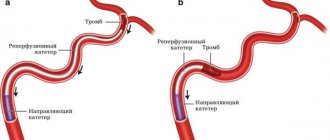
What are blood clots and why do they appear?
Thrombi are clots that form from connections between blood cells. Platelets, sticking together in chains, form lumps that are attached to the walls of blood vessels. In some situations, blood clots form due to disorders of the hematopoietic system, in others - as a result of damage to the inner wall of the vessel.
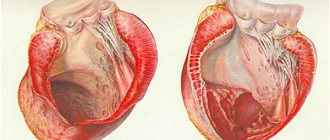
Large growths inside the vein prevent blood flow from passing through the obstructed area. As a result, congestion forms in the veins, leading to varicose veins. When a blood clot blocks the lumen, a heart attack occurs—the death of tissue that has not received oxygen through the bloodstream.
The formation of blood clots is influenced by several factors from a person’s daily life:
- Sedentary lifestyle. Lack of active mobility leads to stagnation of blood in the lower legs. Therefore, constantly sitting at a computer, as well as choosing an escalator instead of stairs, give the blood a reason to stagnate and form clots.
- Insufficient fluid intake. The quality of blood directly depends on what a person eats. With insufficient fluid intake, the blood becomes thick, which means it cannot fully perform its functions and puts a greater strain on the heart. It is easy to pump liquid blood through the system, but thick blood is much more difficult.
- Taking medications that affect the hematopoietic system. In medical practice, drugs are often used to treat certain diseases, one of the side effects of which is blood thickening. Therefore, such medications must be taken simultaneously with anticoagulants that prevent the formation of blood clots.
You can protect yourself from blood clots by regularly exposing your body to physical activity, drinking enough fluids, and including more plant-based foods rich in fiber in your diet.
Thrombophlebitis of deep veins
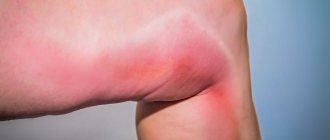
The signs of this type of pathology largely depend on the location of the affected vessel. Among the acute forms, thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the leg stands out in its frequency. It is characterized by the appearance of sudden pain, bursting the muscles of the lower leg. The pain may subside a little if you put your leg in a horizontal position. However, an almost painless manifestation is possible in the presence of other symptoms of thrombophlebitis: swelling, bluish color of the skin and its tension. When pressing on the skin, a dimple remains, which gradually smoothes out.
On the other hand, the disease can pass without any obvious signs at all. With thrombophlebitis of the femoral vein and deep veins of the pelvis, the presence of a blood clot may be indicated by slight swelling on the inner surface of the thigh and mild pain in the groin area. Thrombophlebitis of the iliofemoral segment of the main vein also has subtle signs. It manifests itself as mild pain in the lower back, near the sacrum, and in the lower abdomen. And in some cases, the only symptom may be thromboembolism - when the blood clot has already broken off.
Thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower extremities also manifests itself as a general malaise. Body temperature can rise to 40o. And if the common femoral vein is affected, the patient may have a fever and there are signs of intoxication of the body.
The acute form in almost all cases is characterized by the appearance of acute pain at the site of blood flow disturbance. The swelling may be loose at first and then gradually harden. In the affected area, veins clearly appear on the surface of the skin, and the temperature rises significantly. When making a diagnosis, the doctor places a sphygmomanometer cuff near the affected area and monitors the increase in pressure that causes acute pain. In acute cases, a pressure of 45-60 mmHg is sufficient.
The chronic form by a long course, and the symptoms of thrombophlebitis can appear from time to time for 2-3 years without significant deterioration. The thrombus may be partially destroyed, the patency of the vessel temporarily improves, and the vein wall is overgrown with connective tissue. But since the outflow of blood from the lower extremities is impaired, the symptoms return:
- swelling becomes stable;
- a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the leg haunts when walking;
- severe muscle cramps occur at night;
- dense formations appear under the skin;
- the skin itself acquires ring-shaped pigmentation.
Since such symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities are extremely likely to cause dermatitis, eczema, and trophic ulcers, it is necessary to start treatment as early as possible.
How do blood clots occur?
If a blood clot has formed on the wall of an artery, its appearance can be described in the following stages:
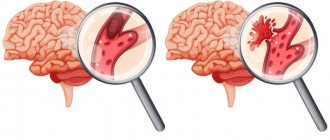
- Some process damages the artery wall.
- The body notices the violation and begins to build protection against blood loss, forming a large number of special blood cells - platelets, which, attaching to the damaged area, form a kind of patch.
- In case of coagulation disorders or changes in the hematopoietic system, platelet formation does not stop on time and continues longer than expected. This causes too much growth to form on the wall. Or platelets, which are in small quantities in the blood, floating past in the bloodstream, stick to the resulting accumulation.
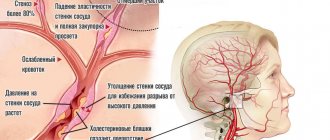
The causes of damage to the walls of blood vessels can be:
- mechanical disruption of the structure due to injury;
- infectious lesion;
- high levels of glucose molecules in the blood;
- immune system dysfunction.
If there are no factors that contribute to the formation of blood clots, any injury or other damage will not lead to a large accumulation of blood cells. Under the layer of platelets, the artery wall will heal and recover, and the crust will resolve over time.
There are several stages of thrombus formation:
- disruption of the structure of the inner surface of the artery;
- activation of blood clotting factors;
- platelet adhesion at the site of injury;
- the appearance of substances that trigger a chain of reactions that form fibrin threads, which contribute to thrombus formation;
- a kind of network of fibrin threads is formed, into which blood cells enter, creating a large clot;
- Over time, the clot thickens, forming a thrombus.
When a blood clot breaks off under the influence of any factors, it begins to move through the bloodstream. Once it hits the nearest bottleneck, the blood flow will be blocked. If a similar situation happens outside a medical facility, it is impossible to save the person.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities is effective for the chronic form of superficial thrombophlebitis and includes a number of measures:
- infrared rays;
- Sollux;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- pulse currents.
These methods are not used in the presence of trophic formations and during periods of exacerbation. A trip to a balneonological resort is possible only after consultation with a doctor and requires a special appointment.
Separately, it is worth noting hirudinotherapia - treatment with leeches. This method is applicable in the acute form and if the patient experiences intolerance to anticoagulant drugs (reducing blood viscosity). In this case, the role of these drugs is played by hirudin, contained in the glands of leeches and entering the patient’s blood. However, their use is strictly individual, has serious contraindications and requires mandatory consultation with the attending physician.
Thrombosis factors
An increased risk of blood clots is caused by:
- Genetic inheritance to predisposition.
- Diseases that force you to limit physical activity, for example, bed rest.
- High degree of blood clotting.
- Arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy and other diseases that disrupt the strength and rhythm of blood flow throughout the system.
- Varicose veins.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Alcoholism.
- Smoking.
- High body mass index.
- Age-related changes in hormone levels in both men and women.
Some of these factors cannot be influenced, for example, genetic predisposition. However, you can protect yourself from the serious consequences of blood clots by maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle.
How to treat thrombophlebitis?
Depending on the form and severity, thrombophlebitis is treated at home or on an outpatient basis. Treatment can be carried out at home for damage to the superficial vessels of the hand, forearm, foot, and leg. In this case, the patient’s physical activity is limited, special ointments are applied locally to improve blood circulation, cold, and elastic bandages. Inside – anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed - magnetic therapy, pulsed currents, etc. Particular attention is paid to prevention.
Treatment for symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities, characterized by damage to the deep veins , is carried out exclusively in a hospital, as there is a threat of embolism. Surgery may be necessary to remove a large blood clot, suppuration, gangrene, etc.
Types of blood emboli
Clots come in different etiologies:
- stagnant;
- inflammatory;
- due to problems with blood circulation.
Forms of leg thrombosis:
- floating;
- appearing near the wall of a venous vessel in the form of clots;
- extended (similar to parietal, but its length is slightly longer);
- lining;
- mixed type neoplasms;
- occlusive.
According to the mechanism of formation:
- consisting of leukocytes, platelets and fibrin strands;
- coagulation - detection of a blood clot in the veins of the leg;
- mixed (shows several types).
By location:
- in the veins;
- in the arteries;
- moving;
- capillary.
Diagnosis of blood clots in leg veins
Before making a diagnosis and starting treatment for thrombosis, the doctor must conduct the necessary examinations.
Main actions and activities:
- Explaining to the patient what a blood clot is and why it can break off.
- Collecting anamnesis, including hereditary.
- Ultrasound with Dopplerography.
- Duplex angioscanning (one of the most informative methods).
- Rheovasography.
- CBC, biochemical analysis, OAM to identify additional pathological conditions.
Tests that allow you to diagnose the disease and find out whether there is an already formed blood clot:
- Lowenberg's sign - measurement using a blood pressure cuff. Blockage of a vessel causes pain when squeezed.
- They bandage the entire leg with an elastic bandage and ask the patient to walk around the room. After the procedure, pain in the legs and dilated saphenous veins appear.
- Pratt's test - the doctor places the patient on the couch and kneads the patient's lower limbs with massage movements. Then he applies a bandage and suggests moving around a little. A positive test result is pain in the calf muscles and swelling.
- A sign of thrombosis when flexing the foot is pale skin in the calves, pain.
- Test with a tourniquet - a compressive element is applied to the upper third of the thigh, with which the person walks for up to half an hour. If the test is positive, distension is felt in the lower extremities.
If necessary, consultation with narrow specialists is carried out.
Consequences and prevention of thrombosis
What is the danger of a blood clot in the legs without timely treatment?
- Spasm of the artery near the affected area with the development of acute arterial circulation disorder.
- Blockage of blood flow into the iliac or femoral veins, which leads to the development of necrosis or gangrene.
- Melting of the vessel with the formation of an abscess, sepsis.
- PE (thromboembolism) is a violation of breathing and circulation with infarction of the lung tissue.
Deep vein thrombosis can be prevented by following simple measures:
- Nutrition control: avoiding fatty broths, trans fats, smoked foods, salt. Inclusion in the menu of substances that reduce blood density.
- Take aspirin regularly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Walking barefoot on small pebbles, sand, and grass in warm weather.
- Cold and hot shower.
- Salt foot baths.
- Self-massage.
- Dosed walking, swimming.
- Place your feet on an elevated surface more often.
- Wearing compression garments.
- Drink plenty of clean water (up to 2 liters per day).
- Regular examinations by specialists.
The formation of blood clots in the veins is a condition that threatens life and health. If the first signs of stagnation are detected, you should inform your doctor and undergo diagnostics.
First aid for a blood clot
It is impossible to independently save a person who has suffered a separation. You should call an ambulance and try to determine the area of the blockage.
It is recommended to give the patient a semi-sitting position, provide access to fresh air and prevent any movement, since stress can lead to the development of bleeding or further advancement of the blood clot.
In the event of loss of consciousness or when the victim dies, it is necessary to immediately begin resuscitation measures until paramedics arrive.
If a vessel has burst and there is bleeding, a tourniquet should be applied to the limb to stop blood loss.