What every person needs to know about heart pain, what are the dangerous symptoms of myocardial infarction, why a heart attack occurs, as well as factors that increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis. What medications are relevant and should be in a home medicine cabinet, and how to provide first aid to a person who has had a heart attack before your eyes. Let's look at all these questions in more detail.
Any doctor in his practice sooner or later encounters such a phenomenon as complaints of pain in the heart area. However, not every pain described by the patient as cardiac may be so. By the way, true heart pain is much less common than pain as a result of the development of other diseases, for example, the stomach and the musculoskeletal system. Women, unlike men, are naturally more protected from various types of troubles associated with heart problems due to the physiological characteristics of the body. Therefore, frequent visitors to the cardiologist’s office are men aged 40 years and older.
Location of the heart
Location of the heart in the body
Let's consider in detail:
The heart is a hollow muscular organ with an approximate weight of 250-300 grams, located at the level of 5-8 thoracic vertebrae with a predominant displacement to the left half of the chest, and has four chambers in its structure, separated by thick muscular partitions. Between these partitions are the heart valves, which allow blood to flow in only one direction. The size of the heart can increase as a result of the development of a number of certain diseases, as well as during intense physical activity, for example, when playing sports.
The heart has reliable protection - the pericardial sac or pericardium. This is the top layer of the heart wall. Next comes the dense muscle layer or myocardium. The inner lining of the heart is called the endocardium.
Our heart constantly needs nutrition in the form of oxygen and nutrients. This nutrition is provided by the coronary vessels through the circulatory system, in which the heart performs the pumping function. As we see, the heart is a complexly organized organ that contracts continuously, with short pauses for rest, which are measured in seconds. Therefore, this organ requires careful treatment and regular examination, especially after 40 years.
The classification of heart diseases is quite large, ranging from various heart rhythm disturbances, inflammatory diseases of the membranes, hypertension, malformations (congenital or acquired), heart vascular diseases and ending with acute vascular disorders that develop mainly against the background of coronary heart disease, which we will talk about in this article.
Heart disease has become younger. Nowadays you won’t surprise anyone with “young” heart attacks, which are more common in men even at the age of twenty.
Does the heart recover after a heart attack?
After a heart attack, it is possible to normalize the functioning of the heart, but it is impossible to restore cells that have lost their functionality. This also applies to cases where a person is provided with timely first aid for a heart attack. However, scientists talk about the possibility of restoring dead heart tissue using regenerative medicine. They plan to achieve this thanks to stem cells that are injected into the heart area, through which the process of regeneration of damaged cardiac tissue can be started.
There are two types of complications that can occur after a heart attack: those that occur almost immediately and those that occur afterward (in the following days, a week, or even a month later).
Complications that occur immediately after a heart attack include:
- arrhythmia - the heart beats irregularly, too fast or too slow;
- cardiogenic shock - a person’s blood pressure suddenly drops, as a result of which the heart cannot supply the body with enough blood to function properly;
- hypoxemia - oxygen levels in the blood become too low;
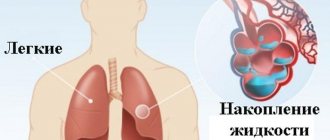
- pulmonary edema—fluid accumulates in and around the lungs;
- deep vein thrombosis - blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs and pelvis, which either block or interrupt blood flow in the vein;
- myocardial rupture - a heart attack damages the heart wall, causing it to rupture.
- Ventricular aneurysm - the ventricle forms a bulge.
Complications that occur after a heart attack include:
- aneurysm—scar tissue accumulates on the damaged heart wall, leading to blood clots, low blood pressure, and abnormal heart rhythms.
- angina pectoris - not enough oxygen reaches the heart, which causes chest pain;
- congestive heart failure - the heart may beat very weakly, causing the person to feel exhausted and experience shortness of breath;
- swelling - fluid begins to accumulate in the ankle area;
- loss of erectile function, loss of libido;
- pericarditis is an inflammation of the lining of the heart that causes severe chest pain.
Symptoms of heart disease
All heart diseases, as a rule, have similar symptoms:
- Chest pain.
Let's take a closer look at the characteristics of heart pain.
Characteristics of heart pain
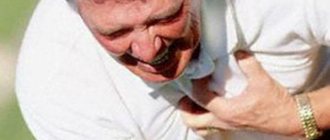
The very first and most indicative clinical gesture characterizing heart pain is the “tie symptom,” that is, the pain is localized in the place where a man usually ties a knot in a tie. This is an indicator of heart pain. Another striking clinical gesture is a clenched fist at the sternum. Heart pain, in most cases, is paroxysmal and temporary. It can be characterized as compressive, most often occurring against the background of physical activity (angina), or sharp, unbearable, with a feeling of lack of air and other symptoms. This kind of pain is the most dangerous.
- Fatigue and weakness.
Most often, this symptom occurs against the background of circulatory failure and, as a rule, indicates oxygen starvation of the heart muscle. Sharp, sudden weakness (“legs gave way”) is a symptom of myocardial infarction.
- Arrhythmia.
Most often, patients complain of increased heart rate, usually occurring at rest, suddenly, for no apparent reason. A feeling as if the heart has turned or is tumbling in the chest also indicates the presence of an arrhythmia. These symptoms may be accompanied by a feeling of shortness of breath, darkening of the eyes and a feeling of fear.
- Frequent fainting.
This symptom usually occurs with certain types of bradyarrhythmia or cardiac hypotension.
- Dyspnea.
Perhaps this is one of the most characteristic symptoms indicating heart problems. At first, these may be short-term episodes of feeling short of air. But, as the underlying disease develops, shortness of breath can be bothersome at rest, and even at night. Sometimes auxiliary muscles, such as the muscles of the shoulder girdle, are involved in the breathing process.
Acute vascular disorders in all their cases are dangerous not only to health, but also to human life. Most often, such attacks are a consequence of the development of a disease - atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial, chronic disease with damage to the arteries caused by damage to the vascular wall.
The development of atherosclerosis is caused by: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, some behavioral reactions, lack of vitamin C, as well as the age and gender of the patient.
Atherosclerosis is the basis for the development of many pathologies of the heart and its vessels, including the development of coronary heart disease.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a disease characterized by an absolute or relative violation of the coronary circulation. People aged 60–75 years and older are most often susceptible to developing this disease. This disease has the following clinical forms:
- Sudden cardiac death.
- Angina:
- First emerged;
- Stable;
- Progressive.
- Myocardial infarction;
- Heart rhythm disturbances;
- Heart failure.
All these clinical forms pose a serious threat not only to health, but also to human life. Therefore, assistance in each specific case must be provided immediately.
Angina pectoris – or in other words “angina pectoris”. It is characterized by pain behind the sternum, which has an increasing and decreasing character, which usually lasts for 5-10 minutes. The most typical attacks are most often provoked by physical activity. Atypical manifestations of angina include: shortness of breath, coughing, heartburn, changes in the location of pain, increasing pain.
A person who has had their first attack of angina needs immediate hospitalization. What can be done before the doctors arrive (self-help or when assisting a patient):
- Calm down, relax, try to breathe evenly and slowly, completely eliminate all physical activity.
- Take a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. This can be done 3 times, with an interval of 5 minutes.
- Sit by the window or take the person out into the fresh air, take a semi-sitting position.
- Carry out a set of distracting procedures: put a warm heating pad or mustard plasters on your feet.
- If an attack occurs for the first time, call an emergency team.
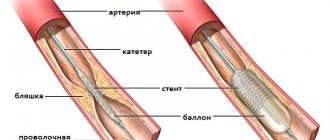
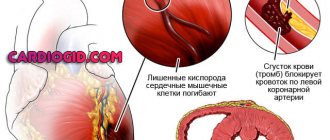
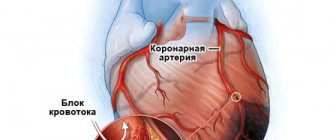
Myocardial infarction is a disease characterized by the formation of a necrotic focus in the heart muscle as a result of an absolute disturbance of blood flow, and, as a consequence, a sharp drop in myocardial contractility.
The causes of a heart attack are most often an “unstable” atherosclerotic plaque and a sudden, strong spasm of blood vessels (usually during emotional stress).
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack is a pathological condition in which the heart muscle is blocked by a spasm or blood clot, resulting in disruption of blood supply. Heart attack and heart attack are the same thing.
How to recognize a heart attack by its signs? The attack can be painless or with characteristic severe symptoms, which include:
- mild, moderate or severe (unbearable) pain in the chest area, often radiating to other parts of the body;
- feeling of panic, fear, melancholy, anxiety, inexplicable restlessness;
- pain in the neck, lower and upper extremities;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness, headache;
- breathing problems;
- loss of consciousness.
Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes. Unpleasant sensations can cause a feeling of tightness or pressure, and can also be accompanied by pain of a cutting, piercing, aching or stabbing nature. If there is no one nearby who can provide first aid until the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to provide self-help for a heart attack. Don’t panic, take a sitting or lying position, try to control your breathing, and if possible, provide access to fresh air (open a window, door). Changing the position does not relieve pain; try not to make unnecessary movements.
Signs of a heart attack
Signs of a heart attack
The main manifestations are characterized by:
- Prolonged chest pain that is not relieved by nitroglycerin.
- Shortness of breath, sudden severe weakness, cold, sticky sweat.
- A feeling of fear, even to the point of psychosis. The person completely loses control over his actions.
- Increased body temperature.
- Reducing criticism of your condition.
- Thread-like pulse, drop in blood pressure.
First aid
First aid:
On this topic ▼
How to call an ambulance or intensive care unit correctly
- Call an emergency team immediately.
- Calm yourself or calm the victim. Allow him to take a position that is comfortable for you (optimally in a lying position).
- Take a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. This can be done three times, with an interval of 5 minutes.
- Provide the victim with a flow of fresh air, unfasten the collar and belt.
- If the arrival of doctors is delayed and the pain is unbearable, you should take an analgin tablet.
- Measure the victim’s pulse and blood pressure every 5 minutes.
- Talk, encourage the person, introduce a set of distracting procedures (put the victim’s legs in a basin of warm water or place heating pads on the calf muscles).
Attention! For elderly and senile people, an attack of myocardial infarction can be painless!! This, in most cases, makes it very difficult to make a diagnosis.
Always remember that a person’s life depends on your quick and decisive actions.
But, as you know, a person is the master of his own destiny and his health. A few simple preventive measures that should go with you throughout life will help you maintain a healthy heart into old age.
Why might doctors miss the first symptoms of a heart attack?
Doctors cannot miss the first symptoms of a heart attack. Ignoring poor health and refusing to visit a doctor can lead to complications or death, especially when a person has chronic diseases.
The causes of a heart attack can vary. It is often caused by the simultaneous action of several factors (alcoholism, stress, autoimmune disorders, thyroid pathologies, hereditary diseases).
Prevention
- First of all, you need to follow a diet. Limit the amount of fats and sugars in your diet, but at the same time, increase the amount of foods containing Omega-3. (fish, vegetables, fruits, seafood, vegetable oils).
- Limit alcohol and tobacco consumption.
- Moderate physical exercise will bring undoubted benefits to your health.
- Try to avoid stressful situations, treat everything with a clear head, calmly, and balancedly.
- If the doctor, according to your diagnosis, has prescribed you medications that need to be taken long-term or for life, then you need to do so. You cannot skip taking medications!
- It is necessary to increase potassium-rich foods in your diet: dried apricots, raisins, baked potatoes. It has been proven that 2-3 dried apricots per day completely satisfy the body's potassium needs.
- Let there always be nitroglycerin in your first aid kit or purse. If necessary, it can be used for self-help or to help others. A drug such as Corvalol, Valocordin or Valoserdin will also not hurt. You can have motherwort or valerian preparations. It is also necessary to have analgin or another painkiller. If necessary, you can use it.
Assessing the risk of myocardial infarction
To prevent a heart attack, you should consult a physician or cardiologist. To identify obesity, the doctor, based on weight and height, will calculate the body mass index for further recommendations. Here at the appointment they will measure your blood pressure and give you a referral for tests. In addition to primary data on cholesterol and glucose, it is desirable to obtain results on other parameters: blood clotting, hematocrit, creatinine, hemoglobin, urea. Based on the data obtained, if necessary, the doctor will prescribe preventive treatment that will help avoid a heart attack.