14.04.2017
Last modified: July 27, 2021 at 03:48 pm
Angiodystonia (otherwise called vascular dystonia, vegetative-vascular dystonia, VSD) is a clinical syndrome manifested by a complex of symptoms associated with disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels.
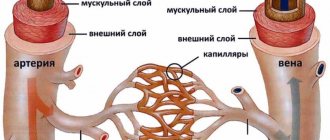
It is not a disease according to the international classification. The syndrome is characterized by pathology of vascular tone. The syndrome can be focal (has a specific localization) or systemic (affect the entire vascular system). Violations of tone are observed, for the most part, in medium-sized vessels.
What controls vascular tone
The name of the syndrome contains part of the answer to your question. Vascular tone is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. In addition, it also ensures the activity of internal organs, innervation of glands, trophic innervation of skeletal muscles and receptors. Consequently, when the autonomic nervous system is damaged, disturbances in the functioning of various organs are observed. Doctors count about 170 symptoms that are manifestations of VSD.
Manifestations
At the initial stage, it is very difficult to detect the presence of angiodystonia of retinal vessels. The disease does not bother you and does not even manifest itself in any way. Only after some time the following symptoms begin to appear:
- decreased visual acuity;
- pulsation inside the eye;
- blurred vision, flashes, clouding;
- reduction of the boundaries of the visible field;
- yellow spots and broken vessels that become visible on the conjunctiva of the eye;
- impairment in the form of farsightedness.
Both eyes or only one may be affected. If the disease develops into a severe form, then even loss of vision is possible.
Where did it come from and in whom does it manifest?
A single cause causing VSD has not been established.
Common reasons include:
- frequent stressful situations
- unstable nervous system
- emotional overstrain
- puberty
- depression
- hypotension (lack of physical activity)
- hormonal disorders
- overweight
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse, excessive consumption of coffee and other substances that affect systemic blood pressure)
Symptoms of VSD, to one degree or another, appear in almost the entire working population. More often observed in those whose work is associated with constant stressful situations, violations of the daily routine, violations of the work and rest schedule, when spending most of the time at the computer or computing machines. Angiodystonia syndrome is often detected in adolescents. This is due to an excessive reaction to external stimuli, instability of the nervous system, which entails “jumps” in pressure.
In many cases, VSD is a concomitant syndrome of another pathology. For example, pathologies of the endocrine system (diseases of the ovaries, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland), diseases of some internal organs (pancreatitis, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis), chronic infections and allergies.
Signs of angiodystonia
Characteristic and most common symptoms that suggest the presence of dystonia:
- unexplained pressure changes
- chronic feeling of fatigue
- dizziness
- loss of consciousness
- sleep disorders
- causeless headaches of various types (dull, aching, shooting)
- tinnitus (often when changing body position)
- numbness in the legs and/or arms
If you observe one or more of the above symptoms in yourself or your loved ones, you should consult a doctor.
Forecast
If you have such a diagnosis, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, take prescribed medications and monitor your lifestyle. The doctor must regularly monitor the patient's condition, even if there are no symptoms. Angiodystonia rarely leads to disability, complete or partial. Such cases are extremely rare in medical practice. In this case, complex treatment should be prescribed, and the symptoms are severe. When prescribing complex therapy, the condition and reaction of the body should be monitored. If there are negative changes, treatment should be changed in accordance with the existing changes.
Angiodystonia of the brain
As the name suggests, this pathology develops in the vessels of the brain. Otherwise it is called cerebral angiodystonia. “Alarm bells” are noises in the head, headaches of various localizations, tinnitus, dizziness and fatigue that does not correspond to physical activity.
Important information: Why does your blood pressure rise and your heart rate increase after eating?
Cerebral angiodystonia is classified according to its location, cause of occurrence, presence of concomitant pathologies, and blood pressure indicators. The adequate choice of diagnosis and further treatment depends on these and many other factors. It must be remembered that one cannot “delay” with such a “harmless”, at first glance, syndrome. The longer you have symptoms, the more likely you are to develop encephalopathy. Encephalopathy is a non-inflammatory disease of the brain, however, its treatment is relatively more complicated than the treatment and prevention of VSD.
Often the diagnosis of cerebral angiodystonia is made in childhood based on the results of ultrasound of the neck vessels. If a violation of the location of the vessels is detected or their tortuosity is greater than normal. Because of this pathology, blood cannot flow normally to the brain and supply it with oxygen. Against this background, symptoms appear that indicate angiodystonia.
In many cases, cerebral angiodystonia is caused not only by concomitant pathologies, but also by an unhealthy lifestyle. Eating fatty foods, alcohol, large amounts of caffeine and smoking affects the blood vessels of the brain. Often, lifestyle changes can alleviate or completely eliminate the symptoms of VSD.
Angiodystonia of the retina
This syndrome develops due to pathology of the retinal vessels. Due to disturbances in the tone of the arteries and veins, the activity of the retina is disrupted - timely narrowing and expansion becomes impossible. This pathology is often one of the first to occur and is an important diagnostic sign for making a diagnosis.
Angiopathy during pregnancy
Since in pregnant women the blood volume increases several times with the growth of the fetus, the blood vessels increase accordingly. Changes in the circulatory system cause angiopathy in pregnant women. Additionally, it is provoked by a hormonal factor, which is observed in the first trimester. In the second and third trimester, a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance occurs due to the functioning of the uteroplacental circulatory system. Another reason that can provoke angiopathy in pregnant women is gestosis. Detection of such a pathology in pregnant women carries risks, since the use of many drugs is not allowed in this situation. In some cases where there is a risk of retinal detachment, the doctor may recommend a cesarean section.
Causes
Can be divided into two large groups:
| Associated with vascular pathology | Associated with pathology of other organs and systems |
| Atherosclerosis | Diseases of the nervous system, injuries of the cervical and thoracic spine |
| Hypertension | Severe forms of diabetes mellitus |
| Increased intracranial pressure | The influence of radioactive radiation, toxic substances |
| Congenital pathologies of the circulatory system | Some autoimmune diseases |
| Thrombosis of arteries of various sizes | Pregnancy (increases the load on blood vessels) |
How to recognize
The first signs, of course, will be a decrease in visual acuity and limited visual fields. In addition, there may be a veil before the eyes, flies or fog. Color vision disturbances are possible. It becomes significantly more difficult to recognize objects located at a considerable distance from you. The appearance of spots on the sclera of the eyes from yellow to red is characteristic. The appearance of red spots indicates the presence of hemorrhages from the retinal vessels.
In addition to the main manifestations, nosebleeds, leg pain and hematuria (the appearance of blood in the urine) may also be observed.
According to the reasons for the occurrence of VSD syndrome, it can be divided into several types:
- Traumatic - occurs when there is a sharp increase in pressure in the vessels of the eye. Occurs when the eye itself is injured, the body is compressed in the neck or chest - hemorrhage occurs in the eye and vision loss occurs. However, if the case is isolated, then vision is restored.
- Hypertensive – associated with the presence of hypertension or traumatic brain injury. In such cases, the uniform narrowing of the retinal arteries is disrupted, intracranial pressure increases, which increases the load on the visual apparatus. With timely initiation of treatment, it is possible to completely restore vision.
- Hypotonic – develops as a result of arterial hypotension. Due to a decrease in pressure in the bloodstream, the retinal arteries dilate, thereby preventing the venous blood flow from functioning normally. With this type of VSD, the patient feels pulsation in the vessels of the neck and dizziness.
- Diabetic – occurs in severe forms of diabetes. In this case, the key role is not in increasing systemic blood pressure, but in reducing the elasticity of the vessel walls. The vessels become brittle and lose their tone. Frequent hemorrhages occur in the retina.
Important information: Blood pressure in athletes
Symptoms and diagnosis of angiopathy
As a rule, angiopathy is associated with the quality of vision. As soon as you notice that your sharpness has sharply decreased, “floaters” or “sparks” begin to appear in your eyes, the picture seems foggy and cloudy - immediately contact an ophthalmologist. The clinical picture may also be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Nose bleed.
- Deterioration of vision.
- Headache.
- Periodically occurring blur of objects.
- Sensation of pulsation in the eyes after intense visual work.
The problem is that in many cases, retinal vascular angiopathy manifests itself rather sluggishly at the initial stage. Therefore, some people are unaware of their problem, although patients feel that their vision has deteriorated. Over time, if retinal angiopathy is not eliminated, gradual rejection of retinal tissue and their necrosis will begin, resulting in complete loss of vision.
Examination of the fundus is considered one of the most reliable methods for diagnosing angiopathy. The ophthalmologist observes changes in the lumens of blood vessels and their passages. In more complex situations, when serious changes occur in the retina or optic nerve head, additional diagnostic methods are needed:
- Ultrasound scanning of the eyes.
- Computer study of the boundaries of the field of view.
- Diagnostic examination using beam.
Damage to the blood vessels of the eye can occur in people of any age, but most often occurs after 30 years of age.
Complications of the disease are expressed in optic nerve atrophy, narrowing of the visual field, loss of vision (partial, complete). There is a classification of diseases that cause retinal angiopathy. Accordingly, for effective treatment it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and find the cause that led to circulatory disorders.
Diagnosis of VSD
Successful diagnosis and further treatment, of course, depends on timely identification of symptoms. And, since the symptoms of angiodystonia often manifest themselves in a complex manner, diagnosis is not particularly difficult. The main diagnostic method is rheoencephalography. This method is based on the study of the resistance of brain tissue, which occurs under the influence of weak high-frequency electrical impulses. This is how data is obtained about the functioning of the brain vessels and their condition. For example, one can judge the elasticity of the vascular wall, its tone, the reactivity of the vessels and their pulse filling.
In addition, ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and cervical spine, ECG to detect changes in the heart, and electroencephalography are used. If the results of the study show evidence of a decrease in blood flow, a decrease in the diameter of the vessel and/or its lumen, a change in the position of the vessels or their tortuosity, then it is necessary to urgently begin therapy.
Varieties
This disease is divided into several types:
- traumatic – caused by a sharp increase in pressure in the vessels of the eyeball;
- hypertensive – caused by hypertension;
- hypotonic – occurs as a result of the development of arterial hypotension;
- diabetic – worries diabetics who do not adhere to treatment and progress their disease.
We will consider two of these varieties in more detail.
Angiodystonia of hypotonic type
With this type of disease, the small arteries of the fundus, which are responsible for feeding the retina, lose their tone, become dilated and tortuous. Under normal conditions, arterioles and venules have a diameter of 2/3, respectively. With hypotonic angiodystonia, this ratio changes and approaches the level of 1/1. As a result of these changes, blood flow slows down significantly due to decreased filling of the arteries. This situation entails insufficient nutrition of the tissues in the fundus of the eye. The presence of hypotonic angiodystonia can be detected by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- presyncope and fainting;
- darkening of the eyes;
- weakness in the body and decreased performance.
Angiodystonia of the hypertensive type
This type of disease involves changes in the capillaries of the retina, which are associated with the following factors:
- impaired microcirculation;
- increased arteriolar tone and decreased elasticity;
- antispasmodic phenomena in small arteries;
- congestion in the venous capillaries.
The vascular system of the fundus reacts sharply to pressure surges. Even the vessels of the brain do not react so strongly to the negative factors that arise with systemic hypertension. Hypertensive angiodystonia is detected by impaired vision.
Treatment
Since VSD is not a disease, treatment is based on eliminating the root cause. If the syndrome was caused by a primary pathology of other organs, then treatment begins with the elimination of this pathology. In addition, part of the therapy is aimed at restoring and maintaining vascular tone. And, of course, symptomatic treatment, which includes normalization of the regime, proper alternation of work and rest cycles, giving up bad habits, gentle constant physical activity.
The doctor selects the exact treatment. If treatment of VSD symptoms is not combined with taking medications to eliminate the underlying pathology, then it is abandoned.
Prevention of VSD
As in most cases, the first thing you should do is try to lead a healthy lifestyle and spend more time in the fresh air. It is recommended to walk about 5 km at a moderate pace several times a week. However, if you have heart disease, then the pace should be slowed down. If you cannot eliminate the constant stressful situation in which you are, then herbal preparations are recommended for use. They are homeopathic, their effect appears within a month to a month and a half from the start of use, but they have significantly fewer side effects, unlike medications, and will help bring your nervous system back to normal.