Blood group, like the Rh factor, are permanent indicators of the human body. And their basis is genetically laid from the moment of the beginning of intrauterine life. However, there are often reports that, under various circumstances, a person blood type changes. Why is this possible and is it dangerous for our health? Or is this process completely normal? Let's find out...
You can read about what blood groups exist in nature and what the Rh factor is in this article.
Changes in blood type over the course of life
Situations where the blood type changes spontaneously and seemingly for no apparent reason are practically unknown to medicine. The bone marrow of a healthy person is programmed by DNA code to produce the same type of blood cells for life. At the same time, special protein antigens are located on each red blood cell, which make it possible to determine Rhesus status and classify blood into group 1, 2, 3 or 4.
Doctors unanimously say that in a healthy person it is impossible to change the blood type and Rh factor over the course of life.
When such cases appear, there is nothing left to do but attribute the result to diagnostic errors . If a change in blood group was detected during repeated laboratory tests, then one should look for good reasons for this.
What are the consequences of blood flow group mismatch?
An immunological conflict occurs when the mother’s blood does not match the child’s blood substance. A conflict in the blood substance group during pregnancy can lead to hemolytic pathology of the baby. Hemolytic disease of the newborn, abbreviated as HDN, threatens the development of hemolysis of red blood cells, resulting in a huge risk of fetal death. In any case, erythroblastosis disrupts the full functioning mechanism of the baby’s circulatory system. With such a pathology, there can be no question of any proper development of the embryo.
Changes in blood type during pregnancy
Most often, reports of changes in blood grouping come from pregnant women who are registered at the antenatal clinic and periodically donate blood for analysis. Indeed, blood type can change during pregnancy . However, it is very important to note that this is a false shift .
It is due to the fact that the expectant mother’s body increases the production of red blood cells. At the same time, due to accelerated hematopoiesis, it is possible to form blood cells that have a small amount of group antigens on their surface or are completely absent. At this point, a blood group test may show a false result.
This is extremely important. After all, if a pregnant woman needs a blood transfusion, it must be carried out according to the “old” blood group (which was determined before pregnancy). Otherwise, a hemagglutination reaction may occur, i.e. red blood cells stick together and precipitate. This situation is life-threatening for both the mother and the fetus.
Treatment
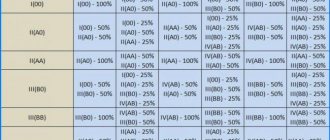
- Compatibility table of parents by blood group and Rh factor for conceiving a child
If a couple turns to doctors for help in time, then the right treatment can help them soon become happy parents. To overcome the problem of immunological inconsistency of spouses, doctors most often give the following recommendations for action:
- It is necessary to use contraceptives for some time to reduce the severity of the female body’s reaction to male sperm.
- It is necessary to undergo treatment with antihistamines.
- It is also necessary to take immunostimulants.
- Sometimes an immunological mismatch can be circumvented by intrauterine sperm injection.
Immunological inconsistency is not a death sentence. Even in this situation, there is still a chance to get pregnant and bear a healthy child, but there may be problems with subsequent attempts at pregnancy.
Changing blood group in pathological conditions
Potentially, the blood type and Rh factor can also change in various genetic and infectious diseases that lead to hematopoietic disorders and direct damage to red blood cells:
- Blood diseases (thalassemia);
- Bone marrow tumors (leukemia, hemoblastosis, hematosarcoma);
- Viral infections (HIV and AIDS, viral hepatitis);
- Bacterial infections (plague, yellow fever, typhus);
- Parasitic infections (malaria);
- Poisoning with chemicals (nitrates, nitrites, aniline dyes, acids, ethers, gasoline, ethyl alcohol).
The red blood cells of each person have individual sensitivity to the listed damaging factors. Therefore, in such diseases, changing the blood group or Rh factor is possible, but not mandatory . However, such changes are temporary. After recovery, the hematopoietic system should produce full-fledged blood cells that a person had before his illness.
"Pros" and "cons" of our blood
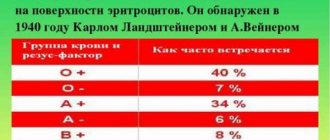
The Rh factor is a qualitative assessment of a blood characteristic parameter, depending on the presence or absence of D antigen in the human body. This indicator is innate (!).
The presence of D-antigen protein molecules is a sign of positive Rhesus (Rh+). Their absence is negative (RH-).
The second case is less common. Its owners are only about 15% of the world's population. The remaining 85% of the population has a plus sign.
There is no intermediate option. There are only two of them: either “positive” or “negative”.
Irreversible change in blood type
This becomes possible with a complete bone marrow transplant. Patients diagnosed with malignant bone marrow tumors need to have it replaced. As a result of this treatment procedure, a person receives a donor organ that produces new blood cells.
It should be noted that bone marrow donors are selected very carefully. The transplanted bone marrow must match the recipient's bone marrow as closely as possible. Therefore, doctors most often choose donors with the same blood type and Rh factor as the recipient.
How is rhesus conflict prevented?
Prevention of Rhesus conflict must be carried out without fail. So that in the future a woman who is Rh negative can safely bear a child, she is given immunoglobulin within three days after birth, designed to stop the production of antibodies. In this case, a different Rh factor during pregnancy in her and the baby will no longer lead to a threat to the health of the child.
The administration of the same injection at the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy is also a preventive measure, but it has a different goal - to prevent an increase in the growth of antibodies in the pregnant woman.
The administration of immunoglobulin is a necessary measure for all women who have a negative Rh factor, which should be carried out not only after childbirth, but also after a medical or instrumental abortion, miscarriage, or blood transfusion.
Idiopathic change of blood group and Rh factor
“All my life there was one group, and now suddenly it has changed for some reason” - is this possible?
In medicine, all diseases and pathological conditions, the cause of which is not fully studied and understood, are usually called “idiopathic”. Changing your blood type is no exception. Therefore, all cases when no one can name the reason for the change that occurred can be classified as an idiopathic change in blood group.
A change in blood type occurs without any clinical manifestations. Calm and quiet. Therefore, we can assume that such changes do not harm human health.
Forms of hemolytic pathology:
| Forms | Description |
| Anemic | When a baby has a low level of hemoglobin and an increased level of unconjugated bilirubin. The condition does not entail any serious consequences and is easily normalized. |
| Jaundice | Occurs due to severe bilirubin intoxication. |
| Edema | The most dangerous form of HDN, leading to the death of the fetus in the womb. If the child manages to survive, then a number of pathologies are detected, including damage to the brain and central nervous system. |
The state of red blood cell hemolysis is characterized by the destruction of the red blood cell membrane and the release of hemoglobin into the plasma fluid. Released hemoglobin in large quantities has a poisonous effect on the body.
Therefore, simultaneously with poisoning and overload of the fetal body with bilirubin and other substances, such a pathology also entails anemia.
The liver does not have time to neutralize free bilirubin on a large scale. And this substance in a neurotoxic form wanders throughout the body of the embryo, disrupting oxidative processes in organs and tissues. This leads to irreversible, destructive consequences, including the death of the child. For this reason, the danger of blood substance group conflict during pregnancy should not be underestimated.
How do you get an incorrect test result?
BG is checked immediately after birth. A newborn child must undergo such an analysis. The standard group verification process is simple:
- Capillary blood is collected,
- The obtained material is transported to the laboratory,
- At the third stage, the group itself is checked using reagents,
- They issue a conclusion.
Even at these 4 stages, laboratory technicians are capable of making mistakes that could cost the life of the diagnosed patient in the future. In addition, the life of another person depends on the incorrectly indicated result if this patient becomes a donor.
Read also: Preparing for blood tests
- Most often, medical staff make a mistake when test tubes with blood are involuntarily confused. It costs nothing to swap them. Not all laboratory technicians approach the blood sampling procedure correctly and responsibly.
- No one has canceled the dishonest attitude of medical staff towards the process of processing and disinfection of test tubes.
- Collected materials are transported in containers so they can be mixed. Mixing of samples occurs, again, due to an unfair attitude towards work.
At this stage, the possibility of obtaining an erroneous result remains. But a greater number of medical errors occur when directly studying the analysis. This happens for the following reasons:
- Incorrect addition of serum directly to the sample,
- Use of expired and low-quality reagents,
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards in the room where diagnostics are carried out,
- Inconsistency in temperature, air humidity or lighting,
- Use of outdated equipment,
- Human factor, inattention, fatigue.
There is no way to protect yourself from such “diagnosis,” especially if the analysis is carried out in a public medical institution. It is better to check the group in several laboratories. It is because of negligent medical staff that most people wonder whether the RF or GK can change.
Can BG change with transfusion?
Transfusion does not affect the BG in any way, however, there are certain exceptions to this rule:
- When identifying blood to a certain group, the health worker made a mistake.
- The patient suffers from a disease of the hematopoietic system (aplastic anemia), after treatment of which, his red blood cells acquire new antigenic properties that were previously suppressed by the disease.
- If the patient has been transfused with a large volume of donor blood: until the “new” red blood cells die, the patient may be diagnosed with another GC for several days.
- The patient underwent a donor bone marrow transplant, before which all his blood progenitor cells were destroyed using chemicals. As a result, the “new” bone marrow can produce cells with a different structure and change the BG. This probability is minimal, but it exists.