What is extrasystole?
Listen, can you feel the rhythm of your heart?
Normally, you should not hear or feel its beating. If this does happen, then this is a reason to think about it and go to the doctor. Moreover, if you feel a slight blow to the chest, and then a pause, and this brings discomfort, then you are faced with an extrasystole. In scientific terms, extrasystole is a process during which a sudden additional contraction of the heart occurs due to an electrical impulse in one of its sections. Extrasystole is the most common type of arrhythmia.
According to statistics, extrasystole is recorded in 70% of healthy people. In more than 65% of cases, ventricular extrasystoles develop, 25% occur in the atrial ones and the rest - in
combined variants of extrasystole.
In its normal state, the heart contracts rhythmically, impulses are generated regularly, the sinus node and the electrical signal move according to the direction, down to the ventricles. But when the work of the heart is disrupted, a premature electrical jump occurs - an extrasystole. After it there is a pause, and then the heart begins to beat rhythmically again.
How does the heart's electrical system work? The sinus node is the main conductor of rhythm; its electrical signal is distributed throughout the atria, lingers slightly in the articular node and spreads throughout the ventricle.
During extrasystole, the sinus node temporarily stops functioning, because of this, the heart seems to turn off for a moment, literally freezing. Then an electrical surge appears in the ventricle and a contraction occurs, the heart begins to beat again, and the rhythm is restored.
What is premature contraction? This is a heart condition in which the heart beats earlier than it should. When the heart functions normally, the organ fills with blood. And when an extrasystole occurs, its work is suspended for a split second.
Heart sinking
Atherosclerosis
Menopause
42935 20 October
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Fading of the heart: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Description
Fading of the heart is a subjective feeling of the absence or skipping of another heartbeat in a certain period of time, accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the heart area, in some cases, dizziness and darkening of the eyes. Heart stopping is a symptom of a wide range of diseases: from the most harmless ones that do not require treatment to serious pathologies that require medical intervention.
Types of heart palpitations
Normally, the heart contracts rhythmically, at approximately equal intervals. The contraction frequency ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
There are several types of heart failure:
- Fading of the heart due to a compensatory pause during extrasystole. There is a sensation of a strong or double heartbeat against the background of a normal rhythm, followed by a short pause felt by the patient.
- Varying intervals between contractions can also cause the heart to feel as if it is stopping (common with atrial fibrillation).
- Pauses of the heart due to blockade of impulses.
- Feeling of freezing with reduced pumping function of the heart (with severe heart failure).
Possible causes of heart failure
First, we list the most common risk factors for cardiac problems:
- Smoking
is one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular disease. This also includes alcohol, caffeine and drugs. - High levels of “bad” cholesterol
- intermediate, low and very low density lipoproteins (IDL, LDL, VLDL). - High blood pressure
.
The feeling of interruptions and pauses in the work of the heart in most cases is caused by extrasystoles, or premature contractions of the heart.
Extrasystoles are often observed in completely healthy people, while there are no signs of myocardial dysfunction, and correction is not required.
However, if attacks of extrasystole exceed the permissible norms per day (diagnosis is carried out using daily ECG monitoring), additional examination and treatment are required.
Less commonly, the cause of heart failure is atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) or blockade of the conduction system of the heart. Atrial fibrillation occurs when the electrical activity of the atria is disrupted with the occurrence of a large number of impulses and chaotic contraction of the atria.
Only a portion of the impulses pass to the ventricles of the heart in an irregular rhythm - hence the fading of the heart, as well as other unpleasant sensations.
Atrial fibrillation can occur in the form of attacks (paroxysms), or it can be permanent. The diagnosis is made based on the results of the ECG.
Blockades of the conduction system of the heart, depending on the severity, manifest themselves in different ways: from asymptomatic to loss of consciousness. Feelings of heart stopping most often occur with 2nd degree atrioventricular block.
There is a gradual depletion of the atrioventricular (AV, AV) node, a decrease in the ability to conduct impulses, and a kind of pause occurs, which the patient clearly feels.
Causes of disturbances in the structure of the conduction system of the heart:
- myocardial infarction with subsequent replacement by connective tissue of destroyed heart structures, including important bundles that conduct electrical impulses from the sinus node;
- coronary heart disease, when due to atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, adequate blood supply to the myocardial areas in the area of the conduction bundles is disrupted and sclerodegenerative fibrosis (replacement with connective tissue) of the affected tissue areas develops;
- myocarditis (inflammatory damage to the heart muscle);
- dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the conduction system of the heart.
Sick sinus node syndrome (SSNS) is a rare condition caused by a decrease in the functional ability of the sinus node to act as the main pacemaker and ensure regular conduction of impulses to the atria, which predetermines the appearance of cardiac slowdown and accompanying arrhythmias.
Patients often complain of dizziness, poor exercise tolerance, shortness of breath on exertion, fatigue and episodes of weakness.
Many cardiac problems, which at first glance are not related to rhythm disturbances, can ultimately lead to the appearance of various arrhythmias, accompanied by a feeling of cardiac arrest. For example, with hypertension, the myocardial wall thickens and the nutrition of heart cells is disrupted, which leads to the appearance of ectopic (irregular) impulses. With various defects of the valve apparatus, without treatment, a gradual change in the structure of the heart muscle occurs with the appearance of connective tissue and disruption of the normal conduction pathways of the heart.
Among the non-cardiological reasons for the feeling of heart failure, it is worth noting the menopause, which is accompanied by changes in hormonal levels and various unpleasant sensations and discomfort not associated with disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
Hypothyroidism may cause a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) and a feeling of pauses in the heart. This is due to insufficient levels of thyroid hormones.
During intoxication (during infectious diseases, with severe sweating, vomiting and diarrhea), a loss of electrolytes (potassium, sodium and magnesium ions) occurs, which leads to disruption of the water-salt balance in the body and the occurrence of various rhythm disturbances.
Taking certain medications may be accompanied by a slower heart rate, slower impulse conduction, and a feeling of heart stopping. These drugs include cardiac glycosides, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, sympatholytic agents, antidepressants, and narcotic analgesics.
In persons with a labile psyche and frequent emotional experiences, a subjective feeling of discomfort in the chest area and cardiac arrest without visible organic pathology is possible.
Which doctors should I contact?
If various disturbances in the functioning of the heart occur, you should consult a cardiologist. To exclude non-cardiological causes of the feeling of heart failure, the cardiologist can refer you to a general practitioner and endocrinologist.
If the cause of heart rhythm disturbances is the use of medications, you must contact your doctor to adjust the dose or replace the drug.
Diagnosis and examination of cardiac arrest
First of all, to detect cardiac arrhythmias, counting the pulse and heart rate is used. When examining a patient, the doctor uses auscultation to listen to the heart rhythm and detect other accompanying symptoms in order to diagnose the disease that has caused the change in heart rate.
If a pathological change in heart rhythm is detected, a therapist or cardiologist will prescribe an electrocardiographic study (ECG).
Symptoms
Like most diseases of the cardiovascular system, extrasystole does not have obvious signs and symptoms. Patients simply do not realize that they are experiencing heart rhythm disturbances. And if they do notice, then unscheduled contractions of the heart do not bother them.
Extrasystole feels comparable to a strong push to the chest and a sharp attenuation afterwards. For a second, the patient may feel as if his heart is turning over. Then everything abruptly returns to its place. Some people have such sensations, while others do not. It all depends on the height of the pain threshold, the tolerance of this kind of symptoms, the number and frequency of extrasystoles. As well as the presence of a patient with a cardiovascular disease. For many people, the presence of extrasystole does not bother them at all and they can live with it.
During frequent or prolonged attacks, oxygen starvation occurs, and feelings of panic and anxiety may occur. Such sensations are explained by the production of the hormone adrenaline, which provokes an even greater disruption of the heart rhythm.
Let's consider the common symptoms of extrasystole in patients with heart pathologies:
- Patients with cerebral atherosclerosis experience dizziness and sometimes fainting;
- Angina attacks occur in patients with coronary heart disease.
Other symptoms of extrasystole may be: fever, weakness, sweating, lack of air and pain in the heart area.
To summarize, we can say that during extrasystole, blood does not enter the brain. Because of this, the patient may feel:
- dizziness;
- fainting (if there are many extrasystoles, the person may lose consciousness);
- heat;
- sweating;
- oxygen starvation;
- weakness;
- heartache;
- anxiety.
Heart rhythm disturbances associated with sleep deprivation
People with involuntary sleep deprivation may experience some of the same heart rhythm problems as insomnia. First of all, these are mild arrhythmias that arise as a result of the already mentioned autonomic dysfunction, and secondly, these are “own” rhythm disturbances, intensified against the background of deteriorating quality of rest.
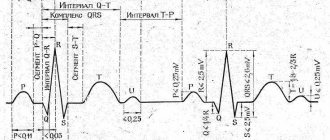
There is evidence of other disorders arising from sleep deprivation. For example, it has been found that short-term sleep with deprivation of the fast phase leads to an increase in the duration of the QT interval, that is, it causes a slowdown in conduction through the ventricles of the heart. The risk of such pathologies is especially high for people who do not have the opportunity to sleep for a long time and make do with short “naps” several times a day.
Causes
Extrasystole of the heart can be caused by a number of reasons, which can be divided into two sources.
The first and most basic is diseases of the cardiovascular system. Extrasystole can occur against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the heart, which are accompanied by organic damage to the myocardium. The second block is external:
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- electrolyte disturbances;
- external influences. For example, being in a stuffy room where there is a lack of oxygen;
- excessive caffeine consumption. This factor causes tachycardia.
Heart rhythm disturbances due to insomnia
With insomnia, heart rhythm disturbances are also sometimes encountered, although usually they are not as pronounced and dangerous as with the disease described above. Most often, especially in physically healthy people, they are limited to sinus tachycardia (increased heart rate) and sinus arrhythmia (alternating acceleration and deceleration of the normal rhythm).
In this case, the reason for the changes that have arisen is that prolonged lack of sleep leads to the appearance of a certain imbalance in the autonomic nervous system towards stressful processes, which increases the load on the heart and leads to similar consequences.
Classification of arrhythmia
Taking into account the place of origin of the electrical impulse and the specifics of its conduction from the pacemaker node to the ventricles, arrhythmias can be systematized as follows:
- violation of the generation of electrical impulses;
- conduction changes (blockades and additional conduction pathways);
- combined rhythm disturbances.
The first class of violations is:
- failures of automaticity of the source of excitation (sinus brady-, tachycardia, sinus arrhythmia, sick sinus syndrome, atrial asystole);
- ectopic bursts (ectopic rhythms, extrasystole, escape complexes, pacemaker migration, paroxysmal tachycardia, flutter, atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation)
Heart blocks
divided according to the topography of the area where the movement of the electric wave slows down/interrupts. Their names correspond to the location. Consider sinoatrial, intraatrial, atrioventricular, and intraventricular blockades.
Congenital anomalies in the presence of additional conduction pathways serve as the basis for the occurrence of ventricular pre-exitation (pre-excitation) syndromes.
Combined
disorders are parasystole, atrioventricular dissociations, a combination of blockades with rhythm disturbances (Frederick's syndrome), etc.
According to forecast
distinguish between: non-dangerous arrhythmias, probably dangerous, life-threatening.
Based on this, disorders are differentiated into those requiring treatment and those subject only to observation over time.
Diagnostics
Even if cardiac arrest is a rare episode, it is a reason to consult a cardiologist. Percussion can determine the expansion of the borders of the heart. During auscultation, muffled heart sounds and the presence of functional or organic noises are heard. To find out the cause of the symptoms, the doctor needs to obtain data from instrumental and laboratory research methods. Typically used:
Treatment
To restart a stopped heart muscle in a medical facility, doctors use:
The listed drugs stimulate the activity of the heart. After the injection is administered, an electrocardiogram is taken. If necessary, the heart is started using a defibrillator, a device that creates an electrical shock. The device is already used in the intensive care unit to deliver the victim alive to the clinic .
Medicines for cardiac therapy
Patients are treated using the following medications:
Proper use of medications allows for effective therapy. The chances of survival for a person whose heart has stopped in his sleep increase many times over.
Some patients require surgery. Patients have a pacemaker implanted into their heart muscle.
Rehabilitation period
When returning home, the patient must follow all medical recommendations:
If the patient takes glycosides and leads a healthy lifestyle, relapse does not occur . A person has a chance to become a long-liver.
Atrial fibrillation. Diagnosis and treatment
This arrhythmia is one of the most common types. Atrial fibrillation is manifested by a feeling of uneven heart contractions: the ventricles contract unevenly, and the atria seem to flutter. Up to 60 years of age, this type of arrhythmia occurs only in 1% of cases, but after 75 years of age it is detected in 30% of patients.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
First of all, it is characterized by a rapid heart rate (130-150 beats per minute), in some cases even a heart rate of up to 180 beats per minute occurs.
Cardiac apnea: where does it come from and how to treat it?
Medicine has long proven that heart disease has a significant impact on sleep. Patients with heart failure usually report having difficulty falling asleep or maintaining normal sleep because their breathing is shortened.
In addition, shortness of breath often increases when the patient lies down, because in this position the blood flows to the heart more intensely, mainly from the lower extremities. For healthy people this is not a problem, but an unhealthy heart cannot cope with pumping blood.
From the history
The term sudden death first appeared in 1917 in the Philippines, where the syndrome was called “bangungut”. Then, in 1959, Japanese doctors called it “smoke”; specialists from Laos, Vietnam and Singapore also wrote about a similar phenomenon.
Having compared the data obtained with information from colleagues from the countries of the Far East and Southeast Asia, the researchers found that it is in these regions that cases of this pathology are very common, and more often among young people. At the same time, such a syndrome practically does not occur among African-Americans.
Source
Prevention can reduce risks
Treatment for apnea is directly related to its cause. Therefore, common methods are: removing obstructions in the nasal passages and correcting the nasal septum. Devices are also used that support the organs of the mouth and throat in the correct position.
Prevention coincides with therapy of the mildest form. It is necessary to adopt a healthy lifestyle, reduce weight to normal, and stop drinking alcohol and tobacco. Training the throat muscles will help: playing wind instruments or singing. The habit of sleeping on your side greatly reduces symptoms and makes breathing easier. And, of course, all ENT diseases will have to be treated in a timely manner.
Source
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia in women and men
It is worth noting that the causes of arrhythmia are not divided by gender and are practically the same in women and men. The only thing is that women may experience pathology due to premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause. Undoubtedly, there are many reasons for the occurrence of arrhythmia. Let's list the main ones.
CPAP therapy is an effective way to restore impaired heart function in a patient with sleep apnea
Thanks to the development of new medical technologies, today there is a reliable, convenient and safe way to restore healthy sleep, ease the work of the heart at night and avoid the danger of heart rhythm disturbances and the risk of sudden death during sleep - CPAP therapy.
On our website you can learn about the features of this method and make an appointment with a specialist - somnologist. The doctor’s task is to determine the nature of your problems, help you choose the optimal model of the device and select the optimal treatment regimen.
CPAP therapy - give your heart a chance
The sooner you wage war on obstructive sleep apnea, the better your chances of eliminating its devastating effects forever. Therefore, do not put off resolving the issue until later, especially since treatment of sleep apnea using a CPAP machine is easily tolerated and almost immediately provides a clear positive result, radically changing a person’s well-being for the better.
Cardiac health and arrhythmia treatment
To prevent heart disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Remember that as soon as you notice the presence of symptoms of any type of arrhythmia, contact your physician or cardiologist. If you feel a sharp deterioration in your health, call an ambulance.
How to stop an attack and what to do next?
The patient's algorithm for freezing in the chest area is related to the cause of the symptoms. The presence of organic cardiac pathology requires the appointment of constant pathogenetic or etiotropic therapy.
In the case of psychogenic genesis of sensations, it is recommended:
avoid stressful situations;- normalize sleep and wakefulness;
- a balanced diet enriched with vitamins and microelements (for the heart - potassium, which is found in bananas and dried fruits);
- adequate physical activity;
- taking plant-based sedatives (for example, Novo-Passit, Valerian extract).
Rare occurrences of symptoms (up to 3 times a month) are most often a physiological phenomenon that occurs in every person. Freezing, which occurs several times a day and lasts up to 4 seconds, requires diagnosis and medical attention.
Depending on the reason, the following is prescribed:
- in case of rare sinus rhythm and hemodynamically significant high-degree atrioventricular block, a pacemaker is used. Before installing an artificial pacemaker, drops of Zelenin, Atropine, and Isadrin are prescribed;
- treatment of extrasystoles is carried out with antiarrhythmic drugs, for example, Etatsizin;
- attacks due to vegetative-vascular dystonia are stopped with the help of sedatives and antispasmodics.
In addition, physiotherapy methods can be successfully used to treat subjective sensations of rhythm disturbances: massage, balneotherapy and others.
Who will help with diagnosis?
If you or your loved ones notice symptoms such as loud snoring and interrupted breathing during sleep, it is advisable to consult a specialist as soon as possible. If you were unable to get to a somnologist, you should contact a neurologist and otolaryngologist. They will be able to determine and eliminate the cause of apnea.
Close people will help you measure the duration of pauses in breathing. During a general examination, your blood pressure will be checked and your heart condition will be determined.
The most reliable diagnostic methods are polysomnography, 24-hour ECG and pulsometry. They monitor all changes in the body: breathing, heartbeat, nerve activity and electrical impulses.
What happens in the body during an apnea attack?
While awake, we can consciously hold our breath for 1-2 minutes, and then resume it at will. For example, when swimming. In a dream, the body has to solve this problem on its own.
During an attack, signals are sent to the brain that the level of oxygen in the blood is too low. As a result, the person instantly wakes up. His blood pressure rises sharply, which puts him at risk of angina and stroke. And tissues with a lack of oxygen become less susceptible to insulin, the hormone that controls sugar levels. This is why there is a lack of strength in the body.
Stopping breathing negatively affects all parts of our body. We can live without air for no more than ten minutes. And the longer the attacks of sleep apnea , the more often they occur during rest, the more severe the consequences will be for the patient.
What symptoms are associated with this sensation?
In medicine, there are more than 200 types of various rhythm disturbances, which most often occur in combinations in patients. A feature of arrhythmias is considered to be specific differences in the electrocardiogram and completely nonspecific clinical signs.
When patients talk about heart palpitations, most often they are talking about:
- non-rhythmic contraction of the myocardium of the ventricles and atria, which is felt as two independent rhythms;
- the presence of frequent extraordinary contractions, after which a compensatory pause occurs;
- incorrect rhythm (different intervals between contractions).
From an objective point of view, freezing can be called a pause in the heart rhythm lasting up to 2 seconds, after which tachycardia develops (rapid heartbeat).