While measuring your blood pressure with a tonometer, did you notice that your blood pressure is higher than normal? It is important to know what high upper pressure means and what consequences it can lead to in the future. You can talk about hypertension and the need for its treatment when the systolic reading regularly jumps up by 20–30 mmHg. Art. Moreover, it is the upper numbers that cause the appearance of characteristic symptoms. The lower levels may be normal or even decreased, but more often they increase almost synchronously. It is important to find out what causes blood pressure to rise, whether the pathology is a primary disease or reflects other processes in the body.
What is upper pressure and how does it manifest itself?
The question of what systolic pressure is responsible for worries every hypertensive patient. The first numbers on the tonometer show the degree of blood pressure at the moment of maximum heart contraction. The higher they are, the more difficult it is for blood flow to move through the vessels. Lower (diastolic) pressure demonstrates how blood moves through the vessels from the heart to the next contraction. Since the lower indicators are passive, it is the upper numbers that are fundamental in diagnosing hypertension.
Not only high surface pressure against the background of increased, normal or decreased lower pressure indicates problems in the body. You can suspect something is wrong based on the following symptoms indicating the development of hypertension:
- dizziness;
- throbbing pain in the occipital or temporal region;
- noise in ears;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fainting;
- dyspnea;
- redness of the facial skin;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- heartache.
Important! If you find yourself with several signs from the list, it means that your upper blood pressure is high, which can lead to a series of complications, some of which are incompatible with life.
Diagnostics
Have you suspected or discovered that you have high blood pressure?
Make an appointment with your GP as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an initial examination, which will allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis and select adequate treatment. In most cases, the diagnosis of systolic hypertension includes:
- Anamnesis collection . The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient regarding the existing symptoms of the disease, lifestyle, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. All this allows the specialist to make an assumption regarding the possible causes of the increase in upper pressure.
- Physical examination . It involves the doctor listening to the heart using a phonendoscope, during which the specialist has the opportunity to determine the presence of a murmur in the heart, disturbances in its sounds, and other associated abnormalities.
- ECG . The most popular diagnostic method for high systolic pressure, which allows you to confirm the diagnosis of “systolic hypertension”, as well as identify heart rhythm disturbances.
In some cases, the patient may be prescribed Holter monitoring (daily cardiogram).
- Ultrasound of the heart . An auxiliary diagnostic method, during which disturbances in the functioning and structure of the heart valves, and serious defects in the structure of the heart muscle are detected.
- Doppleography . _ A diagnostic method that allows you to assess the condition of the vascular system. With systolic hypertension, it is important to monitor the condition of the arteries leading from the heart to other organs and their systems.
- Laboratory research methods . Most often we are talking about a general analysis of urine, blood, and a blood biochemistry test that determines cholesterol and sugar levels.
If necessary, the therapist can refer the patient for consultation to specialized doctors - a cardiologist and an endocrinologist.
What do the indicators depend on?
Despite the fact that upper blood pressure is called cardiac blood pressure, the numbers are influenced by several factors, namely
Hypertensive crisis - what is it?
- heart rate;
- blood ejection rate;
- left ventricular stroke volume;
- distensibility of the aortic walls.
Thus, the upper blood pressure is affected not only by the heart, but also by the blood vessels (large).
Most often, surges in systolic blood pressure are encountered by elderly people, whose vascular elasticity decreases due to age-related changes. But today, hypertension is also diagnosed in young people. The reasons causing the violation may be the following:
- unhealthy diet, replete with fatty, salty, spicy foods;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol;
- sedentary lifestyle);
- increased physical or mental stress;
- stressful situations;
- chronic fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- weather;
- some medicines and traditional medicine.
Obese people suffer from hypertension in 90% of cases
Natural Causes of Dry Mouth
People say that dry mouth appears with age, which means there is no way out, but this is not true. Xerostomia is associated with very specific causes, therefore, they need to be detected and eliminated. Dry mouth can cause:
- Dehydration. If a person hardly drinks water, then there is nothing to produce saliva from. The skin becomes dry and urine is scanty.
- Excessive consumption of salty foods, especially at night.
- Excessive consumption of coffee or hot spices “dries out” the mouth.
- High air temperature. At elevated temperatures, the liquid evaporates too quickly and must be replenished. If this is not possible, then the throat dries out and almost no saliva is released. Temperature dehydration occurs not only in hot weather, but also in winter, when batteries dry out the air.
- Stressful situation. There is an assumption that fear makes your throat dry, and this statement has a basis. An exciting event, preparation for an important event or speaking in public provoke a decrease in saliva production.
- Runny nose. With a stuffy nose, a person is forced to breathe through the mouth, the saliva dries out and does not have time to be released again.
- Dry mouth during sleep. When a person sleeps with his mouth open, he wakes up with a “dry” throat. As a rule, this is a sign of apnea - short-term holding of breath during sleep. A deviated nasal septum also causes your mouth to open during sleep.
Drinking alcohol causes dry mouth and extreme thirst in the morning. Poisoning with low-quality products or overeating gives the same effect. Smoking causes a decrease in saliva production, and consequently, dry mouth.
Sometimes the effect of the absence of saliva is associated with a deficiency of vitamins A and B in the body.
Dry mouth after taking certain medications
Any medications have side effects, one of them is xerostomia. As people age, they take more medications, which is why older people are more likely to suffer from dry mouth. Xerostomia is caused by drugs:
- from edema;
- from allergies;
- from diarrhea;
- from high blood pressure;
- antispasmodics;
- antibiotics;
- tranquilizers;
- psychotropic drugs.
- In total there are about 500 items. If the symptom persists, you should consult a doctor to replace the drug with a harmless analogue.
Chemotherapy for cancer also causes dry mouth.
Radiation therapy as a provocateur of xerostomia
Irradiation of the head and neck for cancer of the oral cavity and pharynx can lead to disruption of the salivary glands. The function is restored over time, but sometimes the problem remains for life. For such patients, there are special aerosols that compensate for the lack of saliva.
Norms
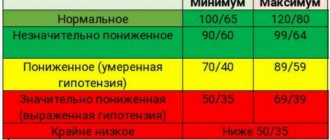
For each person, these indicators may be different. The norm depends on age, gender, weight, race, state of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. Some people feel healthy with a constant blood pressure of 150/100, others feel unwell at 130/90 mmHg. Art.
We are accustomed to considering 120/80 mm Hg as the standard. Art. But this is far from true. It is better to focus on age, since it depends on it what kind of pressure may cause concern. For example, the upper limits of normal:
- up to 20 years - 100/70, 120/80 mm Hg. Art.;
- up to 40 years - 120/80, 130/80 mm Hg. Art.;
- up to 60 years - 130/80, 140/90 mm Hg. Art.;
- over 60 - 150/90 mm Hg. Art.
The average numbers on the tonometer display, which cause concern for the patient’s health, are 140/90 mm Hg. Art. But this is only relevant for a healthy person. For example, in diabetes mellitus, such blood pressure is normal and does not require special correction with medications.
High blood pressure with normal lower pressure is called isolated hypertension, requiring special examination and treatment
Pressure below 100/60 mm Hg. Art. refers to reduced. But for athletes or people constantly exposed to stress, it becomes normal over time. This is how the body adapts to the situation and regulates the person’s condition.
Important! Not only increased, but also decreased upper pressure indicates problems in the body. Low blood pressure is not as dangerous, but can lead to decreased gas exchange in the tissues and lungs. Hypoxia, in turn, in some cases ends in collapse (coma or even death).
Symptoms accompanying dry mouth
In the absence of saliva, the body is unprotected, and therefore “attracts” many accompanying symptoms. Dry mouth is accompanied by: Thirst, a person cannot get drunk;
Feeling of “sticking together” of the tongue, gums and palate;
Bad breath;
The appearance of cracks and sores on the lips;
Tooth decay;
Difficulty swallowing food and water. The throat feels closed and hurts;
Irritation on the tongue;
Loss of taste in food;
Hoarseness.
With a constant lack of saliva, the digestive system begins to suffer, teeth and gums suffer, and problems with the ears and nasopharynx begin. At this time, it is dangerous to move along the street without a mask, as there is a high risk of catching any infection.
If you have dry mouth, the reasons may be natural.
Possible complications of isolated hypertension
The situation when the upper pressure is high and the lower pressure is normal is called isolated hypertension by experts. The disorder is associated with a decrease in the degree of distensibility of the arteries, including the most important one - the aorta. It is she who is normally responsible for receiving blood and suppressing pressure during cardiac output. Elasticity allows blood flow to pass smoothly, but as the rigidity of the arterial walls increases, this ability is lost. Blood cannot circulate through the vessels at an optimal speed, which provokes pressure surges. Small vessels are not affected, so lower pressure readings remain normal.
Over time, this condition can lead to a number of additional disorders, among which the following can be noted:
- heart failure;
- decreased left ventricular function;
- disturbance of the speed of blood flow through large vessels;
- damage to the endothelium and subsequent replacement of deformed areas with rigid connective tissue;
- increased production of enzymes that negatively affect the vascular walls - nitric oxide, angiotensin, renin.
What to do in this case? Treat. Moreover, not only relieve a person from unpleasant symptoms, but also eliminate the cause that caused the disorder. The sooner the problem is diagnosed, the answer is given to the question of why the upper pressure is high and the lower pressure is low, and a treatment regimen is drawn up, the faster you can get rid of the disease and the lower the risk of developing all kinds of complications.
Important! You cannot take medications or be treated with traditional methods without consulting your doctor.
Functions of saliva in the body
Xerostomia is a condition when the salivary glands stop producing enough saliva. This physiological fluid performs certain tasks in the mouth:
- wetting and softening pieces of food;
- fight against viruses and bacteria;
- lubricating the throat for smooth swallowing of food;
- maintaining the correct biological environment in the mouth;
- protecting teeth from caries.
Without the protective function of saliva, it is easier for a person to get infectious diseases.
Symptoms of arterial hypertension:
- intense headache
- dizziness
- nausea, vomiting
- visual impairment, transient blindness
- double vision, flashing spots before the eyes
- numbness of hands, face
- decreased pain sensitivity in the face, lips, tongue
- crawling sensation
- mild weakness in the distal arms
- convulsions
- pain in the heart area
- heartbeat
- feeling of interruptions
- dyspnea
- chills, tremor
- feeling of fear
- irritability
- sweating
- feeling hot
- thirst
Help with uncomplicated hypertensive crisis
- Stop physical activity.
- Sit or lie down with your head elevated and measure your blood pressure.
- You need to calm down and not panic (you can take tincture of valerian, motherwort).
- Restore your breathing - take a few deep breaths and exhales.
- If you have a hypertensive crisis for the first time in your life, you should definitely call an ambulance.
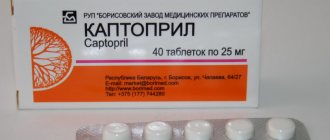
- Regardless of the type of hypertensive crisis, drugs with a rapid onset of the expected effect and a short elimination period should be used as self-help: captopril 25 mg; nifedipine 10 mg; moxonidine 0.2-0.4 mg; propranolol 10-40 mg.
- If the blood pressure level does not decrease or continues to increase, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
Causes of high blood pressure can be:
- refusal to take antihypertensive drugs
- inappropriate use of medications for hypertension
- diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys, adrenal glands
- heart diseases
- preeclampsia in pregnant women
- traumatic brain injuries of the head
- severe burns
- abuse of nicotine, alcohol
- psycho-emotional stress
- significant physical activity
- large meal
- changes in atmospheric pressure