Types of tricuspid valve defects
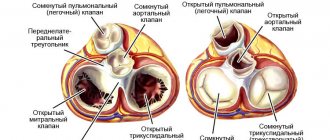
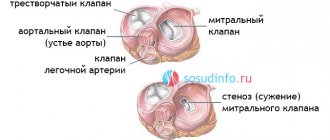
The tricuspid (three-leaf) valve of the heart is located between the right atrium and the ventricle. The valve's job is to prevent blood from returning to the atrium during the systolic phase (contraction phase). At the same time, the physiological structure of the valve ensures unimpeded blood flow during ventricular filling. Tricuspid valve defects are often acquired, that is, they develop throughout life. Less common is congenital valvular atresia, which is usually part of multiple cardiac malformations.
Acquired tricuspid valve defects include:
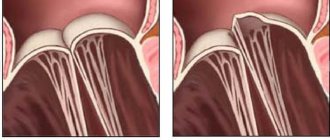
- Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition in which the tricuspid valve leaflets do not close completely, causing some of the blood to return to the right atrium during ventricular contraction. The consequence of tricuspid insufficiency is a decrease in systolic volume in the pulmonary circulation, overload of the right parts of the heart and the development of heart failure of the right side, and then of the mixed type;
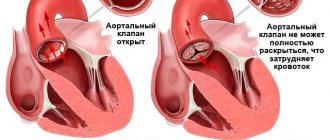
- Tricuspid stenosis is caused by a narrowing of the valve lumen and difficulty in the flow of blood into the ventricle during contraction of the right atrium. Since the muscular layer of the right atrium is not able to overcome prolonged overload and does not have sufficient compensatory reserves, hemodynamic disturbances in tricuspid stenosis lead to the rapid development of severe congestion in the systemic circulation.
Plastic results
Symptoms of stenosis or tricuspid insufficiency disappear immediately after surgery. In the first 1-2 months after it, the patient’s condition will gradually improve if the manipulations went without complications. Negative consequences may include:
- bleeding;
- heart attack;
- formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels;
- disturbances of vision, appetite, sleep (this is normal, goes away within a month);
- infection;
- hemolytic anemia.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To prevent such consequences, scheduled and unscheduled inspections are prescribed. In most cases, the prognosis for tricuspid valve surgery is positive, heart function is restored, and the patient returns to his normal lifestyle.
The postoperative period is complicated by the use of anticoagulants, which reduce blood clotting. Biological implants do not require constant use of anticoagulants, but the lifespan of such prostheses is limited. Observations of patients show that a biological implant lasts an average of 9-10 years.
Mechanical analogues have a long service life; they keep the heart functioning for 20-25 years. But during this entire time you need to take medications that reduce blood clotting. When the life of the implant has passed, it is replaced with the next one. If regular sutures were used during plastic surgery, reoperation may not be necessary. However, long-term patient survival is higher with rings than with conventional suture techniques.
Causes of development of tricuspid valve defects
Experts identify a number of main causes of acquired tricuspid valve defects, including:
- Rheumatic endocarditis (the most common cause of both insufficiency and stenosis);
- Infectious endocarditis of non-rheumatic origin;
- Calcification (deposition of calcium salts) on the valve leaflets and in the area of the valve ring;
- Conditions accompanied by hypertrophy and/or dilation of the right heart (pulmonary hypertension due to damage to the mitral valve, cardiomyopathy). In this case, we are talking about secondary insufficiency resulting from the expansion of the valve ring and the inability of the valves to compensate for the increase in the resulting lumen;
- Tumors of the heart, as well as tumors of the mediastinum, exerting mechanical pressure on its right parts from the outside;
- Consequences of penetrating injuries and surgical interventions.
Clinical picture of tricuspid insufficiency and stenosis
Since the main cause of the development of tricuspid valve defects is rheumatic endocarditis, the development of the disease is often preceded by an increase in temperature and clinical signs of streptococcal sore throat. Valve damage manifests itself as signs of heart failure:
- Fatigue and decreased tolerance to physical activity;
- Labored breathing;
- Cyanosis (blueness) of the skin and mucous membranes;
- Enlarged liver;
- Peripheral edema, mainly in the lower extremities, as well as fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (ascites);
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
Mild forms of tricuspid insufficiency can occur for a long time without significant clinical manifestations, causing complaints only in the stage of decompensation. Symptoms of heart failure due to tricuspid stenosis are usually much more pronounced and are diagnosed at the onset of the disease.
Symptoms
Often, heart valve defects do not appear clinically for a long time, and complaints depend on the severity of the disease. When the disease manifests itself, patients experience shortness of breath, dizziness and fainting during exertion, a feeling of heaviness, chest pain, heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias), swelling, fatigue, and decreased performance. Often the heart’s ability to compensate for defects lasts for a long time. Therefore, patients seek help at a time when it is already difficult to help them due to the “neglect” of the disease, when the heart has exhausted its compensation capabilities and has turned, figuratively speaking, into an “overinflated balloon.”
Diagnosis of tricuspid valve defects
In the cardiology department, patients undergo a thorough modern examination by leading Israeli specialists. In addition to the history, characteristic complaints and clinical signs, tricuspid valve defects cause pathological noises, determined by the doctor during auscultation of the heart. If valve damage is suspected, patients undergo a number of additional tests, the main of which are:
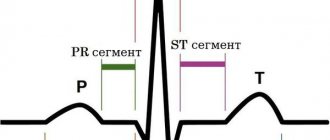
- Electrocardiography (recording of electrical potentials of the conduction system of the heart). The method allows you to diagnose myocardial hypertrophy and heart rhythm disorders. Patients with tricuspid defects often experience atrial fibrillation and intraventricular conduction disorders;
- X-ray examination - overview of the chest and computed tomography of the heart;
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which has important diagnostic value for accurate assessment of the size of the right ventricle
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart – echocardiography;
- Invasive methods, such as cardiac catheterization, are often used in preparation for surgery, as well as to exclude ischemia (coronary circulatory insufficiency).
How to get treatment in Israel
By choosing our multidisciplinary complex, you get the opportunity to visit the right specialists and undergo all types of diagnostics in one place. Our own developments and exchange of experience with foreign partners make our clinic one of the best in the world.
To avoid the costs of intermediaries, use our official website. You can submit a request to visit the children's cardio center by filling out an electronic form. A Russian-speaking representative of the international department will contact you within two hours and answer all questions.
An integrated approach to the treatment of tricuspid valve defects
Conservative treatment of tricuspid defects caused by rheumatic endocarditis includes a course of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. Modern antiarrhythmic drugs and drugs that improve the condition of patients suffering from heart failure are widely used. Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are indicated for high risk of thrombotic complications in patients with atrial fibrillation, as well as after operations to replace the valve with a mechanical implant.
Surgical treatment is recommended for significant hemodynamic disturbances. It includes the following procedures:
- Percutaneous balloon commissurotomy is used in some cases of tricuspid stenosis. This minimally invasive procedure can dilate a moderately deformed annulus fibrosus without the need for open surgery;
- Tricuspid valve annuloplasty. An operation that restores the anatomical integrity and mobility of the valve leaflets. This intervention is preferable for most tricuspid defects. Successful restoration of a natural valve prevents the need for valve replacement'
- Surgery to replace the tricuspid valve is currently used for severe forms of the defect that are not subject to an organ-preserving procedure. High-quality mechanical and biological prostheses take over the function of the affected valve and restore normal blood circulation.
Cardiac surgeons choose the type of operation depending on the type of tricuspid defect, the degree of valve damage and the severity of hemodynamic disorders. High professionalism and extensive experience of specialists contribute to the optimal choice of treatment method.
One of the advantages of treatment at Herzliya Medical Center is the opportunity to undergo a full range of necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation procedures within one hospital. The individual approach of the clinic’s specialists to the problems of each patient allows us to achieve the desired result in an extremely short time.
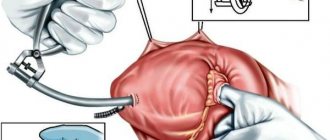
Carrying out the operation
Reconstruction of the valve apparatus occurs in a hospital setting, in the operating room. Before this, the patient is given premedication: sedatives and hypnotics are administered intravenously. Throughout the entire process, assistants will monitor the patient’s condition using connected equipment. When sleep comes, the surgical team begins manipulations.
- The surgeon makes an incision in the chest. If you get to the heart through the intercostal space, you won’t have to cut the sternum bones. In most cases, the doctor opens the chest, then gets to the valve layer by layer.
- The heart is forcibly stopped and a heart-lung machine is connected. During the process, this device will saturate the blood with oxygen and give it the desired temperature while the heart is “turned off.”
- Then the surgeon’s actions will depend on the pathology itself. To restore the lumen, the valves can be cut and sutured; most often, sutures are placed around the circumference of the valve. There are several suturing techniques; for moderate dilatation, de Vega sutures are usually used. If valve closure is corrected, rings, half rings or tape are most often sewn in. The implantation of such structures is called “annuloplasty”. If it is impossible to restore the function of the tricuspid valve, its leaflets are removed and a prosthesis is placed in their place.
- Before turning off the AVR, the doctor checks the operation of the operated or prosthetic valve. The shortcomings are corrected, the heart-lung machine is turned off.
- The incision site is sutured in layers, the external seams are treated with sterilizing agents. Then apply a tight bandage.
- The patient's condition is assessed again and he is transferred to the intensive care unit. When the anesthesia wears off, the patient is placed in an intensive care unit.
After the operation, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors for another week. This is necessary in order to monitor the results of plastic surgery and prevent complications. In the first days, bed rest, moderate drinking, and diet are indicated. After the final check, the patient is discharged home.