Mitral valve plastic surgery is performed for pathologies of this part of the heart that cannot be cured with conservative methods. Reconstruction of the valve allows you to restore all its functions, prevent heart failure, and save the patient’s life. During the operation, plastic structures are used to completely rehabilitate the heart and avoid repeated problems with the valve. The procedure has its own characteristics, preparation and recovery rules.
Causes of development of mitral valve defects
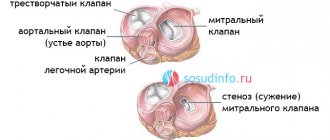
The disease may be based on fundamentally different defects in the valve structures. To choose effective treatment tactics, it is important to accurately determine the form of the defect and the cause of its development.
- Valve leaflet defects often occur with infective endocarditis and myocarditis, and rheumatic heart disease. Perforated, loosely closing leaflets are not able to hold blood in the left ventricle during heart contractions. The blood is pumped back into the left atrium and then into the lungs.
- Fusion of valve leaflets . The most common cause of mitral stenosis is rheumatism (acute rheumatic fever); less commonly, this defect develops after infective endocarditis or heart injury. The calcified valves, welded together, impede the normal flow of oxygen-enriched blood into the left ventricle and further to the tissues and organs.
- Rupture of the chordae tendineae most often occurs in systemic connective tissue diseases and acute endocarditis. The valve leaflets move (prolapse) into the atrium, reducing the efficiency of the heart.
- Rupture or sclerosis of the papillary muscles is an acute, life-threatening condition that develops with infarction of the papillary muscles against the background of coronary heart disease (CHD) or heart tumors. When the papillary muscles are damaged, the valve leaflets lose their fixation point, and the valve completely stops functioning.
Approaches to the treatment of mitral valve defects
The first step in treating clinically significant mitral valve disease is drug therapy. It includes drugs that slow down the heart and reduce the force of its contractions (beta blockers), antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs for infectious etiologies of the defect. Drug therapy improves the patient’s condition to a certain extent, but only high-quality surgical correction of the mitral valve can radically eliminate the cause of the disease.
Depending on the form of the defect, cardiac surgeons use one of the following procedures:
- Annuloplasty is the replacement or reconstruction of the support ring that surrounds the mitral valve and securely fixes it between the left atrium and the ventricle.
- Chordplasty – restoration of the integrity of damaged tendinous chords or their lengthening.
- Commissurotomy is the surgical separation of fused valve leaflets.
- Valve leaflet plastic surgery – correction of the shape, size or anatomical position of the valve leaflets.
- Prosthetics is the complete replacement of a damaged mitral valve with a biological or mechanical prosthesis.
According to the results of multicenter clinical studies and practical experience of leading cardiac surgery centers, preference is given to robotic surgery using the daVinci system and catheter surgical techniques.
4.Is it possible to treat heart valve diseases without surgery?
There are alternative options to traditional surgery for treating heart valve diseases. For some patients with mitral valve stenosis (narrowing) or pulmonary valve stenosis, an air (balloon) valvotomy procedure may be recommended.
It helps open a narrowed artery.
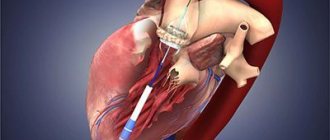
During this procedure, a special catheter is placed into a blood vessel in the groin area and guided towards the heart. The tip of the catheter is inserted into the narrowed valve. Once there, the tiny balloon at the end of the catheter expands (inflates) and deflates several times to widen the valve opening. After this, the balloon is removed. During balloon valvotomy, an echocardiogram may be performed to view the valve more completely.
daVinci Robotic Surgery - a combination of surgeon experience and robotic precision
Robotic surgery using the daVinci system allows you to successfully perform both reconstructive surgeries and complete mitral valve replacement. Such interventions combine the advantages of minimally invasive surgery and high precision of manipulation due to computer control of endoscopic instruments.
Patients receive a number of important benefits when using the daVinci robot:
- Shorter hospitalization period (up to 7 days).
- Short stay in the intensive care unit.
- Low risk of bleeding, no need for transfusion of blood and its components.
- Low risk of reactive postoperative pericarditis and pleurisy.
- Rapid restoration of physical activity (the next day after surgery, the patient can move around the clinic).
- Invisible postoperative scars measuring 1-2 cm, the chest is not opened.
The daVinci robot has over 20 years of experience. During this time, the system has undergone a number of modifications to improve the functional and aesthetic results of treatment. Modern cardiac surgery centers use the latest modification of the robot – da Vinci Xi®. To date, it is the only robotic device approved by the FDA for mitral valve surgery.
Relative limitations to the use of the daVinci system include the high cost of the equipment and the small number of qualified cardiac surgeons who are fluent in the technique of working with it. Also, endoscopic interventions are not performed in patients with pulmonary hypertension, aortic stenosis or insufficiency, severe liver dysfunction.
Areas of work of the department
Recent decades have been characterized by the intensive development of areas related to molecular biology, genetic engineering, biotechnology, etc. In the field of medical science, these areas are united and mutually penetrate each other, which ensures the acquisition of new knowledge about the human body as a whole, about its organs and systems. Since the 50s, various biomaterials used in cardiovascular surgery have been widely used, such as: fascia lata, dura mater, the use of vessels as conduits, cadaveric materials (homografts, xenografts), the use of pericardium (auto- and xeno) . Pericardium, both xeno- and auto-, is of greatest interest in use in vascular surgery, surgery of congenital heart defects and reconstructive interventions on heart valves. There is much controversy regarding the xenopericardium, since over a certain period of time degenerative changes occur in the tissue - which leads to irreversible calcification. With regard to the autopericardium, the question of the durability of the tissue remains unclear - in some cases it does not undergo degeneration and calcification for 15-20 years after use. We continue our search to extend the service life of biomaterials in cardiovascular surgery.
Aortic valve surgery
The aortic valve is a semilunar valve, which consists of three cusps (right and left coronary and non-coronary cusps) that are attached to the annulus fibrosus, and is located in the terminal outflow tract of the left ventricle.
Currently, enormous strides have been made in the development of methods for treating aortic stenosis. They were created and improved from year to year as mechanical and then biological prostheses. It should be noted that patients with aortic valve stenosis are symptomatic, in case of insufficiency, patients may not notice complaints for many years before progressive dilatation of the left ventricle occurs, so early surgery is indicated for such patients.
Currently available prosthetic aortic valves are:
Mechanical aortic valve prosthesis
Frame bioprosthesis
Frameless prostheses were introduced into clinical practice in order to improve the hemodynamic data of bioprostheses and bring them closer to a more physiological function. This type of prosthesis allows valve replacement to be performed in patients with a narrow fibrous annulus of the aortic valve. Frameless prostheses (BioLAB-KB/A) began to be used in 2009 and more than 60 operations have been performed with good long-term results.
Frameless xenopericardial bioprosthesis
Bioprosthesis ready for implantation
In the 60s and 70s, the results of bioprosthetic heart valves, namely the aortic valve, were not so satisfactory. And at that time, the ideal method was proposed by Professor Donald Ross, who proposed in 1962 to use aortic allografts as a bioprosthesis, as well as the operation that bears his name (Ross operation), which is currently not performed in all centers, but provides the most a long time without re-operation and a high quality of life without anticoagulants (sports, safe pregnancy), as well as for children.
Operation Ross
The Ross procedure is an operation to replace a patient's diseased aortic valve with a patient's own pulmonary valve. The pulmonary valve is then replaced with a cryopreserved donor valve. In children, adolescents and older patients leading an active lifestyle, this operation has an advantage over traditional prosthetics. The durability of the pulmonary valve exceeds that of biological prostheses, which undergo early degeneration in young patients. There is also no need for anticoagulant therapy, which allows patients to lead an active lifestyle. This is especially important for women of childbearing age, since anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Ross' operations (schematic representation)
The Department of Emergency Surgery of the PPS has experience in more than 80 operations from 2001 to the present.
Replacement of the aortic valve and ascending aorta with donor valves – allo- and xenografts
Devitalized modified biological tissue
Most cardiovascular surgeons strive to optimize both their skill and scientific knowledge in the field of reconstructive heart valve surgery, since aortic valve reconstructive surgery dates back to the 80s and the techniques were not so widespread. Currently, reconstructive interventions of the aortic valve are included in the range of interventions of a modern surgeon.
In our center, these interventions have been performed since the late 90s.
Valve-sparing interventions on the aortic valve
with expansion of the fibrous ring (annuloectosis) and aneurysmal expansion of the sinuses of Valsalva and the ascending aorta (David's operation).
Operations on the ascending aorta and arch
are performed for dissections or aneurysms, which in most cases is accompanied by aortic valve disease, and in these cases a one-stage operation is performed - replacement of the ascending aorta and aortic valve (the aortic valve prosthesis can be either mechanical or biological, depending on the indications)
Operation Bentall De Bono
Minimally invasive aortic valve surgery
Traditionally, operations on the valve apparatus are performed through a midline approach, but the increasing number of elderly patients and with concomitant diseases prompted us to introduce less invasive interventions for faster recovery of patients in the postoperative period - to improve pulmonary function, reduce pain, reduce trauma and reduce blood loss. We have accumulated experience in more than 300 operations using mini-sternotomy.
Reasons for performing mini-approaches in aortic valve surgery:
- Cosmetic effect of the operation
- Reduced pain in the postoperative period
- Fast recovery after surgery
- Does not affect the speed of the operation
- Can be performed on repeat patients
Types of mini-accesses (the most popular access for aortic valve diseases is J-shaped ministernotomy):
Mitral valve surgery
Surgical treatment of the mitral valve consists of mitral valve replacement and reconstructive (valve-saving) interventions.
Mitral valve replacement is used for a number of valve diseases: rheumatic valve disease, infective endocarditis, neoplasms, degenerative (fibroelastic deficiency) valve disease, congenital valve malformations.
Mitral valve replacement:
Mechanical aortic valve prosthesis
Biological prostheses in the mitral valve position are implanted in patients over 65 years of age.
Biological prostheses
Mitral valve repair began to be performed even before the advent of the first artificial heart valve prostheses. Valve reconstruction involves restoring normal physiological function of the valve, which requires the skills of a cardiovascular surgeon skilled in a number of maneuvers. But it is worth noting that valve reconstruction is not possible in all cases. In socially highly developed countries, the problem of rheumatic disease has been almost completely solved, and in a number of countries this disease is absent and in most cases degenerative valve disease and myxomatosis prevail, in which it is possible to perform reconstructive interventions with a high percentage of success. However, less developed countries have higher rates of prosthetics. For the patient, first of all, the possibility of performing reconstructive interventions is always considered, since the patient’s quality of life is high, and there is no need for constant use of anticoagulants.
Various types of mitral valve reconstruction have become widely used since the early 1980s. For valve reconstruction, the following are used: resection of part of the affected leaflets with restoration of integrity, prosthetics of native chords with artificial chords made of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), translocation of part of the leaflets and chords, and reconstruction of the mitral valve is always complemented by stabilization of the fibrous ring with support rings of various types (rigid, semi-rigid, strips of PTFE).
Reconstructive interventions on the mitral valve
Mitral valve annuloplasty using special PTFE support strips
Echocardiography evaluates the function of the mitral valve (the valve is healthy, there is no insufficiency on the valve).
Tricuspid valve surgery
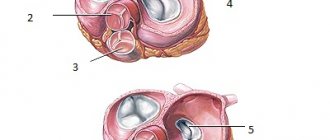
The tricuspid valve consists of three leaflets (anterior, posterior, septal), which are attached to the fibrous ring; chords extend from the leaflets, which are attached to the papillary muscles, ensuring normal operation of the valve.
Tricuspid valve dysfunction occurs mainly secondary to pathology of other valves. It primarily occurs with infectious lesions, tumors and injuries to the chest.
When replacing the tricuspid valve, the same bioprostheses are used as when replacing the mitral valve.
Mechanical prostheses in the tricuspid valve position are used extremely rarely, due to frequent prosthesis-dependent complications and the complexity of constant anticoagulant therapy.
Mechanical aortic valve prosthesis
Tricuspid valve prosthesis
Bioprosthetics of the tricuspid valve
Reconstructive interventions on the tricuspid valve
Annuloplasty of the tricuspid valve on a support ring
Suture repair of the tricuspid valve
Reconstruction of the tricuspid valve in cases of extensive infection
Modeling of tricuspid valve leaflets:
- The diameter of the fibrous ring will be equal to the length of the base of the septal leaflet (a), with a margin of 5 mm, to create commissures and convexity of the leaflets,
- It is believed that the size of the front flap corresponds to the base of the meter (c), which will correspond to a + 5, with a margin of 5 mm,
- For the rear leaf (b) – a-5, or, b=2/3c= c-1/3c,
- The radius is (r) – d/2+5,
- Length of chords (L) – (r+5)/3x2.
Diagnostic capabilities of the emergency surgery department of the teaching staff
The department has all the necessary range of diagnostic tests. With the assistance of other laboratories and divisions of the Center, the following are carried out on the basis of the department:
- ECG, precordial cardiac mapping and 24-hour (Holter) ECG monitoring
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring
- Stress ECG tests (bicycle ergometry, treadmill test)
- Echocardiography (Doppler ECHO-CG, transesophageal ECHO-CG)
- Transcranial Dopplerography
- Doppler ultrasound and duplex scanning of main and peripheral arteries and veins
- Invasive electrophysiological studies
- Computed tomography (CT), including electron beam CT
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Ultrasound examination of internal organs (ultrasound)
- Pulmonary function test (spirometry)
- All types of laboratory tests
- X-ray diagnostics
- Gastroscopy
- Radionuclide diagnostic methods
- Positron emission tomography (PET): the only diagnostic method in Russia today that allows you to determine the condition of the myocardium at the cellular level
- Invasive diagnostic methods (coronary angiography, shuntography, ventriculography, probing of the heart cavities, angiography of any vascular areas)
NeoChord – plastic surgery of chordae tendineae on a beating heart
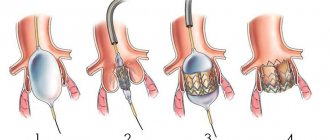
The development of the NeoChord DS1000 system was the result of numerous clinical studies that demonstrated the superiority repair over complete replacement . NeoChord DS1000 has been successfully used for repair of chordae tendineae in patients with severe mitral regurgitation due to mitral valve prolapse.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, through a mini-thoracotomy access (incision length no more than 5-6 cm). In this case, the patient is not connected to a heart-lung machine; the heart maintains its natural rhythm.
Under strict visual guidance using 2D or 3D transesophageal echocardiography, the NeoChord DS1000 system is inserted into the left ventricle. The cardiac surgeon replaces the damaged chord with an artificial one and controls its tension. At the same time, the movement of the valve leaflets is reflected on the echocardiograph monitor in real time - this allows you to immediately evaluate the result of the operation and, if necessary, correct the position or tension of the chord.
To date, the NeoChord procedure has been successfully performed on more than 1,000 patients in Europe and the USA. The results of long-term postoperative follow-up confirm the safety of the technique and its effectiveness in the correction of mitral valve prolapse.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the procedure are heart failure in combination with impaired valve function. Signs of such a problem are:
- swelling of the limbs. Most often the legs swell, but in some cases the same phenomenon occurs in the thighs, genitals, and abdomen;
- difficulty breathing. As a rule, this is shortness of breath, sometimes there may be a lack of air, pain when breathing in the chest area;
- pressing and throbbing pain in the chest;
- blue lips, gray skin color, “bruises” under the eyes;
- worsening of symptoms with physical activity.
Such signs indicate a developing disease; in the first stages, the problem may not manifest itself at all. Based on the patient’s complaints, the doctor prescribes several types of diagnostics, then clarifies the diagnosis. If a serious disorder in the mitral valve is confirmed, the type of surgical intervention is discussed.
Reconstruction of the heart is a difficult task, so it is carried out only if other methods do not help the patient. To prescribe plastic surgery, the attending doctor prescribes a series of examinations to the patient to ensure the need for such manipulations. For mild forms of the disease, drug treatment is most often used. Also, other types of therapy are sought if the patient has severe kidney and liver diseases, acute infections, pneumonia, gastric ulcers, diabetes mellitus, poor blood clotting, and sepsis.
Mitral repair is prohibited for people who have just suffered a stroke or extensive myocardial infarction.
If mitral repair is necessary, doctors weigh all the risks. Even against the background of some contraindications, surgery can be performed if it is intended to save the patient. Before prescribing this procedure, they must undergo training.
MitraClip – gentle one-stage reconstruction of the mitral valve leaflets
MitraClip technology is also used as part of the “Respect when you can, resect when you should” approach to cardiac surgery, which demonstrates the benefit of reconstructing a patient's native mitral valve over replacing it with an artificial prosthesis.
The MitraClip system allows you to firmly connect deformed or damaged valve leaflets using a microsurgical clamp made from an alloy of durable and metabolically inert metals - cobalt and chromium. During the procedure, the MitraClip is inserted into the femoral vein and moved into the left atrium under echocardiography guidance. This method of inserting a catheter into the heart does not require opening the chest and significantly reduces operational risks.
MitraClip securely fixes the valve leaflets in the required position, restoring normal blood flow from the left atrium to the ventricle. Using intraoperative echocardiography, the cardiac surgeon immediately assesses the quality of the reconstructed valve and, if necessary, installs an additional clamp.
Thanks to the successful results of clinical studies (European COAPT and EVEREST II studies), the MitraClip technique has been included in updated medical guidelines for the surgical treatment of mitral regurgitation. The MitraClip system is recommended for use in older patients with high surgical risks - such an operation is easier to tolerate compared to classic open cardiac surgery, but cannot fully replace complex reconstruction of the mitral valve.
Find your heart surgeon at the Braunschweig Clinic
The Department of Cardiology is a highly specialized center for cardiac surgery at the Braunschweig Clinic, with a professional team of specialists who collaborate with other departments and clinics to offer a range of surgical procedures, including heart valve replacement. The head of the department, Professor Dr. Wolfgang Harringer, believes that the main goal of the team is to help the patient find the optimal way to restore normal heart function, thereby prolonging his life. Any type of treatment is based on what benefits it has individually for the patient. Valve replacement surgery is performed in our department using different methods, ranging from traditional to the latest.
If you have questions regarding mitral or aortic valve replacement and would like to know the cost of the operation, please contact us. We will help you restore your health.
Clinics and treatment costs
For successful minimally invasive mitral valve reconstruction, two main points are important: the availability of equipment and sufficient experience of the surgeon. Among the multidisciplinary and cardiology clinics that accept patients from all over the world, it is worth noting the following:
- University Hospital Oldenburg, Department of Cardiac Surgery
- University Hospital Essen, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery
- University Hospital Ulm, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery
- University Clinic named after. Goethe Frankfurt am Main, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery
- University Hospital Tübingen, Department of Adult and Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery
The estimated cost of treatment is:
- Diagnosis of mitral valve insufficiency or prolapse – from €467
- Treatment of mitral valve insufficiency or prolapse with minimally invasive reconstruction – from €10,025
- Treatment of mitral valve insufficiency or prolapse using minimally invasive prosthetics – from €10,082
- Treatment of mitral valve insufficiency or prolapse using the Mitralign system – from €29,066
- Treatment of mitral valve insufficiency or prolapse using the Carillon system – from €27,326
- Cardiac rehabilitation – from €566
The exact cost of treatment can be determined after an initial consultation, assessment of the patient’s condition and selection of surgical technique. The cost of treatment is also affected by the presence of concomitant diseases and the need for rehabilitation after completion of the main course of treatment.
Send a request for treatment
Recovery after plastic surgery
Heart surgery requires gradual rehabilitation. In the first month after plastic surgery, it is recommended to take very good care of the entire body: give up bad habits, follow the prescribed diet, and avoid stress.
During this period, you need to avoid foods that are too salty, fried, or fatty. Also, drinking plenty of water additionally puts a strain on the cardiovascular system; you should try to drink no more than 1.5 liters of water per day. Alcohol is completely excluded.
It is imperative to undergo routine examinations. The doctor will evaluate the effectiveness of the plastic surgery and the patient’s condition and adjust the treatment. If your health worsens in the postoperative period, this is a reason to call an ambulance or come to an unscheduled appointment. Physical activity should be reduced, sometimes go for leisurely walks, breathe fresh air.
In most cases, such an operation ends successfully for the patient. Over time, all functions of the heart are restored, and the person can return to an active lifestyle, which is confirmed by reviews.
After the first 4 weeks, an examination is scheduled to ensure the success of the procedure. To do this, you need to undergo an ultrasound of the heart, cardiography, urine and blood tests. In the first year after plastic surgery, the patient visits the doctor every month, then twice a year, if there are no complaints.
Competent choice of clinic and cardiac surgeon is the basis for successful treatment
One of the keys to successful mitral valve surgery is a thorough preoperative examination and selection of an appropriate surgical technique. This is possible in a specialized cardiac surgery center or a large multidisciplinary university-level clinic, where doctors are not limited in equipment for carrying out innovative interventions. Most often, clinics in European countries with developed healthcare systems have such capabilities.
If you have chosen a prestigious foreign clinic, then you should take into account the specifics of registering for treatment for foreign patients - the need to receive an invitation from the clinic, preparation and translation of medical documentation, waiting for hospitalization for several months, paying for medical services at a higher rate, and so on. . To go through all stages of the medical program more comfortably and safely, you can use the services of Booking Health.
Booking Health is the only certified medical tourism operator in the world (ISO 9001:2015 certificate), which has been organizing treatment for patients from 75 countries in leading clinics in the world for more than 10 years. Booking Health specialists will help you with such important points:
- Choosing the right clinic based on the annual qualification profile
- Direct communication directly with the attending physician
- Preliminary preparation of a treatment program without repeating previously conducted examinations
- Ensuring favorable prices for clinic services, without surcharges and coefficients for foreign patients (savings up to 50%)
- Make an appointment for the desired date
- Control of the medical program at all stages
- Assistance in purchasing and shipping medications
- Communication with the clinic after completion of treatment
- Control of invoices and return of unspent funds
- Organization of additional examinations
- Service of the highest level: booking hotels, plane tickets, transfers
Leave a request with medical and contact information on the official Booking Health portal, and a competent consulting doctor or medical coordinator will contact you on the same day.