Types of tinnitus, their causes and symptoms
Ringing in the ear without pain usually does not cause discomfort to a person.
There are several main types:
- emission knock;
- myogenic knock;
- non-emission knock.
Most often, the clinical syndrome is detected in people suffering from diseases of the heart, blood vessels and hearing organs. Elderly patients are at risk.
Emission knock
During the examination, this type of knocking is heard not only by the patient, but also by the doctor.
- Most often, the clinical syndrome is diagnosed in people suffering from various circulatory disorders. The main cause of knocking is considered to be a narrowing of the vascular lumen and the formation of clots in the arteries and veins.
- If the blood flow is disturbed, then the person feels extraneous noise in the ears. The syndrome can be considered a sign of the development of atherosclerosis. Elderly patients hear the knock more clearly if the vascular lumen is severely narrowed or partially blocked by a blood clot.
- Knocking appears after intense sports training or physical labor. The heart pumps a large volume of blood at this moment. In most cases, the noise disappears on its own after the pulse normalizes during rest.
- Knocking often occurs in women in the 2nd-3rd trimester of pregnancy. Violation of the functional activity of the auditory organs can provoke an excess of thyroid hormones and iron deficiency in the blood.
Myogenic murmur
Myogenic noise can be conditionally classified as emission-type knocking. Most often, the clinical syndrome indicates involuntary contractions of the stapedius muscle and palate tissue. It often occurs due to hypertonicity of the tensor tympani (rattling muscle).
The myogenic noise may be heard by the doctor during the examination.
The main reasons for the development of the clinical syndrome are considered:
- psycho-emotional disorder;
- progressive sclerosis;
- brain tumors.
People suffering from neuroses and multiple sclerosis complain about myogenic noise.
Non-emission knock
Non-emission noise can be classified as subjective sounds. No one hears them except the patient. The clinical syndrome is considered a sign of a number of pathologies; the noise is not provoked by external sources.
The main reasons include:
- otitis of varying severity;
- long-term use of medications that affect the quality of hearing;
- systematic surges in blood pressure.
Subjective noise sometimes indicates the development of a serious mental disorder. In hypertension, there is an increase in blood pressure, against which a subjective murmur occurs. The auditory receptors do not receive enough oxygen.
Hearing loss can occur due to injury or diseases of infectious etiology. The knocking occurs in one ear or two at the same time. Medicines that cause ototoxicity include salicylates, diuretics and aminoglycosides.
Diagnostics
To diagnose tinnitus, audiometry is usually performed. This study involves measuring hearing acuity with an audiometer. Based on the results of the audiogram, the doctor can detect ear diseases and identify the nature of this phenomenon.
A more objective picture of the pathology can be obtained by combining this method with tympanometry. It consists of creating variable pressure in the ear canal, due to which middle ear dysfunction can be detected.
The main causes of tinnitus without pain
Knocking in the ear without pain occurs for a number of reasons:
- pathologies of blood vessels and heart;
- disturbances in the functional activity of the brain;
- osteochondrosis;
- mechanical injuries;
- overwork;
- vascular aneurysms.
Causes of noise and knocking in the ear without pain
Ringing in the ear can cause hearing problems. Provoking factors include the presence of inflammatory processes, in which there is a narrowing of the passage and a violation of the outflow of intra-ear secretions.
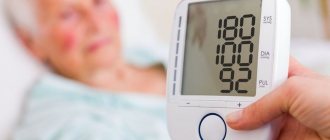
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Pathologies of the cardiovascular system include atherosclerosis. The disease develops gradually. Most often, tinnitus, as a clinical syndrome, occurs against the background of blockage of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques and loss of elasticity of the walls of veins and capillaries. A person hears the sound of blood in the ears, which passes through the vessels in impulses to the brain. The knocking gets louder at night.
Elderly people constantly experience tinnitus. This is most often caused by a violation of the functional activity of the sound nerves. The knock does not cause discomfort, the person does not experience any pain. The syndrome has no cure.
Tinnitus also occurs against the background of pathologies of the blood vessels located inside the hearing organs. Capillaries react to pressure surges, so against the background of arterial hypertension, noise often occurs in the ear canal.
Cerebrovascular diseases
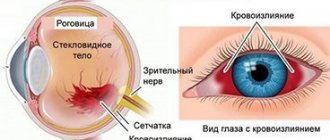
Tinnitus may indicate pathological changes occurring in the blood vessels of the brain. Most often, the patient experiences a pulsation, similar in rhythm to a heartbeat. Vascular malformation is considered the main cause of objective or subjective tinnitus.
This is a congenital disease characterized by an abnormal plexus of blood vessels in the brain. With pathology, small tangles form, preventing blood from entering the capillaries.
The disease is accompanied by a decrease in sound perception; the patient constantly feels a continuous pounding in the ears. The noise can be a sign of the growth of a benign or malignant tumor in the cavities of the skull. The symptom indicates insufficient blood supply to the organ, which arose against the background of compression of the vessel by the neoplasm.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a disease during which dystrophic and degenerative lesions of the joints and vertebrae are observed. The pathology is accompanied by poor circulation, tinnitus and severe headaches.
The main reasons for the development of osteochondrosis are:
- nervous overstrain;
- hereditary factor;
- improper, sedentary lifestyle;
- flat feet, scoliosis;
- systematic physical overexertion.
With osteochondrosis, blood flows poorly to the brain. This is caused by compression of large blood vessels by the vertebrae. A person constantly feels pounding in his ears at night. Osteochondrosis is diagnosed in people regardless of age.
Associated symptoms include:
- decreased hearing acuity;
- slight numbness of the tongue;
- noise or pounding in the ears;
- weakness of the upper limbs;
- fast fatiguability;
- dizziness;
- lack of coordination.
Ringing in the ears is also observed with spastic spasms of the neck muscles (myoclonus).
Injuries
Knocking without pain in the ear often occurs due to injury. After a fall or blow, you should consult a doctor. The specialist must carefully examine the patient, confirm or rule out injury to the outer parts of the ear.
When struck with a blunt object, there is a high risk of rupture of cartilage tissue. Blood can accumulate in this area, forming a hematoma. In the absence of adequate treatment, tissue infection may occur, which will subsequently lead to necrosis. Noise or pounding in the ears during injury is caused by the accumulation of blood in the external passage. Clots block the ear canal.
When the eardrum ruptures, patients complain of:
- noise in the ear;
- loss (partial or complete) of hearing;
- sharp pain that occurs immediately after an injury or fall.
If the external structure of the eardrum was damaged during mechanical impact, then most often the sound-conducting function of the hearing organs is not impaired.
The discomfort quickly goes away on its own.
With a pronounced rupture, which is combined with fractures of the auditory bones, severe conductive hearing loss is formed, accompanied by severe tinnitus. If the base of the stapes is damaged, vestibular type disorders may occur.
Overwork
Often, tinnitus occurs due to overwork. Most often, the clinical syndrome disappears on its own. Chronic lack of sleep and overload of the body with physical labor can lead to the formation of tinnitus. Sounds (not only knocking, but also hum, clicking) that are formed inside the organ of hearing are most often subjective.
There are several forms of noise:
- high frequency;
- low frequency.
Knocks and low-pitched hums are much easier for humans to tolerate. Against the background of overwork, a number of accompanying signs that characterize the condition may appear. Patients complain of slight dizziness, ear congestion, headache and fatigue.
It is recommended to refrain from physical activity and try to sleep more. The doctor can select vitamin and mineral complexes that help restore intellectual and motor activity.
Tumor of the brain or hearing organs
A knocking sound in the ear without pain may indicate a tumor in the brain or hearing organs. Neoplasms of malignant and benign types are localized in the middle and outer structures. Most often, the tumor is diagnosed in older people. In childhood, sarcoma can be observed. In men, cancer of the auditory organ is diagnosed 3-4 times more often (compared to women).
Predisposing factors for tumor formation include:
- radioactive and ultraviolet exposure;
- mechanical organ injuries;
- pathologies of an inflammatory nature of a chronic course.
The characteristic signs of pathology are:
- pain syndrome;
- conductive hearing loss;
- autonomic disorders;
- pounding in the ears;
- dizziness with loss of coordination;
- decreased hearing quality.
A brain tumor refers to the growth of tumors in various cavities of the skull. In pathology, damage to endocrine structures, blood vessels, nerve endings and cerebral tissues is observed.
The tumor is diagnosed in both children and adult patients.
Predisposing factors include:
- traumatic brain injury;
- atherosclerosis;
- Hippel-Lindau disease;
- phakomatosis.
The tumor may be congenital.
Characteristic symptoms of the pathology include:
- motor activity disorders;
- dizziness;
- vomiting;
- lingering headache;
- convulsions;
- psychoemotional disorders.
In some cases, sensory disturbances are added to the above-described symptom complex. Most often they occur with pyramidal insufficiency.
Aneurysm as a cause of audible heart rhythm
With an aneurysm, the myocardial wall becomes thinner and bulges. The area loses its ability to contract. An aneurysm occurs against the background of myocardial infarction.
Predisposing factors include:
- heart failure;
- tachycardia;
- arterial hypertension;
- coronary heart disease.
In rare cases, the pathology may be caused by rheumatism, tuberculosis or syphilis.
With an aneurysm, the following is observed:
- fever;
- pounding in the ears;
- increased sweating;
- bradycardia;
- weakness;
- dyspnea.
With aneurysms, there is a high risk of developing fibrous type pericarditis.
What diseases can hide tinnitus?
The sound itself that a child hears not only brings him psychological discomfort, but can also hide a rather serious somatic pathology. For example:
- Vascular murmur may indicate a hidden oncological process in the brain or middle ear.
- Pulsating sounds and hissing tones may indicate vascular pathologies, such as aneurysm and arterial stenosis, abnormal arrangement of blood vessels;
- Subjective noise may indicate damage to the structures of the nervous system.
- Intense low-frequency noise may mask ear damage at the level of the cochlea. Due to inflammation of the structures of the inner ear, sound transmission is disrupted and hearing loss develops.
- Non-vibrator noise may indicate muscle-articular disorders, namely dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint and malocclusion.
To identify hidden pathologies, specialists use a multidisciplinary approach when examining and treating young patients.
What does pounding in your ears mean while lying down at night?
If a clinical syndrome occurs in a person before bedtime, when he assumes a horizontal position, then the main reason for its development is considered to be stress and overwork. During the day, many events could occur that negatively impact the patient’s psycho-emotional state.
He is not able to completely abstract himself from problems and relax as much as possible. The clinical syndrome usually does not bother a person during the daytime, when he is actively working. Ringing in the ears is caused by vasodilation. In a horizontal position, the blood flow speed is restored. The noise disappears when sleep sets in.
Types of tinnitus
Otorhinolaryngologists distinguish several types of sound effect:
- Objective (vibrator noise) is pulsating or continuous in nature and occurs due to vibrations of an anatomical formation or pulsation of blood vessels. This type of sound can be heard with a phonendoscope and is quite rare.
- Subjective (non-vibratory noise) is heard only by the patient. It is formed when the impulse of the auditory analyzer (auditory nerve, cochlea) is interrupted for some reason, that is, the sound-conducting pathways are affected. This noise effect is recorded in the presence of cerumen, otitis media, intoxication, acoustic trauma and dysfunction of the auditory tube.
According to localization, noises can be generated in the center of the skull, shifted to one ear, or heard simultaneously in both ears. Note that noise in the head, as a rule, excludes pathology of the ears, while noise in the ear does not at all exclude the possibility of the formation of a pathological process inside the skull.
The clinical classification provides for 4 degrees of noise manifestation: from subtle manifestations that do not cause discomfort, to an obsessive constant symptom with sleep disturbance and the psycho-emotional state of the child.
How is the cause of tinnitus diagnosed?
Ringing in the ear can be considered a symptom of a number of pathologies that affect the internal systems of the body. It is strictly forbidden to independently select drug therapy or traditional medicine. It is necessary to contact an otolaryngologist: a specialist will determine the exact cause of tinnitus and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnostic methods include:
- measurement of hearing acuity;
- pneumatic otoscopy;
- MRI of the spine;
- CT scan of the brain;
- Vascular ultrasound.
If necessary, a specialist may prescribe a blood test to determine the number of white blood cells or ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). Based on the results, the doctor confirms or excludes the presence of neoplasms.
A consultation with a cardiologist may be necessary, provided that the patient has detected problems with the heart and blood vessels. When diagnosing osteochondrosis, treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
Classification
According to the sound characteristics, tinnitus is divided into tonal - continuous sounds of the same frequency (ringing, whistling, low-frequency hum) and non-tonal - periodic unpleasant auditory sensations in the form of clicks, crackling, rumble. According to the duration, the symptom is divided into acute (up to 3 months), subacute (from 3 to 12 months) and chronic (lasting more than 1 year). In clinical practice, tinnitus is classified depending on the cause of its occurrence:
- Subjective noise
. Often caused by prolonged exposure to loud sounds on the auditory analyzer. Extraneous sounds are heard only by the patient, which prevents the person from concentrating on the actions being performed or talking. - Neurological noise
. This type of tinnitus is caused by damage to specific nerve receptors in the inner ear, as occurs in Meniere's disease. Patients experience a strong buzzing sensation, usually accompanied by dizziness. - Somatic noise
. It can be associated with damage to any organ, pathological impulses from which excite the auditory analyzer. Somatic tinnitus is in some cases triggered by movements and touches. - Objective noise
. The rarest type of disorder, which is caused by deformations of the ear vessels and pathology of the muscular system. Extraneous “pulsating” sounds can be heard by the doctor when using a stethoscope.
To assess discomfort, Soldatov’s classification is used, which subdivides ear noise according to severity. At grade 1, performance is preserved, the person is adapted to extraneous sounds. The appearance of intense noise at night indicates a transition to stage 2. A constant strong hum, which interferes with the performance of usual duties, is disturbing at stage 3; with a complete loss of performance, stage 4 of the disease is diagnosed.
Drugs for treatment
To eliminate tinnitus, the otolaryngologist selects drug treatment based on the diagnosis.
The therapy includes different groups of drugs:
| Category | Name | Therapeutic effect |
| Drops, ointments (for ear inflammation) | Otinum | Drops that have an antiseptic and analgesic effect. The drug relieves inflammation. |
| Sofradex | The ointment eliminates inflammation and fights infection. Has a mild antiallergic and analgesic effect. | |
| Combinil | The drops have an antibacterial effect. The drug is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. | |
| ACE inhibitors (for heart and vascular diseases) | Enap | It goes on sale in tablet form. Has an antihypotensive effect. |
| Diroton | The tablets normalize blood pressure. The drug prevents the development of heart failure. | |
| Kapoten | Antihypotensive drug in tablet form. A prophylactic against myocardial infarction. | |
| Nootropics (for cerebral vascular damage) | Glycine | The drug is in tablet form. It has an adrenergic blocking and antioxidant effect. |
| Piracetam | It has several forms of release: capsules, solution, tablets. It has a psychostimulating and nootropic effect. | |
| Pantogam | Release form: syrup and tablets. Has anticonvulsant and nootropic effects. | |
| Chondroprotectors (for osteochondrosis) | Teraflex | Available in capsule form. Promotes the restoration of cartilage tissue. |
| Alflutop | Release form: solution for injection. The drug restores metabolic processes inside cartilage. | |
| Structrum | Available in capsule form. It has anti-inflammatory, chondroprotective and regenerating effects. |
When overworked, experts recommend taking vitamins. The drugs listed above have contraindications.
Treatment
It is important to understand pulsation in the ear, it is a symptom that does not need to be treated, its cause must be diagnosed and treated.
Rules
Experts recommend that patients follow these rules:
- — Observe the rules of personal hygiene, promptly remove wax from the ears;
- — Do not drink alcohol and stop smoking tobacco products;
- - Perform a neck massage to relieve any pulsation;
- - Do not listen to music at full volume with headphones;
- — when indicated, use sedatives and psychotropic drugs in a timely manner;
- - walks in the fresh air are useful;
- - exclude fried and other unhealthy foods from the diet, give preference to fruits and vegetables;
- - physical activity will also be very useful;
- - perform neck gymnastics;
- - in the cold season, it is mandatory to wear hats;
- - eliminate sources of stress;
- - normalize blood pressure.
These recommendations will help improve the general condition of the body, as well as prevent the recurrence of pulsation in the ears.
General restorative therapy
- Drugs that improve microcirculation of cerebral vessels - Vinpocetine, Cerebrolysin, Piracetam.
- Medicines that normalize heart function - “Korglikon”, “Strofanthin”, “Digoxin”,
- Drugs that help cope with stress - “Novopassit”, “Persen”, “Tenoten”.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures – magnetic therapy, ultrasound, microcurrent therapy and others.
Treatment of otitis media
Use ear drops containing NSAIDs – “Otipax”, “Otinum”; containing glucocorticoids - "Anauran", "Polydexa", containing an antibiotic - "Normax", "Otofa" and containing an antifungal agent - "Candibiotic".
- — Antibacterial therapy begins after a laboratory examination of the ear discharge and an analysis to determine sensitivity to antibiotics. Patients are usually prescribed Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, Cefolexin.
- — When carrying out antibacterial therapy, it is also necessary to take probiotics - “Linex”, “Normobakt”, “Acipol”.
- - Medicines that reduce body temperature and painkillers - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.
- - To relieve swelling, antihistamines are indicated - Suprastin, Zodak, Zyrtec, Claritin.
- — It is necessary to instill vasoconstrictor drugs into the nose to facilitate nasal breathing - “Vibrocil”, “Tizin”, “Nazivin”.
- — Immunomodulators – “Likopid”, “Polyoxidonium”.
This is what a comprehensive treatment for otitis looks like, which allows you not only to completely get rid of the disease, but also from pulsation in the ear.
Removing wax plugs
This procedure is best performed by an otolaryngologist, but it is possible to remove wax plugs yourself. First, you need to soak them; this can be done by dropping a three percent solution of hydrogen peroxide into the ear.
After some time, we fill the syringe with an infusion of herbs and, tilting our head towards the sore ear, begin to pour it in; we need to do this so that the water pours back out. After the procedure, we instill anti-inflammatory drops into the ear for three days.
If the plug is loose, it can be removed using A-Cerumen ear drops; these drops are instilled and after three minutes they are placed on the sore ear. Sulfur dissolved by this substance flows out on its own.
- Noise in the ears and head, causes and treatment. Folk remedies and medications for ear noise
Treatment of osteochondrosis
To treat this disease, patients are prescribed NSAIDs that reduce pain and inflammation - Voltaren, Nise, Ortofen.
This is the basis of therapy, which is supplemented with vitamin therapy and muscle relaxation. Patients with osteochondrosis are advised to take exercise therapy, spinal traction, massage and manual therapy.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Treatment boils down to normalizing blood pressure, also fighting atherosclerosis and strengthening the walls of blood vessels.
Medicines prescribed:
- "Bisoprol"
- "Amlodipine"
- "Maxonidine"
- diuretics – “Veropshiron”, “Hypothiazide”,
- vascular drugs – “Actovegin”, “Cavinton”,
- antiplatelet agents – “Cardiomagnyl”, “Aspirin”.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine does not guarantee a quick and complete cure. They must be used in combination with drug therapy. Decoctions and infusions based on medicinal herbs are prepared in accordance with the recipe, strictly following the instructions.
Effective for atherosclerosis:
- Melissa infusion. 50 g of dry leaves of the plant are poured with hot water (150 ml). The product is infused for 30-40 minutes, expressed and taken 50 ml 3 times a day.
- Clover infusion. 50 g of raw materials are poured with boiling water (250 ml). Express after 60 minutes. take 50 ml 3 times a day.
- A decoction of rowan bark. The raw materials (100 g) are ground in a blender, placed in an enamel container, filled with water (1 l) and boiled in a water bath for 60 minutes. Take 100 ml 2 times a day.
If the pounding in the ear is caused by an inflammatory process, then onion juice should be instilled into the passage.
Potential Complications
If tinnitus appears suddenly and bothers a person for a long time, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The clinical syndrome may become chronic. The causes of noise can be depression and stress. In the absence of adequate treatment, there is a high risk of developing panic attacks, various phobias and the appearance of suicidal tendencies.
If the root cause of tinnitus is pathology of the cardiovascular system, then if left untreated, a heart attack, stroke and other serious complications may develop (including cardiac arrest and death).
Knocking without pain in the ears is a common complaint from patients to the otolaryngologist. Experts do not recommend self-medication: after the examination, the exact cause of the discomfort should be identified. Uncontrolled use of medications, the use of folk remedies, selected independently, without the knowledge of the doctor, can aggravate the situation.
Causes of noise not related to hearing aids
If there is noise in the ear, and unbearable pain also occurs, the causes of this condition will not necessarily be related directly to the hearing aid. Often the cause of tinnitus and pain is such diagnoses and conditions as:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- metabolic problems;
- diabetes;
- osteochondrosis;
- side effects from taking certain medications;
- poisoning with alcohol or toxic substances.
If unpleasant symptoms do not go away, but only intensify, the best decision would be to consult an ENT doctor to understand the cause of this pathological condition.