Retinal angiospasm is a functional disorder that is caused by a narrowing of the central retinal artery or its branches, occurring without organic lesions in the blood vessels. In other words, such a condition occurs with intense contraction of the walls of blood vessels due to a temporary sharp narrowing of them, which can limit or completely cut off the blood supply to the tissues.
Vascular angiospasm is not a disease as such, but such a condition cannot be left without attention and the necessary diagnosis of the vascular system of the organ of vision. Otherwise, it can cause serious visual impairment, because narrowing of the central retinal artery often leads to its complete obstruction.
Angiospasm of the retina - what is it?
Retinal angiospasm is a dysfunction of the human visual apparatus, which is preceded by an atypical sharp narrowing of the central artery of the retina, as well as the vessels branching from it. In this case, there are no changes at the organic level in the vascular wall.
There are a number of clinical symptoms characteristic of this pathology, namely:
- The appearance of dots before the eyes, which patients often call “spots”;
- Blurred vision, difficulty focusing;
- Discomfort appearing in the periorbital region;
- Distorted perception of color, shape and size of nearby or distant objects.
In more than 90% of cases, such disorders are caused by insufficiently good blood flow in the central artery. They occur due to improper functioning of the human cardiovascular system. Most often, the disease begins to progress against the background of arterial hypertension or atherosclerosis. In approximately 25% of cases, doctors cannot determine the etiology of vascular spasms in the retina.
Ophthalmologists diagnose vasospasm in patients at any age, but in most cases in people over 40 years of age. It has been scientifically proven that men are 2 times more likely to go to medical institutions with a similar problem than women.
Spastic contraction in the middle layers of the retinal arteries in children is usually caused by pathologies in the structure of the peripheral nervous system, including autonomic dysfunction. In the matter of the etiology of this disease, modern medicine is practically powerless - there is no reliably proven assumption regarding the nature and causes of this pathology.
Angiospasm is a disease of the retina, which in adults in the vast majority of cases occurs against the background of other diseases, such as:
- Diabetes mellitus is a disruption of the endocrine system, which is caused by a relative or absolute deficiency of the pancreatic hormone insulin, as a result of which an increase in the level of glucose in the patient’s blood is observed.
- Hypertension is a malfunction of the cardiovascular system. The disease occurs against the background of dysfunction of vascular regulation centers.
- Atherosclerosis is a chronic artery disease caused by disturbances in a wide group of different compounds, i.e. lipids (fatty acids are among them), and is accompanied by an increased content of cholesterol in the inner lining of blood vessels.
Angiospasm of the retina can occur as a result of intoxication, in which an unregulated increase in the tone of the vascular wall occurs. This is possible in case of poisoning with heavy elements such as lead or carbon disulfide. Corresponding reactions are not uncommon among people employed in hazardous work environments who are diagnosed with chronic intoxication syndrome. The pathology is characterized by bilateral damage to the paired organs of vision (angiospasm of the retina of both eyes also often indicates a disorder of the nervous regulation of tone).
Adherence to bad habits is another point that is highlighted by doctors as one of the fundamental factors in the development of functional disorders of the central nervous system. Narrowing of the retinal artery can occur due to exposure to nicotine and tar in smokers, as well as alcohol in those who abuse alcoholic beverages. These harmful substances lead to temporary deformation of the walls of blood vessels, but gradually such effects provoke dilatation.
Causes of angiopathy
Changes in retinal vessels can be caused by various reasons. This pathology develops differently and is the object of study not only by an ophthalmologist, but also by other doctors, such as a neurologist, endocrinologist, etc. This is due to the fact that in the eye the veins and arteries of the retina are accessible for observation, unlike the blood supply to other human organs .
There is a huge list of reasons leading to the development of angiopathy in both eyes. Here are just some of the causes of retinal angiopathy:
- Diabetes.
- Smoking.
- Blood diseases.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Arterial or intracranial hypertension.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Hypotension or hypertension.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Injuries.
- Heredity.
- Elderly age.
All changes impair the nutrition of the retina, resulting in oxygen starvation.
Diagnosis of retinal vasospasm
Anamnestic data, the results of a visual examination in combination with additional diagnostic methods allow the ophthalmologist to establish vasospasm of the retinal vessels as a diagnosis. The list of studies within the framework of pathology detection includes:
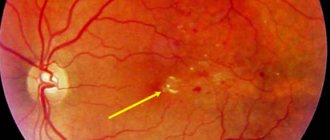
- Ophthalmoscopy. After examining the fundus of the eye, the doctor visually determines a sharp narrowing of the veins in the retina. The vessels are full of blood, but a somewhat swollen, pale pink optic disc is visible. The foveal reflex, like the macular reflex, is not diagnosed during vasospasm.
- OCT. During scanning of the central part of the retina, thickening is visible. In this case, the foveal recess is greatly smoothed, and retinal reactivity is reduced, while the shape of the curve is atypically straight.
- Non-contact tonometry method. During an attack, the specialist observes a slight increase in IOP (intraocular pressure), and after its relief, a normalization of ophthalmotonus.
- Angiography. The ophthalmologist visualizes the changes taking place in the retinal vessels. Diagnosis occurs as part of studying the characteristics of fluorescein circulation. During vasospasm, the internal blood-retinal barrier for contrast remains impenetrable.
Treatment of angiopathy
Various methods are used in the treatment of retinal angiopathy. Therefore, it is important to understand exactly what form of the disease arose. After identifying the main cause, therapy is prescribed, aimed primarily at its correction, and the following are prescribed as auxiliary measures:
- Medications, eye drops.
- A low-calorie diet with limited simple carbohydrates and salt.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Massage of the cervical-collar area.
To prevent the appearance of angiopathy or delay its progression in case of damage to the ocular vessels, it is recommended to consult a specialist in a timely manner. Early initiation of treatment guarantees a favorable prognosis. If you have any chronic diseases or symptoms of visual impairment, do not delay visiting an ophthalmologist. Proper treatment and improved lifestyle can delay the development of the disease for a long time.
Angiospasm of the retina: treatment
For vasospasm, etiotropic therapy is not carried out, since it has not yet been developed in modern medicine. Methods of pathogenetic treatment of the disease are used, which are aimed at reducing pressure and dilating blood vessels undergoing spasms, as well as restoring impaired blood flow in the ischemic zone.
If the unfavorable manifestations of vasospasm are not eliminated in a timely manner, this can lead to a severe decrease in vision and, as a consequence, to a partial or complete loss of the ability to see.
Therefore, the doctor, having diagnosed the corresponding pathology in the patient, immediately after the examination prescribes antispasmodics to the patient. As part of treatment, electrophoresis and vasodilators are recommended.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, as well as saluretics, help reduce intraocular pressure. In cases where the desired effect does not occur, a special irrigation system can be installed in the retrobulbar space. The pathology is also stopped by instillation of solutions of special drugs: beta-adrenergic receptor blockers. Sometimes medications are administered intramuscularly (this mainly happens when the disease is accompanied by high blood pressure).
Short-term narrowing of small branches of the central nervous system is not considered dangerous, but if the attack lasts more than 10-15 minutes, irreversible serious changes occur in the retina due to lack of trophism. Therefore, the prognosis for the treatment of the disease varies - it all depends on the form of the pathology. As for the prevention of vasospasm, it usually comes down to enhanced monitoring of blood pressure, as well as blood glucose levels.
On the Ochkov.Net website you can view a large selection of contact lenses from popular manufacturers and order them in a few clicks.
Complications
Prolonged spasm can lead not only to a decrease in visual acuity, but also to its complete loss. The frequency of attacks causes severe discomfort and disability due to the fact that patients lack the ability to anticipate the period of development of the next fragment. The progressive form of the disease entails an increase in intraocular pressure. Over time, the patient develops secondary ophthalmopyrtension and develops ocular migraine. Rapid attacks are tolerated without complications.
Manifestations of the disease
Retinal vascular angiopathy is painless and practically asymptomatic and is detected during an ophthalmological examination. Patients may complain of decreased visual acuity and blurred vision; progression of myopia; the appearance of lightning and flashes in the eyes.
In some cases, increased nosebleeds and temporary loss of vision are noted. An ophthalmological examination reveals retinal dystrophy.
What vascular complications are most dangerous after coronavirus?
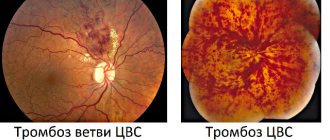
The most common and severe complication after coronavirus are thrombosis, especially with stenosis - narrowing of blood vessels, and rupture of aneurysms (protrusion of the vessel wall with its thinning). It must be taken into account that the vascular endothelium damaged by the virus is restored slowly, and the processes occurring in the body place an increased burden on the entire circulatory system.
Thrombi, jelly-like clots of blood, cellular components and proteins, are formed due to damage to blood vessels, and even against the background of thickening (clotting disorders) of the blood. They grow over time and circulate in the blood without the patient suspecting or feeling that a blood clot is forming.
Such blood clots can block arteries in the heart and brain. Therefore, a complication of coronavirus can be a heart attack or stroke. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is no less life-threatening. Moreover, often blood clots that block the vessels of the lungs initially form in the deep veins of the legs, after which they break off and move. Therefore, if you have symptoms such as:
- sudden causeless shortness of breath,
- chest pain,
- blood in cough discharge,
- chest wheezing,
- fainting, cold sweat, and dizziness,
- a sharp increase in heart rate at rest.
We can talk specifically about TELA. The patient is urgently recommended to undergo a CT scan of the pulmonary artery with contrast. Unfortunately, in most cases, such a diagnosis is post-symptomatic, just like the diagnosis of a stroke. Computed tomography in such cases is the preferred method for visual assessment of blood vessels.
Prevention of angiopathy
Treatment is not just about taking medications. It is very important to maintain a proper diet and change your lifestyle. The diet should be low in salt and animal fats, high in potassium and magnesium. The patient should also increase physical activity. If intense exercise is contraindicated for a person, it is necessary to select a set of gymnastic procedures adapted to his activity and capabilities. Sometimes walking or cycling is enough. It is important that the exercises are performed systematically, that is, they are part of your daily routine.
In order for the blood vessels, including the blood vessels of the eyes, to be in normal condition, it is important to follow simple rules:
- Do not abuse alcohol, get rid of nicotine addiction.
- Prevent the development of hypertension, diabetes and other provocateurs of hypertensive angiopathy.
- Periodically undergo courses of treatment if the disease is chronic.
- Carry out a preventive examination every year, even if there are no obvious vision problems.
- When angiopathy is detected in pregnant women, in order to avoid retinal detachment, a cesarean section is recommended.
The eyes are an important organ, without which a person would not be able to receive information from the outside world. Retinal angiopathy can deprive a person of a normal life and make him disabled. Therefore, any visual impairment, even minor, must be accurately diagnosed and corrected in an ophthalmology clinic. And serious diseases - diabetes and hypertension - must be constantly monitored.