role in ensuring the safety of mother and child.
- For hypermenorrhea. Dysfunctional-pathological uterine bleeding requires clarification of the cause and selection of adequate treatment tactics. A coagulogram using the Sukharev method is carried out as part of a comprehensive laboratory and hardware diagnostics.
- In preparation for artificial conception. Hemostatic disorders can provoke bleeding during in vitro fertilization, during embryogenesis, and subsequent labor. Excessive thrombus formation causes blockage of the blood vessels of the placenta, which leads to fetal death and miscarriage.
A coagulogram using the Sukharev method is used in the selection of oral contraceptives, many of which affect the rheological properties of blood. The study is indicated for patients taking Heparin for a long time.
A hematological test is carried out to clarify the clinical picture of DIC syndrome - a pathological process with nonspecific physiological characteristics, which is characterized by the formation of disseminated blood clots. Among the numerous indications for laboratory testing of blood clotting time are autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular dysfunctions, and genetic pathologies.
The test is performed if excessive viscosity of the hematological fluid is suspected, due to excessive concentration of fibrin protein or increased secretion of platelets. A coagulogram is prescribed during a comprehensive examination of patients prone to spontaneous nosebleeds.
Factors influencing the test result
During the active menstrual cycle, minor deviations from the standard are observed. Among the physiological factors influencing the result of a hematological test, the gestation period is distinguished. Hormonal changes in the body change the rheological properties of the blood.
Clotting according to Sukharev's method distorts the use of oral contraceptives. Small deviations from the established norm are acceptable when using birth control pills or capsules. The patient's age is considered to be a factor influencing the test result.
In newborns, blood clots faster than in adults due to the absence in the infant’s body of some biochemical compounds involved in the hemostasis system and the immaturity of the protective mechanism of thrombus formation. In elderly patients, on the contrary, the concentration of fibrin protein is increased, which reduces coagulation time.
The test result is affected by:
- the current physiological state of the body;
- diet;
- drinking alcohol;
- smoking;
- deficiency or oversaturation of vitamins, minerals, microelements;
- completing a course of drug therapy;
- concomitant pathologies of internal organs.
Tumor processes, inflammation, and hyperactivity of the spleen distort the results of laboratory diagnostics. When the body dehydrates, the blood becomes more viscous, and when a large volume of drinks is consumed before the procedure, it becomes thinner.
Features of individual interpretation of sample results
Changes in coagulation can be considered normal if they are considered in the context of the current state of the human body. Deviations from average values can be observed in the following cases:
- During pregnancy, the female body prepares for future childbirth, and to prevent blood loss, the coagulation rate increases,
- In older people, the rate of coagulation decreases,
- Patients who come to the doctor in a state of exhaustion show a long blood coagulation time,
Video about blood clotting mechanisms:
Before interpreting the results, the doctor talks with the patient to obtain information about possible factors that explain the accelerated or delayed blood clotting. If there is no such data, then the doctor has reason to suspect pathology and prescribe an additional examination.
Preparing for the test
Blood sampling for study by laboratory methods is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The procedure is extremely simple and quick. No special preparation is required for the test. Before the test, you are allowed to drink a small amount of liquid without sugar or gases.
3 days before the scheduled date, you must stop taking medications that affect the rheological properties of the blood. Women are not recommended to take the test during menstruation. 24 hours before taking blood from your finger, you should not eat fried, salty, or hard-to-digest foods.
To obtain an accurate result, you should not take the test against the background of heavy physical exertion, nervous strain, or strong emotional excitement. Within 30 min. You should not smoke before the procedure.
Determination methods and standards
A blood test for clotting and bleeding duration is carried out in the laboratory in several ways . Capillary or venous blood can be collected.
Tests are taken in the morning; before this, it is better for the patient to give up breakfast, smoking and physical activity, since these factors affect blood flow. The increase or decrease in blood circulation also depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
It is necessary to pay attention to the following indicators, in addition to the temporary criterion of coagulation and bleeding:
- amount of antithrombin 3;
- amount of fibrinogen;
- prothrombin time.
A coagulogram consists of several tests and indicators. The norm for the duration of bleeding and blood clotting is different for all tests.
Method according to Sukharev
The subject of the study is capillary blood . Using this test, it is possible to determine the period of transition of fibrinogen to fibrin.
After puncturing the finger, the first drops are removed, and then a small amount of blood is taken using a special vessel (Panchenkov apparatus). The vessel is put into operation, tilting to the sides, until the liquid thickens.
Features of the study
Biological material is collected into a cylindrical laboratory flask with a scale. Blood clotting time according to Sukharev’s method is determined using a precise chronometer.
The viscosity of the hematological fluid is checked by rocking the laboratory laboratory from side to side at the same angle or using a Panchenkov apparatus, which allows you to automate the process. The time of the beginning and end of blood thickening is taken into account.
The first indicator ranges from 30-120 seconds. depending on the patient’s age and physiological state of the body. Coagulation is considered completely complete when the control sample stops moving along the walls of the laboratory vessel.
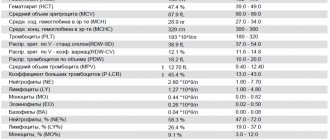
The norm for completing a full coagulation cycle is 2-5 minutes. The test shows the rheological properties of blood, but the cause of their violation is determined by other diagnostic methods. Biochemical factors influencing the coagulation rate are presented in the table.
| Index | Meaning |
| Fibrin protein concentration | The main parameter of coagulation. The protein compound produced by hepatocyte cells in the blood of an adult patient is contained in a volume of 2-4 g/ml. |
| Antithrombin III | Biochemical regulator of coagulation. The normal antithrombin value is 75-125% in adult patients, 80-120% in children over 12 months, 30-80% in infants. |
| Prothrombin index | The ratio of the clotting cycle period of the tested biomaterial to the control sample. The norm is considered to be 93-107%. |
| Thrombin time | With proper operation of the hemostatic mechanism, the value falls within the time range of 14-20 seconds. During this period of time, prothrombin is converted into thrombin, which increases blood viscosity. The biotransformation process is slowed down by some medications - Aspirin, Heparin, Warfarin. |
| APTT | The laboratory indicator demonstrates partially activated thromboblastin time. Used to monitor the condition of patients in the treatment of DIC syndrome. APTT norm is 29-39 sec. |
| Bleeding period | Shows the rate at which bleeding stops after capillary damage. After puncturing the skin with a scarifier, the blood should stop appearing after 2-3 minutes. |
| Clotting time | The laboratory indicator represents the interval between the collection of biological material and the formation of a blood clot. |
| D-dimer | A biochemical compound arising from the breakdown of fibrin. The standard blood level is 250 mcg/l. |
Coagulability according to Sukharev (the norm depends on the age of the patient, the current physiological state of the body, and other influencing factors) is a simple laboratory test that clearly demonstrates all phases of the enzyme process.
How to donate blood for clotting
Determination of bleeding time is carried out using capillary blood; for other clotting tests, material must be taken from a vein.
The tests are carried out on an empty stomach; you can only drink water before the analysis. If you are taking any medications, you should tell your doctor about this, as some medications may affect the results obtained.
By regularly taking hemostasiogram tests, you can promptly diagnose many dangerous ailments.
Increased blood clotting and thrombus formation
Many factors can lead to increased blood clotting, restriction or blockage of blood flow, and as a result, blood clots. Blood clots can travel through arteries and veins, causing serious consequences including sudden death from embolism.
Indications for examination
Normal blood clotting is 2-5 minutes (according to Sukharev). An analysis to determine this indicator (coagulogram, hemostasiogram) is prescribed for:
- diseases of internal organs;
- suspected hereditary hemostatic pathologies;
- pregnancy;
- varicose veins, thrombus formation;
- diabetes mellitus;
- prescribing coagulants;
- during the preoperative and postoperative period.
Risk factors
Increased hemocoagulation often occurs when:
- increased number of blood cells and hemoglobin, radiation, cancer;
- hyperfunction of the spleen, acidification and dehydration of the body, most often associated with poor bowel function;
- increased consumption of sugar and carbohydrates;
- overweight, pregnancy, prolonged bed rest, sedentary lifestyle and sedentary work;
- lack of specific hormones and enzymes, use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy.
Sometimes the tendency to hyperclotting is congenital. This pathology is called thrombophilia. It is caused by a congenital decrease in the level of anticoagulants C and S, antithrombin III, coagulation factor VII, heparin cofactor II, dysfibrinogenemia, sickle cell anemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, increased activity of Hageman factors, Rosenthal factors and antihemophilic globulin. With this pathology, patients report similar cases among close relatives. Sometimes hereditary thrombophilias cause miscarriages in women.
Blood thickening in old age threatens to disrupt brain activity, and in pregnant women it can negatively affect the condition of the mother and fetus. Poor rheology leads to ischemia of organs and tissues, which negatively affects the condition of the entire organism.
How to suspect increased coagulability
- A sign indicating increased hemocoagulation is thrombus formation. If you notice painful bluish “vessels” or nodules on the limbs, this is a reason to consult a doctor and be examined for blood clotting indicators.
- Another symptom that should alert you is problems with the functioning of the heart. They should encourage you to get tested.
If the coagulogram indicators do not correspond to the norm, treatment must be started urgently to prevent thromboembolism.
Norms of blood clotting time according to Sukharev in children, adults and pregnant women
The period of complete coagulation is influenced by plasma factors, which differ in different groups of patients. The normal clotting time according to Sukharev’s method is the same for men and women and is 5-7 minutes.
In children, the coagulation period varies depending on age. In the first year of life, the hepatobiliary mechanism does not produce sufficient amounts of fibrinogen and vitamin K, an important factor in protein synthesis.
In infants, clotting time is not determined. For children over 12 months. The standard indicator is the completion of the coagulation process in 10-12 minutes. The clotting period of hematological fluid increases in girls after the start of the menstrual cycle.
In old age, blood thickening is observed due to natural physiological reasons. For this category of patients, the coagulation rate is set at 1.5-2 minutes.
Similar indicators are recorded in women during menstruation or pregnancy. When carrying a child, the hormonal balance changes. The body produces special protective bodies that affect the blood clotting process.
Interesting Facts
Such a rare and life-threatening genetic disease as hemophilia (a blood clotting disorder) causes serious harm only to the male half of the population. A woman can only be a carrier of this gene with pathology, but the disease itself does not affect her health in any way.
There are several names of diseases associated with disturbances in the number of platelets in the blood and their activity:
- Absolutely any deviations in these indicators are called thrombocytopathy.
- If the level of platelets in the blood is low, then this pathology is called thrombocytopenia.
- If the level of such a main component of blood as platelets is higher than normal, then this is the disease thrombocytosis.
- When impaired functional activity is detected, the disease is called thrombasthenia.
At Harvard University, a group of scientists and students discovered an interesting relationship between the amount of fibrinogen (a protein that is produced in the liver and converted into fibrin, the basis for clot formation during the activation of the blood clotting process) and the number of human contacts in society. Based on the research results, it was concluded that the narrower the circle of contacts with people, the higher the level of fibrinogen. And this, in turn, causes irreparable harm to health, especially detrimental to the cardiovascular system. Therefore, communicating with other people is beneficial not only for mental health, but also for physical health!
Some private laboratories provide the service of taking biological material for blood clotting testing directly at home, i.e., you do not need to go to the laboratory yourself. This is very convenient for disabled people, elderly people and small children.
Possible reasons for deviation of analysis indicators from the norm
The standard coagulation time is modified by pathological or physiological factors. Any test results cannot serve as a basis for making a final diagnosis. Reduced or increased blood clotting time is a reason for in-depth diagnosis.
Typical pathological causes of coagulation disorders:
- autoimmune processes;
- DIC syndrome;
- genetic disorders;
- cardiac diseases;
- vascular pathologies;
- infectious lesions;
- chronic or acute inflammation.
Disorders of hemostatic function are provoked by recent injuries, hepatobiliary pathologies, and vitamin K deficiency. Most pathological causes require medical intervention and the selection of adequate treatment tactics depending on the etiological factor, the nature and severity of the blood clotting disorder.
Downgrade parameters
Hypocoagulopathic conditions are divided into congenital and acquired. Hereditary causes of deterioration in blood clotting are due to morphological changes in the vascular walls, abnormalities in platelet synthesis, and inhibition of plasma factors.
Acquired forms of hypocoagulopathy are often associated with immune, infectious-toxic, and dysmetabolic diseases. Impaired platelet hemostasis leads to a deterioration in the coagulability of hematological fluid. Coagulation is reduced by renal failure or splenic dysfunction.
Coagulability according to Sukharev (the norm depends on the age of the patient, which affects the parameters of fibrinolysis) slows down with bone marrow metastases, anemic conditions, eclampsia in pregnant women - a severe manifestation of late toxicosis. Septic and necrotic processes worsen coagulation.
The main reasons for a decrease in hemostatic parameters are considered to be:
- congenital or hereditary defects of vascular walls caused by collagen abnormalities;
- immune factors;
- inflammatory processes with the release of large amounts of prostaglandins into the blood;
- thrombocytopenia or thrombocytopathy – quantitative and qualitative changes, respectively;
- hemophilia types B and C;
- deficiency of plasma factors of the prothrombin complex associated with hepatitis, cirrhosis, dysbacteriosis;
Hypocoagulopathic conditions are particularly dangerous for patients over 40 years of age and women during gestation or menopause. In complex treatment, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, synthetic antihemophilic globulin or thrombolytic concentrate are used.
Increasing parameters
This condition is called hypercoagulopathy or hyperviscose syndrome.
Increased blood density accompanies:
- hypoxia – a decrease in oxygen concentration in the blood, biological tissues, anatomical structures;
- food poisoning;
- diabetes;
- toxic liver damage;
- antiphospholipid syndrome is an autoimmune disease caused by the production of antibodies to fatty compounds, which serve as the basis of cell membranes;
- leukemia;
- polycythemia – an acute tumor proliferative myelopathic disease of the hematopoietic system;
- thrombophilia – a genetically determined recurrent predisposition to vascular thrombosis.
Increased blood clotting parameters are often associated with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, a B-cell lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. The pathology is characterized by the entry into the hematological fluid of an excess volume of monoclonal immunoglobulin of the LgM type.
Metabolic disorders - amyloidosis, metabolic syndrome and others - contribute to blood thickening. Hyperquagulopathy occurs against the background of functional insufficiency of the adrenal cortex. Among the reasons for increased blood clotting parameters are thermal burns, varicose veins, and pancreatitis.