Photo: UGC When asked how many liters of blood are in a person, any student who is familiar with biology will answer: “5-6 liters.” And this will not be a complete answer. The numbers given are the average. This volume is theoretically observed in a man of average build and weight. In fact, the volume of blood depends on how old a person is, what weight he has, and what gender he belongs to. Let's look at the issue in more detail.
Why measure blood volume?
Blood volume is measured in order to identify various diseases, the development of which causes abnormalities associated with the volume of circulating blood. Blood volume is also measured for blood loss during surgery. Blood volume measurements are also performed to detect conditions such as hypercythemia (increased red blood cell count), anemia (decreased red blood cell count), hypovolemia (low blood volume), and hypervolemia (increased blood volume).
The blood will tell. What diseases can be calculated using conventional analysis?
How to make up for the loss?
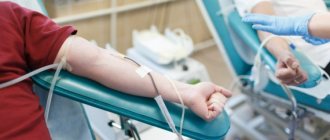
Today this problem is solved with the help of donor blood transfusions. This procedure is necessary for severe injuries, surgeries, and childbirth. Most often, plasma is transfused, which makes up about 60% of the total volume. The donor's blood must match the patient's group and Rh factor.
According to the existing law, you can donate no more than 450 ml of blood (or 600 ml of plasma) at a time. In addition, there are restrictions on the frequency of donation and the weight of the donor (4 times a year for women, 5 times for men, the interval between donations is at least 60 days, the donor’s weight is at least 50 kg). This order is due to the fact that the loss of 10% of blood can lead to a deterioration in health and the development of anemia.
Blood volume in the human body
The volume of blood in the human body varies, and this is quite natural - there is no clear single indicator for all people. After all, in the end, height indicators and weights are different for all people. Blood volume changes with age, while many other changes occur in the body. On average, blood volume is 4-5 liters . At the same time, there is less blood in the female body, and its volume is about 3.5 - 4.5 liters .
But again, in pregnant women, blood volume increases rapidly, and there is significantly more of it. In addition, lifestyle also affects blood, its volume and quality. Those who regularly engage in physical activity, lead an active lifestyle, and choose sports have more blood. Those who have large muscle mass have more blood, while those who lead a sedentary lifestyle and do not have developed muscles have less blood.
How much blood is there in a person?
Functions
Blood performs essential functions in the human body. It constantly circulates in a system consisting of large and small blood vessels that penetrate all organs and tissues, with the exception of the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes, articular cartilage, cornea, hair and nails.
Red cells deliver oxygen to tissues due to the ability of hemoglobin to reversibly bind to its molecules. Platelets are directly involved in coagulation during bleeding: they rush to the site of vessel damage and form a blood clot at this site. Leukocytes are the body's main defenders from internal and external harmful agents.
Blood transports oxygen from the lungs to tissue cells, and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs, carries metabolic products, nutrients, hormones, enzymes, biologically active substances, and is also responsible for the delivery of final metabolic products to the organs of the excretory system. It regulates temperature and maintains water, electrolyte and acid balance in the body.
How much blood does a person lose in liters during mild, moderate and severe blood loss?
Compensated blood loss is considered to be a decrease in circulating blood volume by ten to fifteen percent. Such patients have normal or moderately low blood pressure, a compensatory increase in heart rate and slight weakness.
For reference. Moderate blood loss is considered to be a decrease in the amount of blood by fifteen to thirty percent.
Such blood loss manifests itself:
- decrease in pressure,
- weakness,
- thirst,
- heart rhythm disturbances and compensatory tachycardia,
- sweating,
- increased breathing,
- dizziness.
With a loss of thirty to thirty-five percent of circulating blood volume (CBV), moderate blood loss is noted. Patients are restless, there is severe pallor, blueness under the eyes, impaired skin turgor, profuse sweating, cyanosis, a sharp decrease in pressure, impaired renal function, arrhythmias, and significant tachycardia.
Symptoms of severe blood loss (severe cyanosis, arterial hypotension, respiratory, cardiac and renal failure, impaired consciousness, etc.) develop when the volume of blood volume decreases by thirty-five to forty percent;
- Red blood cells in the blood: functions, normal content and reasons for deviation from reference values
Attention! The loss of more than forty percent of blood is accompanied by severe shock with the development of multiple organ failure.
Main cast
Human blood is mostly composed of plasma. Red blood cells carry oxygen and make this liquid red. Platelets carry out blood clotting, and with the help of leukocytes, the body fights all kinds of infections. Moreover, the composition of the blood may change. The main reason for this is human disease.
Basic composition of blood
- How many liters of blood are there in a person and how much can be lost without consequences
How to determine a person's blood volume?
For this purpose, a certain amount of a contrast agent, usually a harmless dye, is injected into the blood. After it is distributed throughout the riverbed, a fence is made to determine its concentration.
Another way is to inject radioactive isotopes and count the number of red blood cells that contain them. The amount of blood is determined by the level of its radioactivity.
Blood transfusion is used to normalize blood volume in the body.
Definitive blood tests
These types of blood tests are very different from those listed above in that they do not diagnose any disease or health condition of a person, but simply indicate the peculiarity of his circulatory system. These include tests to determine blood type, Rh factor and coagulation. As a rule, these studies are mandatory for people in special professions, as well as for all pregnant women. Blood is taken for analysis from a vein and does not require special preparation of the patient.
Safe minimum
Everyone should know how many liters of blood there should be in the human body so that it does not threaten his life. Experts believe that if a person loses more than 2 liters of biofluid, this will lead to death. This pathological condition can be diagnosed against the background of exposure to a variety of unfavorable factors. In most cases, blood loss occurs with sudden and heavy bleeding. Pathology can also be diagnosed during surgical interventions and during the recovery period. During treatment of various diseases, patients may be diagnosed with bleeding. A fairly common cause is hemodialysis.
Normally, a person should have at least 3 liters of biofluid. That is why, if he suffers from bleeding, then he needs to be provided with emergency medical attention. In order to save a life in case of blood loss, a donor transfusion is performed. Donors who have the same group donate blood to help people. The safe volume of biofluid is 450 milliliters. Safe plasma collection is 600 milliliters. Plasma donation can be carried out no more than twice a month. Donors are allowed to donate biofluids once every 4 weeks. This period is quite enough to restore the qualitative and quantitative blood composition.
Literature:
- Malakhova, Galina Ivanovna. The most effective ways to cleanse all body systems - Moscow: Tsentrpoligraf, cop. 2011. – 159 pp.; 20 cm.
- Study of the kinetic patterns of ethanol metabolism: textbook / E. I. Stepanovskikh, Yu. N. Makurin; Ural State tech. University - UPI; scientific ed. V. F. Markov. – Ekaterinburg: USTU-UPI, 2007. – 39 p.
- Toxicological chemistry. Metabolism and analysis of toxicants: a textbook for universities: a textbook for students of medical and pharmaceutical universities / [E. Yu. Afanasyeva and others] ; edited by N.I. Kaletina. – Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. – 1015 p.
- Chemical-toxicological study of the kinetics of ethanol in blood, exhaled air, saliva and urine: for a medical examination for intoxication: abstract of thesis. ... Candidate of Pharmaceutical Sciences: 04.14.02 / Tatyana Oskarovna Barinskaya; [Place of protection: First Moscow. honey. univ. them. THEM. Sechenov]. – Moscow, 2011.
Peripheral blood of a healthy child
Erythrocyte system : erythropoiesis begins with a bone marrow stem cell that is sensitive to erythropoietin (a glycoprotein produced in response to tissue hypoxia in the fetal liver and the child’s kidney), and proceeds through its differentiation into an erythroblast, then into a pronormocyte, basophilic normocyte, polychromatophilic normocyte, oxyphilic normocyte, reticulocyte.
Of the estimated 18 divisions that occur during the transformation of a stem cell into a mature red blood cell, erythropoietin significantly stimulates the final 8-10 divisions. The preceding cell divisions that give rise to erythropoietin-sensitive erythroid progenitor cells are largely erythropoietin-independent.
The lifespan of red blood cells is 100-120 days. With the help of phagocytic macrophages of the spleen, liver, lungs, and lymph nodes, an average of 1.4% of red blood cells are destroyed per day.
Content:
- How ethanol gets into urine and how it is excreted
- How long does alcohol stay in urine?
- What factors influence the removal of toxins from urine?
- How to reduce alcohol content in urine 4.1. Is it possible to speed up the elimination of alcohol using folk remedies 4.1. What methods are available at the clinic?
There are situations in life when a person needs to undergo laboratory tests for the presence of alcohol.
This applies, first of all, to drivers, athletes, and people engaged in hazardous work. They are subject to periodic testing for ethyl alcohol content. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to very accurately determine the concentration of hazardous substances and the last date of intake. So that the test results do not interfere with your plans and do not become an unpleasant surprise, it will be useful to know how much alcohol remains in the urine and blood. This will allow you to properly plan a celebration or meeting with friends on the eve of donating biological fluids for research.
How ethanol gets into urine and how it is excreted
First, alcoholic drinks pass through the mouth and esophagus into the stomach. A fifth is broken down here, and the remaining 80% moves to the small intestine, is absorbed through the walls and enters the bloodstream. Thus, the breakdown products of ethyl alcohol penetrate into all organs and systems, including the liver and kidneys, where alcohol completes its “march” through the body. Harmful substances are excreted mainly through urine , but a certain percentage can also be released:
- through the pores of the skin with sweat;
- thanks to the respiratory function with exhaled air flow;
- with breast milk, if a nursing woman allows herself to drink.
Of course, using the above methods, a small percentage of ethanol is removed; the bulk passes through the urinary organs.
How long does alcohol stay in urine?
But the rate of removal of alcohol breakdown products is influenced by the strength, quality and portions of the intoxicating drink, gender, age, psychological and physical indicators of human health. There is an unshakable rule: the higher the degree, the longer the period alcohol is detected in urine:
- Strong drinks (vodka, whiskey, cognac) can be detected in the blood for 3 days, and in urine for 4-6 days.
- Beer, gin and tonic and other low-alcohol liquids are eliminated very quickly. When consuming no more than 100 ml of such drinks, it is impossible to determine the presence of ethanol and its metabolites in the urinary system after 1-2 hours. With a dose of 300 ml this period increases to three hours.
- Champagne and other sparkling wines are not detected in urine 1.5 hours after drinking. But if a person takes about 0.5 liters of this noble potion at a time, then for another 9 hours it is necessary to refrain from submitting urine for examination. The result will be positive.
The cleansing process slows down in people suffering from various dysfunctions of the excretory organs. If these ailments make urination difficult, then toxic substances remain in the body for a longer time. The metabolic rate is also affected by the percentage of adipose tissue in the total body weight. In thin people, alcohol is removed more slowly, and in overweight people, these processes proceed faster.
What factors influence the removal of toxins from urine?
As noted above, the speed of removal of harmful substances is affected by the strength of the intoxicating potion used. Low-alcohol cocktails always leave a smaller imprint on the composition of biological fluids. In addition, some other points should be noted that directly affect the cleansing time:
- quality of alcohol : counterfeit, handicraft and industrial alcohol-containing products, due to toxic and harmful impurities, not only settle for a long period in all organs, but also pose a real threat to life;
- amount of drink taken : a small portion of 50-100 ml will not linger in the urine for long, but exorbitant volumes are very difficult to excrete and can cause severe alcohol poisoning;
- psychological and physiological characteristics : gender, age, the presence of chronic illnesses and mental disorders can cause a slowdown in metabolic reactions.
How to reduce alcohol content in urine
There are no more effective cleansing techniques than detoxification measures. It is best to carry out such procedures with medical assistance. But there are also some measures available at home to boost metabolism and remove harmful compounds.
Is it possible to speed up the elimination of alcohol using folk remedies?
If a person does not want or does not have time to visit the clinic, then the following recommendations allow you to quickly remove alcohol from urine on your own after a party:
- drink plenty of fluids , if there are no contraindications, then teas or herbal infusions with a diuretic effect will help;
- use available drugs with absorbent properties , for example, activated carbon;
- maintain a proper daily routine with good sleep and walks in the fresh air;
- visit a sauna or bathhouse to increase sweating;
- intensify sports or physical labor if your health allows.
How long ethyl alcohol lasts in urine depends not only on the drinking regime, but also on nutrition. During this period, you should not eat fatty, spicy, fried foods. Enriching your menu with fruits, vegetables and herbs will help cleanse. Decoctions of medicinal herbs will be useful: knotweed, mint, chamomile, birch buds, rose hips, dill seeds. For drinking, preference should be given to still water, strong tea and milk . And you shouldn’t limit yourself when having sex, because it is the most effective method of enhancing metabolic processes.
What methods are available to the clinic?
In any situation, it is not recommended to take medications without the consent of doctors. Most drug treatment clinics offer free telephone consultations, during which a specialist will give professional and effective recommendations. You should not trust advertised drugs for alcohol removal: Alka-Seltzer, Alka-Prim, Medichronal, etc. Basically, they only eliminate specific odors, but do not speed up the purification of blood and urine. If you need to quickly remove alcohol breakdown products, you should seek the help of a qualified narcologist. Only a specialist knows how long alcohol lasts in urine and what optimal cleansing methods are applicable for a particular patient. Depending on the patient’s individual indicators, the doctor selects medicinal or hardware cleaning methods. Infusion therapy can be done at home, but detoxification using medical equipment can only be done in a clinical setting . Even if you think that your well-being after wild fun does not require medical intervention, do not neglect consulting with a narcologist. Recommendations from a specialist will help you quickly remove the breakdown products of alcohol and avoid serious consequences for physical and mental health.
Is it possible to speed up the cleansing of the body?
What can be done to ensure that alcohol is no longer detected in biological fluids used in laboratory diagnostics? These tricks will help:
- Drink plenty of fluids and go to the toilet as soon as you feel the urge to urinate.
- Make time for physical activity. If your health condition does not allow you to go for a run or do regular exercises, you should at least take a walk.
- Adopt absorbent type activated carbon.
Among the compositions that help hide the fact of drinking the day before: infusions of knotweed herbs and birch buds, decoctions of rose hips, parsley and dill.
Can I drink before taking a urine test?
Doing this is highly undesirable. Laboratory diagnostics are carried out for a reason, and in order to confirm or refute a specific diagnosis, evaluate the functioning of internal organs. Drinking on the eve of a medical examination often leads to false results.
In turn, erroneous tests can lead to the selection of ineffective treatment, which is dangerous.
Therefore, if you have to take urine and blood tests, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle for three days. Important
not only
do not drink anything “hot”,
but
also eat right
, giving up fatty, spicy, smoked and sweet foods.
What determines the speed of urine purification?
Drinkers often wonder why the duration of urine cleansing differs so much from person to person. This phenomenon is explained by the following factors:
- The quality of the alcohol consumed.
Of particular danger are technical alcohol-containing liquids, which are used by some alcoholics due to the lack of real “intoxicants”. This alternative is moving towards a meeting with death. - Volume.
The larger it is, the more severe the intoxication. 100 ml are excreted many times faster than 200 or 500. - The degree of the drink taken.
Concealing the fact of taking low-alcohol compounds is always easier than drinking cognac or vodka. - Physiological characteristics of the patient.
This refers to age, gender, body weight, and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases. Much also depends on diseases that prevent normal urination - if they exist, natural detoxification reactions are inhibited.
How long does alcohol stay in urine?
The higher the degree, the slower the alcohol is excreted:
- Forty-degree drinks
stay in the blood for about three days, in the urine - from four to six. - Low-alcohol compounds
(beer, gin and tonic, etc.) are preserved less. So, if you drink them in an amount of 100 ml, then within an hour or two the urine will not contain ethanol impurities. If you take a dose of 300 ml, the elimination time will increase to three hours. - Champagne
, used in an amount of 100 ml, ceases to be detected in urine after an hour and a half. It will take quite a lot of time to “neutralize” 500 ml of sparkling wine - about nine hours.
If the drinker has delayed urination or was unable to go to the toilet, the cleansing process is delayed.
Interesting to know:
thin people eliminate alcohol more slowly. Conversely, individuals with increased body weight are more likely to clear toxic alcohol toxins.
Alcohol detoxification
The absorption of ethanol in the liver is accompanied by general intoxication of the body, also called a hangover. This condition is manifested by a deterioration in general health, headaches and muscle pain, vomiting and nausea, dehydration, high blood pressure and rapid heartbeat.
Usually a hangover occurs in the morning, after drinking, and lasts 6-10 hours. To restore water balance, it is useful to drink salty and sour drinks. It is better to limit your food to chicken broth without vegetables, so as not to injure the gastric mucosa.
Removing alcoholic beverages at home
You can help your body fight a hangover on your own, but all measures will not bring quick results. At home, it is useful to take a shower and drink salty fermented milk drinks: kumiss, ayran. Fruit juices and vegetable brines are also useful: cucumber, tomato, cabbage. The latter contain lactic acid, which stimulates the release of alcohol.
WITHDRAWAL FROM BINGE BINGE AT HOME
Alcohol removal tablets
Alcohol elimination tablets are divided into two types: the first contain malic or lactic acid, which promote the breakdown of ethanol (Zorex, Corrda, Antipohmelin, etc.). The latter bind toxins and remove them unchanged (Polysorb, Enterosgel, activated carbon). All of them help to significantly speed up the withdrawal of alcohol. It is also useful to take acetylsalicylic acid, which normalizes temperature, relieves pain and helps thin the blood, relieving stress on the heart.
Rapid elimination with droppers
To quickly get rid of traces of yesterday's fun and restore your performance, it is better to consult a doctor for a medicinal drip. This way, the drugs will immediately enter the bloodstream and quickly spread to all cells. This method allows you to get rid of hangover symptoms in just 1 hour, and you can achieve complete elimination of alcohol within 4-5 hours from the start of the procedure.
Article prepared by an expert
Terekhova Anna Vladimirovna
psychologist-consultant on socio-psychological work with addicted clients and their families. More than 9 years of experience.
Similar articles:
Codependency and how to deal with it
The effects of hallucinogenic mushrooms
Addiction to nasvay
Drug addiction: causes, types and consequences
Internet gambling: how not to play in online casinos
Why is a hematocrit disorder dangerous?
In the presence of pathological fluid losses (dehydration due to diarrhea, vomiting, etc.), due to impaired vascular permeability, the amount of plasma decreases and so-called blood thickening occurs.
An increase in blood viscosity may also be due to erythrocytosis or hereditary coagulopathies, accompanied by an increased tendency of platelets to adhesion and aggregation. Blood thickening leads to:
- a significant increase in the load on the cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system),
- blood clot formation,
- kidney damage, etc.
A decrease in the number of all formed elements is observed with damage to the bone marrow and a decrease in its hematopoietic function (leukemia). In this case, blood clotting is impaired, the body’s resistance to infectious agents is reduced, and oxygen exchange in organs and tissues is disrupted.
A decrease in the number of red blood cells indicates anemia of various origins. A decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin leads to oxygen starvation in organs and tissues, heart rhythm disturbances, decreased immunity, constant weakness, hair loss, brittle nails, etc.
Plasma protein deficiency is accompanied by the development of edema, decreased immunity and impaired renal and liver function.
An imbalance of electrolytes in the blood can manifest itself as convulsions, tremors, muscle spasms, life-threatening arrhythmias, edema, heart block, and acute renal failure.