Rh conflict during pregnancy is a well-studied issue by doctors. Scientists have developed effective methods for diagnosing and treating pathology, and also selected effective methods of prevention.
Immunoprophylaxis of Rhesus conflict is a model of outstanding success in the medical field. When scientists introduced methods of prevention, the percentage of child mortality from complications decreased by almost 30 times. Previously, Rh conflict caused the death of 46 children out of 100,000, but now the figure has dropped to 1.6.
Let’s understand the terms: what is “Rh factor” and “Rh conflict”?
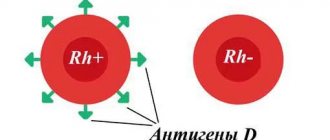
The Rh factor (Rh factor) of a person depends on the presence of D antigens on the membranes of red blood cells. If these antigens are present, then the blood is Rh positive (Rh+); if not, it is negative (Rh-). The vast majority of people are carriers of D antigens, and only 15% of the world's population do not have them.
The Rh factor is a genetic trait that is inherited and remains with a person for life. This feature cannot be changed by any means. Blood Rh does not affect a person’s well-being and health and becomes important in two cases:
- during a blood transfusion;
- during gestation.
Rh conflict (Rh sensitization) during pregnancy is a pronounced immune reaction of the female body to the blood of the fetus. An immune reaction can only occur if the pregnant woman is Rh-, her partner is Rh+, and the child has inherited the father’s Rh-ness.
With any other variants, Rh sensitization cannot appear ⇩⇩⇩
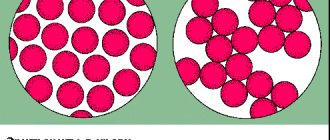
In the fetus, Rh begins to form from 6–8 weeks of gestation. If after this period there is contact between the red blood cells of the mother and the fetus, the pregnant woman’s body will begin to produce antibodies. This process is called sensitization: the female body perceives the fetal red blood cells as “enemies” and turns on immune defense against them. Rh conflict is in many ways reminiscent of an allergic reaction, when the immune system sees a threat in substances that pose no danger to the body.
Maternal antibodies, which are synthesized during Rh conflict, are able to “attack” the red blood cells of the fetus, causing their massive hemolysis (destruction). This leads to the release of indirect bilirubin, a toxic substance that damages fetal tissue.
Due to the danger of Rh conflict, all couples planning a pregnancy are advised to take a blood group and Rh factor test . This simple procedure will not take much time, but will give you valuable information about possible problems after conception. The study is performed in any diagnostic laboratory.
Pregnancy in women with Rh negative blood
The issue of Rh conflict during pregnancy is one of the few in medicine in which all the i’s are dotted and not only diagnostic and treatment methods have been developed, but also, most importantly, effective prevention.
The history of immunoprophylaxis for Rhesus conflict is a rare example of unconditional success in medicine. After all, after the introduction of a set of preventive measures, child mortality from complications of Rh-conflict decreased from 46 to 1.6 per 100 thousand children - that is, almost 30 times.
What is Rh conflict, why does it occur and what can be done to minimize the risk of its occurrence?
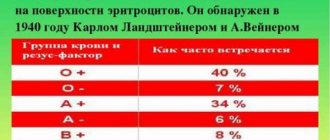
The entire population of the planet, depending on the presence or absence of the protein designated by the letter “D” on erythrocytes (red blood cells), is divided respectively into Rh-positive and Rh-negative people. According to approximate data, about 15% of Europeans are Rh-negative. When a Rh-negative woman becomes pregnant with an Rh-positive man, the probability of having a Rh-positive child is 60%.
In this case, when the fetal red blood cells enter the mother’s bloodstream, an immune reaction occurs, as a result of which the fetal red blood cells are damaged, anemia and a number of other serious complications occur.
During physiological pregnancy, fetal red blood cells penetrate the placenta in the first trimester in 3% of women, in the second - in 15%, in the third - in 48%. In addition, massive reflux occurs during childbirth, after termination of pregnancy (abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole), invasive procedures (chorionic villus biopsy, amniocentesis), and antepartum hemorrhage when there is a threat of miscarriage.
The total risk of developing Rh conflict in Rh-negative women pregnant with a Rh-positive fetus in the absence of prevention is about 16%. In women who undergo prophylaxis, this risk decreases to 0.2%.
And now the most interesting thing is what this prevention is and what needs to be done to keep the situation under control.
All women who apply to a medical institution to register their pregnancy, as well as those who apply to terminate an unwanted pregnancy, are prescribed a test to determine their blood type and Rh factor. Sexual partners of women who are Rh negative are also recommended to undergo testing to determine their Rh status. If, by a happy coincidence, a man also has a negative Rh factor, then there is no risk of Rh conflict and there is no point in carrying out immunoprophylaxis.
Women with Rh-negative blood and Rh-positive blood of a partner who wish to terminate an unwanted pregnancy are recommended to receive an injection of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin within 72 hours after the termination. The mechanism of action of this drug is based on the fact that the injected antibodies bind fetal red blood cells that have entered the maternal bloodstream and prevent the development of an immune response.
Rh-negative women registered for pregnancy are prescribed a monthly blood test for anti-Rh antibodies. In this way, it is determined whether there was contact between the blood of the mother and the fetus, and whether the woman’s immune system reacted to the foreign protein.
If by 28 weeks there are no anti-Rhesus antibodies in a woman’s blood, she is referred for prophylactic administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. This prevention is carried out from 28 to 30 weeks of pregnancy. After this, the determination of anti-Rhesus antibodies in the mother’s blood is not carried out.
If, according to the results of the examination, anti-Rh antibodies are detected in a woman before 28 weeks of pregnancy, she is sent for an in-depth examination to determine the severity of the Rh conflict, timely prescription of treatment and, if necessary, emergency delivery.
After the birth of a child of an Rh-negative woman, the Rh factor is determined. And, if the baby is Rh-positive, the woman is also given anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin within 72 hours after birth.
Other situations requiring prophylactic administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin:
- spontaneous miscarriage or non-developing pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- hydatidiform mole;
- antepartum hemorrhage with threatened miscarriage;
- invasive intrauterine interventions during pregnancy.
The only controversial issue at the moment is the determination of the Rh factor of the fetus during pregnancy. To do this, starting from 10 weeks of pregnancy, a woman’s blood is taken, the genetic material of the fetus is isolated from it and, based on a genetic study, the Rh status of the unborn child is determined.
On the one hand, this study would allow 40% of Rh-negative women carrying an Rh-negative fetus to avoid monthly determination of anti-Rhesus antibodies and the administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin.
On the other hand, this study does not appear in the official order of the Ministry of Health, is not included in the compulsory medical insurance system and is performed only on a paid basis.
Thus, at the moment, a clear algorithm for the management of pregnant women with Rh-negative blood has been developed. And following this simple algorithm will allow a woman to give birth to one, two or more healthy babies.
Obstetrician-gynecologist at antenatal clinic No. 14 Khivrich E.B.
The likelihood of an immune reaction in a pregnant woman with Rh-
If a woman is pregnant for the first time, then the risk of her developing antibodies tends to zero: the likelihood of contact between the blood of the fetus and the mother is too small. As a rule, contact occurs during the birth of the baby, after which the immune reaction starts. With each subsequent pregnancy, the immune reaction increases and the risk of developing Rh sensitization increases.
In addition, the likelihood of sensitization increases:
- induced and spontaneous abortions;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- premature placental abruption;
- amniocentesis (examination of amniotic fluid);
- chorionic villus biopsy (examination of the tissue of the outer membrane of the embryo);
- cordocentesis (examination of fetal cord blood);
- some obstetric manipulations. For example, external obstetric rotation (turning over the fetus, which is in a position unfavorable for childbirth);
- increased permeability of the blood-placental barrier;
- abdominal organ injuries.
Tactics for managing Rh-negative pregnant women
When registering a pregnant woman, the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes a Rh factor test for the woman. The future father of the child must undergo a similar test or have confirmation of a previously completed test. If it turns out that the pregnant woman is Rh- and her husband is Rh+, then the pregnancy is monitored more closely: the woman is regularly tested for anti-Rh antibodies ( immunoglobulins M and G).
The first antibody test is taken after the pregnant woman is registered and her Rh factor is determined. If antibodies are detected, then the pregnancy is considered Rh-sensitized. In this case, antibody testing is carried out every month. Depending on the course of pregnancy, medical history, and antibody levels, a woman can be observed both in a antenatal clinic and in a specialized center, where further medical tactics are determined and the issue of the method and timing of delivery is decided.
If, after registration, no antibodies were detected in a woman, then she continues to be regularly tested for immunoglobulins M and G until delivery or until a prophylactic immunoglobulin injection at 28 weeks of gestation.
Prevention of Rh incompatibility
All pregnant women with Rh- who do not have antibodies are recommended to administer anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin at 28–30 weeks of gestation. This drug is able to bind D antigens that have entered the woman’s blood, and thus prevent an immune reaction.
Women who have undergone immunoglobulin therapy do not need to be tested for antibodies in the subsequent months of pregnancy: After administration of the drug, a small amount of antibodies will be present in the blood, and this is absolutely normal.
An immunoglobulin injection is performed not only at 28–30 weeks of gestation. It must also be done within three days after:
- abortion;
- miscarriage;
- performing amniocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy;
- childbirth if the child was born with Rh+.
After the baby is born, umbilical cord blood is taken for analysis and sent to a diagnostic laboratory to determine the baby's Rhesus. Typically, the results of the study are ready within a day. If the baby is Rh-, then there is no risk and the woman does not need to administer anything. If the baby is Rh+, then the woman must be given immunoglobulin, which allows her to exclude an immune reaction in subsequent pregnancies.
Immunoglobulin is supplied to hospitals in limited quantities, and there may not be enough of it for all women giving birth. Therefore, it is better to find out in advance where it is available and reserve the drug at the pharmacy.
Another indication for the use of immunoglobulin is bleeding during pregnancy. A pregnant woman with Rh- needs to be extremely attentive to her body. If even slight bleeding occurs or spotting appears from the vagina, it is necessary to give an immunoglobulin injection as quickly as possible so that antibodies against the fetus do not develop. Remember that you only have 72 hours to administer the drug! And during this time, you need to have time to get tested for antibodies, since an immunoglobulin injection is performed only if they are absent.
Rhesus conflict. Prevention
Laboratory control of Rh immunization is carried out by determining Rh antibodies in the blood of a pregnant woman:
- If both the father and mother have Rh negative blood, it is not advisable to determine antibodies during pregnancy; — If the Rh-negative genotype of the fetus is determined based on the results of a non-invasive test, antibody determination is not carried out; — Rhesus immunization is determined when the antibody titer is 1:4 or more; — There is a risk to the fetus when the antibody titer is 1:16 or more; — Determination of antibodies is carried out upon registration, at 18-19 and 28 weeks, with the appearance and increase in titer - the frequency of studies increases. ⠀
Prevention of Rh immunization in Rh negative women
1) Administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin 2) Preservation of the first and subsequent pregnancies, the woman should avoid abortion.
Anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin (antibody) protects against the immune reaction without having a negative effect on the fetus and newborn.
Application schemes
— A dose of 300 mcg is administered intramuscularly at 28 weeks of pregnancy (provided there are no antibodies in the blood) — If prophylaxis is not carried out at 28 weeks, it is carried out as soon as possible — Additional prophylaxis 125 mcg (I trimester) or 300 mcg (II, III trimester ) after invasive procedures during pregnancy (amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, cordocentesis, cervical suturing, embryo reduction), after abdominal trauma and after the appearance of bleeding
What else is worth knowing
- Prevention is also carried out in case of unsuccessful completion of pregnancy - instrumental or medical abortion, spontaneous miscarriage and intrauterine fetal death - After birth, the Rh factor of the child is determined and in the case of positive blood - the woman is administered 300 μl of immunoglobulin, no later than 72 hours after birth, with negative blood - prophylaxis is not carried out - The dose of immunoglobulin is increased in case of placental abruption, during cesarean section, during manual examination of the postpartum uterus - If for some reason prophylaxis after childbirth is not carried out, it is possible to administer immunoglobulin up to 10 days of the postpartum period.
Prevention is carried out to prevent immunization in the future, when carrying subsequent children.
Possible consequences of an immune conflict
Maternal antibodies, penetrating the fetal bloodstream, destroy its red blood cells. This is how hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborns occurs, which leads to the development of anemia, intoxication, and disruption of the functioning of various organs.
The edematous variant of hemolytic disease can be diagnosed during pregnancy by performing an ultrasound of the fetus. Ultrasound examination reveals:
- swelling of the placenta;
- polyhydramnios;
- accumulation of exudate in the abdominal and pleural cavity;
- hypertrophy of the liver, spleen, myocardium, thickening of the intestinal walls;
- “Buddha pose” - the fetal abdomen is enlarged in size, and the legs are placed in different directions
With the icteric variant of hemolytic disease, clinical symptoms appear after the birth of the child:
- a blood test reveals a high level of indirect bilirubin;
- the baby's skin becomes jaundiced;
- a newborn may experience an enlargement of the spleen, liver, heart, and lymph nodes.
What is the manifestation of rhesus conflict?
What is a conflict of Rh factors during pregnancy ? In simple words, this is a conflict between the immune system of a pregnant woman and the child’s red blood cells, which are “foreign” to her body. Each person is protected from the invasion of foreign agents into his body by his own immunity. The baby's red blood cells, entering the mother's blood, cause the woman's body to produce antibodies that suppress and destroy the fetus's red blood cells. This process is very dangerous for the child.
The liver and spleen of the fetus begin to work hard, recycling destroyed red blood cells. Bilirubin increases in the baby’s body, and it is very toxic, which has a bad effect on the functioning of all systems and organs of the child. The baby develops anemia, hypoxia sets in, and signs of hemolytic disease appear.
Treatment of the consequences of Rh sensitization
The most effective way to treat severe Rh incompatibility is intrauterine blood transfusion, which is performed if the fetus has severe anemia. During the procedure, red blood cells are injected into the fetal umbilical cord vein under ultrasound guidance.
The procedure allows you to:
- improve the condition of the fetus by maintaining the volume of red blood cells above critical;
- smooth out the immune reaction of the female body.
However, even intravenous blood transfusion is not a panacea for hemolytic disease of the fetus. In the future, this procedure must either be repeated, or the question of early delivery must be raised.
After the birth of the child, a neonatologist treats him. If necessary, the baby is placed under a special photo lamp. Ultraviolet rays penetrate the skin and promote the formation of a water-soluble form of bilirubin, which is quickly eliminated from the body.
If a baby has hemolytic disease, breastfeeding is prohibited for several weeks. If there is no hemolytic disease, then the mother is allowed to breastfeed after an immunoglobulin injection. The drug is administered once, which helps prevent the development of Rh conflict in the next pregnancy.
Causes
The Rh factor is an antigen (protein) that is found on the surface of red blood cells - erythrocytes. It may be present (Rh positive) or absent (Rh negative). According to medical statistics, about 85% of people are Rh positive, the remaining 15% are Rh negative.
Rh conflict occurs either when transfusion of Rh-incompatible blood occurs, or during pregnancy of a woman with Rh negative, if the blood of the fetus is Rh positive.