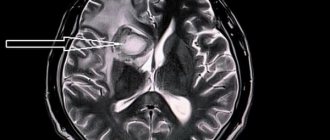
Rheoencephalography (REG) is one of the methods for diagnosing cerebral vessels using weak electrical impulses. Blood has the highest electrical conductivity compared to other media in the body. And since blood circulation is most intense in the brain, this method allows one to evaluate not only the blood vessels, but also the state of the internal structures of the brain. REG is a non-traumatic, absolutely painless and quite informative method of research; it allows the doctor to assess the speed of blood flow, tone, elasticity and blood supply of the vessels of the head. The advantages of this research method are known to every neurologist. Rheoencephalography provides a detailed picture of intracerebral vessels, regardless of their size, can be used in any conditions and allows one to obtain differentiated information about the condition of veins and arteries. At the same time, rheoencephalography is a fairly simple and absolutely comfortable procedure for the patient.
Indications for use
It is necessary to have a child have an REG of the head if he/she has:
- regular headaches of unknown origin;
- hearing or vision impairment;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- tinnitus;
- fainting conditions;
- swelling of the face;
- coordination problems.
The procedure is also prescribed to control blood circulation after operations, neck and head injuries. In some cases, the examination is part of an analysis of the effectiveness of drug therapy and non-drug treatment.
When is the study scheduled?
REG and its interpretation may be required in the following conditions:
- Changes in cerebral vessels.
- Assessing the compensatory capabilities of bypass blood flow.
- Assessing the sufficiency of venous outflow, determining the degree of hypertensive syndrome.
- Dizziness.
- Diagnosis of headaches.
- Presence of noise in the head.
- For injuries of the cervical spine and head.
- Deterioration of memory, vision, hearing.
- Hypertension.
- Vascular crises.
- Meteosensitivity and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Referral for research
Many specialists use this study and recommend it to their patients as it is more accessible than, for example, magnetic resonance imaging. Although rheoencephalography cannot be compared with MRI in terms of information content, sometimes this study is enough to make a diagnosis.
The results of rheoencephalography of cerebral vessels may be required by neurologists, vascular and neurosurgeons, as well as general practitioners.
Preparation for the event
Before the examination, the patient must eat 1.5 hours before the appointment. Light, familiar food is recommended. Breastfed children are examined immediately after feeding. On the day of the test, you do not need to give your child drinks with caffeine and taurine: coffee, tea, cola, kvass.
You need to tell your child that a completely painless procedure awaits him. He must understand that during the doctor’s manipulations he needs to relax and not worry. The more calmly he behaves during the analysis, the more accurate data the diagnosticians will be able to obtain.
Acute cerebral circulatory disorders. Symptoms
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 17 million people are diagnosed with stroke every year. Five million of them die, another 5 million remain disabled.
Table 2. Types of NMC
| NMK | Kinds | Development mechanism |
| Ischemic. | Cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke). | Stopping the blood supply to a part of the brain. |
| Transient NMC. | Lasts up to a day. | |
| Transient cerebrovascular ischemic attack. | Occurs periodically. | |
| Hemorrhagic. | Intracerebral hemorrhage. | Rupture of a vessel with subsequent effusion of blood into the brain tissue. |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage. | Hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space. | |
| Non-purulent thromboembolism. | Thrombosis. | Blockage of a vessel by a thrombus. |
| Embolism. | Blocking of a vessel with an embolus. |
How the research is carried out
Before the examination begins, the child lies on his back or sits on a chair in a comfortable position. If the child is worried, parents are allowed to be present.
After this, the specialist attaches electrodes to the areas of the head being examined. For diagnostics, a rheographic attachment and a recording device are used. The equipment records the indicators on a special tape. During the examination, the specialist may ask the child to follow simple commands: turn or tilt his head. A functional test allows you to obtain the most complete information. The procedure lasts no more than 10-20 minutes. A transcript of the results is provided 30 minutes after completion of the manipulations.
General characteristics of the method
Rheoencephalography is a non-invasive functional diagnosis. Using REG, you can also obtain information about the general functionality of the vascular walls, the magnitude of pulse blood filling, vascular resistance and reactivity of brain vessels. The study evaluates the overall functionality of the venous and arterial systems. The research does not require expensive equipment or specially equipped rooms.
The study is carried out using a device called a rheograph. In the diagnostic room, the doctor places electrodes treated with a special conductive compound on the scalp. They are fixed using an elastic rubber band, after which the device begins to record incoming impulses. The rheograph records them in the form of graphic symbols (curved lines), which are later deciphered by the doctor. During the procedure, the doctor may ask the patient to change his body position, turn his head, stand up and lie down. The fact is that changing the position of the head allows the specialist to draw conclusions about the nature of the disorders - to understand whether they are functional (situational) or organic, associated with certain diseases.
Content:
- General characteristics of the method
- Progress of the study
- Which is better: rheoencephalography (REG) or electroencephalography (EEG)?
It is important to understand that rheoencephalography is not enough for a comprehensive study of veins and arteries. The method describes only the functional state of the elastic walls of blood vessels, and this is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. REG allows you to detect a problem in a particular part of the brain and concentrate on its further detailed study. Such blood flow parameters are diagnosed as blood viscosity, blood flow speed, vascular tone, the level of blood supply to a particular part of the brain, and the specifics of blood circulation.
Indications/contraindications for REG
Initially, REG was used to monitor brain function in real time. Currently, the method is used to diagnose atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, its prevalence and stage. In case of traumatic brain injury, the study provides important information about the size of the injured areas, the presence of intracranial hematomas, their depth and the severity of the condition.
| Indications | Contraindications |
| Acute/chronic vascular pathologies of the brain (for example, vertebrobasilar insufficiency) | Mechanical head injuries |
| Atherosclerosis (chronic pathology of the arteries, in which cholesterol accumulates in the lumen of blood vessels) | Chronic/severe headache |
| Migraine (a neurological disease characterized by frequent, unbearable headaches) | Dizziness |
| Stenosis (persistent narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels) | Abrasions/wounds on the diagnosed area |
| Impaired circulatory functionality | The study is not recommended for newborns and infants |
| Stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident) | |
| General diagnosis of vascular condition after traumatic brain injury | |
| Evaluation of the effectiveness of therapy or individual drugs | |
| Intracranial hypertension (increased pressure in the cranial cavity) |
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS) of cerebral vessels | 3600 rub. |
What the study shows
The value of the survey is that:
- Based on rheoencephalography of the vessels of the head, specialists receive significant information about the condition of the object of examination. Among them is the opportunity to study vascular tone, their elasticity, blood circulation speed and blood inflow/outflow.
- The use of rheoencephalography makes it possible not only to identify abnormalities in the vessels of the brain, but also to monitor blood flow after complex operations or severe injuries.
- With the help of REG, various pathologies are detected, and the severity of the pathological process is established.
In this case, the high speed of obtaining results is of no small importance.
What problems are being identified?
During the examination, the following are diagnosed:
- Why is a study of the blood vessels of the brain and neck performed?
- presence of traumatic brain injuries;
- localization of hematomas formed as a result of head trauma;
- pre-stroke condition;
- damage to blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques (atherosclerosis);
- thrombus formation in the vessels of the brain;
- predisposition to increased blood pressure;
- diseases associated with circulatory disorders.
The procedure facilitates the task of making an accurate diagnosis, on the basis of which the doctor prescribes an adequate course of treatment. With the help of it, he subsequently monitors the effectiveness of therapy.
Due to the complete safety of such an examination for the patient’s health, it can be performed repeatedly.
One of the most significant advantages of encephalography is the ability to distinguish between pre-stroke indicators, which have certain differences for men and women.
Other features of the method
Specialists obtain even more information by conducting functional tests.
The simplest and most accessible of them is with nitroglycerin. This substance helps reduce vascular tone. This test is used to differentiate organic and functional disorders.
Symptoms
Angiodystonia of the visual organs rarely manifests itself as a disturbance in the perception of visual images.
, especially at the initial stage of development. This is why the disease is almost never detected in the early stages. As it progresses, the patient may notice:
- sensation of painless pulsation in one eye;
- the appearance of sudden flashes of light in the field of vision;
- gradual deterioration of vision - narrowing of its fields (darkening or clouding of the image at the edges), general blurriness of the picture;
- development of myopia.
Important! One of the visually recognizable signs of retinal angiodystonia is a change in the color of the sclera: yellowish spots form on it, pinpoint hemorrhages or a clear pattern of capillaries periodically appear.
The disease may also be accompanied by additional symptoms indicating the root cause of the pathology:
- in the traumatic form - headaches, paresthesia, dizziness and fainting, deterioration of cognitive functions and memory, chronic fatigue;
- with hypertension - acute headaches, sudden jumps in blood pressure to a maximum, accompanied by nausea;
- with hypotension - apathy, weakness, dizziness and nausea.
The higher the degree of pathological changes in the retina, the more intense the symptoms of the disease.
Diagnostics
Retinal angiodystonia is diagnosed using a standard set of procedures
designed to detect vascular anomalies:
- rheoencephalography - study of cerebral vessels to determine the intensity of blood supply;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels - ultrasound examination of individual basins of the bloodstream, which reveals arterial and venous insufficiency;
- electrocardiography is a classic method for recognizing signs of systemic cardiovascular disorders;
- retinal angiography.
The most informative research method is ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye using a special lens. This method allows the doctor to visualize vascular changes in the retina, establish their location and determine the degree of complexity. To find out the causes of the disease, laboratory blood tests are carried out (for sugar, hormones, etc.).
Prevention
To avoid the sudden appearance of cerebrovascular accidents, you need to lead an active lifestyle. Do as much physical activity as possible, morning exercises. Walk more, swim, take a contrast shower. Be sure to monitor blood pressure.
You should stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
It is recommended to consume more foods rich in vitamins C, D, E, and fiber. Minimize the intake of fried, fatty, spicy, salty foods. If you have chronic diseases, they must be treated. If you have hypertension, monitor your blood pressure.