Everyone has experienced headaches (cephalalgia). The cause of the occurrence can be absolutely anything: from serious disturbances in the functioning of the body to minor ones. But it is worth noting that painful pulsation in the head is a “bell” in order to go for a diagnosis.
This type of pain may indicate serious problems.
The main causes of cephalalgia
Acute pain in the head and throbbing prevents a person from living a normal life and doing business. If pain appears once, this does not necessarily indicate the presence of dysfunction in the body. In cases where a person experiences cephalalgia more and more often, and the pain lasts longer and longer, there really is a problem in the body. It needs to be eliminated, and only a specialist can handle it.
Doctors identify a number of main reasons that cause this symptom, namely:
- VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- atherosclerosis;
- sinusitis, sinusitis;
- migraine;
- eye diseases;
- hematomas;
- tumors;
- neuralgia;
- stress.
Vegetovascular dystonia
Pulsating pain is called background pain. It occurs due to a decrease in the tone of cerebral vessels, stagnation of blood, and spasms of the arteries. The difference between pain that appears due to VSD is that “jolts” do not depend on the person’s pulse.
Atherosclerosis
If a patient has problems with the vascular system, he begins to suffer from pulsation in the temporal and occipital areas of the head. But the zones can change, and the sensations can become oppressive over time.
Sinusitis, sinusitis
The reason lies in the cold you suffered, namely its complications. In order not to encounter cephalalgia, it is imperative to cure all viral and infectious diseases. The same applies to a runny nose.
Migraine
Migraine is manifested by a pulsation, which patients describe as if it were pounding right under the skin, and the pain is localized in one part of the head at the top.
Scientists have not yet proven the definitive causes of such pain, and the exact forms of manifestation of the disease have not yet been determined.
But still, there are several possible causes of migraine development, namely:
- food products (several types of cheeses and sausages);
- weather sensitivity;
- smells of ammonia, ammonia, perfume;
- serious physical activity;
- emotional outburst;
- uncomfortable body position for a long time.
A migraine can torment a person for more than one day. There are cases when the pain lasts 3 days. Most often, cephalalgia caused by this problem manifests itself in unbearably severe pain, and can go away after a few hours. Doctors note the fact that females suffer more from this.
At the end of a migraine attack, a person notes that he has severe weakness and a tendency to sleep.
Eye diseases
The following reasons that can provoke pulsation are eye diseases. A large number of people turn to specialists with complaints such as blurred vision, nausea, dizziness, photophobia, and acute pain radiating to the eye. A competent doctor will immediately determine that these are symptoms of angle-closure glaucoma - high intraocular pressure.
Cephalgia can develop due to tension in the optic nerve, which occurs due to incorrectly selected diopters of glasses or lenses. But in such cases, dizziness also appears.
Hematomas, tumors
Pulsating pain of a strong nature, which is clearly localized in one of the areas of the head, may indicate the presence of damage or a neoplasm. Also in this case, it is worth noting the presence of nausea and vomiting.
If such symptoms are noticed, you must quickly contact a specialist to diagnose a tumor or other problem and begin to treat it.
Stress
All overwork and emotional turmoil can result in severe headaches. Constant nervous tension and stress can create a “fellow traveler” for you for the whole day, namely cephalgia.
Neuralgia
Another common reason why such unpleasant sensations occur in the temple and head area. Dental problems, trigeminal neuralgia - all this provokes pain.
Other causes of cephalalgia
Osteochondrosis and a number of other problems associated with the cervical spine can provoke throbbing pain.
In winter, pulsation in the back of the head often occurs. This is explained by hypothermia and a sharp narrowing of blood vessels.
Lack of normal rest, disruption of sleep quality and routine can cause headaches.
Bad habits are also included in this list of “provocateurs”. They not only harm health, but can also cause discomfort to a person in the form of cephalgia. If a person often drank coffee and decided to abruptly stop, this can also provoke this problem, since the blood vessels are not able to return to normal so quickly.
Not everyone knows, but what we eat can also cause throbbing in our temples. These products include: chicken liver, cheeses, sausages, bacon, nuts, yogurt.
What diseases cause noise in the head?
There are a huge number of causes of noise in the head and ears. It can occur due to severe fatigue, insomnia, neurosis, stress, after excessive physical exertion, against the background of increased body temperature, taking medications, as well as illnesses and traumatic brain injuries.
At risk of developing tinnitus are city transport drivers, factory and airport workers, and musicians.
What causes noise in the head? It can become a symptom of the following diseases:
- neuritis of the auditory nerve, Meniere's disease, otosclerosis, sensorineural hearing loss, otitis, labyrinthitis and other pathologies of the auditory analyzer;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- brain tumors;
- atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, stroke, heart failure, arrhythmia, vegetative-vascular dystonia, as well as other heart and vascular diseases that lead to deterioration of cerebral circulation;
- mental disorders;
- endocrine diseases.
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears and head, according to statistics, is felt by about 10-15% of the world's population. The frequency of its occurrence increases with age, as the likelihood of developing vascular and other diseases increases.
Let's take a closer look at what causes noise in the ears and head.
Migraine
The main symptom of a migraine is a severe headache that affects one side of the head. In addition to this, the patient experiences visual disturbances and ringing in the ears.
Cervical osteochondrosis
The appearance of tinnitus and buzzing in the head, dizziness, headaches that pulsate in the temporal or occipital region may be associated with compression of the blood vessels in the neck and impaired circulation of the auditory analyzer, which occurs with cervical osteochondrosis.
Vascular diseases
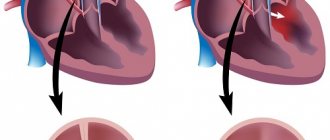
The cause of severe noise in the head and throbbing headache can be an aneurysm or thrombosis of cerebral vessels. These are life-threatening pathologies that cause stroke and intracranial hemorrhage.
High pressure
The appearance of noise in the head due to increased pressure is associated with excessive filling of blood vessels. Other signs of hypertension include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, and nausea. With strong surges in pressure, a feeling of tingling in the heart area, swelling in the temples and fog in the head appears, vision deteriorates, spots appear before the eyes, and the person may lose consciousness. In this case, you need to urgently call an ambulance.
In case of a hypertensive crisis, a person needs emergency medical care
Arterial hypertension is often accompanied by impaired cerebral circulation, which causes a buzzing in the head to occur on a constant basis. If your blood pressure fluctuates frequently, you need to undergo comprehensive treatment. Otherwise, hypertension can cause a heart attack or stroke, which can be life-threatening.
Intracranial pressure
The occurrence of a headache and noise in the head in an adult in the morning, after getting out of bed, is a sure sign of increased intracranial pressure. Other characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- nausea;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- fatigue, lethargy, decreased mental activity;
- irritability;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- hearing impairment;
- increased sweating;
- disturbance of consciousness from stupor to coma (in severe cases).
Headache with increased intracranial pressure is bursting. It gets worse when lying down, coughing or sneezing. During the day, when the person is in an upright position, the symptoms gradually subside as the pressure decreases.
Atherosclerosis
Pathologies of the blood vessels of the brain often lead to throbbing headaches and noise in the head. The most common cause is atherosclerosis. Due to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels, their elasticity decreases. As a result, blood circulation is disrupted, a buzzing sensation appears in the head, and the patient hears something pulsating in the temples.
With age, there is a natural wear and tear of the blood vessels of the brain and a decrease in the elasticity of their walls.
Pulsating noise occurs due to atherosclerotic narrowing, spasm of blood vessels. It is a sign of blood passing through a narrowed artery.
Thyroid problems
Endocrine disorders can negatively affect hearing. Noise or ringing in the head or ears is a symptom of hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism. Associated signs of thyroid disease: drowsiness or insomnia, weight gain or loss, nervousness, irritability, forgetfulness, increased heart rate.
Other diseases
The appearance of noise in the head and ringing in the ears is most often associated with vascular diseases. If it is accompanied by a feeling of pressure, fullness in the head, severe headache and dizziness, balance disorders, then you should be examined for the presence of tumor processes.
Often, noise in the ears and head is a sign of diseases and injuries to the auditory analyzer. The main reasons include:
- acute or chronic otitis – inflammation of the middle ear;
- sensorineural hearing loss – hearing loss caused by damage to various parts of the auditory analyzer;
- labyrinthitis – inflammation of the inner ear;
- neuritis of the auditory nerve - accompanied by a violation of the transmission of impulses from the labyrinth to the brain;
- otosclerosis – manifested by impaired mobility of the auditory ossicles in the middle ear;
- Meniere's disease - increased fluid pressure in the inner ear;
- damage to the eardrum;
- Acoustic neuroma is a benign neoplasm;
- age-related deafness.
In addition to ringing or humming, there is a feeling of stuffiness, fullness inside the ear, hearing problems, disturbances of the vestibular system, which include dizziness, nausea, and balance disorders.
The appearance of noise in the head and other sounds is sometimes associated with depression, neurasthenia and other disorders of the central nervous system. Diagnosis of these causes is difficult, since organic disorders cannot be detected during the examination.
Less commonly, noise in the head occurs due to multiple sclerosis, diabetes, kidney disease, and anemia.
Cephalgia in children
Pulsating discomfort in a child that is not accompanied by fever, cough and runny nose should alert parents. In such cases, it is important to consult a doctor. Such manifestations may indicate problems with the child’s health.
The phenomenon can be triggered by:
- disease of the vascular system;
- neuralgia;
- migraine;
- injury;
- emotional condition;
- poor nutrition;
- the presence of provoking external factors.
Treatment of cardiovascular diseases
Carrying out examinations will determine why the heartbeat radiates to the head, after which the doctor will prescribe treatment. For atherosclerosis, it is necessary to use complex therapy aimed not only at strengthening the walls of blood vessels, but also at normalizing blood pressure. The specialist also recommends taking medications that improve blood composition and prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques.
For pathologies of the veins or arteries, treatment is prescribed individually - much depends on the general condition of the patient and the nature of the course of the disease. It is recommended to undergo a course of drug therapy - a stroke may develop against the background of vasoconstriction. Most often, medications are prescribed to prevent the formation of blood clots.
For high or low blood pressure, it is recommended to take medications that stabilize blood pressure. With the permission of a specialist, you can supplement drug therapy with home remedies. Herbal decoctions or tinctures will help normalize blood pressure, strengthen blood vessels, and improve heart function.
Cephalgia and pregnancy
Most often, girls in this position suffer from migraines, and the illness appears from physical activity, food, lack of sleep, stress, and fatigue. There are also other reasons that cause throbbing pain in women in the position:
- VSD;
- blood pressure problems;
- problems with blood supply;
- voltage;
- disorders in the brain;
- sinus inflammation;
- glaucoma.
For pregnant women suffering from cephalalgia, there are recommendations to combat discomfort, namely:
- do a light massage;
- restful sleep;
- take a contrast shower.
Regarding pain relief with medications, in this case it is important to consult a specialist, since not all painkillers are approved for pregnant women.
Treatment methods
If you experience sharp pain in your heart, you must take a sitting position and unfasten your collar and cuffs. If your blood pressure is elevated and you suspect an angina attack, you should take a nitroglycerin tablet. It is also important to provide access to fresh air into the room. If symptoms do not go away after 15–30 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.
The treatment regimen is selected individually, depending on the exact diagnosis, the patient’s age and other factors. During an exacerbation of diseases, hospital treatment may be necessary, but then it is necessary to follow doctors’ orders at home. Thus, the treatment regimen may include the following steps:
- taking medications - prescribed individually, necessary for long-term use for certain diseases;
- proper nutrition - to reduce the load on the heart, you need to avoid fatty and salty foods;
- surgery - is prescribed only if there is a threat to life due to a blood clot or heart defects.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, treatment is carried out both in an inpatient and outpatient setting. At the center you can receive 24-hour medical supervision, as well as recommendations for doing it at home. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the timely use of medications, as well as proper nutrition and other factors.
Elderly age
The older a person is, the more often he suffers from throbbing pain in the head, and most often this is associated with pressure and changes in the cervical spine. But there are also a number of reasons that pose a danger to older people, and these include:
- presence of a tumor in the brain;
- presence of hematomas in the brain;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- temporal arteritis;
- intoxication;
- presence of infectious diseases;
- stroke.
Pain in the head can also be a consequence of menopause in women, weather sensitivity, which occurs in any gender, and depression.
Diagnosis of headaches and noise
In the fight against noise in the head, diagnosis plays an important role. One of the most important stages in the treatment of pathology is establishing the cause.
At the initial appointment, it is important for the neurologist to hear all the patient’s complaints. He studies medical history, asks about recent head injuries, hearing problems, and stress. Afterwards, the neurologist examines the cervical spine to identify areas of vascular compression, checks reflexes, and conducts motor tests to identify possible neurological disorders.
If, after studying the anamnesis, it becomes obvious that the ringing in the head is due to diseases of the ENT organs or mental disorders, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist or psychotherapist, respectively.
Diagnosis of noise in the head is painless and safe
To make a correct diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory tests are required. Let's consider what examinations a doctor can prescribe for noise in the head:
- otoscopy – microscopic examination of the ear and eardrum;
- audiometry – involves measuring hearing acuity, determining auditory sensitivity to sounds of different frequencies;
- MRI of the brain - shows tumors, stroke, ischemic areas, increased intracranial pressure and other problems;
- CT or MRI of the cervical spine is informative for diagnosing osteochondrosis, hernia and protrusions that lead to compression of arteries and nerve endings;
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels - helps to identify the cause of hypoxia (lack of oxygen), aneurysm, thrombosis and other vascular diseases;
- MRI of the inner ear - shows neuritis, tumors, consequences of the inflammatory process, age-related changes;
- laboratory research - a clinical and biochemical blood test is prescribed.
Magnetic tomography is of great importance in the diagnosis of ringing in the ears and head. With its help, it is possible to identify any diseases of the brain, hearing organs, blood vessels, damage to the soft tissues of the head and neck, and assess the severity of the consequences of injuries suffered. MRI can be done at the SmartMed clinic, where a modern MRI scanner is installed, which has high resolution.
Causes of pain by nature and location
You can determine the cause of throbbing pain in the head by analyzing the place where the patient feels it. Sensations can move around the skull, but most often they appear in a specific part.
Pain in the back of the head
Pain in this part of the skull is characteristic of high blood pressure. It also manifests itself as a pressing character, becoming more pronounced if you turn and tilt your head. It is worth noting that such a sensation in the back of the head can warn of the development of a stroke.
But there are also such provoking factors that cause pain in the back of the head as diseases of the cervical spine, namely:
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis.
The pain disappears when the cause is eliminated, and with it the patient feels a relieved state in the shoulders and neck, cramps disappear, and sleep improves.
Pain on the left
Characteristic of migraine. Associated symptoms:
- visual impairment;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- photophobia;
- loss of orientation.
Pain on the right
Pulsation of a jerking nature indicates trigeminal neuralgia. The pain affects the area of the eye, forehead, temple and jaw. In cases where the pain persists, you need to consult a doctor.
Discomfort in the temporal region
A number of diseases can manifest themselves in this way, for example:
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- migraine;
- increased blood pressure;
- intoxication;
- VSD.
Frontal region
Pain in the frontal part of the head is accompanied by convulsions, disturbances of consciousness and blurred vision. They may indicate increased intracranial pressure.
Also, pain in the forehead can be caused by sinusitis, respiratory infections and eye diseases. It may also be the result of the development of a malignant brain tumor.
Discomfort when moving your head
If unpleasant pulsating sensations in the head become more pronounced while moving the head, this may indicate diseases such as:
- neuritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- inflammation of the sinuses.
Symptoms typical for such cases are:
- nausea;
- prostration;
- dizziness;
- fever;
- partial paralysis
Patients with such complaints are promptly sent for hospitalization and treatment.
Pain and nausea
The cause of such changes in the body may be food poisoning. Throbbing in the head and nausea indicate changes in the brain or nervous disorders. The attack can also be triggered by head injuries.
Pulsation in the head without accompanying pain
The most common cause of such changes is disruption of the central nervous system or cardiovascular system.
Why does the right side of my head hurt?
Physiological reasons
Episodic hemicranias are detected in many healthy people and disappear after taking an anesthetic, sleep, and rest. There is a connection with external circumstances and no tendency to relapse. Provoking factors are considered to be acute and prolonged stress, mental and physical overload. The right side of the head can also hurt due to alcohol intoxication, frequent smoking, or abuse of caffeine-containing drinks.
Migraine
A distinctive feature of migraine is paroxysmal unilateral pain with periodic change of half of the head. For unknown reasons, the disease most often manifests itself as pain in the right side of the head. Painful sensations are localized in the area of the eye, forehead, temple, and less often in the occipital region. They often start in one place and then cover the entire half of the head.
For most types of migraine, symptoms persist for a period of several hours to 3 days. Some signs depend on the type of disease:
- Simple migraine.
The most common. Accompanied by classic attacks without an aura, sometimes preceded by a prodrome in the form of impaired performance, deterioration of the emotional state. Nausea, vomiting, light and sound phobia are noted. - Migraine with aura.
Paroxysms are the same as in the previous case. They are preceded by an aura, which is most often represented by visual disturbances. There may be unusual sounds and smells, sensory disturbances, and difficulty speaking. - Vestibular migraine.
A typical feature is dizziness, which occurs at the prodrome stage and may persist or disappear with the onset of the headache. Sometimes different variants of the aura are observed. - Ocular migraine.
Along with visual disturbances (flickering, the appearance of scotomas, loss of parts of the visual field) that precede cephalalgia and persist for 10-20 minutes, this type of migraine differs from others in its atypical duration - less than 3 hours. - Ophthalmoplegic migraine.
Another variant of the disease with ophthalmological disorders and unusual duration. Symptoms persist for more than a week. Disturbances from the oculomotor, and less commonly, trochlear or abducens nerves occur on days 1-4. Diplopia, mydriasis, strabismus, and drooping eyelids are possible.
If the duration of a migraine attack (except for types with ocular symptoms) is more than 3 days or paroxysms during this time continuously occur one after another, migraine status is diagnosed. This condition is characterized by high pain intensity, wave-like decrease and increase in symptoms, and progressive dehydration caused by repeated vomiting.
Paroxysmal hemicrania
It occurs with episodes of extremely intense pain in the right or left half of the head with the epicenter in the orbit, temporal zone, crown, back of the head, and forehead. It can be provoked by sudden turns of the head, drinking alcohol, or strong emotions. Pain sensations are stabbing, boring, burning, pulsating, aching. The duration of the episode is 5-45 minutes; in severe cases, up to 40 attacks occur during the day. Paroxysmal hemicrania is accompanied by autonomic disorders: lacrimation, local hyperhidrosis, feeling of heat, nasal congestion.
Pain in the right side of the head
Hypnic headache
This primary cephalgia is characterized by its occurrence only during sleep. Separately, the right or left half of the head is affected in 40% of patients; in other cases, the pain is bilateral. At the beginning of the attack, the patient awakens, after the end of the paroxysm he falls asleep again. Hypnic headache is dull, moderate, rarely severe. Diagnosed in people of the older age group, once it appears, it continues to bother throughout life.
Cluster headache
Unlike migraines, the left side of the head is affected more often than the right, but right-sided cephalgia is also possible. The majority of patients are young men. Attacks of cluster headaches develop suddenly, increase within 1-3 minutes, and stop after 15-120 minutes. The painful sensations are extremely intense. Localized mainly in the orbital area, stabbing, burning, tearing, pressing. They decrease with moderate physical activity, so during paroxysm patients constantly move.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Pain in half of the head is typical for the spondylogenic form of the disease. The left and right halves are affected equally often, the localization is determined by the side on which blood flow disturbances occur in the vertebral artery. The pain is provoked by movements of the neck, its severity clearly depends on the position of the head. Painful sensations with vertebrobasilar insufficiency appear in the back of the head, cover the temple, forehead, orbit, and radiate to the upper limb. Accompanied by autonomic and cerebellar disorders, visual and hearing disorders.
Other cerebral pathologies
Pain in the right side of the head is observed with brain tumors, limited arachnoiditis of the corresponding localization. With neoplasms, it appears in the early stages of the disease, strong or moderate, bursting, deep, often observed in the form of attacks. With arachnoiditis, it occurs chronically, gradually progresses, worries mainly in the morning, and is supplemented by neurosis-like symptoms.
Other reasons
Right-sided cephalgia can be detected in the following diseases:
- Sinusitis.
The pain syndrome is bursting, pulsating, provoked by sinusitis or sinusitis of the right paranasal sinuses. It is more pronounced in the forehead area, extending to the temple. Nasal discharge and general signs of an inflammatory process are characteristic. - Mastoiditis.
Manifests simultaneously with acute purulent otitis media or a few days after its onset. There is intense pain behind the ear, spreading to adjacent parts of the head, increased temperature, and drainage of pus from the ear. - Temporal arteritis.
Rheumatic pathology is caused by damage to the temporal artery and is accompanied by throbbing, dull pain in the temple. The pain intensifies at night and gradually progresses. Combined with general intoxication manifestations. - Spinal diseases.
Pain in the right side of the head is caused by right-sided compression of nerves and blood vessels. It is detected in patients with osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia. Neck pain is typical and gets worse with movement. Possible muscle weakness, numbness of the right hand.
How to quickly relieve an attack of cephalalgia
In cases where a headache does not appear frequently or systematically, and a person definitely does not have diseases that can provoke it, then you can deal with the discomfort on your own. To do this, it is not necessary to use strong medications and call a doctor.
When you feel a severe headache, forget about bad habits, such as smoking and give up alcohol. You should also not apply ice or increase the dose of the analgesic yourself unless your doctor recommends it.
There are a number of actions that need to be taken so that a person with a headache begins to feel better, namely:
- Bring fresh air into the room.
- Free the patient from tight clothing and constricting jewelry, unbutton the shirt collar and raise his legs so that they are higher than head level.
- Reduce indoor lights and sounds to a minimum.
- Give water, it can also be a decoction of soothing and relaxing plants.
- Take a warm foot bath and apply a compress to your head.
- It is necessary to warm a person in cases where the pain intensifies and there is chills.
- Lightly massage the temple area, neck, head, while the person should lie down.
If the above methods do not help within 30 minutes, and only get worse, give the patient an analgesic. If this does not help, then call the ambulance doctors.
Methods for diagnosing pain in the left hemisphere
To determine why the left side of your head hurts, you will need a full examination. Neurologists diagnose diseases that can lead to this symptom. According to their recommendations, a number of examinations are carried out, the results of which can be informative in determining the cause of the headache and making a diagnosis:
- collecting medical history data - it is important for the doctor to know about the conditions for the occurrence of headaches, its nature and strength, as well as the patient’s lifestyle and habits, old injuries and diseases;
- Ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels (Dopplerography) is a method by which you can evaluate the speed of blood flow and the degree of filling of blood vessels;
- encephalography is a technique that allows you to examine the functional activity of the brain;
- MRI is one of the main diagnostic methods, more often used to identify tumors, but it is also informative for other pathologies.
At the Clinical Brain Institute you can undergo a full examination and determine the cause of your headache. The test results will show a complete clinical picture, on the basis of which it will be possible to select an individual treatment and prevention regimen.
When to contact a specialist
The appearance of a throbbing headache is already a “bell” that you need to see a doctor and get checked. And few people know that there are situations that oblige the patient to contact a specialist to alleviate the condition, and sometimes even save a life.
If you notice that:
- The pain lasts for more than one hour, and medications do not help.
- The pulsation becomes stronger, despite the fact that the patient does nothing.
- Pain in the occipital region appears immediately after a person wakes up or awakening occurs due to unbearable sensations that do not allow doing anything.
- A buzzing sensation is often felt in a certain area of the head.
- The pain causes dizziness, nausea, vomiting, partial paralysis, clouding of consciousness, and inability to speak normally.
- Intense pulsating beats that do not stop for several days.
- Changes in blood pressure, which are accompanied by headaches.
- The nature of the throbbing pain constantly changes.
If you notice any of the above changes, you should immediately consult a doctor or an ambulance, as serious problems may be hidden behind this.
Expert advice
In the last decade in Russia, the number of complaints about tinnitus has increased. Patients describe their symptoms in different ways. Some hear the ticking of a clock, others hear squeaking, buzzing, grinding, humming, gurgling. Moreover, often a person, referred by a neurologist or otolaryngologist, ends up with this complaint to a psychologist.
We are talking about “phantom” auditory perception. This is not an auditory hallucination, which is usually caused by brain pathology, but an exceptional “product” of the nervous system. Tinnitus as a mental disorder occurs in 10-15% of adults. It is impossible to cure this condition with medications or instrumental methods. Patients work with a psychologist, and the noise in the head goes away.
If this is your case, avoid stress, nervous tension, get more rest and relaxation. Then “phantom” noises will not bother you.
But first of all, it is necessary to exclude organic pathology.
Dzhgarkava Tea Gochaevna
Therapist-cardiologist Experience 5 years
What to do if a vein in your temples is swollen?
If a change in the condition of the venous vessels is a consequence of an external influence, to eliminate the cosmetic defect it is enough to neutralize the irritating factor. When a pathological condition develops against the background of temporal arteritis or impaired venous outflow, then complex therapy is used, which consists of the following groups of drugs:
This expansion of blood vessels is normalized with glucocorticoids, angioprotectors, and vitamins.
- Glucocorticoids. They reduce negative symptoms and are used over a long period of time. A drug such as Prednisolone is widely used.
- Vasodilator medications. Necessary for improving blood circulation and vascular functionality. They use "Agapurin" and "Dibazol".
- Preparations for stabilizing blood consistency. During the treatment period, the condition of the circulatory system is monitored. If necessary, blood thinners are prescribed, namely Aspirin.
- Angioprotectors. Used to prevent the formation of blood clots and venous disorders. These include “Ascorutin” and “Gepatrombin”.
- Vitamin complexes. Necessary for normalizing vascular tone. Products that contain nicotinic acid, vitamin E, C and K are used.
If the root cause of the dysfunction of blood vessels, which leads to swelling of the veins, is considered to be an infectious lesion, then antiviral and antibacterial drugs are used. Nutrition and drinking regime are also corrected. In severe cases, surgical intervention is used in the form of bypass surgery and angioprosthetics, which is used in the development of oncology and thrombosis.
Return to contents
Preventive measures to prevent cardiovascular diseases
The first requirement for preventing heart or vascular disease is proper nutrition. The following products should predominate in the diet:
- fish (improves heart function, strengthens blood vessels);
- fruits, greens, vegetables (saturate the body with fiber, replenish the deficiency of elements necessary for the functioning of the cardiovascular system);
- legumes, dried fruits (reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol);
- fermented milk products with minimal fat content.
Use flour dishes, salt, and tonic drinks in moderation - they have a detrimental effect on blood vessels and the heart. It is better not to include by-products in the menu - they are rich in cholesterol.
To reduce the risk of developing pathologies of the cardiovascular system, it is recommended to carefully monitor physical activity. Regular exercise helps improve the functioning of the heart muscle, strengthen blood vessels and increase their elasticity.
We should not forget how important it is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. It is recommended to properly distribute the daily routine and devote time to proper rest and sleep.
If you feel your heart beating in your head, you should not attribute this symptom to simple fatigue or lack of sleep. The situation can be much more serious and this is just the first bell signaling the development of a serious illness. Doctors recommend immediately undergoing a medical examination, which will help not only to accurately determine the factor provoking the illness, but also to undergo a timely course of treatment.