Basic Compatibility Concepts
Let's look at the basic concepts of blood compatibility.
Isoagglutininogens (A and B) are specific proteins on red blood cells, which are essentially antigens.
Isoagglutinins (alpha and beta) are antibodies to antigens found in plasma.
When isoagglutininogens A interact with isoagglutinins alpha, red blood cells stick together (agglutination) and hemolyze. The same thing happens with the interaction of isoagglutininogens B and isoagglutinins beta, that is, they are incompatible.
Thus, so that trouble does not happen to our “carrier of life,” nature conceived certain combinations of agglutinins and agglutininogens, forming four groups.
Blood groups according to the ABO system
Thus:
- The first blood group (I) or 0 is characterized by the absence of agglutinogens and the presence of both types of agglutinins in the plasma;
- The second blood group (II) or A – is characterized by the presence of agglutininogens A on red blood cells and agglutinins beta in plasma;
- The third blood group (III) or B - here, on the contrary, there is agglutininogen B on the erythrocyte, and agglutinin alpha in the plasma;
- The fourth blood group (IV) or AB is characterized by the complete absence of agglutinins, and both A and B agglutininogens are found on red blood cells.
The influence of blood on character and lifestyle
Holders of the third positive blood group delight everyone with their easy-going and open character.
They quickly find a common language with other people, make new acquaintances and do not lose confidence and optimism even in very difficult situations. They have a strong sense of justice and stand up not only for their relatives, but also for strangers. People with such blood were greatly influenced by their historical origins from nomads, who are always in search of something new and make unexpected decisions, easily adapt to different conditions around them, such people have no constancy.
People with positive blood type 3 are suitable for creative professions, which is explained by their restless nature.
Men are characterized by such qualities as wit, charm, and assertiveness. The peculiarity of women is inconstancy, they are flighty and charming, they always have many fans. Most carriers of the third blood group have no health problems, but few suffer from dysfunction of the endocrine glands. Common pathologies are diabetes and multiple sclerosis. In many cases, people with this type of blood experience poor concentration and constant fatigue.
Transfusion compatibility
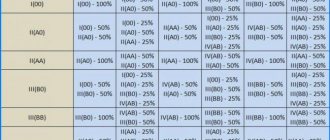
During blood transfusion, they strictly focus on blood group compatibility. Single-group blood is transfused, but in exceptional cases, in its absence, in an emergency situation, transfusion of the first group, in a small amount, is permissible. The first group is the universal donor. Patients with the fourth group can be transfused in small quantities from any other group. It is called the universal recipient. This is clearly shown in the compatibility table.
How does a child turn out with the third group?
Group B(III) of the antigen structures has only B. This means that one of the parents must have this antigen. This situation is possible if both parents have 3-4 or mixed groups:
- third + fourth;
- third or fourth + first (without antigens);
- third or fourth + second.
One thing is clear: a baby with the third group cannot appear from parents with the first and second, since they both do not have the B-antigen. This rule is used to establish paternity and determine identity in forensic practice.
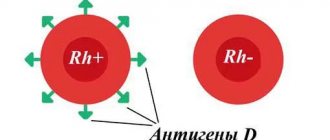
Pregnancy and Rh factor
It is important to know before birth what Rh factor the mother and father have in order to predict the Rh conflict in the child. Yes, this happens too. If the mother is Rh negative and the father is positive, the child may inherit a positive Rh factor. As a result, the mother’s body will perceive the child as a foreign body and produce antibodies to its red blood cells. This situation is fraught with complications during pregnancy and childbirth, including fetal death. Therefore, it is very important to prevent blood incompatibility between mother and child.
As a rule, conflict does not occur during the first pregnancy, but in subsequent pregnancies the likelihood is high.
What therapeutic and diagnostic measures are used to maintain pregnancy and give birth to a healthy child? There is a special serum aimed at neutralizing maternal antibodies at high risk.
Constant monitoring and strict adherence to all doctor’s prescriptions is necessary if there is a possibility of developing Rh conflict.
A pregnant woman needs to be tested for the presence of antibodies and repeat them twice a month until 35 weeks, and after that - twice a week. This will allow you to identify the beginning of an incompatibility conflict and take a number of necessary measures:
- perform a chorionic villus biopsy, thereby accurately determining the rhesus of the fetus;
- administer immunoglobulin for prophylactic purposes;
- perform amniocentesis or induce labor if necessary.
This serum is also administered to prevent the production of antibodies:
- After an abortion;
- With an ectopic pregnancy;
- After a miscarriage;
- After childbirth;
- After analyzing the amniotic fluid.
What diseases does blood predict?
Nature has provided those with the third blood group with good immunity for survival in any conditions. A higher fertility of women has been established compared to other groups. The highest concentration of sex hormones is found in the body of women and men.
There are risk factors for development:
- spinal osteochondrosis;
- intestinal tumors;
- inflammation of the lung tissue;
- urinary system infections;
- septic postpartum complications for women;
- chronic fatigue;
- depressive states;
- autoimmune processes.
Compatibility tests
During blood transfusion, the following tests are performed:
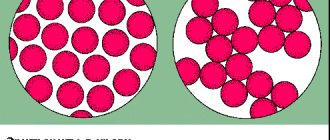
- An individual compatibility test is carried out by mixing the recipient's serum and donor's blood in a special test tube. The result is assessed by the presence or absence of agglutination, manifested in the formation of sediment in the form of flakes;
- The Rh factor compatibility test is carried out by mixing a drop of donor blood and two drops of recipient serum. If there is agglutination, the blood is not compatible;
- A biological test is carried out just before the transfusion by administering 10-15 ml of donor blood and observing the patient for three minutes for signs of incompatibility. At the same time, the color of the skin, urine, pulse, temperature and blood pressure are assessed.
Agglutination is a sign of incompatibility
How to balance your diet
The diet for blood group 3 is aimed at preventing possible diseases. It takes into account products in terms of benefits and degrees of harm.
People with group No. 3 can practically tolerate any food well, because they are maximally protected. However, there is a certain balance in nutrition, preference for certain types of foods. It can be expressed by dividing possible products into three groups.
Which is definitely useful
Lamb, poultry, and rabbit are recommended; among fish, halibut, salmon, sturgeon, flounder, sardine, cod, and pike are preferred.
Dairy products from skim milk, goat milk, Mozzarella cheese, olive vegetable oil, mayonnaise, mustard. The only nuts offered are walnuts and almonds. Legumes are red. Porridge made from oatmeal, rice, millet. White bread.
Vegetables, fruits: beets, carrots, eggplants, cabbage, parsley, parsnips, bananas, grapes, pineapple, ginger. You can drink green tea.
Allowed temporarily
Meat products from beef, turkey, liver. Fish: carp, herring, squid. Butter, hard cheeses, flaxseed oil. Legumes - green peas. Rye bread. Drinking white or red wine, black tea and coffee is rarely possible.
Vegetables, fruits: potatoes, cucumbers, green onions, garlic, pumpkin, spinach, oranges, watermelon, pears, cherries, currants, figs, raisins, prunes, peaches, apples, lemon.
If you decide to eat according to your blood type, you just have to look at some foods
Not recommended
Eastern recommendations are against chicken, goose, duck, ham, pork, and heart dishes. Perch, crayfish, smoked salmon, shellfish, processed cheese, ice cream, sunflower and corn oil, ketchup, seeds, peanuts, lentils, buckwheat, millet and barley porridge, and baked goods are contraindicated.
Vegetables, fruits: tomatoes, radishes, corn, pomegranate, rhubarb, persimmon. Alkaline mineral waters, strong alcohol.
Complications
When incompatible blood is transfused, severe complications develop - transfusion shock, and later acute renal failure occurs. Their treatment is difficult and lengthy, and the prognosis may be unfavorable.
No one is immune from blood transfusion. Trauma, internal or external bleeding, complication of gastric ulcer and other acute conditions accompanied by blood loss. All of them require immediate replenishment of the main liquid tissue of our body.
It is also important to know the group and Rh factor for future parents in order to anticipate possible complications during a planned pregnancy.
What are blood groups?
The main “participants” that make up a certain blood group are red blood cells. On their membrane there are about three hundred different combinations of protein compounds, which are controlled by chromosome No. 9. This proves the hereditary acquisition of properties and the impossibility of changing them during life.
It turned out that using only two typical antigen proteins A and B (or their absence 0) it is possible to create a “portrait” of any person. Because corresponding substances (agglutinins) are produced in the plasma for these antigens, they are called α and β.
This resulted in four possible combinations, also known as blood groups.
Why is Rh conflict dangerous?
Antibodies that are produced to foreign proteins upon contact between the blood of a woman and the fetus destroy the red blood cells of the unborn child. He develops anemia and also increases bilirubin levels, which usually occurs when red blood cells break down. Bilirubin is toxic and has a negative effect on the brain. The bone marrow of the unborn baby cannot cope with the production of new red blood cells; the spleen and liver are involved in the process. As a result, they increase in size, and this leads to an increase in pressure in the veins, swelling of the subcutaneous fat and other tissues. Such disturbances in fetal development are called hemolytic disease, which can lead to brain pathologies and even intrauterine death. Thus, Rh conflict has the following consequences for the child:
- swelling (dropsy);
- jaundice;
- hypoxia;
- anemia;
- mental retardation;
- intrauterine death.
For the health of the mother, Rh conflict does not pose a danger and manifests itself as an allergic reaction.
Methods for determining blood groups
Methods for determining group membership depend on the serum or erythrocyte standard used. The most popular are 4 methods.
Standard simple method
It is used in medical institutions, at medical and obstetric stations.
The patient's red blood cells are collected in capillary blood from a finger, and standard sera with known antigenic properties are added. They are produced under special conditions at “Blood Transfusion Stations”; labeling and storage conditions are strictly observed. Two series of sera are always used in each study.
On a clean white plate, a drop of blood is mixed with four types of serums. The result is read in 5 minutes.
The group to be determined in the sample where there is no agglutination. If it is not found anywhere, then this indicates the first group; if in all samples, it is the fourth group. There are cases of questionable agglutination. Then the samples are looked at under a microscope and other methods are used.
Double cross reaction method
It is used as a clarifying method when agglutination is doubtful with the first method. Here red blood cells are known and serum is collected from the patient. The drops are mixed on a white plate and also assessed after 5 minutes.
Coloclonation method
Natural serums are replaced by synthetic anti-A and anti-B zoliclones. No control set of sera is required. The method is considered more reliable.
If there is no reaction to anti-A agglutinins in the top row, then the patient’s red blood cells do not contain the corresponding antigens; this is possible in the third group
Express determination method
Provided for field use. Blood type and Rh factor are determined simultaneously using plastic cards with wells in the “Erythrotest-group card” kit. They already contain the necessary dried reagents on the bottom.
The method allows you to determine the group and Rh factor even in a preserved sample. The result is “ready” after 3 minutes.