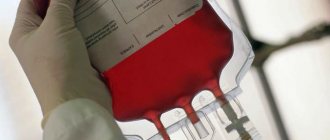
Blood type: transfusion compatibility
At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, researcher K. Landsteiner discovered that human blood is distinguished by specific proteins, and different types of it turn out to be incompatible - when mixed, they form clots. This is how the concept of “blood compatibility” came into circulation, and later – “blood group compatibility” .
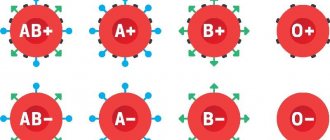
As a result of the research, three blood groups were identified, and later another one was added. Today there are two systems for naming these groups:
- Roman numerals I, II, III and IV.
- Latin letters A, B and zero (0).
In the relationship of these systems, blood groups are designated as follows: I(0), II(A), III(B) and IV(AB).
This discovery and knowledge of which blood groups are compatible with each other became decisive for practical use in medicine. But for a wide range of people, I think it is enough to know that there is incompatibility or compatibility by blood type.
Blood: Stephanie S. Gardner. Complex Set-Up, Simple Procedure / WebMD. — 2021. — 04 December.
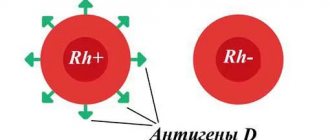
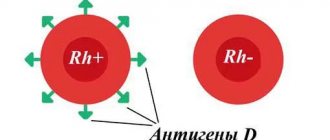
When blood group compatibility is determined, another component is taken into account - the Rh factor. This is a special protein, not everyone has it: those who have it are considered Rh positive, Rh(+); those who don’t have it are Rh-negative, Rh(–).
This applies to all blood types, which we also see on the WebMD website. And I tell patients that this indicator is not related to belonging to any group, but it is important to take it into account during pregnancy or various operations.
My medical scientist colleagues continue research into blood groups and their prevalence among the population.
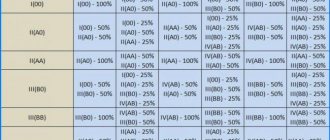
What is the compatibility of blood group and Rh factor? Based on personal experience, I tell patients how the table helps determine the compatibility of blood groups :
Blood group compatibility: Nur.kz
By comparing the data, we determine which blood groups are suitable for each other and which blood groups are not compatible:
- For patients with group B(+), blood groups 1 and 3 are compatible with any Rh.
- There is no compatibility between blood groups 2 and 3.
- If a person has a negative blood group, compatibility is possible with all groups, but also with a negative Rh factor.
Blood transfusion: UGC
Which group is the most common?
Which blood is most in demand in medicine for donation, rare or common? let's figure it out.
Based on statistics, we note that the first group is most common. Approximately half of the entire population of the planet is its carrier. C II (A) – 40% of the population. Only 9% of people are in the third group, and 4% are in the fourth. The vast majority (85%) have Rh+. And only 15% have a Rh negative factor.
We conclude that there are more people with I(0) Rh+ blood, which is why it is the most common. IV (AB) Rh- is considered the rarest. Sometimes it is very necessary, so it is collected and stored in special jars where it can be purchased. You can find out how much blood type 4 costs at a bank or from a doctor.
Read also: Prescribing a test for bilirubin in newborns, what is it for?
Why know your blood type
The physiological fluid that distributes oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and utilizes waste products of cells is not homogeneous in composition. It includes red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. In addition, several blood groups are distinguished and classified according to the Rh factor, a specific antigen. If the indicators do not match, the transfusion causes rejection and leads to the death of the recipient.
- Blood type of parents and children - how to determine what the child will have
For most adults, a stamp with the main parameters - group and Rh factor - is placed in the passport and on the first page of the medical card. But when entering the hospital, a compatibility test is required. This must be done to eliminate Rhesus conflict. Compatibility is checked not only when transfusion is necessary, but also when planning pregnancy. There is an opinion that it is better when sexual partners have the same parameters. But it's not right. All groups of physiological fluid are suitable for each other.
Unfavorable conditions for gestation occur when Rhesus mismatches occur, but not in all cases. For example, during the first pregnancy, only 98% of women experience problems. But when you conceive again with the same partner, antigens begin to be produced - the immune system has managed to “remember the aggressor.”
To prevent Rhesus conflict, it is necessary to register as early as possible. Especially when a woman’s status is negative, and a man’s status is positive. It is dangerous when there is a discrepancy in these parameters between the mother’s body and the fetus. Sometimes treatment is required at the planning stage. Incompatibility of Rh factors makes it difficult to conceive.
Even 40-50 years ago it was believed that the first blood group was suitable for everyone. Plasma and red blood cell transfusions are now being carried out. If these parameters do not match, the immune system begins to produce antibodies that destroy blood cells. Based on the parameters of physiological fluid, it is possible to predict the course of pregnancy, determine the compatibility of a child with future parents, and diagnose oncological processes at an early stage.
In what cases is blood transfusion required?
Transfusion is done due to severe blood loss. If the patient loses about 30% of blood within a few hours, then this procedure should be performed. It is also done urgently if a person is in shock after surgical treatment.
Transfusions are often prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed with anemia, serious blood diseases, inflammatory processes in the body and purulent-septic diseases, strong and severe intoxications of the body.
The procedure is prescribed to people with the following diseases:
- leukopenia – a sharp decrease in the level of leukocytes,
- hypoproteinemia – low level of protein in the blood,
- sepsis - infection of the blood by microbes,
- violation of ESR.
For transfusion, blood with all its components, drugs and blood substitutes are mixed. Medicines are added to the donor’s normal blood to increase the therapeutic effect, while reducing the risk of complications after the procedure.
Red blood cells are often injected into the patient's body. To do this, the red blood cells are first separated from the frozen plasma. After this, a liquid with a high concentration of red cells is poured into the recipient’s body. This method is used for anemia, acute blood loss, with the development of malignant tumors, after tissue and organ transplantation.
Read also: How to determine the rarest blood group, description of types
A mass of leukocytes is infused for agranulocytosis, when the level of these cells rapidly decreases, and for the treatment of severe complications of diseases of an infectious nature. After the procedure, the level of white cells in the blood increases, which has a beneficial effect on the course of recovery.
When to use fresh frozen plasma:
- severe blood loss,
- DIC syndrome,
- hemorrhages - blood leaks through damaged vessel walls,
- overdose of coagulants,
- diseases of an infectious nature.
Patients with blood diseases especially need transfusions. Some patients have to do this procedure once a week, or even more often.
Transfusions are also given to people after chemotherapy. If the tumor has affected the bone marrow, after therapy not only malignant cells stop growing, but also healthy ones.
Women often need transfusions after a difficult birth during which they lost a lot of blood. Sometimes doctors do not recommend using a man's blood for this. Women's is considered safer, and for a young mother this is especially important.
Characteristics of blood groups and the universality factor
I is the zero group (0). It is considered the most compatible with others, since it does not contain unique antigens - protein molecules of erythrocytes - inherent in all other groups. This is the universal blood group.
Her plasma contains two types of antibodies: α-agglutinin and OI-agglutinin. If there is a positive Rh factor, a person with B “zero B” becomes a universal donor: his blood can be transfused to anyone, but only biomaterial of the same group will suit him. 50% of the world's population has this property.
- Negative Rh factor during pregnancy consequences
II (A) is a less universal group for transfusion; it can be “given” only to people with group II or IV. It contains only OI-agglutinins. In their absence, agglutinogen comes to the rescue.
III (B) has some similarities with the second. It can be transfused only to carriers of groups 3 or 4 if they have the same Rh factor, they are suitable for each other. It also contains OI-agglutinin and agglutinogens.
IV (AV), which has only agglutinogens, is present in a very small number of people: 5% of the total population. Any blood is suitable for them, but it can only be “given” to people with exactly the same blood group.
Universal donors and recipients
In the case of transfusion of red blood cells (the main component of the material for transfusion), people with group 0 and negative Rh D are considered universal donors. Representatives of AB (IV) and positive Rhesus D are recognized as universal recipients. These statements are true only in terms of the interaction of foreign particles of the recipient A and B for transfusion of red blood cells and reactive sensitivity to foreign Rhesus cells D. People with the HH system (Bombay phenotype) are an exception; it is permissible for them to receive material for transfusion only from HH donors, since they have antibodies against the H antigen present in red blood cells.
People with antigens A and B or atypical antibodies are excluded from the list of donors. Antibody A and B reactions are not always taken into account. The reason is that a small amount of plasma containing foreign particles is transfused. For example, when 0 and D Rh- blood is transfused to a recipient with A and D Rh+, no immune reactions will occur between the recipient's B antibodies and the red blood cells.
It is worth noting that a small volume of plasma in the donor material used for transfusion has antibodies A, which can react with foreign particles on the membrane of red cells, but a dangerous reaction will not occur, since the effect will be weakened.
Surface antigen erythrocytes, with the exception of A, B and Rhesus D, are capable of provoking harmful effects if they begin to interact with the corresponding antibodies to activate a protective reaction. The transfusion process is complicated by the fact that platelets and leukocytes have independent systems of surface foreign particles and after transfusion, sensitization (increased sensitivity) to foreign cells may occur. Plasma of group 0, with antibodies A and B, can only be used for recipients of group 0, since antibodies react aggressively to antigens of the contacted group. AB plasma transfusion can be performed in patients of any AB0 group.
In modern medicine, the recipient is transfused with blood that is strictly compatible with his group and Rh factor. The use of a universal one is resorted to only in cases where the risk is justified. The cause may be an emergency situation and the risk of death. If blood of the required type and Rh factor is not available, doctors use universal blood.
How to find out your group and Rh factor?
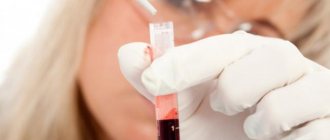
Modern medicine offers a quick and reliable blood test to determine the group and presence of antigen. The procedure is quick and results are ready within 30 minutes. To determine the group, reference blood is added to blood samples and the classification is determined based on the results of the reaction.
If you carefully study your medical record and look at your passport, you can find out your blood type without visiting the clinic. From the first days of birth, blood is taken from the child for tests, this information is stored in the card. When you first go to the hospital at an older age, the data is duplicated in your passport.
So, having considered all types of blood and their compatibility, we can conclude that the first group 0 (I) is universal for transfusion, and only the owner of group AB (IV) can become an ideal recipient. Doctors (in order not to take risks) usually carry out transfusions of the same blood and only in rare cases, in non-standard and critical situations, are guided by the rules of compatibility with the obligatory consideration of Rh factors.
A little history
Attempts at blood transfusion began several centuries ago. In those days, they did not yet know about possible blood incompatibility. Therefore, many transfusions ended unsuccessfully, and one could only hope for a lucky break. And only at the beginning of the last century one of the most important discoveries in hematology was made. In 1900, after numerous studies, an immunologist from Austria, K. Landsteiner, discovered that all people can be divided by blood into three types (A, B, C) and, in this regard, proposed his own transfusion scheme. A little later, his student described the fourth group. In 1940, Landsteiner made another discovery - the Rh factor. Thus, it became possible to avoid incompatibility and save many human lives.
However, there are cases when a transfusion is urgently needed, and there is no time or opportunity to look for a suitable donor, for example, this was the case at the front during the war. Therefore, doctors have always been interested in the question of which blood group is universal.
The process of determining blood identity
An important point in transfusion is to determine the identity of the biological fluid and the presence of infections in it. To do this, a blood sample is taken for a general analysis, the resulting amount is divided into two parts and sent for research. In the laboratory, the first one will be checked for the presence of infections, the amount of hemoglobin, etc. The second one is used to determine the blood type and its Rh factor.
Indications for transfusion and risks
Blood transfusion is a test for the body, and for this reason, indications are needed to perform it. These include the following pathologies and abnormal conditions of the body:
- Diseases based on a lack of red blood cells (anemia), as a result of which the body is unable to independently form a sufficient number of these elements.
- Hematological diseases of malignant type.
- Significant blood loss resulting from injuries or accidents.
- Severe intoxication, the correction of which is impossible by other means.
- Complex operations that involve tissue damage and bleeding.
The introduction of donor material into the body increases the load on many systems, enhances metabolic processes, which provokes the development of pathologies. Therefore, a number of contraindications to the procedure are taken into account:
- myocardial infarction,
- suffered thrombosis,
- heart muscle defects,
- disorders of the kidneys and liver,
- acute form of cardiopulmonary failure,
- disorders in cerebral circulation, etc.
Complexes with this research
Future dad Comprehensive examination to prepare a couple for conception 4,430 ₽ Composition
Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization 3,860 ₽ Composition
Preparation for IVF for a man Examination to prepare a man for the IVF procedure 3,330 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 8,890 RUR
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators RUB 3,260
- Joining IVF RUB 13,150